What is the survival rate for a carcinoid tumor?
If the lung carcinoid tumor has spread to the lymph nodes, five-year survival rates can range from 37 to 80%....What Is the Survival Rate for a Carcinoid Tumor?*SEER StageFive-Year Relative Survival RateLocalized97%Regional94%Distant67%All SEER stages combined94%Dec 8, 2020
Can carcinoid tumor be cured?
When detected early, a carcinoid tumor may be removed completely using surgery. If carcinoid tumors are advanced when discovered, complete removal may not be possible. In some situations, surgeons may try to remove as much of the tumor as possible, to help control signs and symptoms.
Is chemo Effective for carcinoid tumors?
Unfortunately, carcinoid tumors usually do not respond very well to chemo. It is mainly used for carcinoid tumors that have spread to other organs, are causing severe symptoms, have not responded to other medicines, or atypical carcinoids that are dividing quickly. Sometimes, it may be given after surgery.
Is lung carcinoid cancerous?
Lung carcinoid tumors (also known as lung carcinoids) are a type of lung cancer. Cancer starts when cells begin to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the body can become cancer, and can spread to other areas.
What is typical carcinoid tumor of lung?
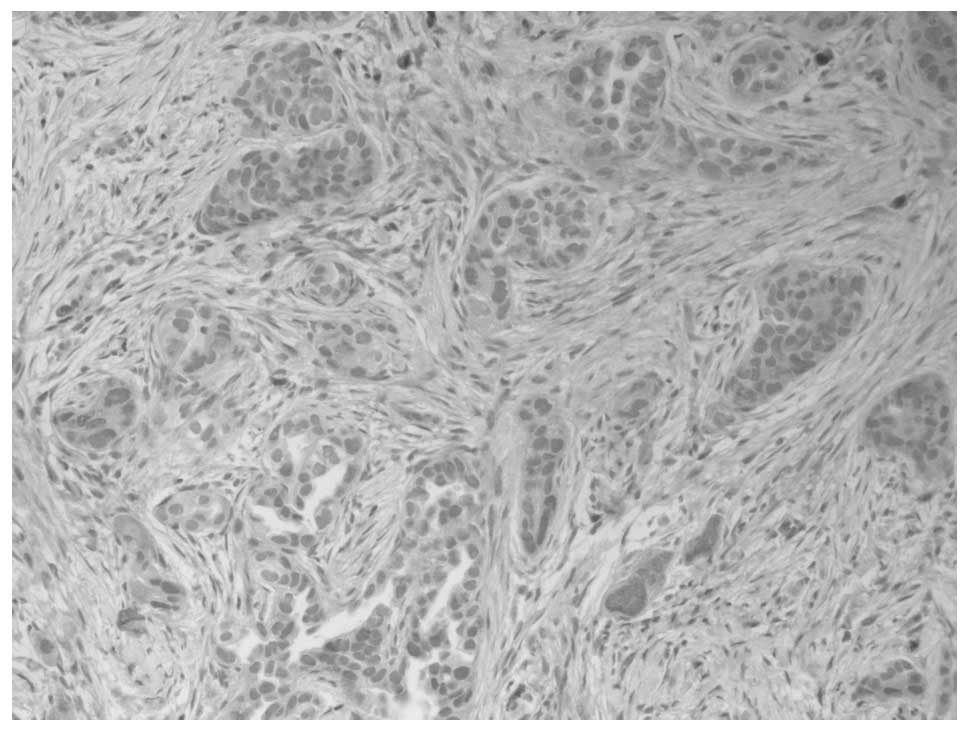
What is a lung carcinoid tumor? A lung carcinoid tumor is a type of cancerous tumor made up of neuroendocrine cells. These cells are found throughout the body, including the lungs. They are similar to endocrine cells because both produce hormones or hormone-like substances.
Is carcinoid tumor serious?
Carcinoid tumors are cancerous, but have been called cancer in slow motion, because if you have a carcinoid tumor, you may have it for many years and never know it. In rare cases, usually after a carcinoid tumor has spread, it can cause symptoms called carcinoid syndrome.
Are carcinoid tumors terminal?
Early diagnosis leads to a 97 percent survival rate. Carcinoid syndrome itself is not deadly in that it describes a group of symptoms. Carcinoid syndrome is caused by a neuroendocrine (carcinoid) tumor, and that may lead to liver dysfunction and death in cases where cancer has spread (metastasized).
What is the most common location for carcinoid tumors?
The most common locations of gastrointestinal (GI) carcinoid tumors are the small intestine and the rectum. Other common sites include , the colon (large intestine), the appendix, and the stomach.
How do you shrink carcinoid tumors?
Surgery is often the best option for small carcinoid tumors that have not spread. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy may be used to shrink tumors, although they often may not be successful.
Are lung carcinoid tumors rare?
Carcinoid tumors are a rare type of lung cancer. Only 1% to 2% of lung cancers are carcinoid tumors. They usually grow slowly. They are a type of neuroendocrine tumor, meaning that they start in special cells, called neuroendocrine cells, that are found in the lungs and throughout the body.
What are the symptoms of lung carcinoid tumors?
Signs and symptoms of carcinoid lung tumors include:Chest pain.Wheezing.Shortness of breath.Diarrhea.Redness or a feeling of warmth in your face and neck (skin flushing)Weight gain, particularly around the midsection and upper back.Pink or purple marks on the skin that look like stretch marks.
Do lung carcinoid tumors come back?
Follow-up after lung carcinoid treatment Report any new symptoms or problems, because they could be caused by the cancer spreading or coming back, or by a new disease or second cancer.
Is carcinoid syndrome a death sentence?
Carcinoid syndrome itself is not deadly in that it describes a group of symptoms. Carcinoid syndrome is caused by a neuroendocrine (carcinoid) tumor, and that may lead to liver dysfunction and death in cases where cancer has spread (metastasized).
How do you shrink carcinoid tumors?
Surgery is often the best option for small carcinoid tumors that have not spread. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy may be used to shrink tumors, although they often may not be successful.
Should carcinoid tumors be removed?
Because most carcinoid tumors grow slowly and some do not cause any symptoms, completely removing all metastatic carcinoid tumors may not always be needed. But in some patients, surgery to remove all visible cancer is the best option.
Do carcinoid tumors come back?
Gastrointestinal carcinoid tumor recurrence is a substantial concern among those who are undergoing or have completed their initial treatment. Recurrence means that the malignant cells have reappeared within the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, or have spread to other tissues or organs within the body.
What Is A Lung Carcinoid Tumor?
A lung carcinoid tumor is a type of cancerous tumor made up of neuroendocrine cells. These cells are found throughout the body, including the lungs...
How Common Are Carcinoid Tumors of The Lung?
Lung carcinoid tumors are quite rare, accounting for only 1% to 2% of all lung cancers. There are about 4,500 new cases of lung carcinoid tumors di...
What Causes Lung Carcinoid Tumors?
The cause of lung carcinoid tumors is still unclear. They do not seem to be related to smoking, air pollutants, or other chemicals. However, there...
What Are The Symptoms of Lung Carcinoid Tumors?
About 25% or more of people with lung carcinoid tumors do not have any symptoms. Often these types of tumors are found when a patient undergoes dia...
What are the factors that determine the treatment of carcinoid tumor?
The main factors in selecting a treatment are the type of carcinoid, the size and location of the tumor, whether it has spread to lymph nodes or other organs, symptoms you are having, and if you have any other serious medical conditions.
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
What is the difference between a pulmonologist and a radiation oncologist?
A pulmonologist: a doctor who specializes in medical treatment of diseases of the lungs. A radiation oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with radiation therapy. You might have many other specialists on your treatment team as well, including physician assistants, nurse practitioners, nurses, nutrition specialists, social workers, ...
What is a radiation oncologist?
A radiation oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with radiation therapy. You might have many other specialists on your treatment team as well, including physician assistants, nurse practitioners, nurses, nutrition specialists, social workers, and other health professionals. Health Professionals Associated with Cancer Care.
What is the number to call for cancer treatment?
Call our National Cancer Information Center at 1-800-227-2345 and speak with one of our trained specialists. Palliative Care. Find Support Programs and Services in Your Area.
Is treatment information given here official policy of the American Cancer Society?
The treatment information given here is not official policy of the American Cancer Society and is not intended as medical advice to replace the expertise and judgment of your cancer care team. It is intended to help you and your family make informed decisions, together with your doctor.
What is the name of the doctor who treats cancer?
A medical oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with medicines such as chemotherapy and targeted therapy. A pulmonologist: a doctor who specializes in medical treatment of diseases of the lungs. A radiation oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer ...
What is a lung carcinoid tumor?
A lung carcinoid tumor is a type of cancerous tumor made up of neuroendocrine cells. These cells are found throughout the body, including the lungs. They are similar to endocrine cells because both produce hormones or hormone-like substances. In other ways, they resemble nerve cells because both can secrete neurotransmitters.
Can a carcinoid tumor be removed?
Many lung carcinoid tumors can be treated with surgery alone, except in cases where the tumor has spread to other organs. In cases where the carcinoid cannot be completely removed, palliative surgery may be performed to remove most of the tumor or to relieve symptoms. The main types of surgical treatment are:
What is a tumor that grows in the lungs?
Sometimes neuroendocrine cells grow too quickly and form a small tumor known as a carcinoid tumor. Carcinoid tumors may form in other organs of the body besides the lungs. In fact, only about 2 out of 10 carcinoid tumors are found in the lungs. There are two types of lung carcinoid tumors: typical and atypical.
What is the procedure to remove a tumor from the lungs called?
Lobectomy: This type of surgical procedure involves the removal of a portion of the lung called a lobe. It may be performed to remove a peripheral carcinoid tumor (one that is located at the edge of the lungs). One lobe of the lung is removed during a lobectomy. The removal of two lobes is called a bilobectomy.
What are the two types of lung cancer?
There are two types of lung carcinoid tumors (or cancerous tumors made up of neuroendocrine cells): typical (slower) and atypical (faster and more likely to spread to other organs). Some people do not have symptoms, but symptoms may include coughing or wheezing. Treatment may include surgery, radiation and/or chemotherapy.
How many carcinoids are in the lung?
Typical carcinoids account for about 9 out of 10 lung carcinoids. They grow slowly and rarely spread beyond the lungs. Atypical carcinoids are much rarer than typical lung carcinoids. They tend to grow faster than typical carcinoids.
Where are central and peripheral carcinoids found?
Central carcinoids are found in the walls of the large airways of the lungs. Peripheral carcinoids form closer to the edges of the lungs in the smaller airways. Both central and peripheral carcinoids usually are typical carcinoids. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
What is the best treatment for carcinoid lung cancer?
The only treatment for carcinoid lung tumors is surgery. Some doctors may also recommend chemotherapy and radiation. This article will look at the symptoms, stages, and treatment of lung carcinoid tumors.
Can a carcinoid lung tumor be treated with radiation?
Hormone-like symptoms are also possible and may include excessive male-pattern hair growth in females and facial flushing. The only treatment for carcinoid lung tumors is surgery . Some doctors may also recommend chemotherapy and radiation. This article will look at the symptoms, stages, and treatment of lung carcinoid tumors.
What is a carcinoid lung tumor?
Summary. A lung carcinoid tumor is a rare type of lung cancer not usually associated with smoking. Carcinoids are tumors that develop from neuroendocrine cells found in different parts of the body, such as the lungs and digestive tract. While some people may not experience symptoms of carcinoid lung tumors, others may experience breathing symptoms ...
Can a carcinoid lung tumor cause coughing?
Doctors may find the cancer when testing a person for another medical condition. Symptoms of carcinoid lung tumors may include: coughing or wheezing. blood in phlegm. symptoms of pneumonia. facial flushing. shortness of breath. high blood pressure.
Does smoking cause carcinoid tumors?
Smoking does not seem to cause typical carcinoids in the lung. Typical carcinoids grow slowly and do not usually spread outside of the lungs.
Do carcinoid tumors spread outside the lungs?
Typical carcinoids grow slowly and do not usually spread outside of the lungs. Atypical carcinoids are different from typical carcinoids because they grow faster and may spread to other body organs. They develop more commonly in people who smoke compared with typical carcinoid lung tumors.
Can a lung tumor be a carcinoid?
Doctors may find early signs of carcinoid lung tumors when doing lung biopsies for other medical conditions. “Tumorlets” in the lungs are small clusters of neuroendocrine cells that resemble lung carcinoid tumors. Most often, tumorlets do not develop into carcinoid tumors, but sometimes they do.
Do carcinoid tumors spread outside the lungs?
They grow slowly, and they don’t usually spread outside of the lungs. Atypical carcinoid tumors grow faster, and they’re more likely to spread, or metastasize, outside of the lungs. Doctors also refer to lung carcinoid tumors based on their location.
How many lung cancers are carcinoid?
Only 1% to 2% of lung cancers are carcinoid tumors. They usually grow slowly. They are a type of neuroendocrine tumor, meaning that they start in special cells, called neuroendocrine cells, that are found in the lungs and throughout the body.
What is a carcinoid tumor?
Carcinoid tumors are a rare type of lung cancer. Only 1% to 2% of lung cancers are carcinoid tumors.
Is a carcinoid tumor more common in women than in men?
Carcinoid tumors are more common in women than in men. Race/ethnicity. These tumors are more common in whites than in other racial and ethnic groups. Family history. Your risk is higher if you have family members with carcinoid tumors.
What is a biopsy of a tumor?
A biopsy is a sample of tissue taken from your tumor and checked under a microscope . It can be done two ways. If you have a nonsurgical biopsy, you’ll probably be sedated. Your doctor may insert a bronchoscope, a type of thin, flexible camera, into your lungs to look at the tissue.
What is the best treatment for a tumor that can't be removed?
If your tumors can’t be removed with surgery or have spread or returned, your doctor may recommend targeted therapy, a special type of chemotherapy. The FDA approved everolimus (Afinitor) for this purpose in 2016. Certain drugs can ease symptoms caused by hormones that your tumors release and may slow their growth.
What is the rarest type of lung cancer?
Carcinoid tumors are a rare type of lung cancer. Only 1% to 2% of lung cancers are carcinoid tumors. They usually grow slowly. They are a type of neuroendocrine tumor, meaning that they start in special cells, called neuroendocrine cells, that are found in the lungs and throughout the body.
What percentage of lung cancer is caused by carcinoid tumors?
Lung Carcinoid Tumor Treatment. Lung carcinoid tumors make up less than 5 percent of all lung cancers. Lung carcinoid tumors tend to grow slower than other types of lung cancer. They are also known as lung neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) because they are made up of neuroendocrine cells (cells that receive messages from the body and release hormones).
What is the procedure for lung cancer?
The types of surgery for lung carcinoid tumors include: 1,3. Lobectomy – removal of a portion (lobe) of the lung ; if two lobes are removed, it is referred to as a bilobectomy.
Why do lung cancers grow slower?
They are also known as lung neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) because they are made up of neuroendocrine cells (cells that receive messages from the body and release hormones). 1,2.
Do carcinoid tumors spread?
Typical carcinoid tumors grow slowly and rarely metastasize (spread) beyond the lungs. Typical carcinoid tumors make up approximately 90 percent of lung carcinoid tumors. Atypical carcinoid tumors grow faster than typical carcinoid tumors and have an increased chance of metastasis. Atypical carcinoid tumors are less common than typical carcinoid ...
Is a carcinoid tumor atypical or unresectable?
1,2. The extent of the disease for lung carcinoid tumors is characterized as resectable tumors (those that can be removed with surgery) and unresectable tumors (those that can’t be completely removed with surgery). 1.
Why is somatostatin used in lung cancer?
Because lung carcinoid tumors are made up of neuroendocrine cells, which produce hormones, somatostatin analogs can be an effective treatment to help reduce symptoms and potentially shrink the tumor. 4. Octreotide (Sandostatin ®) was the first somatostatin analog to be developed.
What type of surgery is done for lung cancer?
The types of surgery for lung carcinoid tumors include: 1,3. Lobectomy – removal of a portion (lobe) of the lung; if two lobes are removed, it is referred to as a bilobectomy. Sleeve resection – removal of sections of the airway above and below the tumor along with the tumor itself; the sections of the airway are then reconnected.
Can a carcinoid tumor be removed?
Surgery. When detected early, a carcinoid tumor may be removed completely using surgery. If carcinoid tumors are advanced when discovered, complete removal may not be possible. In some situations, surgeons may try to remove as much of the tumor as possible, to help control signs and symptoms.
How to diagnose carcinoid tumors?
Tests and procedures used to diagnose carcinoid tumors include: Blood tests. If you have a carcinoid tumor, your blood may contain high levels of hormones secreted by a carcinoid tumor or byproducts created when those hormones are broken down by the body. Urine tests. People with carcinoid tumors have excess levels of a chemical in their urine ...
What tests are used to diagnose carcinoid tumors?
Diagnosis. Tests and procedures used to diagnose carcinoid tumors include: Blood tests. If you have a carcinoid tumor, your blood may contain high levels of hormones secreted by a carcinoid tumor or byproducts created when those hormones are broken down by the body. Urine tests.
What happens if you have a carcinoid tumor?
If you have a carcinoid tumor, your blood may contain high levels of hormones secreted by a carcinoid tumor or byproducts created when those hormones are broken down by the body. Urine tests. People with carcinoid tumors have excess levels of a chemical in their urine that's produced when the body breaks down hormones secreted by carcinoid tumors.
Can cancer cells die from targeted drugs?
By blocking these abnormalities, targeted drug treatments can cause tumor cells to die. Targeted drug therapy is usually combined with chemotherapy for advanced carcinoid tumors. Drugs that deliver radiation directly to the cancer cells.
How to treat cancer in the liver?
Carcinoid tumors commonly spread to the liver. Treatments may include surgery to remove part of the liver, blocking blood flow to the liver (hepatic arter y embolization), and using heat and cold to kill cancer cells.
Does PRRT work for cancer?
In PRRT for carcinoid tumors, the drug is injected into your body, where it travels to the cancer cells, binds to the cells and delivers the radiation directly to them. This therapy may be an option for people with advanced carcinoid tumors. Treatment for cancer that spreads to the liver.
Can a carcinoid tumor be removed?
Resectable stage carcinoid tumors, which may be treated with surgery alone. Unresectable stage tumors, which can't be completely removed or treated with surgery (Additional options for these tumors may include radiation, chemotherapy, or clinical trials .)
What percentage of carcinoid tumors are in the lungs?
There are two types of carcinoid tumors: Typical carcinoids are more likely to grow slowly and not spread outside the lungs. They make up about 90 percent of lung carcinoid tumors, according to the ACS . Atypical carcinoids grow more quickly and may spread to other parts of the body.
What is a lung tumor?
These are the cells that produce chemical messengers called hormones. Carcinoid—or neuroendocrine—tumors may develop throughout the body.
What are the symptoms of a lung tumor?
Hormone substances may spread through the body and cause symptoms that include flushing of the chest and face, diarrhea and shortness of breath.
How rare is lung cancer?
Lung carcinoid tumors are rare, accounting for 1 to 2 percent of all lung cancers, according to the American Cancer Society (ACS). Fewer than 4,500 cases are diagnosed in the United States every year. Lung carcinoid cancers tend to occur at an earlier age than other cancers.
What percentage of lung cancers are carcinoid?
There are two types of carcinoid tumors: Typical carcinoids are more likely to grow slowly and not spread outside the lungs. They make up about 90 percent of lung carcinoid tumors, according to the ACS . Atypical carcinoids grow more quickly and may spread to other parts of the body.
Where are carcinoid tumors found?
Lung carcinoid tumors may also be classified based on where they occur in the lung: Central tumors, the more common type, are found in the large airways near the central part of the lungs. Peripheral tumors form in smaller airways toward the outer parts of the lung.
What percentage of lung tumors are carcinoid?
Typical carcinoids. These tumors grow slowly and usually stay in your lungs. This type makes up about 90 percent of all carcinoid lung tumors and are less frequently linked to lifestyle choices, like smoking.
What percentage of carcinoid lung tumors are caused by smoking?
Typical carcinoids. These tumors grow slowly and usually stay in your lungs. This type makes up about 90 percent of all carcinoid lung tumors and are less frequently linked to lifestyle choices, like smoking. Atypical carcinoids.
Where do carcinoid tumors originate?
Most carcinoid tumors originate in your lungs or your gastrointestinal tract. of all cases of lung cancer. Other forms of lung cancer include small cell lung cancers and non-small cell lung cancers. Growth control is the main concern when it comes to the role cancer cells play in carcinoid tumors.
What age do carcinoid tumors form?
The condition is more prevalent in people with the following backgrounds, conditions, and experiences: age 45 to 55. female gender.
Can carcinoid tumors spread to other parts of the body?
The good thing to know about carcinoid tumors in your lungs is that they are usually slow-growing and rarely spread to other parts of your body . This makes them one of the easier cancers to treat. The treatment process can be difficult and usually involves removing all or a part of your affected lung.
What is the name of the tumor that grows slowly and stays in your lungs?
Carcinoid tumors. Symptoms. Causes. Treatment. Outlook. Bottom line. Lung carcinoid tumors are a rare type of lung cancer. Most forms of this cancer grow slowly and stay within your lungs. Despite these tumors’ usually slow growth, their location along major parts of your airway can lead to obstruction or breathing problems.
Is lung cancer a rare disease?
Bottom line. Lung carcinoid tumors are a rare type of lung cancer. Most forms of this cancer grow slowly and stay within your lungs. Despite these tumors’ usually slow growth, their location along major parts of your airway can lead to obstruction or breathing problems. Continue reading to learn more about these types of tumors, ...