Medication
Nov 23, 2021 · Examples include: Special diets. Nutritional supplements. Fish oils. Ointments and creams. Acupuncture. Chiropractic treatment. Homeopathy.
Nutrition
The treatment of cutaneous lupus erythematosus is centered upon formulating a regimen of topical and systemic therapies designed to reduce disease activity and minimize cosmetic damage. Sun avoidance and sunscreen are important preventative measures proven to minimize cutaneous lupus erythematosus exacerbations.
What are the best treatments for lupus?
In recent decades, SLE treatment has moved from the use of hydroxychloroquine, systemic glucocorticosteroids and conventional immunosuppressive drugs to biologic agents, of which belimumab is the first and only biologic agent approved for the treatment for SLE to date.
Is aspirin the only treatment for lupus?
These include: aspirin warfarin (Coumadin) heparin or low-molecular-weight heparin (Lovenox or Fragmin)
Is systemic lupus erythematosis life threatening?
Aug 04, 2021 · Approach Considerations Management of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) often depends on disease severity and disease manifestations, [ 8] although hydroxychloroquine has a central role for...
How do you treat lupus?
Aug 19, 2019 · ABSTRACT: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease presenting with varying degrees of organ and system involvement. Treatment currently includes antimalarials, glucocorticoids, immunosuppressants, and biologics.

What is the most effective treatment for lupus?
Steroids Synthetic cortisone medications are some of the most effective treatments for reducing the swelling, warmth, pain, and tenderness associated with the inflammation of lupus. Cortisone usually works quickly to relieve these symptoms.
What is the first treatment for lupus?
Early Progress With Lupus Treatment Involves Antimalarials and Corticosteroids. The first medication used for lupus, quinine (an antimalarial), was described by Payne in 1894 (Payne, 1894).
Is lupus curable or treatable?
Lupus (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus) Lupus is an autoimmune disease that can cause joint pain, fever, skin rashes and organ damage. There's currently no cure for lupus and it requires life-long management.Apr 19, 2021
What is the latest treatment for lupus?
People living with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) have a new drug option. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved anifrolumab (Saphnelo) in early August — the first new drug approved for SLE in 10 years.
What are the 4 types of lupus?
When people talk about lupus, they may be referring to the most common form—systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). However, there are actually four kinds. Click or scroll to read more about each of them: SLE, cutaneous lupus, drug-induced lupus, and neonatal lupus. I was just diagnosed with SLE.
What vitamins help with lupus?
Vitamins. Vitamin E, zinc, vitamin A, and the B vitamins are all beneficial in a lupus diet. Vitamin C can increase your ability to absorb iron and is a good source of antioxidants.Apr 6, 2009
What are the top 5 signs of lupus?
What are the common symptoms of lupus?loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and weight loss.shortness of breath.joint inflammation, stiffness, and pain.swollen glands.muscle pain.chest pain when you take a deep breath.hair loss.sun sensitivity.More items...
What are the 11 symptoms of lupus?
What are the 11 signs of lupus?Butterfly-shaped rash.Raised red patches on your skin.You're sensitive to light.Ulcers in your mouth or nose.Arthritis in two or more joints, plus swelling or tenderness.Inflammation in the lining of your heart or lungs.Seizures or other nerve problems.Too much protein in your urine.More items...
What were your first signs of lupus?
SymptomsFatigue.Fever.Joint pain, stiffness and swelling.Butterfly-shaped rash on the face that covers the cheeks and bridge of the nose or rashes elsewhere on the body.Skin lesions that appear or worsen with sun exposure.Fingers and toes that turn white or blue when exposed to cold or during stressful periods.More items...•Jan 27, 2021
How does hydroxychloroquine help lupus?
How does Plaquenil work? Plaquenil changes the way your immune system works. In some kinds of lupus, your immune system attacks your body instead of protecting it. Plaquenil tries to quiet or slow down the immune system.
What is the life expectancy for lupus?
With close follow-up and treatment, 80-90% of people with lupus can expect to live a normal life span. It is true that medical science has not yet developed a method for curing lupus, and some people do die from the disease. However, for the majority of people living with the disease today, it will not be fatal.
What are the side effects of hydroxychloroquine?
Hydroxychloroquine may cause side effects. Tell your doctor if any of these symptoms are severe or do not go away:headache.dizziness.loss of appetite.nausea.diarrhea.stomach pain.vomiting.rash.Oct 15, 2020
What is the treatment for SLE?
Patients suffering from SLE are typically treated with corticosteroids and immunosuppressive agents (1). An eminent direct or indirect target of novel therapeutic approaches has been the lupus B cell (2–4).
What is RC18 in Lupus?
B cells are being targeted directly or indirectly in patients with lupus. RC18 is a recombinant human BLyS receptor antibody fusion protein and it is used in a phase III placebo-controlled study plus standard treatment with primary outcome an SRI response rate at week 52 (59).
What is Daratumumab used for?
Daratumumab, a mAb approved for the treatment of multiple myeloma, is an IgG1k mAb directed against CD38 causing depletion of plasma cells. Long-lived plasma cells are residents in niches in the bone marrow or (perhaps more importantly) in inflamed tissue and they do not respond to immunosuppressants, including B-cell-targeting treatments. Two patients with severe manifestations of SLE received daratumumab at a dose of 16 mg/kg of body weight once a week for 4 weeks followed by maintenance treatment with I.V. belimumab ( 18 ). Daratumumab treatment resulted in remarkable clinical outcomes not only of severe manifestations such as lupus nephritis, autoimmune hemolytic anemia and autoimmune thrombocytopenia but also on less severe manifestations such as arthritis, skin rashes, pericarditis, cutaneous vasculitis, alopecia, and mucosal ulcers. Daratumumab treatment was also associated with favorable serologic responses. Importantly, previous therapeutic interventions with a variety of agents such as bortezomib, mycophenolate mofetil, and cyclophosphamide were ineffective. Despite the extremely small number of patients, data are encouraging supporting further evaluation of daratumumab in meaningfully larger numbers of patients with SLE. It is of interest however that the authors did not ascribe their anti-CD38 mAb-mediated clinical effect (s) exclusively to reductions of plasma cell numbers. Other circulating cells also express CD38 and their numbers decreased following daratumumab treatment. Among them are subsets of B cells, plasmacytoid dendritic cells, and a greatly expanded CD38 + T cell subpopulation. Only recently it was shown by Katsuyama et al. that this expanded CD38 + CD8 + T cell subset is responsible for the significantly compromised cytotoxicity encountered in patients with lupus ( 19 ).
What are the B cells in Lupus?
The B cell, as a major component of the adaptive immune system, may mediate autoimmune disease. B cells are not only capable of producing autoantibodies after their differentiation into plasma cells, but they also present autoantigens to T cells and they secrete cytokines. Therefore, B cells represent an established and clear target of treatment approaches; lupus B cells have been targeted either directly via regimens that cause B cell depletion or indirectly via regimens affecting B cell survival, or via inhibiting their antigen-receptor-initiated function.
Does obexelimab inhibit CD19?
Therefore, obexelimab inhibits the activation of B cells without depleting them. In a phase II study, 104 patients were randomly assigned to receive obexelimab or placebo after achieving low disease activity by intramuscular (IM) steroids and after discontinuing previous immunosuppression ( 13 ). Maintenance of improvement was observed through day 225 in 42% of patients in the obexelimab group and in 28.6% of patients in the placebo group ( p = 0.18). Nevertheless, patients in the obexelimab group showed a significantly longer time to loss-of-improvement (median: 230 vs. 131 days for patients in the placebo group, p = 0.025). Remarkably, a group of patients displaying a quite decreased risk of flare during obexelimab treatment has been recently identified ( 14 ). In this subgroup of patients, evaluation of gene expression by RNA-sequencing showed that CD27 was the dominant biomarker, followed by other T-cell genes such as CD28 and TCF7. Even though obexelimab targets B but not T cells, these findings suggest that T cells, directly or indirectly, guide obexelimab results.
Can Rituximab be used for Lupus?
Rituximab (RTX) causing B cell depletion can also be administered according to the ACR and EULAR guidelines in refractory lupus nephritis despite failed clinical trials, and is often used off-label for other manifestations as well, based on the encouraging results of diverse studies.
Is lupus erythematosus a multisystem disease?
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune multisystem disease with a variable presentation and manifestations ranging from mild to severe or even life-threatening. There is an ongoing and unmet need for novel, disease-specific, effective and safe treatment modalities.
What is the best treatment for lupus?
Corticosteroids. Prednisone and other types of corticosteroids can counter the inflammation of lupus. High doses of steroids such as methylprednisolone (Medrol) are often used to control serious disease that involves the kidneys and brain.
How to help someone with Lupus?
Connect with others who have lupus. Talk to other people who have lupus. You can connect through support groups in your community or through online message boards. Other people with lupus can offer unique support because they're facing many of the same obstacles and frustrations that you're facing.
What does a low platelet count mean in a lupus test?
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate. This blood test determines the rate at which red blood cells settle to the bottom of a tube in an hour.
What are the challenges of living with Lupus?
The challenges of living with lupus increase your risk of depression and related mental health problems, such as anxiety, stress and low self-esteem. To help you cope, try to:
What are the side effects of lupus?
Side effects include weight gain, easy bruising, thinning bones, high blood pressure, diabetes and increased risk of infection. The risk of side effects increases with higher doses and longer term therapy. Immunosuppressants. Drugs that suppress the immune system may be helpful in serious cases of lupus.
What are the tests for Lupus?
Laboratory tests. Blood and urine tests may include: Complete blood count. This test measures the number of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets as well as the amount of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells. Results may indicate you have anemia, which commonly occurs in lupus. A low white blood cell or platelet count may occur in ...
Can you take care of Lupus at Mayo Clinic?
If you receive care for lupus at Mayo Clinic, consider registering for this online class: Living Well with Lupus. Diagnosis and treatment. Take steps to care for your body if you have lupus. Simple measures can help you prevent lupus flares and, should they occur, better cope with the signs and symptoms you experience.
What is lupus erythematosus?
What is lupus? Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), commonly known as lupus, is an autoimmune illness that affects many organs and systems in the body. Lupus is a chronic condition, but symptoms tend to cycle in alternate periods of "flares" (or "flares-ups") and remissions.
What to do if your primary care doctor suspects you have lupus?
If your primary care doctor suspects you may have lupus, contact a rheumatologist to confirm the diagnosis and get appropriate treatment. HSS is top-ranked for rheumatology by U.S. News & World Report and offers a dedicated team of specialists and resources at the Lupus and APS Center of Excellence.
How many times does lupus occur in Caucasian women?
The incidences of lupus in women of African descent is three times that of incidences in Caucasian women. The incidences of lupus in women of Asian descent are twice that of incidences in Caucasian women. The incidences of lupus in women of Latin descent are twice that of incidences in Caucasian women. Age: Symptoms that lead to a lupus diagnosis ...
What tests are used to diagnose lupus?
A diagnosis for lupus is generally based on laboratory tests that exclude other diseases which may have similar symptoms (such as Lyme disease), and specific serologic tests – blood tests that determine the presence of certain antibodies.
What are the symptoms of Lupus?
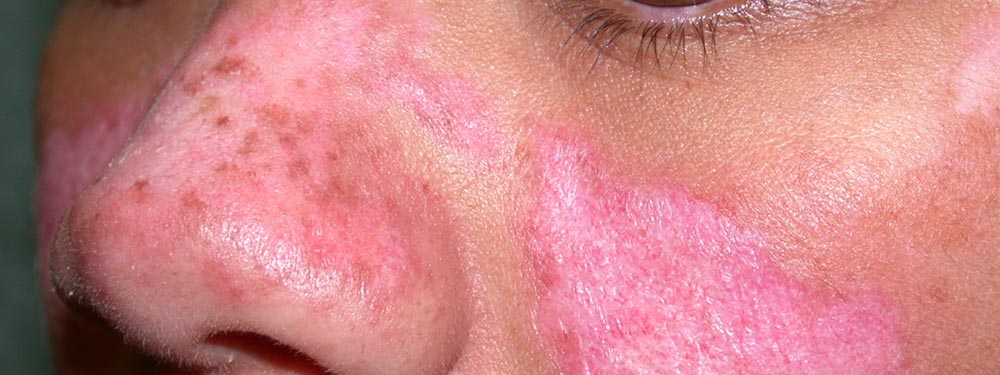
Symptoms vary from person to person, but the typical lupus patient is a young woman who develops arthritis of the fingers, wrists or other small joints, hair loss, a rash (often on the face, in butterfly pattern over the nose and cheeks).
What are the factors that affect the risk of lupus?
Gender, race and ethnicity, and age are all key factors. Younger women, and especially younger women of color, are most at risk. Gender: Most lupus patients are female. The ratio of women to men who have lupus is about 9 to 1.
How old do you have to be to get Lupus?
Age: Symptoms that lead to a lupus diagnosis most commonly appear in people between 15 and 44 years of age.
Why is SLE considered a grounds for hospital admission?
Fever in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is grounds for hospital admission because of the difficulty of distinguishing a disease flare from infection in these immunocompromised hosts.
Where do SLE rashes occur?
Photosensitive systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) rashes typically occur on the face or extremities, which are sun-exposed regions. Although the interphalangeal spaces are affected, the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) and proximal interphalangeal (PIP) and distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints are spared.
What is the B-lymphocyte stimulator?
The monoclonal antibody belimumab (Benlysta), a B-lymphocyte stimulator–specific inhibitor, has been found to reduce disease activity and possibly decrease the number of severe flares and steroid use in patients with SLE when used in combination with standard therapy. [ 122] .
Can SLE cause fewer live births?
One study suggested that women with SLE have fewer live births than the general population. [ 150] . In this study, decreased live births were associated with exposure to cyclophosphamide and high SLE disease activity. SLE can also flare during or after pregnancy.
Does heparin help with SLE?
In pregnant patients with SLE and antiphospholipid syndrome, unfractionated or low-molecular-weight heparin and aspirin may reduce the risk of pregnancy loss. For additional information, see Antiphospholipid Syndrome and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Pregnancy. Previous.
What drugs cause lupus erythematosus?
Drugs that commonly cause DILE include hydralazine, procainamide, isoniazid, minocycline, diltiazem, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors.
What is the treatment for SLE?
Treatment is dependent on presentation and options include antimalarials, glucocorticoids, immunosuppressants, and biologics. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may also be used to treat inflammation and pain.
What are the current treatments for SLE?
However, many agents have come and gone from pipelines without gaining approval. As of early 2019, rigerimod (Lupuzor), interferon-alpha (IFN) kinoid, atacicept, and obexelimab are in various stages of phase III investigations, and their approvals are highly anticipated. Targets for new drug development include major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II receptors, IFN-alpha, BLyS/a proliferation–inducing ligand (APRIL), and CD19/FcyRIIb receptors. Additional potential novel products that are already approved in the United States but not currently indicated for SLE include ustekinumab and baricitinib, which target interleukin (IL)-12/IL-23 and Janus kinase (JAK)1/JAK2 inhibitors, respectively. Further investigation of these agents is warranted.
How does SLE treatment work?
SLE treatment has made significant progress over the past decade; however, the management of SLE is complex, with a multitude of complications and various treatment options. Patients require a comprehensive plan for care and management of complications from both the disease and therapy. Pharmacists can be integrated into the care of SLE patients, especially in the areas of drug monitoring, adherence, and adverse-effect management as well as vaccination services and pain management. As pharmaceutical companies become increasingly interested in SLE, the investigational drugs in the pipeline will also continue to increase and, perhaps, beat the odds and lead to product approvals.
What is SLE treatment?
ABSTRACT: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease presenting with varying degrees of organ and system involvement. Treatment currently includes antimalarials, glucocorticoids, immunosuppressants, and biologics. Delayed diagnosis of SLE and decreased quality of life warrant an improvement in classification as well as in treatment.
How common is SLE in the world?
Incidence rates of SLE around the world are approximately 1 to 10 per 100,000 person/years, and prevalence rates range from 20 to 70 per 100,000 person/years. Persons of African, Asian, or Hispanic descent are at a higher risk of presenting with SLE than persons of European descent. 1.
What are the biological agents used for SLE?
Biological Agents: Biological agents used in the treatment of SLE include rituximab and belimumab, both monoclonal antibodies. Rituximab targets B cells and is used to treat renal and CNS presentations of SLE. This agent is recognized as a second- or third-line agent for active disease.
What is the best treatment for lupus?
Belimumab (Benlysta) is the first drug created just to treat lupus. Given intravenously (in a vein) or subcutaneously (under your skin), it targets specific immune cells. It may help reduce your need for steroid treatment, but it hasn’t been tested thoroughly for the most severe forms of lupus.
How to treat lupus?
A healthy lifestyle will help you feel better and prevent flares. It can also help prevent problems linked to lupus, like kidney disease, heart attack, and stroke. Try these tips: Eat a well-balanced diet.
Can lupus cause heart problems?
Corticosteroids weaken this immune response. Your doctor may prescribe them if lupus causes problems in your heart, lungs, kidneys, brain, or blood vessels.
Does acupuncture help with Lupus?
In fact, some supplements may make your lupus symptoms worse. But some research has found that acupuncture, meditation, and biofeedback can relieve pain and stress when used alongside traditional treatments. This is called complementary medicine.
Can you take immunosuppressive drugs with corticosteroids?
In some cases, you may use immunosuppressive drugs along with corticosteroids. That way, you'll be taking a lower amount of each type of drug, reducing the possible side effects. With both types of drugs, you and your doctor need to weigh the risks of side effects against how well they ease your lupus symptoms.
Can you take lupus medication without a prescription?
Sometimes, you may have a fever. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs ( NSAIDs) can usually help with these problems. You can buy them without a prescription.
Does malaria help with lupus?
Some medications that treat malaria can also treat lupus. They might help with skin rashes, mouth sores, and joint pain. They may also lower your chance of blood clots, which is a concern in some people with lupus.
How to treat SLE?
The treatments may include: anti-inflammatory medications for joint pain and stiffness, such as these options available online. steroid creams for rashes. corticosteroids to minimize the immune response.
What is the physical exam for Lupus?
Your doctor will do a physical exam to check for typical signs and symptoms of lupus, including: arthritis, which is swelling or tenderness of the small joints of the hands, feet, knees, and wrists. No one single test is diagnostic for SLE, but screenings that can help your doctor come to an informed diagnosis include:
What are the long term complications of SLE?
Possible complications may include: blood clots and inflammation of blood vessels or vasculitis. inflammation of the heart, or pericarditis. a heart attack.
What are the symptoms of SLE?
Common symptoms include: severe fatigue. joint pain. joint swelling. headaches. a rash on the cheeks and nose, which is called a “butterfly rash”. hair loss.
How to reduce the likelihood of triggering symptoms?
Talk with your doctor about your diet and lifestyle habits. Your doctor might recommend eating or avoiding certain foods and minimizing stress to reduce the likelihood of triggering symptoms. You might need to have screenings for osteoporosis since steroids can thin your bones.
Does SLE affect women?
SLE affects women more than men. Women also may experience more severe symptoms during pregnancy and with their menstrual periods. Both of these observations have led some medical professionals to believe that the female hormone estrogen may play a role in causing SLE.
Can SLE cause kidney failure?
seizures. inflammation of lung tissue and the lining of the lung, or pleuritis. kidney inflammation. decreased kidney function. kidney failure. SLE can have serious negative effects on your body during pregna ncy. It can lead to pregnancy complications and even miscarriage.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Specialist to consult
Alternative Medicine
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.