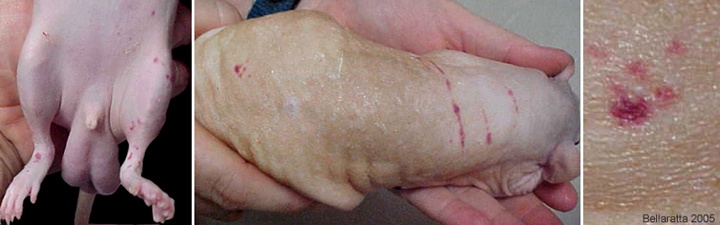
What to do if your rat has a mammary tumor?
Benign mammary tumors are treated by surgical removal of the tumor by a veterinarian. These surgeries are typically very simple and are not stressful to the rat. Unfortunately, benign tumors have a high incidence of reoccurring. Because malignant mammary tumors invade surrounding tissues and organs, they are often very difficult to remove.
What is a mammary tumor in rats?
Malignant (aggressive and spreading) tumors that are found under the skin anywhere on the underside of the body, from the chin to the tail, as rats have widely distributed mammary (breast) tissue.
How are mammary tumors treated?
Treatment of mammary tumors in small mammals currently relies on surgical excision of the tumor and the associated mammary gland. Mammary tumors in rodents, both benign and malignant, typically grow by expansion until they reach a size that causes the overlying skin to become traumatized and infected.
Can a tumor on a rat be removed without surgery?
Where a tumor is inoperable or the rat is not well enough for an anesthetic, there are less effective non-surgical options. These will not remove the tumor but they may slow down or stop it from growing.

Can rats live with mammary tumors?
Rat mammary glands extend along the underline from the neck to the pelvis, so mammary tumors can occur anywhere along the length of the body. They are common in male and female rats and can appear as early as a few months of age....Yarmouth Veterinary Center.DayOpenCloseSATURDAY8:00am**12:00pmSUNDAY**4:00pm5 more rows
How do you treat a mammary tumor?
Benign tumors are cured by surgery, although the development of new mammary tumors (both benign and malignant) is possible. There is a poorer prognosis with malignant mammary tumors and it also depends on what type of cancer.
What causes mammary tumors in rats?
Mammary Tumors These tumors are often stimulated by estrogen and usually occur after a rat stops ovulating at around 18 months of age. Unfortunately, about half of all female rats will get mammary tumors, and it is not uncommon for them to get several during their life either at the same time or one after the other.
How do you treat a tumor on a rat?
Treatment. Mammary tumors and large lipomas are often surgically removed, especially if they are suspected to be cancerous or causing ambulation issues in your rat. Some growths are difficult to completely remove and regrowth is common. Cysts are usually lanced, allowing fluid to ooze out.
How much is it to remove a mammary tumor?
Cost of treatment If only one mammary gland needs to be removed, the surgery will cost approximately $500. For longer procedures, such as a full mastectomy, we charge between $800-$1,200.
Can a mammary tumor burst?
At first the tumor is small and may feel like a pebble or dried pea. The tumor should be removed as soon as possible in hope of removing it completely. If left alone, mammary tumors get larger and harder and ultimately burst through the skin creating a smelly, infected ulcer.
How long can a rat survive with a tumor?
A rat that has a benign tumor and tumor removal and spay will typically live a full life. Many younger rats have lived up to an additional 2 years following surgery. Surgery is not the right choice for some rats.
What foods prevent tumors in rats?
This study demonstrated that whole apple extracts effectively inhibited mammary cancer growth in the rat model; thus, consumption of apples may be an effective strategy for cancer protection.
How do you shrink a benign tumor?
Conventional chemotherapy is occasionally used to shrink non-cancerous brain tumours or kill any cells left behind after surgery. Radiotherapy involves using controlled doses of high-energy radiation, usually X-rays, to kill the tumour cells. Chemotherapy is less frequently used to treat non-cancerous brain tumours.
Should I remove rat tumor?
Rats are prone to tumors, commonly in the mammary glands and in the uterus. These tumors can be benign or malignant. Removing them as soon as they are noted makes for a much better prognosis.
Is it common for rats to get tumors?
Rats are genetically predisposed to a high incidence of tumors and cancers. Some tumors may be malignant while others are benign. In all cases, however, it is advisable to remove the tumor to help reduce the fatalities as a result of the cancerous growths.
How do you humanely put down a pet rat?
The only humane way to euthanize a rat at home without veterinary help is with carbon dioxide (CO2). Euthanasia with CO2 is approved by the American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA). Concentrated CO2 is a central nervous system depressant and actually causes anesthesia.
Is mammary neoplasia common in rats?
Mammary Neoplasia is common in the rat. The most common tumour type is a benign fibroadenoma. Mammary tissue is extensive in the rat, extending from the neck to the flanks, so mammary neoplasia should be considered when a rat is presented with a mass within this region.
Can a rat have fibroadenomas?
The rat may present with one or more subcutaneous masses, which are encapsulated in the cases of benign fibroadenomas. The masses can be of variable size and may become very large. They may ulcerate and begin to prevent normal activities such as eating, drinking and moving.
How do you treat a benign mammary tumor in a rat?
Benign mammary tumors are treated by surgical removal of the tumor by a veterinarian. These surgeries are typically very simple and are not stressful to the rat. Unfortunately, benign tumors have a high incidence of reoccurring. Because malignant mammary tumors invade surrounding tissues and organs, they are often very difficult to remove.
How old are rats when they develop mammary tumors?
Older rats (>18 months) are more likely to develop mammary tumors. Estimates are that more than half of the female rat population will develop a mammary tumor by age 2 if unspayed.
What are the two types of mammary tumors?
Classification of Tumors. Mammary tumors can be divided into two groups, mammary fibroadenomas and mammary adenocarcinomas. A mammary fibroadenoma is a benign mammary gland tumor. Fortunately, mammary fibroadenomas are more common than their malignant counterparts, mammary adenocarcinomas. Benign mammary tumors are fibrous, noninvasive, ...
Why is it so hard to remove a mammary tumor?
Because malignant mammary tumors invade surrounding tissues and organs, they are often very difficult to remove. Often, the best alternative in consideration of the rat’s quality of life is humane euthanasia performed by a veterinarian.
What hormones are involved in the growth of mammary tumors?
The development and growth of mammary tumors is dependent on the concentration of receptors for the hormones estrogen and prolactin. It has been found that benign mammary tumor growth is caused by an increase in prolactin.
What happens when a rat's tumor dies?
When the tissue dies, toxins are released into the blood, and toxemia and septicemia (blood poisoning) can occur. Septicemia will cause organ failure which ultimately causes the rat to die.
Where are mammary tumors found?
While these tumors can occur anywhere within mammary tissue, they are most commonly found in the armpit, abdomen, and groin area. Mammary tumors can occur in young rats but are typically diagnosed in rats over 18 months old.
How big is a mammary tumor in rats?
Although most mammary tumors in rats are benign, if not treated will continue to grow becoming quite large measuring from several millimeters to several centimeters, and encompassing up to half the body weight of the rat.
What are the factors that contribute to the development of mammary tumors in rats?
Several factors appear to play a role in the development of spontaneous mammary tumors in the rat such as age , sex, genetics, endocrine, environment , and diet (Percy, Barthold, 2001). Studies have shown that of those factors the most important influence in tumorigenesis is diet. It is well known that caloric intake affects tumor incidence in rats.
What is a soft, circumscribed, or somewhat flat appearing growth that can be movable on palpation
Typically seen as a soft, circumscribed (round), or somewhat flat appearing growth that can be movable on palpation, to a more firm and attached growth (seen more in malignancy) anywhere along the region of mammary tissue.
How does a tumor affect a rat's ability to feed itself?
These tumors just by virtue of how large they can grow will not only impinge on other organs, but also inhibit the rat’s mobility , result in difficulty grooming, and interfere with the rat’s ability to feed itself. Weight loss eventually occurs as the tumor’s growth deprives other tissues and organs of needed nutrients.
Where is mammary tissue found in rats?
Etiology. Mammary tissue is extensive in rats and is found ventral, lateral and dorsal, running from the shoulder and chin area to the base of the tail. Tumors can arise anywhere that this tissue type is present, but is most often seen at the pit of the arm, abdomen, and groin of female rats.
Can you spay a female rat?
If surgery for mammary tumor removal is being performed on female rats it is worthwhile to discuss with the vet the possibility of also spaying if the rat’s general health status is good. Since benign mammary tumors are hormone dependent, and malignant mammary tumors are initially hormone dependent, spaying females will significantly reduce or remove those hormones that influence these tumors.
Can a mammary tumor be found in rats?
These tumors may also occasionally present in males. The most common mammary tumor found in rats is the mammary fibroadenoma, a benign encapsulated tumor.
What is a tumor in a rat?
Tumors (neoplasias) are growths that we, as rat owners, see all too often. Learning about the different types of cancers will help us to identify problems as they occur, treat sooner, and better understand the disease processes involved. Any abnormal growth, swelling, bump, or lump on your rat can be a potentially serious issue.
Do you check your rats daily?
It is essential that you check your rats often, even daily, for any physical abnormalities and that you watch their behavior and their movement for any abnormalities. Advanced Health Check. Not every lump is going to be a tumor, not every tumor is going to be cancerous, and not every cancer is going to be fatal.
How do you treat mammary tumors in small mammals?
Mass removal. Treatment of mammary tumors in small mammals currently relies on surgical excision of the tumor and the associated mammary gland. Mammary tumors in rodents, both benign and malignant, typically grow by expansion until they reach a size that causes the overlying skin to become traumatized and infected.
How common are mammary gland tumors in rats?
The reported incidence of mammary gland tumors may range from 30% to 90% in aged female rats, and approximately 16% of male rats may be affected. Most mammary tumors in rats are fibroadenomas;
What mammals have mammary gland tumors?
Among small mammals, mammary tumors are reported most commonly in rats (Rattus norvegicus), mice (Mus musculus), and African pygmy hedgehogs (Atelerix albiventris). Mammary gland tumors have also been reported in guinea pigs (Cavia porcellus) and hamsters. Disease is typically seen in middle-aged to geriatric animals.
What are the differential diagnoses for mammary tumors in rabbits?
Diagnosis. Important differential diagnoses for mammary tumor include mastitis and mammary gland hyperplasia, as well as abscess and granuloma. Mammary gland disorders are often accompanied by ovarian and/or uterine abnormalities in the rabbit.
What type of tumors are found in guinea pigs?
Reported tumors include mammary gland adenocarcinoma, malignant mixed tumor , liposarcoma, papillary cystadenoma, and carcinosarcoma. Fibroadenomas have been reported in male and female guinea pigs, but are rarely seen in practice. Malignant tumors can metastasize to regional lymph nodes, abdominal viscera, or lungs.
What is the disease that affects mice?
Unlike rats, mice are more commonly affected by mammary adenocarcinoma. These tumors are usually soft, fleshy, infiltrative, highly vascular, and they often metastasize to the lungs. Mammary tumors in mice are also usually associated with a retrovirus called the mammary tumor virus or the Bittner agent.
Where can you find mammary glands?
Mammary tissue can occur anywhere along the shoulder, neck, ventrum, flank or tail base in rats and mice. Mammary gland tumors are typically seen in middle-aged to older animals. Mammary tumors are more common in male guinea pigs than in females, which is unique among mammals. Neoplasia is relatively common in African pygmy hedgehogs, ...
What is the most common tumor in female rats?
Mammary Tumors. The most common tumor in female rats is the benign mammary tumor. These tumors are often stimulated by estrogen and usually occur after a rat stops ovulating at around 18 months of age. Unfortunately, about half of all female rats will get mammary tumors, and it is not uncommon for them to get several during their life either at ...
What type of tumor is most common in rats?
Because these tumors derive from fibrous tissue they are usually quite hard, but they are benign and may be easy to remove. They are most common on the side or back. Squamous cell carcinoma is another form of malignant cancer in rats.
How to diagnose a malignant mammary tumor?
A malignant mammary tumor tends to be smaller and to not grow as fast. Ultimately the only way to properly diagnose the type of tumor is by biopsy, which usually means removing the mass and submitting it to a lab for evaluation.
How to tell if a rat has a pituitary tumor?
One symptom that is common with a pituitary tumor is a quite distinctive posture: first the front, then the hind legs are held out stiffly forward and cannot be flexed by the rat. When you pick the rat up, the arms and legs will often be held forward, although sometimes the hands are curled.
Why does my rat have a lump in his neck?
Salivary glands can enlarge as an inflammatory response to the Sialodacryoadenitis (SDA) virus or a bacterial infection. A lymph node can enlarge in response to a bacterial infection or cancer.
What is the most common cancer in rats?
Squamous cell carcinoma is another form of malignant cancer in rats. It is reported that this type of tumor is commonly found on the face and should be suspected with any swelling or abscess in this area. Another very common place for cancers to appear is directly below the ear.
Can a rat have a tumor on the side of his leg?
These cancers also often bleed severely. Fibrosarcoma can also be seen in rats, and these tumors commonly occur on the leg, but can also occur on the side.
What is the most common reproductive tumor in rats?
Mammary Fibroadenomas. The most common kind of reproductive tumors in rats. Can be found in the mammary (breast) tissue, and are usually benign (not malignant). Found in both female and male rats.
Why are tumors common in rats?
Some are more common than others, of course. For example, mammary adenocarcinomas are common in rats because of their widely distributed mammary tissue. Tumors of the pituitary gland increase in occurrence in relation to increased consumption of high-calorie foods.
Can a tumor be removed early?
It is best to remove the tumors as soon as possible in order to avoid the worst complications. Chances of recurrence may also be minimized if the tumor is removed early.
Do rats have cancer?
Rats are genetically predisposed to a high incidence of tumors and cancers. Some tumors may be malignant while others are benign. In all cases, however, it is advisable to remove the tumor to help reduce the fatalities as a result of the cancerous growths.
How long does it take for a rat to get a tumor removed?
Knowing the problems that arise for a rat who is living with a tumor, most rat owners opt to get the tumor removed within a few weeks of it appearing.
What happens if a rat has a tumor?
This leads to rapid weight loss and general decline.
What is a tumor in a rat?
Fibroadenomas – benign, fibrous tumors of the mammary tissue in rats, which are encapsulated (confined to a specific area). Mammary tissue is widely distributed in the rat’s body and these tumors can appear around the armpit, side, groin, neck, belly and lower shoulder. Pituitary adenomas – benign adenomas of the anterior lobe ...
Why do rats get cancer?
As for most mammals, cancerous growths in rats increase with age. This is partly because of the cumulative effect of diet and environmental toxins over time and also as a result of the aging process. Most mammary tumors show from around 20 months onwards.
How to tell if a rat has a tumor?
Most tumors are easy to spot quite quickly as lumpy areas, often under the armpits or in the groin. It’s advisable to regularly check your rats (perhaps once a week ) by gently running your hands over the areas when mammary tissue occurs.
What is the most important influence on the survival of a laboratory rat?
According to the textbook, The Laboratory Rat (American College of Laboratory Animal Medicine Series) diet has the most influence. Adlib feeding (regardless of diet ) increases tumor occurrence in rats and reduces longevity.
When do rats get menopause?
Rats generally experience menopause around 18 months of age and after that, tumors that are affected by hormones start to develop. Most pituitary tumors contain (have receptors for) a single pituitary hormone, and the most common pituitary tumor in rats is the prolactinoma. These tumors grow under the influence of prolactin, ...
What are the problems with mice and rats?
Most problems in mice and rats are dermatopathies, respiratory infections, and neoplasia.
How long does it take for a rat to ovulate?
Rats have an average litter size of 8–18 pups. Weaning takes place at ~21 days. Both male and female mice are sexually mature by 6–8 weeks and have a breeding life of 9 months. Estrous cycle length in female mice is 4–5 days, and estrus lasts 10–20 hours. Female mice ovulate ~6–10 eggs.
What is the best cage for mice?
The best cages are made of a material that is easy to clean and deodorize and is indestructible to rodent chewing or digging in the corners. The cage floor can be solid but should be waterproof and easy to clean. Wire mesh floors should be avoided, because rats and mice can trap their feet and especially hindlimbs in the openings, resulting in fractures and injuries.
Why do rats have incisors?
Dental problems are commonly seen in pet mice and rats because of their continually erupting teeth. Overgrown incisors are seen most frequently in rats and mice, in contrast with cheek teeth malocclusion seen in guinea pigs and chinchillas.
Why is it so hard to collect blood in mice?
Blood collection can be difficult in small rodents, especially in mice because of their small body and blood vessel size. In both rats and mice, the saphenous vein or lateral tail vein can be used to collect small amounts of blood for blood smears, blood glucose measurement, etc.
How tall should a rat cage be?
Consequently, minimal cage heights of 12–15 inches (30–38 cm) for rats and 7–8 inches (18–20 cm) for mice are recommended. Environmental enrichment is important for both mice and rats.
How long does it take for a mouse to have a litter?
Gestation lasts 19–21 days; pseudopregnancy from sterile matings lasts 12 days. Mice have an average litter size of 5–12 pups. Weaning takes place at ~21 days. Male mice and rats produce a small amount of sperm daily at puberty (eg, 40–50 days in a rat).

Definition
Clinical Signs
Etiology
- Mammary tissue is extensive in rats and is found ventral, lateral and dorsal, running from the shoulder and chin area to the base of the tail. Tumors can arise anywhere that this tissue type is present, but is most often seen at the pit of the arm, abdomen, and groin of female rats. Although mammary tumors can occur at a younger age they have a higher occurrence after 18 months of …
Diagnostics
- Palpation of ovoid, discoid, or varied shaped mass. May be well demarcated. Large mass may show ulceration or necrosis. Rat may appear cachectic as tumor continues to grow. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), for small animals (if available), may be useful with soft tissue tumors. Histologic examination of tissue. Microscopic examination of aspirate.
Treatment
- Excision and removal of tumor is recommended. Note: preanaesthetic fasting of rats is not necessary since vomiting does not occur in this species. Free access to both food and water should be provided until just prior to anesthesia (Flecknell, 1991). Pre or post-op prophylactic broad-spectrum antimicrobials may be indicated in elderly, debilitated or immunocompromised r…
Nursing Care
- Provide hospital cage during recovery, or if there are concerns that their cage mates may groom sutures or wound site.
- Provide clean bedding daily such as felt, soft t-shirt type material or ink-free paper towels. Avoid using material such as terry cloth type towels that can ravel. Also avoid litter-type bedding, p...
- Provide hospital cage during recovery, or if there are concerns that their cage mates may groom sutures or wound site.
- Provide clean bedding daily such as felt, soft t-shirt type material or ink-free paper towels. Avoid using material such as terry cloth type towels that can ravel. Also avoid litter-type bedding, p...
- Provide additional warmth to maintain body temperature within normal limits. It is essential that the rat does not become overheated or dehydrated. The rat should also be able to move away from the...
- Medicate for post-op pain as needed.
Outcome
- Post-op pain is relieved.
- Incision site is free from infection.
- Medication regimen given if deemed appropriate.
- Increased comfort, mobility, and quality of life.
Prevention
- Offering a diet that is nutritiously low in fat, calories, amines, and nitrates is recommended.
- Consideration should be given to spaying female rats. Documentation supports that ovariectomy prevents, or reduces frequency of, the development of spontaneous mammary tumors.
- Routine health checks will aid in early detection of mammary tumors. Detection and treatme…
- Offering a diet that is nutritiously low in fat, calories, amines, and nitrates is recommended.
- Consideration should be given to spaying female rats. Documentation supports that ovariectomy prevents, or reduces frequency of, the development of spontaneous mammary tumors.
- Routine health checks will aid in early detection of mammary tumors. Detection and treatment while the growth is still small decreases operative time, enhances recovery period, and improves outcome.