How long should encephalopathy last?
Factors that contribute include changes in blood flow and, initially, a disturbance in neurotransmitter function followed by failure of energy metabolism and cellular depolarization. Treatment of these conditions is largely supportive, with special attention to the management of cerebral perfusion pressure.
When to query for encephalopathy?
Metabolic encephalopathy treatment guidelines Richard K. Olney, Michael J. Aminoff, in Neurology and General Medicine (Fourth Edition), 2008Metabolic encephalopathy is a diffuse but potentially reversible disorder of cerebral function that often impairs the state of arousal and cognitive function and is due to a metabolic or toxic cause. When ...
Is metabolic encephalopathy reversible?
Oct 01, 2020 · Lifestyle modification such as the Mediterranean diet, exercise, and quitting smoking are the preferred treatment of metabolic syndrome. Metabolic Syndrome Quiz Metabolic syndrome is serious and you should be concerned.
Is severe hepatic encephalopathy reversible?
Metabolic encephalopathies usually develop acutely or subacutely and are reversible if the systemic disorder is treated. If left untreated, however, metabolic encephalopathies may result in secondary structural damage to the brain. Table 38-1. Classification of the Major Metabolic Encephalopathies. There are two major types of metabolic encephalopathies, namely those …

Can metabolic encephalopathy be cured?
Metabolic encephalopathies usually develop acutely or subacutely and are reversible if the systemic disorder is treated. If left untreated, however, metabolic encephalopathies may result in secondary structural damage to the brain.
Is metabolic encephalopathy the same as dementia?
Toxic‐metabolic encephalopathy can be distinguished from dementia primarily by the patient's level of consciousness acutely deteriorating and subsequently fluctuating. For example, dementia takes at least 6 months or longer to appear in the most rapidly developing illnesses, such as Creutzfeldt‐Jakob disease.
Is metabolic encephalopathy life threatening?
[Metabolic encephalopathy can be a potentially life-threatening complication from valproic acid]Feb 2, 2008
What does metabolic encephalopathy mean?
Metabolic encephalopathy is a problem in the brain. It is caused by a chemical imbalance in the blood. The imbalance is caused by an illness or organs that are not working as well as they should. It is not caused by a head injury. When the imbalance affects the brain, it can lead to personality changes.
Can metabolic encephalopathy come on suddenly?
Symptoms can develop suddenly and disappear within a few hours. However, for some, encephalopathy can be more serious, especially if you have a history of dementia or previous brain injury.
What medications can cause metabolic encephalopathy?
Many drugs may cause toxic encephalopathy....Toxic encephalopathy.Type of therapeutic agentDrugsAntineoplastic agentsMethotrexate (± seizures, leukotoxic damage)IfosfamidePaclitaxel (± seizures)Cisplatin (± seizures, leukotoxic damage)32 more rows
Can you recover from encephalopathy?
Mild cases of encephalitis are usually short and result in a full recovery. However, despite improvements in diagnosis and treatment, encephalitis still leads to death in about 10% of patients.
Can encephalopathy be reversed?
In reversible encephalopathy, such as from organ failure, metabolic conditions, or infections, symptoms usually go away when you fix the problem that's causing them, and you may be able to regain your previous mental abilities.Aug 24, 2021
How long can you live with encephalopathy?
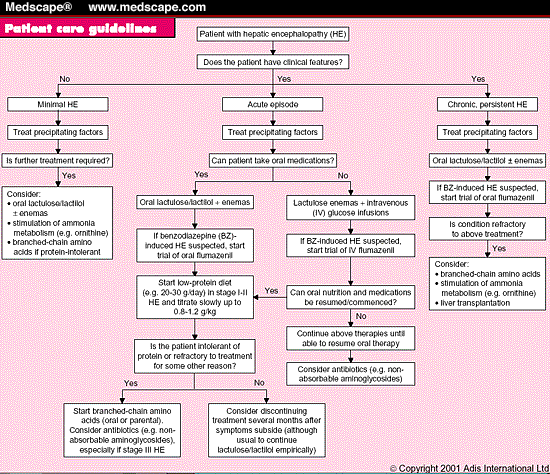
In patients with compensated cirrhosis, median survival is greater than 12 years. By contrast, in patients experiencing a decompensation, commonly defined by ascites, hepatic encephalopathy (HE), variceal haemorrhage and jaundice, survival is far shorter at two years or less[3-5].May 14, 2020
Is metabolic encephalopathy a stroke?
Disorders of Mitochondrial DNA. Metabolic encephalopathy, lactic acidosis and stroke-like episodes (MELAS) is the prototypical metabolic disorder that presents with acute metabolic stroke. In approximately 80% of cases, MELAS is caused by a missense variant of the MT-TL1 mitochondrial gene (m. A3243G).
What are the symptoms of metabolic encephalopathy?
The common signs and symptoms of metabolic encephalopathy include: Delirium is considered the most common symptom of metabolic encephalopathy. It is characterized by confused thinking and disrupted attention usually accompanied by disordered speech and hallucinations. Dementia (loss of memory)
What are the main features of metabolic syndrome?
The main features of metabolic syndrome include insulin resistance, hypertension (high blood pressure), cholesterol abnormalities, and an increased risk for clotting. Patients are most often overweight or obese. Lifestyle modification such as the Mediterranean diet, exercise, and quitting smoking are the preferred treatment of metabolic syndrome.
What does it mean when you have ammonia in your blood?
A high level of ammonia in the blood is a possible indication of metabolic encephalopathy. Metabol ic encephalopathy is usually diagnosed through the blood, urine, and spinal fluid samples. Blood tests may also show if there is an infection or if there are drugs or toxins in the blood. Computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging ( MRI) ...
Why is prompt diagnosis important?
Prompt diagnosis and intervention are important as exemplified in the management of hypoglycemic patients. Patients given glucose at the onset of symptoms recover completely. Delayed treatment may lead to seizures or coma, which may be reversed within hours or days with partial recovery.
What causes brain swelling?
Preexisting health conditions such as diabetes, liver disease , kidney failure, or heart failure, may lead to the accumulation of toxic products in the body. These may cause brain cell swelling and hamper their function. For example, recurrent abnormal sugar levels in the blood may lead to confusion and even a coma.
Is delirium a medical emergency?
Delirium should be treated as a medical emergency. Monitoring of respiratory and circulatory functions is a priority, with neurological, laboratory, and neuroimaging evaluations. The patient should be usually placed in a placid, stress -free environment and encouraged to engage in cognitive activities.
Does dexmedetomidine lower delirium?
As per research, dexmedetomidine, midazolam, or lorazepam reduces the occurrence and episodes of delirium. Patients are maintained on a low- protein diet to lower their blood am monia levels because ammonia is a by-product of protein metabolism.
What are the symptoms of metabolic encephalopathy?
Encephalopathy can cause abnormal thought processes including confusion, poor memory, hallucinations , and even psychotic thinking. muscle weakness in one area.
What causes encephalopathy?
The causes of encephalopathy are both numerous and varied. Some examples of causes of encephalopathy include: 1 Infectious (bacteria, viruses, parasites, or prions) 2 Anoxic (lack of oxygen to the brain, including traumatic causes) 3 Alcoholic (alcohol toxicity) 4 Hepatic (for example, liver failure or liver cancer) 5 Uremic (renal or kidney failure) 6 Metabolic diseases (hyper- or hypocalcemia, hypo- or hypernatremia, or hypo- or hyperglycemic) 7 Brain tumors 8 Many types of toxic chemicals (mercury, lead, or ammonia) 9 Alterations in pressure within the brain (often from bleeding, tumors, or abscesses) 10 Poor nutrition (inadequate vitamin B1 intake or alcohol withdrawal) 11 These examples do not cover all of the potential causes of encephalopathy but are listed to demonstrate the wide range of causes. Although numerous causes of encephalopathy are known, the majority of cases arise from several major categories (some examples in parentheses):#N#infection (HIV, Neisseria meningitides, herpes, and hepatitis B and hepatitis C)#N#brain anoxia or brain cell destruction (including trauma) 12 Some drugs may cause encephalopathy; for example, posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) may occur due to the use of drugs like tacrolimus and cyclosporine. This syndrome manifests with symptoms of headache, confusion, and seizures.
What are the causes of brain cancer?
Anoxic (lack of oxygen to the brain, including traumatic causes) Alcoholic (alcohol toxicity) Hepatic (for example, liver failure or liver cancer) Uremic (renal or kidney failure) Metabolic diseases (hyper- or hypocalcemia, hypo- or hypernatremia, or hypo- or hyperglycemic) Brain tumors.
What is metabolic encephalopathy?
“ Metabolic encephalopathy ” is a general term that encompasses any process affecting global cortical function by altering the biochemical function of the brain. It should be suspected when there is altered consciousness without focal neurologic signs. The characteristic features of metabolic encephalopathy are gradual onset rather than abrupt onset, fluctuating levels of consciousness, increased spontaneous motor activity (restlessness, tremors, myoclonus, rigidity), and normal pupillary and ocular reflexes with conjugate eye movements. Common contributing factors are the use of multiple drugs that act on the brain, as well as major surgery, organ failure, electrolyte disturbance, and endocrine disease. Other risk factors are advanced age, sepsis, preexisting neurologic or psychiatric disease, and severe nutritional deficiency. Of these factors, the most important is the effect on the brain of drugs, particularly sedative-hypnotics, opioids, and psychotropic medications.
What happens to metabolic encephalopathy after birth?
Several metabolic encephalopathies typically manifest abruptly after birth, as the newborn relies on his or her own immature metabolism to replace placental function. Others manifest later but unexpectedly or can be provoked by a small metabolic disturbance imposed on an apparently normal neurological substrate ( Table 107-5 ). In all cases, a systematic examination and a basic metabolic screening must be urgently undertaken. Empirical intervention should commence while the results of more laborious assays are pending. The combination of some symptoms and the results of initial exploratory tests allows for the reasoned initiation of urgent therapy. In the newborn, the predominant manifestation of neurometabolic diseases includes progressive depression of consciousness, feeding difficulties, vomiting, and intractable seizures. An enlarged fontanel indicates the development of cerebral edema and signifies the need for rapid plasma filtration to remove a toxic metabolite. Imaging should be performed, as specific cerebral structural abnormalities can be indicative of certain disorders, such as necrosis of the basal ganglia in organic acidurias, leukoencephalopathy in MSUD, elongated cerebral vessels in Menkes disease, and perisylvian atrophy in glutaric aciduria type I. Multiple cerebral necrotizing lesions (poliodystrophy) with hepatopathy and lactic acidosis are typical of Alpers syndrome. In some cases, cofactor or vitamin supplementation is initiated in the presence of a specific clinical syndrome. For example, neonatal convulsions can be due to pyridoxine dependency, folinic acid responsive encephalopathy, biotinidase deficiency, or molybdenum cofactor deficiency, the first three of which are treatable by supplementation. Original newborn screening results should be retrieved and verified for all neonates and repeated during metabolic crises. Commercially available comprehensive screening of dried blood cards by tandem mass spectroscopy constitutes a suitable method for the diagnosis of patients of all ages in whom a metabolic disease is suspected. Later in childhood, fulminant metabolic encephalopathies manifest with better defined manifestations. Leigh syndrome causes acute neurological disability due to striatal necrosis and rhombencephalopathy easily detectable by magnetic resonance imaging and often associated with more extensive cerebral abnormalities. Reye syndrome combines cerebral edema with acute hepatopathy that can be induced by drugs or represent the manifestation of an underlying fatty acid oxidation defect. Intermittent ataxia can also be the manifestation of a disorder of energy metabolism or of organic aciduria. In all cases, bedside measurement of blood glucose and urine ketones should be immediately peformed. Blood count, serum electrolytes, blood gases, lactate, pyruvate, ammonia, serum amino acids, blood carnitine and acylcarnitines, urine organic acids, and urinary ketone bodies should also be assayed and neuroimaging (magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy) performed. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis should always include determination of glucose, lactate, pyruvate, and amino acids.
How long does it take for dementia to develop?
For example, dementia takes at least 6 months or longer to appear in the most rapidly developing illnesses, such as Creutzfeldt‐Jakob disease. Once individuals develop dementia, the cognitive impairment remains on a stable, although deteriorating, course that may be exacerbated by a toxic‐metabolic encephalopathy.
What are the factors that affect the brain?
Of these factors, the most important is the effect on the brain of drugs, particularly sedative-hypnotics, opioids, and psychotropic medications. Metabolic encephalopathy has a variable presentation, ranging from agitation to depressed consciousness and coma.
What drugs cause myoclonus?
Those with uremia, penicillin intoxication, meperidine (Demerol) treatment, and other metabolic encephalopathies have myoclonus. Narcotic and barbiturate intoxication causes miosis (contracted pupils), and amphetamines, atropine, and other sympathomimetic drugs dilate pupils.
What causes a person to have a disordered consciousness?
The list of metabolic encephalopathies is extensive and includes such disparate conditions as hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, hepatic encephalopathy, drug overdose, bacterial meningitis, and the postseizure state. The principal reason for grouping together this wide variety of disorders is that the neurologic examination may appear quite similar regardless of the underlying etiology. Nevertheless, the cause of the metabolic encephalopathy is the fundamental determinant of treatment and prognosis. Thus, considering the biochemistry of metabolic encephalopathies is of prime importance in their differentiation.
What is metabolic encephalopathy?
Metabolic encephalopathy is the term used to describe damage to the brain caused due to serious impairment of body’s metabolic activity. The damage can be temporary or permanent. Systemic diseases such as diabetes, cirrhosis of liver, kidney failure, heart failure all can cause metabolic encephalopathy. Symptoms of metabolic encephalopathy may ...
What is the main aim of treatment?
The main immediate aim of treatment is to neutralize toxins that are built up in the blood. In the hospital patient is continuously monitored for his respiratory and circulatory function. Reversing of the underlying problem is the basic priority. Even with treatment there is possibility of residual damage to the brain function.
What are the causes of liver damage?
Infection in patients suffering from liver damage. Serious illnesses that may change the whole metabolic process in the body. Over dose of certain medicines such as narcotics and sedatives. Dehydration caused due to diarrhea and vomiting. Exposure to various toxic chemicals and metals.
What is the term for a disease of the brain that alters brain function or structure?
Encephalopathy is a term for any diffuse disease of the brain that alters brain function or structure. Encephalopathy may be caused by infectious agent (bacteria, virus, or prion), metabolic or mitochondrial dysfunction, brain tumor or increased pressure in the skull, prolonged exposure to toxic elements (including solvents, drugs, radiation, paints, industrial chemicals, and certain metals), chronic progressive trauma, poor nutrition, or lack of oxygen or blood flow to the brain. The hallmark of encephalopathy is an altered mental state. Depending on the type and severity of encephalopathy , common neurological symptoms are progressive loss of memory and cognitive ability, subtle personality changes, inability to concentrate, lethargy, and progressive loss of consciousness. Other neurological symptoms may include myoclonus (involuntary twitching of a muscle or group of muscles), nystagmu...
Can encephalopathy cause permanent damage?
However, the encephalopathy may cause permanent structural changes and irreversible damage to the brain. Some encephalopathies can be fatal. Treating the underlying cause of the disorder may improve symptoms. However, the encephalopathy may cause permanent structural changes and irreversible damage to the brain.
What are the symptoms of encephalopathy?
Depending on the type and severity of encephalopathy, common neurological symptoms are progressive loss of memory and cognitive ability, subtle personality changes, inability to concentrate, lethargy, and progressive loss of consciousness.
Can encephalopathy be fatal?
Some encephalopathies can be fatal. Encephalopathy is a term for any diffuse disease of the brain that alters brain function or structure. Encephalopathy may be caused by infectious agent (bacteria, virus, or prion), metabolic or mitochondrial dysfunction, brain tumor or increased pressure in the skull, prolonged exposure to toxic elements ...
What is the treatment for seizures?
Anticonvulsants may be prescribed to reduce or halt any seizures. Changes to diet and nutritional supplements may help some patients. In severe cases, dialysis or organ replacement surgery may be needed. Encephalopathy is a term for any diffuse disease of the brain that alters brain function or structure.
What tests are used to diagnose encephalopathy?
Blood tests, spinal fluid examination, imaging studies, electroencephalograms, and similar diagnostic studies may be used to differentiate the various causes of encephalopathy. Treatment. Treatment is symptomatic and varies, according to the type and severity of the encephalopathy.
What are the symptoms of a symtom?
Other neurological symptoms may include myoclonus (involuntary twitching of a muscle or group of muscles), nystagmus (rapid, involuntary eye movement), tremor, muscle atrophy and weakness, dementia, seizures, and loss of ability to swallow or speak.
What is the diagnosis of encephalopathy?
Diagnosis and Treatment . What to Expect . "Encephalopathy" means damage or disease that affects the brain. It happens when there’s been a change in the way your brainworks or a change in your body that affects your brain. Those changes lead to an altered mental state, leaving you confused and not acting like you usually do.
What is nonconvulsive status epilepticus?
Nonconvulsive status epilepticus. This happens when you have seizuresover and over in your brain, though they may not cause any physical symptoms. Types of encephalopathy that are irreversible include: Chronic traumatic encephalopathy. This condition is caused by repeated head injuries, which damage the brain.
What is the cause of Hashimoto's disease?
Hashimoto’s encephalopathy. This type is linked to a thyroidcondition called Hashimoto’s disease. The cause isn’t clear, but it may be that your immune systemattacks your brain and changes the way it works. Metabolic encephalopathy.
What happens when blood sugar is too high?
For example, if blood sugargets too high in diabetes, it can lead to confusion and even a coma.
What is the condition that causes brain damage?
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy. This condition is caused by repeated head injuries, which damage the brain. Today, it’s best known for its ties to high-impact sports like football and boxing. Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. It happens when your brain doesn’t get enough oxygen, which leads to brain damage.
What happens if you don't get enough oxygen?
It happens when your brain doesn’t get enough oxygen, which leads to brain damage. It can happen after cardiac arrest, carbon monoxide poisoning, drug overdose, or near-drowning. Symptoms. The symptoms you have depend on the type and cause of your encephalopathy, but some of the most common ones are: Confusion.
What to do if you have seizures?
Seizures. If you notice any of these symptoms in yourself or someone else, you should call your doctor or go to the emergency room. Diagnosis and Treatment. To diagnose the disorder, your doctor will give you a physical examand ask you about your medical history, especially any medications you’re taking.