Stylecraze.com
1. Drumstick Leaves...
2. Vitamins B12 And Folate...
3. Blackstrap Molasses...
4. Green Veggies...
5. Vitamin C...
6. Probiotics...
7. Figs...
8. Beetroot...
Learn More...Top10homeremedies.com
1. Inculde Beetroot in Your Diet...
2. Consume Probiotics...
3. Eat Fermented Foods...
4. Drink Blackstrap Molasses in Water...
5. Drink Spinach Juice...
6. Drink Pomegranate Juice...
7. Eat a Concoction of Sesame Seeds...
8. Chow Down on Dates...
Learn More...Rapidhomeremedies.com
1. Beetroot-Apple Juice...
2. Sesame Seeds...
3. Blackstrap Molasses...
4. Spinach...
5. Tomatoes...
6. Pomegranate...
7. Parsley...
Learn More...How to fix macrocytic anemia?
Severe cases of macrocytic anemia can be avoided by:
- Consumption of food rich in vitamin B 12 at least in two meals. ...
- Vegetarians can add plant protein to their diet such as beans and other foods with folic acid such as lentils, oranges and dark leafy greens
- Reduce or avoid alcohol consumption and mostly, especially if you suffer from nutritional deficiency
What is the best remedy for anemia?
How Is Anemia Treated?
- Goals of Treatment. The goal of treatment is to increase the amount of oxygen that your blood can carry. ...
- Dietary Changes and Supplements. Low levels of vitamins or iron in the body can cause some types of anemia. ...
- Medicines. ...
- Procedures. ...
- Surgery. ...
What are the most common causes of macrocytic anemia?
What foods increase red blood cells?
- red meat, such as beef.
- organ meat, such as kidney and liver.
- dark, leafy, green vegetables, such as spinach and kale.
- dried fruits, such as prunes and raisins.
- beans.
- legumes.
- egg yolks.
What are the goals of treatment for pernicious anemia?
Treatment of pernicious anemia usually consists of:
- vitamin B-12 injections that are followed closely over time
- following the blood level of vitamin B-12 over the course of therapy
- making adjustments accordingly in vitamin B-12 dosing

What is the most common cause of microcytic anemia?
Iron-deficiency anemia (IDA): This anemia is the most common cause of microcytic anemia. Thalassemias: These are blood disorders that affect your body's ability to make hemoglobin and red blood cells.
How long does it take to recover from microcytic anemia?
Once iron deficiency is identified and a cause established, the most effective therapy is reversal of the identified cause (e.g., removal of colonic polyp) and the administration of iron supplementation. Usually, this can be accomplished with oral iron preparations. The treatment phase usually takes about 6 months.
What does it mean if you have microcytic anemia?
Microcytic anemia is defined as the presence of small, often hypochromic, red blood cells in a peripheral blood smear and is usually characterized by a low MCV (less than 83 micron 3). Iron deficiency is the most common cause of microcytic anemia.
How is Macrocytic anemia treated?
The first line of treatment for many people is correcting nutrient deficiencies. This can be done with supplements or foods like spinach and red meat. You may be able to take supplements that include folate and other B vitamins. You may also need vitamin B-12 injections if you don't absorb oral vitamin B-12 properly.
Can microcytic anemia be cured?
Treatment can be relatively straightforward if simple nutrient deficiencies are the cause of microcytic anemia. As long as the underlying cause of the anemia can be treated, the anemia itself can be treated and even cured. In very severe cases, untreated microcytic anemia can become dangerous.
What is the fastest way to cure anemia?
If you have iron-deficiency anemia, taking iron orally or getting iron administered intravenously along with vitamin C is often the fastest way to raise your iron levels. Iron is necessary to produce hemoglobin in red blood cells, which helps the RBCs carry oxygen to organs and other tissues of the body.
Which vitamin causes microcytic anemia?
Iron deficiency hypochromic microcytic anemia is caused due to disruption of iron supply in diet due to decreased iron content in the diet, pathology of the small intestines like sprue and chronic diarrhea, gastrectomy, and deficiency of vitamin C in the diet.
Is microcytic anemia rare?
Among rare congenital microcytic anemias, most frequent forms are non syndromic sideroblastic anemias and iron refractory iron deficiency anemias (IRIDA). Sideroblastic anemias is characterized by mitochondrial iron overload and presence of ring sideroblasts in patient bone marrow..
How do you test for microcytic anemia?
In microcytic hypochromic anemia, seek a source of bleeding. The appropriate laboratory tests are serum iron level and TIBC and either serum ferritin level or stain of bone marrow specimen for iron.
Can enlarged red blood cells go back to normal?
Macrocytosis is often reversible with treatment. Usually taking vitamin B12 or folate supplements or eating foods containing these nutrients can reverse the condition. 2 If it is caused by an underlying condition, such as leukemia, treatment of that illness may resolve macrocytosis, a much less concerning condition.
What are the two most common causes of macrocytic anemia?
The most common causes of macrocytic anemia include vitamin B12 deficiency and folate deficiency....Macrocytic anemia may be caused by underlying diseases, so various blood tests are done to check for:Liver diseases.Thyroid function.Levels of vitamin B12 and folate.
Which nutrients are needed to prevent microcytic anemia?
Eating a balanced diet high in iron, vitamin B12, vitamin C, and folic acid can be helpful for almost anyone with anemia. People who do not get enough iron in their diets may need to take supplements under a doctor's supervision.
What is the most common cause of microcytic anemia?
The AAFP states iron deficiency is the most common cause of microcytic anemia.
What are the symptoms of anemia?
Irritability, tiredness, and pale skin may be symptoms of severe anemia.
What happens if you don't have red blood cells?
Without this protein, red blood cells will not form properly or work as well as they should. The lack of this protein causes anemia, which can range from mild to severe depending on how many genes are affected. An article in The BMJ states that iron deficiency anemia and thalassemia are the most common causes.
What is the term for a cell that is smaller in size and can carry less oxygen?
When there is a lack of hemoglobin in a red blood cell, the cell is smaller in size and can carry less oxygen. Microcytic anemia is not one condition, but rather describes several different types of anemia.
What is the condition that affects the bone marrow's ability to produce red blood cells?
Congenital sideroblastic anemia is an inherited blood disorder that affects the bone marrow’s ability to produce red blood cells. Though it can cause microcytic anemia, it is less common than the other causes.
What is the term for anemia of chronic disease?
Anemia of chronic disease. Certain chronic diseases and conditions can cause microcytic anemia. This is usually called anemia of inflammation and chronic disease (AI/CD). Chronic infections or inflammation can interfere with the way the body processes iron.
What causes anemia in the body?
Some of the conditions that can cause this type of anemia include: kidney disease. certain cancers, such as Hodgkin’s disease, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, and breast cancer. inflammatory diseases such as diabetes, heart failure, Crohn’s disease, inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus.
Small red blood cells can cause symptoms of anemia
Heidi Moawad is a neurologist and expert in the field of brain health and neurological disorders. Dr. Moawad regularly writes and edits health and career content for medical books and publications.
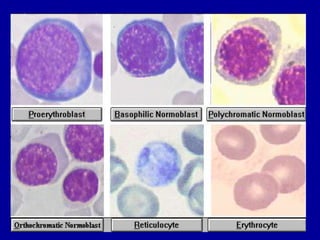
Types
There are several types of microcytic anemia. Each of these conditions makes it difficult for the body to produce healthy red blood cells.
Symptoms of Microcytic Anemia
The symptoms of microcytic anemia develop over time. They tend to be vague and not specifically unique to anemia.
What Causes Microcytic Anemia?
Microcytic anemia occurs when the body cannot make red blood cells of normal size. This can happen if you are deficient in certain components of the red blood cells or can occur due to illnesses that prevent proper red blood cell development. 5
How Microcytic Anemia Is Diagnosed
Microcytic anemia can cause signs that are detected on a physical examination, but it doesn’t always do so. Microcytic anemia is diagnosed with blood tests. 7 Sometimes, additional specific blood tests are used to determine the cause.
What Are the Treatments for Microcytic Anemia?
There are many different treatments for microcytic anemia. Some treatments are used to help resolve the symptoms, and other treatments are used to help your body produce normal red blood cells.
Prognosis: What to Expect
Microcytic anemia can improve with treatment. It may take weeks or months for you to feel better and for your blood tests to show improvement. Depending on the cause, you may need to continue long-term treatment to prevent microcytic anemia from recurring.
How much iron is needed for microcytic anemia?
Therapy includes 325 mg of ferrous sulfate three times a day orally. Of this, up to 10 mg of iron can be absorbed from the gut and is the preferred initial treatment.
What causes hypochromic microcytic anemia?
Hypochromic microcytic anemia is caused by any factor which reduces the body's iron stores. Hemoglobin is a globular protein that is a major component of RBCs it is manufactured in the bone marrow by erythroid progenitor cells. It has four globin chains two of which are alpha-globin chains while the other two are beta-globin chains, these four chains are attached to a porphyrin ring (heme) the center of which contains iron in the form of ferrous (reduced iron) capable of binding four molecules of oxygen. Reduced iron stores halt the production of hemoglobin chains, and its concentration begins to decrease in the newly formed RBCs since the red color of RBCs is due to hemoglobin the color of the newly formed RBCs begins to fade thus the name, hypochromic. As the newly produced RBCs contain less amount of hemoglobin, they are of relatively small size when compared to normal RBCs, thus the name, microcytic.
What is the name of the type of anemia in which the circulating RBCs are smaller than the usual size?
Microcytic, hypochromic anemia, as the name suggests, is the type of anemia in which the circulating RBCs are smaller than the usual size of RBCs (microcytic) and have decreased red color (hypochromic).
How to diagnose iron deficiency anemia?
The first test to perform is complete blood count (CBC) which will indicate the presence of anemia after a thorough physical exam. CBC will show different RBC indices like MCV and MCHC. These parameters comment on the quantity of hemoglobin inside the RBCs they are both usually decreased in hypochromic microcytic anemia. The Next test to perform is iron studies which take a look at transferrin saturation, total iron-binding capacity, and ferritin. TIBC is usually increased in iron deficiency anemia, while transferrin saturation is markedly decreased in iron deficiency anemia. Ferritin levels below 12 ng/ml in the absence of scurvy are a reliable indicator of iron deficiency anemia. However, a low or normal ferritin level does not exclude the diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia because ferritin is an acute-phase reactant protein, and its level increase during the time of infections. As iron levels fall, transferrin levels increase in compensation. [6][7][8]
Why is iron deficiency hypochromic microcytic anemia caused?
Iron deficiency hypochromic microcytic anemia is caused due to disruption of iron supply in diet due to decreased iron content in the diet, pathology the small intestines like sprue and chronic diarrhea, gastrectomy, and deficiency of vitamin C in the diet.
How does anemia affect blood volume?
Anemia reduces the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood and lead s to tissue hypoxia. Usually, it is diagnosed by hematocrit (the ratio of packed RBCs to blood volume) and the hemoglobin concentration.[1][2][3][4] Anemia is defined as the reduction in circulating red-cell mass below normal levels. Anemia is a very common condition which is ...
What is the reduction in circulating red blood cells?
Anemia is defined as the reduction in circulating red-cell mass below normal levels. Anemia is a very common condition that is widespread in the human population. Circulating red blood cells (RBCs) contain a protein known as hemoglobin, that protein has four polypeptide chains and one heme ring that contains iron in reduced form. Iron is the main component of hemoglobin and is the prime carrier of oxygen. Decreased iron reserves in the body affect the production of hemoglobin which, subsequently hinders the transport of oxygen to organ systems of the body. Anemia reduces the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood and leads to tissue hypoxia. Usually, it is diagnosed by hematocrit (the ratio of packed RBCs to blood volume) and the hemoglobin concentration.[1][2][3][4]
How Can Iron-Deficiency Anemia Be Prevented ?
Eating a well-balanced diet that includes iron-rich foods may help you prevent iron-deficiency anemia.
What are the best treatments for thalassemia?
These treatments include blood transfusions, iron chelation therapy, and folic acid supplements. Other treatments have been developed or are being tested, but they’re used much less often.
What happens if you don’t get enough iron ?
In the short term, getting too little iron does not cause obvious symptoms. The body uses its stored iron in the muscles, liver, spleen, and bone marrow. But when levels of iron stored in the body become low, iron deficiency anemia sets in. Red blood cells become smaller and contain less hemoglobin. As a result, blood carries less oxygen from the lungs throughout the body.
How to get iron out of your body?
You can enhance your body’s absorption of iron by drinking citrus juice or eating other foods rich in vitamin C at the same time that you eat high-iron foods. Vitamin C in citrus juices, like orange juice, helps your body to better absorb dietary iron.
Why does thalassemia cause lack of oxygen?
The lack of oxygen occurs because the body doesn’t make enough healthy red blood cells and hemoglobin. The severity of symptoms depends on the severity of the disorder.
Why are people at higher risk of death from thalassemia?
People who have had their spleens removed are at even higher risk because they no longer have this infection-fighting organ.
What does a low hemoglobin level mean?
This test checks your hemoglobin and hematocrit levels. Hemoglobin is an iron-rich protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to the body. Hematocrit is a measure of how much space red blood cells take up in your blood. A low level of hemoglobin or hematocrit is a sign of anemia.
What is the diagnosis of microcytic anemia?
Microcytic anemia is defined as the presence of small, often hypochromic, red blood cells in a peripheral blood smear and is usually characterized by a low MCV (less than 83 micron 3).
What is the most definitive test for differentiating iron deficiency from the other microcytic states?
The absence of iron stores in the bone marrow remains the most definitive test for differentiating iron deficiency from the other microcytic states, ie, anemia of chronic disease, thalassemia, and sideroblastic anemia.
What is the absence of iron stores in the bone marrow?
The absence of iron stores in the bone marrow remain …. Microcytic anemia is defined as the presence of small, often hypochromic, red blood cells in a peripheral blood smear and is usually characterized by a low MCV (less than 83 micron 3). Iron deficiency is the most common cause of microcytic anemia.
What is the treatment for hemolytic anemia?
Sickle cell anemia. Treatment might include oxygen, pain relievers, and oral and intravenous fluids to reduce pain and prevent complications. Doctors might also recommend blood transfusions, folic acid supplements and antibiotics.
How to treat iron deficiency?
Iron deficiency anemia. Treatment for this form of anemia usually involves taking iron supplements and changing your diet. If the cause of iron deficiency is loss of blood — other than from menstruation — the source of the bleeding must be located and the bleeding stopped. This might involve surgery. Vitamin deficiency anemias.
What is the treatment for thalassemia?
Most forms of thalassemia are mild and require no treatment. More severe forms of thalassemia generally require blood transfusions, folic acid supplements, medication, removal of the spleen, or a blood and bone marrow stem cell transplant.
Why do you need a bone marrow transplant?
You might need a bone marrow transplant if your bone marrow can't make healthy blood cells. Anemias associated with bone marrow disease. Treatment of these various diseases can include medication, chemotherapy or bone marrow transplantation. Hemolytic anemias.
What is the treatment for folic acid deficiency?
This might involve surgery. Vitamin deficiency anemias. Treatment for folic acid and vitamin C deficiency involves dietary supplements and increasing these nutrients in your diet. If your digestive system has trouble absorbing vitamin B-12 from the food you eat, you might need vitamin B-12 shots.
What is CBC in anemia?
A CBC is used to count the number of blood cells in a sample of your blood . For anemia, your doctor will be interested in the levels of the red blood cells contained in your blood (hematocrit) and the hemoglobin in your blood. Normal adult hematocrit values vary among medical practices but are generally between 40% and 52% for men and 35% ...
What is the purpose of a red blood cell test?
A test to determine the size and shape of your red blood cells. Some of your red blood cells might also be examined for unusual size, shape and color.