
Potentially Malignant microcalcification by texture
| Microcalcification texture | Probability of DCIS | Most frequent grade |
| Powderish: fine, indiscernible, cotton b ... | 47% | Low Grade |
| Crushed Stone: coarse, granular, angular ... | 61% | low to Intermediate |
| Casting | 96% | High grade |
What are the chances of microcalcifications being cancerous?
”Probably benign” calcifications have a less than 2% risk of being cancer. In other words, about 98% of the time, these type of calcifications are considered not to be cancer. Typically, they will be monitored every six months for at least one year. Are most microcalcifications benign? • Microcalcifications are small and may appear in clusters.
How often are microcalcifications malignant?
They are less concerning if they are scattered throughout an entire breast or even both breasts. Some radiologists consider five or more calcifications in a cluster to be possibly suspicious of an underlying cancer. However, this is not a definite cutoff number — others recommend additional testing even if there are fewer than five in a cluster.
Can microcalcifications be cancerous?
Microcalcifications can also give an idea of the extent of the disease. They are usually noncancerous, although some patterns can be a sign of cancer. Information about the size, density, and distribution of breast microcalcifications can give an idea about the benign or malignant nature of the cancer.
Do breast calcifications mean that I have breast cancer?
While calcifications are usually harmless, they can be a sign that a woman is at risk for developing breast cancer and needs more testing. For instance, if the cluster of calcifications is tight or they are noted to present as lines of tiny calcifications, the radiologist may recommend additional mammogram images for further testing.
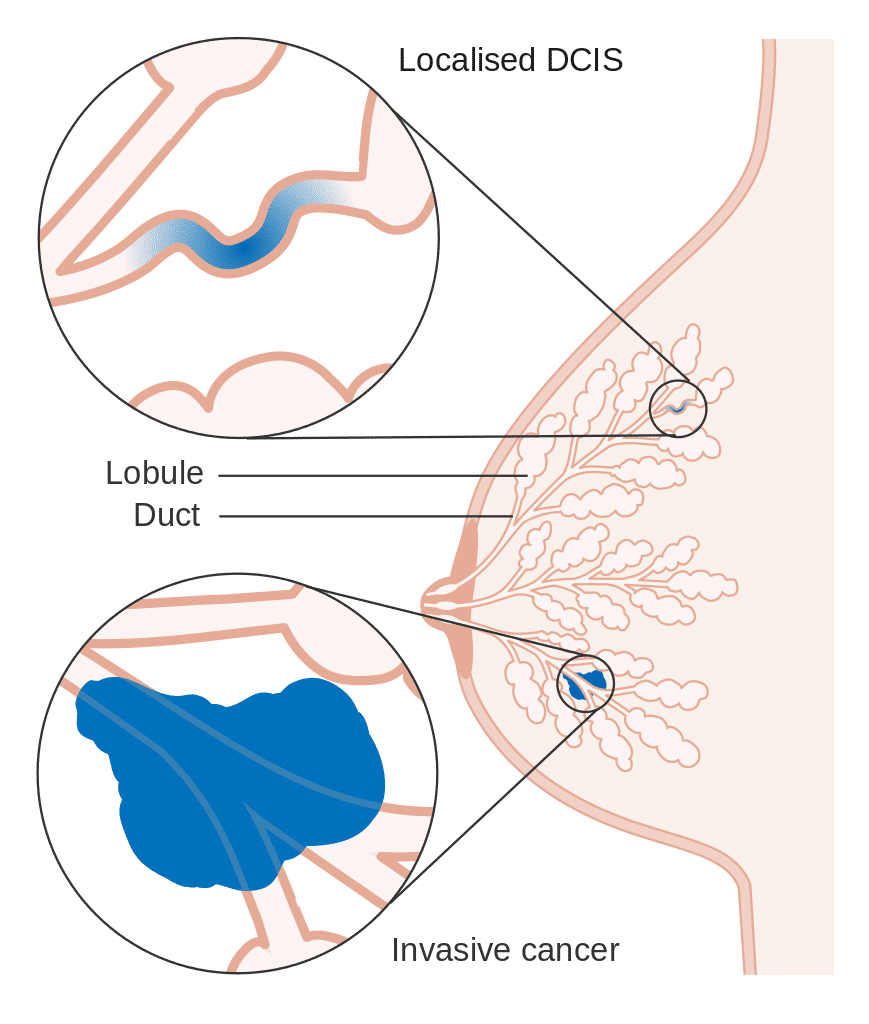
What if my breast calcifications are malignant?
Although breast calcifications are usually noncancerous (benign), certain patterns of calcifications — such as tight clusters with irregular shapes and fine appearance — may indicate breast cancer or precancerous changes to breast tissue.
What stage cancer are microcalcifications?
Are breast calcifications a sign of cancer? They're often benign, but calcifications can sometimes be an early sign of breast cancer. “The most common form of cancer we see with calcifications is ductal carcinoma in situ, which is considered stage 0 cancer,” Dryden says.
Can microcalcifications be advanced cancer?
Microcalcifications (the smaller type of calcifications) can sometimes put women at an increased risk of developing breast cancer. If microcalcifications occur in small lines or small clusters, a woman might be at increased risk of developing breast cancer.
What percentage of breast microcalcifications are malignant?
The rate of malignancy was 40.0% (543 of 1357) for cases with a single cluster of microcalcifications, 50% (112 of 224) for those with multiple clusters and 60.0% (303 of 505) for those with dispersed microcalcifications.
Do I need a mastectomy for DCIS?
Most women with DCIS or breast cancer can choose to have breast-sparing surgery, usually followed by radiation therapy. Most women with DCIS or breast cancer can choose to have a mastectomy. You have small breasts and a large area of DCIS or cancer. You have DCIS or cancer in more than one part of your breast.
What percentage of stereotactic biopsies are malignant?
In a study of 3,765 percutaneous large-core breast biopsies performed with either stereotactic or sonographic guidance, 5 (0.1%) were found to be malignant at 6-month follow-up examination.
Are all microcalcifications malignant?
Microcalcifications are tiny calcium specks seen on a mammogram. Most of the time, they are not cancer. However, these areas may need to be checked more closely if they have a certain appearance on the mammogram.
How often are breast microcalcifications cancerous?
Sometimes, breast calcifications are the only sign of breast cancer, according to a 2017 study in Breast Cancer Research and Treatment. The study notes that calcifications are the only sign of breast cancer in 12.7 to 41.2 percent of women who undergo further testing after their mammogram.
How long is recovery after stereotactic biopsy?
Watch for excessive bleeding, redness, skin changes, swelling or pain. Bleeding under the skin could present as a hard area (lump) that could take up to 6 weeks to resolve.
Is a stereotactic biopsy considered surgery?
Stereotactic breast biopsy is a non-surgical method of assessing a breast abnormality and is performed by a specially trained radiologist on an outpatient basis. A stereotactic breast biopsy is an option when a mammogram shows a breast abnormality such as: A suspicious solid mass.
How do you get rid of breast calcifications?
How are breast calcifications treated?Monitoring the tissue for any concerning changes.Removing the breast tissue or the entire breast.Chemotherapy and/or radiation.Targeted drug therapy.
Are microcalcifications always DCIS?
Calcifications can be due to DCIS. However, not all calcifications are found to be DCIS. Many women develop benign (not cancer) calcifications in their breasts as they get older. If you have calcifications, further mammograms will be done to see the calcifications in more detail.
What is the procedure to remove calcified breast tissue?
A surgeon will perform the biopsy in an operating room under local or general anesthesia. Prior to the surgical procedure, a radiologist may use X-rays to identify the calcified breast tissue and will then mark the tissue to be removed -- with either a thin wire or with dye.
What is calcification in breast?
Breast calcifications are small calcium deposits that develop in a woman's breast tissue. They are very common and are usually benign (noncancerous). In some instances, certain types of breast calcifications may suggest early breast cancer. There are two types of breast calcifications: macrocalcifications and microcalcifications.
Can calcium cause calcification in breast?
A number of factors can cause calcification in a woman's breast, including normal aging, inflammation, and past trauma to the area. Calcium from your diet does not cause breast calcifications.
Is microcalcification a cancer?
Microcalcifications are small calcium deposits that look like white specks on a mammogram. Microcalcifications are usually not a result of cancer.
Can calcifications be seen on a mammogram?
Breast calcifications do not cause symptoms, as they are too small to be felt during a routine breast exam. Usually, breast calcifications are first noticed on a mammogram.
What is the classification of calcifications on mammograms?
The American College of Radiology (ACR) Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) classifies calcifications on mammograms into three categories: typical benign, intermediate concern and higher probability of malignancy, according to types and distribution of calcifications.
What is benign calcification?
Benign calcifications are typically larger, coarser, round with smooth margins and have a scattered or diffuse distribution. Malignant calcifications are typically grouped or clustered, pleomorphic, fine and with linear branching.
Why are calcifications important?
However, calcifications are important because they can be the first and earliest sign of malignancy. For detection and analysis of microcalcifications, high-quality images and magnification views are required. The American College of Radiology (ACR) Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) classifies calcifications on mammograms ...
What is the survival rate of a woman with a crushed stone microcalcification?
Women with ‘ crushed stone ‘ microcalcifications, overall, tend to have a 15 year survival rate of 87% to 95%.
What does increased carbonate content in microcalcification mean?
Increased carbonate content in a microcalcification indicates that a cancer is growing in the viscinity.
How high is DCIS cure rate?
DCIS has an extremely high cure rate, generally over 95%. Casting microcalcifications are perhaps the most serious indicators of the different textures frequently encountered, but their presence is not a significant prognostic indicator.
What are the factors that affect breast cancer staging?
Other factors traditionally associated with breast cancer staging and grading such as tumor size, nuclear features, and lymph node metastasis. Casting microcalcifications tend to be associated with tumors that have already reach a higher grade based on traditional measurements.
How long does it take for a breast cancer patient to relapse?
Overall, the average relapse-free interval for patients with confirmed breast cancer associated with casting-type microcalcifications, is about 27 months.
Can casting microcalcifications cause lymph node metastasis?
Casting breast microcalcifications, when found in women who turn out to have multifocal DCIS, can often have higher incidence lymph node metastasis. Casting microcalcifications tend to be indicators of increased risk for systemic disease, and the presence of casting microcalcifications can influence adjuvant therapy decisions once the breast cancer is fully staged.
Is microcalcification a sign of breast cancer?
The presence of microcalcifications in an initial screening may or may not be indicative of acute or potential breast cancer. Research as to the predictive value of different microcalcification presentations is ongoing. However, there is reasonable evidence to suggest that of the three most common microcalcification textures, ...
What are the different types of breast microcalcifications?
Types of Breast Microcalcifications. Breast microcalcifications can be divided into many types based on their form, size, density, and distribution. Breast microcalcifications can occur in many different shapes or forms. They can be linear, round, granular, coarse, monomorphic when all of them having the same shape, ...
Why are microcalcifications important?
The Importance of Microcalcifications. Microcalcifications are actually calcium deposits and are seen as tiny, white dots on a mammogram. They are much less common and are mostly a result of mutations in the breast tissue , though they can be caused by other factors. The appearance of microcalcifications is widely used in the detection ...
What is suspicious breast cancer?
If the distribution of the microcalcifications is linear and they are in round, oval, or amorphous form, they are termed as ‘suspicious’. Radiologists usually term a variable distribution density where the breast microcalcifications are closely packed at one place and widely spread at another as ‘suspicious’, and not definitive, for cancer.
What does a calcification in breast look like?
an X-ray of the breast). Macrocalcifications look like large white dashes or dots and are mostly noncancerous and no further tests are required usually.
What is benign lobular calcification?
Benign lobular calcifications are usually round in shape and have a relatively higher density. They normally have pearl-like or well-defined contours and smooth borders. If the acinar lumen are small, they look punctate and have tiny spots on them.
Can radiology tell if breast microcalcifications are benign or malignant?
Radiologists rely on breast microcalcifications as a possible indicator for breast cancer; however, only histological analysis can confirm this. When studying microcalcifications, if different findings lead to the same result (benign or malignant), then those predictions can be considered reliable. In general, when the distribution ...
Can breast microcalcifications be clusters?
When size is considered, breast microcalcifications can be either large or small, or in clusters with a mix of small and large microcalcifications. Furthermore, breast microcalcifications can have low, high, or variable density.
What are the different types of breast calcifications?
The two types of breast calcifications are microcalcifications and macrocalcifications.
How are breast calcifications diagnosed?
Calcifications may appear as bright white spots on mammograms. You can't feel them from the outside, so the only way to detect them may be through a mammogram.
When breast calcifications are a sign of cancer
Microcalcifications in a certain pattern may signal cancer, because when breast cells are growing and dividing, they make more calcium. So, if there’s an area of the breast where this growth is occurring, the calcium deposits would be grouped together.
What's next?
If you have microcalcifications, your doctor may order another mammogram, or a biopsy, or he or she may wait to order another mammogram after six months.
