Can lymphatic filariasis be cured?
What is filariasis symptoms and treatment?
How do you prevent lymphatic filariasis?
What antibiotics treat filariasis?
In filariasis, it is primarily used to target Wolbachia, an endosymbiotic bacterium in onchocerciasis and lymphatic filariasis.Jun 21, 2018
How is lymphatic filariasis diagnosed?
Is filariasis and lymphatic filariasis the same?
Is there any vaccine for filariasis?
Is there any cure for elephantiasis?
Can doxycycline cure filariasis?
Is doxycycline an antibiotic?
What is Hetrazan tablet used for?
What causes lymphatic filariasis?
How long does it take to treat lymphatic filariasis?
Treatment of lymphatic filariasis in adults and children > 18 months of age involves either a 1 day or 12 day treatment course of DEC (6mg/kg/day). One day treatment is generally as effective as the 12-day regimen. For tropical pulmonary eosinophilia (TPE), a longer DEC treatment course of 14-21 days is generally recommended.
What is the serologic test for lymphatic filariasis?
Serologic enzyme immunoassay tests, including antifilarial IgG1 and IgG4, provide an alternative to microscopic detection of microfilariae for the diagnosis of lymphatic filariasis. Patients with active filarial infection typically have elevated levels of antifilarial IgG4 in the blood and these can be detected using routine assays.
How long does doxycycline kill worms?
Some studies have shown adult worm killing with treatment with doxycycline (200mg/day for 4–6 weeks).
Where to contact the Division of Parasitic Diseases?
For questions regarding diagnostic considerations, contact the Division of Parasitic Diseases at [email protected]
Is DEC contraindicated for lymphatic filariasis?
DEC is contraindicated in patients who may also have onchocerciasis. Prior to DEC treatment for lymphatic filariasis, onchocerciasis should be excluded in all patients with a consistent exposure history due to the possibility of severe exacerbations of skin and eye involvement (Mazzotti reaction). In addition, DEC should be used with extreme caution in patients with circulating Loa loa microfilarial levels > 2,500/mm 3 due to the potential for life-threatening side effects, including encephalopathy and renal failure. Neither steroids pre-treatment nor slow dose escalation prevents these complications. Consultation with a tropical medicine specialist is recommended in these scenarios .
What is lymphatic filtration?
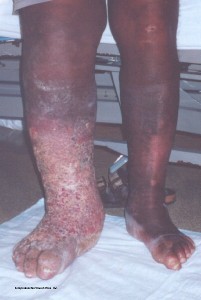
Lymphatic Filariasis (commonly known as elephantiasis and abbreviated as LF) is caused by a parasitic thin worm (filarial nematode) that infects humans through mosquito bites . The worms multiply in the body and create blockages within the lymphatic system.
What is the best treatment for LF?
Once the infection is positively confirmed by lab results and the microfilariae are isolated, there are several safe and rapidly acting drugs that are available for treating LF. There are yearly dosages of medicines available. These are called diethylcarbamazine (DEC). They act fast and kill the worms in the blood. It is also important to break the infection transmission chain by keeping at drug therapy for several years without break and also undertaking community drug administration. There is no filariasis vaccine in the world but efforts are on to develop one.
What causes swelling in the lymphatic system?
The worms multiply in the body and create blockages within the lymphatic system. This results in fluid collection in various tissues of the body. It leads to massive swelling with severe pain and causes frequent fever from other opportunistic infections arising as a result of these stagnant fluids.
How to treat worms in the body?
The primary strategy for treatment is to kill the active worms circulating in the blood and also prevent infected people from transmitting these worms to others. While drugs can kill the worms, there is still risk of lymphedema (swelling) developing. This would require specialized care and the course is to prevent it from deteriorating further. Some basic methods include: 1 Regular and careful cleaning and washing of swollen areas with antibacterial soap and water daily 2 Keeping the swollen part elevated and moving it to improve lymphic fluid flow 3 Usage of anti fungal, anti bacterial creams on wounds if any 4 Encourage mobility using compression bandage support, for the swollen limbs
Why is elephantiasis called elephantiasis?
Given the severe enlargement of limbs, they resemble that of an elephant and hence the name elephantiasis. This further decreases the ability of the lymphatic system to fight other infections and opportunistic skin infections occur leading to hardening of skin. It is an irreversible condition at this advanced stage.
How to get rid of swollen limbs?
Regular and careful cleaning and washing of swollen areas with antibacterial soap and water daily. Keeping the swollen part elevated and moving it to improve lymphic fluid flow. Usage of anti fungal, anti bacterial creams on wounds if any. Encourage mobility using compression bandage support, for the swollen limbs.
Is microfilariae nocturnal?
However, it is not as easy as it sounds. Microfilariae are nocturnal in their activity this means they circulate actively in the blood only at night.
Why is lymphatic filariasis a permanent disability?
Lymphatic filariasis is a leading cause of permanent disability worldwide. Communities frequently shun and reject women and men disfigured by the disease. Affected people frequently are unable to work because of their disability, and this harms their families and their communities.
What is the disease of the lymphatic system?
Lymphatic filariasis, considered globally as a neglected tropical disease (NTD), is a parasitic disease caused by microscopic, thread-like worms. The adult worms only live in the human lymph system. The lymph system maintains the body’s fluid balance and fights infections.
How to prevent lymphatic filariasis?
If you live in or travel to an area with lymphatic filariasis, avoiding mosquito bites is the best way to prevent it.
How is lymphatic filariasis eliminated?
Lymphatic filariasis is targeted for elimination globally. The elimination strategy is based on annual treatment of whole communities with medications that prevent the disease from spreading. Hundreds of millions of people are being treated each year.
What is the disease of the lymphatic system?
Lymphatic filariasis, considered globally as a neglected tropical disease (NTD), is a parasitic disease caused by microscopic, thread-like worms. The adult worms only live in the human lymph system. The lymph system maintains the body’s fluid balance and fights infections.
Is lymphatic filariasis a permanent disability?
Lymphatic filariasis is a leading cause of permanent disability worldwide. Some people will develop lymphedema (a complication of LF). However, proper care of patients with lymphedema can help them feel better and prevent the lymphedema from getting worse.
