Generally, most cases of lumbar spondylosis are considered mild, and the following treatment options are conventionally used:
- Chiropractic care
- Physiotherapy
- Anti-inflammatory/pain medication
- Light exercises, such as yoga or water aerobics
What is the best exercise for spondylolisthesis?
- Start by lying on the ground with your knees bent, feet flat on the ground and arms folded over the chest. ...
- Slowly lift your head and shoulders off the floor until a contraction in the abdominals is felt.
- Hold for three seconds, and then lower to starting position.
- Repeat 10 times.
Why is a lumbar puncture done between L3 and L4?
Originally Answered: Why is a lumbar puncture done between L3 and L4? Because that is below the tip of the spinal cord, generally at T12 to L1 and in an area where arthritis is typically less present and the spine can flex more easily allowing the inter-laminar space to open up when the patient curls up on their side.
Is lumbar radiculopathy a permanent illness?
People can develop radiculopathy as the result of an injury, or it may occur for no apparent reason. Those individuals aged 30 to 50 years old are most likely to experience radiculopathy, in the cervical and lumbar spine areas. There are many potential causes of radiculopathy, including poor lifting technique, poor posture, and back injuries.
What is decreased lumbar lordosis?
What is decreased lumbar lordosis? Summary. Flatback = the loss of the normal lumbar lordosis. Syndrome = a collection of symptoms that occur together. Flatback syndrome is a condition in which the lower spine loses some of its normal curvature. It is a type of sagittal imbalance, or front-to-back imbalance in the spine.
Can lumbar spondylosis be cured?
There is no treatment to reverse the process of spondylosis, because it is a degenerative process. The treatments for spondylosis target the back pain and neck pain that spondylosis can cause. Therefore, the treatment of spondylosis is similar to the treatment of back pain and neck pain.
Which medicine is best for lumbar spondylosis?
Tylenol (acetaminophen) and NSAIDs are the mainstays of pain control in those with lumbosacral spondylolysis (lumbar spondylolysis). Moreover, a short course of narcotic analgesics can help those who are in significant acute pain initially.
Is lumbar spondylosis serious?
Spondylosis is common, but it is usually not serious. Many who have it experience no pain, though it can be painful for some. Most patients with spinal osteoarthritis will not need surgery.
What should be avoided in lumbar spondylosis?
There should be restriction of heavy lifting, excessive bending, twisting or stooping and avoidance of any work or recreational activities that causes stress to the lumbar spine.
Is walking good for lumbar spondylosis?
1. Walking strengthens the muscles that support your spine. Your trunk, core, and lumbar (lower back) muscles play a vital role in maintaining the stability and movement of your lower back. These muscles can become deconditioned and weak from a sedentary lifestyle, causing malalignment of the spine.
Is walking good for spondylosis?
Cervical spondylosis treatment Symptoms of cervical spondylosis can usually be relieved in three main ways: i) Exercise, including specific home stretches to relieve the symptoms, as well as activities like walking and swimming.
What are the warning signs of spondylosis?
Spondylosis SymptomsHeadaches.Loss of bladder control.Muscle spasms.Pain and soreness in the neck, shoulders, or lower back; pain may worsen with standing (if it originates in the lower back) or moving the head (if it originates in the neck)Stiffness.Tenderness.More items...•
What is the main cause of spondylosis?
Spondylosis is caused by wear and tear on the components of the spine. The major risk factor for developing spondylosis is age. In fact, by age 60 most people will show signs of spondylosis on X-ray.
What does spondylosis pain feel like?
Common symptoms are stiffness and mild pain that gets worse following certain movements or long periods without moving, while sitting for a long time, for example. More severe symptoms include: a grinding or popping feeling when moving the spine. weakness in the hands or legs.
What is the best exercise for spondylosis?
Best Exercises for Ankylosing Spondylitis1 / 10. Press Up to Stretch Your Spine. ... 2 / 10. Wall Sit for Better Posture. ... 3 / 10. Plank for a Stronger Core. ... 4 / 10. Try Standing Leg Raises to Loosen Tight Hips. ... 5 / 10. Do Chin Tucks to Stretch Your Neck. ... 6 / 10. Roll Your Shoulders to Loosen Up. ... 7 / 10. ... 8 / 10.More items...•
How do you fix lumbar spondylolisthesis?
The most common types of surgery used to correct spondylolisthesis are: laminectomy (removing the part of the bone causing pressure); and/or spinal fusion (fusing the vertebrae together to stabilize the affected area). In some cases, both procedures may be done together.
How long does it take to recover from spondylosis?
The majority (85% to 90%) of young patients recover in three to six months with proper treatment. Recovery time can be longer and is different for each person. Spondylolisthesis (spon-dee-low-lis-thee-sis), or slipped vertebra, is a condition that involves the forward slippage of one vertebra over the one under it.
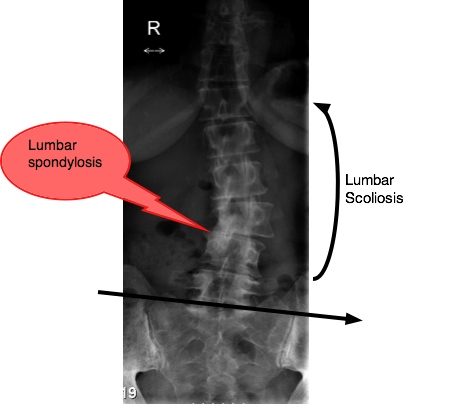
What is lumbar spondylosis?
Lumbar spondylosis is a degenerative condition that develops gradually over time, being more common in older individuals. This condition can also be referred to as spinal osteoarthritis. It occurs due to the wear-and-tear of the bones that happens from normal everyday movement. The lower spine is composed of disc-like structures that are cushioned by soft gel-like sections in between them. The purpose of these sections is to promote flexibility and absorb the load of stress applied to the vertebra. Degeneration of these areas causes a loss of elasticity and a propensity to be torn or damaged. If this type of damage were to occur, it may lead to a condition called disc prolapse, disc herniation, or a slipped disc—a common feature of lumbar spondylosis.
How to diagnose lumbar spondylosis?
A neurological exam will also allow the doctor to assess nerves, muscle strength, and reflexes. This initial assessment will need to be complemented by more definitive diagnostic testing, which in the case of lumbar spondylosis, comes in the form of image testing. The following are some of the various tests:
Why is lumbar spondylosis progressive?
Aging: The most common cause as the passage of time can lead to changes in the bones of the spine and other problems . Unfortunately, this often means that the disease is progressive and irreversible. Being over the age of 40 increases one’s risk for lumbar spondylosis. Abnormal spinal movement: Frequent overuse of the back as seen during sports ...
How long does lumbar spondylosis pain last?
But when symptoms do appear, they can present as pain ranging from mild to severe, initially presenting as stiffness in the mornings lasting for more than 30 minutes. Additions symptoms of lumbar spondylosis include: Localized pain. Pain after prolonged sitting.
What does prolonged sitting do to the lumbar vertebrae?
Prolonged sitting: Puts pressure on the lumbar vertebrae.
What is the lower spine?
The lower spine is composed of disc-like structures that are cushioned by soft gel-like sections in between them. The purpose of these sections is to promote flexibility and absorb the load of stress applied to the vertebra. Degeneration of these areas causes a loss of elasticity and a propensity to be torn or damaged.
Can lumbar spondylosis cause difficulty standing?
Treating lumbar spondylosis. Having chronic lower back pain can cause a lot of difficulty standing or even sitting, so many treatment options focus on relieving this aspect of lumbar spondylosis. In the case of severe disc prolapse, surgery may be required. Generally, most cases of lumbar spondylosis are considered mild, ...
What is the best treatment for lumbar spondylosis?
Treatments aim to reduce the pain that can result from lumbar spondylosis and include: Physiotherapy (considered the main conservative treatment for lumbar spondylosis) Medications, including: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), either prescribed, or over-the-counter, such as Advil, Motrin or Aleve.
Why does lumbar spondylosis weaken?
There is no one cause of lumbar spondylosis, but it is associated with aging as the bones, joints, ligaments and intervertebral discs in the lumbar spine degenerate and weaken due to natural wear and tear.
What is lumbar osteoarthritis?
The term encompasses all degenerative conditions that affect the lumbar spine, including: Low back osteoarthritis (OA) and facet joint OA: a type of spinal osteoarthritis that occurs when the cartilage surrounding the facet joints breaks down and wears away, causing inflammation. Bone rubs on bone which can cause painful bone spurs (bony ...
What causes bone spurs?
Bone rubs on bone which can cause painful bone spurs (bony overgrowths called osteophytes) to form in the place of cartilage. Bone spurs can cause spinal stenosis (the narrowing of the spinal canal) and lead to nerve compression and damage. Spondylosis deformans: bone spurs that grow around a degenerating intervertebral disk.
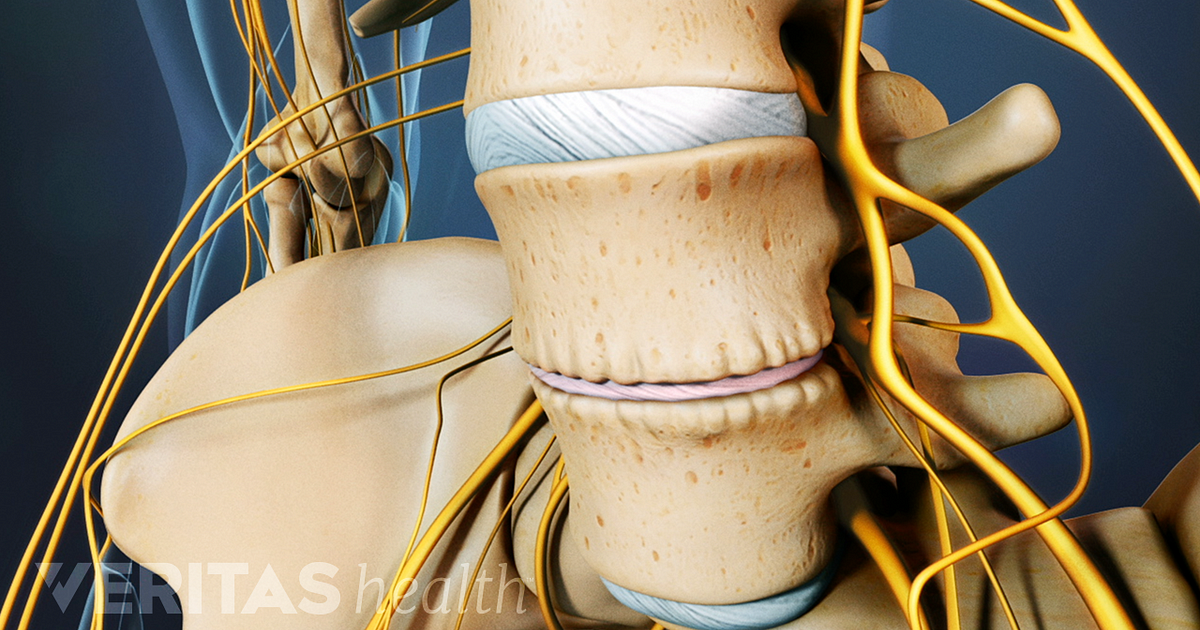
What is the degeneration of the lumbar spine?
Tough, fibrous intervertebral discs between the vertebrae act as shock absorbers for your spine and allow your back the flexibility to bend and twist. Lumbar spondylosis is the degeneration of the lumbar spine, and is sometimes known as spinal arthritis.
What is the Greek word for vertebrae?
Spondylosis is the Greek word for vertebrae. Your low back is made up of the last five bones (vertebrae) of your spine, called the lumbar vertebrae or lumbar spine. Those vertebrae are connected by facet joints, which are lined with a smooth, rubbery layer of cartilage, separating the vertebrae and allowing their movements to be smooth and painless.
What is the pain in the lower back?
Decreased range of motion and flexibility, either in the low back or legs, especially first thing in the morning or after periods of inactivity. Stiffness or tenderness in the low back. Numbness and tingling and/or shooting or radiating pain (known as lumbar radiculopathy) from the low back into the buttock or leg (s)
What is lumbar spondylosis?
Lumbar spondylosis is an age-related degeneration of the vertebrae and disks of the lower back. These changes are often called degenerative disk disease and osteoarthritis. The common condition is marked by the breakdown of one or more of the disks that separate the bones of the spine. The disks provide cushioning between ...
What tests are used to diagnose spondylosis?
Our spine specialists diagnose spondylosis based on your history of symptoms, a physical exam, and imaging tests that may include X-rays, CT scan, or MRI. Most people with lumbar spondylosis can be treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or pain relievers, heat or ice applications, and physical therapy.
What are the different regions of the spine?
The spine is divided into the following regions: 1 The cervical region (vertebrae C1-C7) encompasses the first seven vertebrae under the skull. Their main function is to support the weight of the head, which averages 10 pounds. The cervical vertebrae are more mobile than other areas, with the atlas and axis vertebra facilitating a wide range of motion in the neck. Openings in these vertebrae allow arteries to carry blood to the brain and permit the spinal cord to pass through. They are the thinnest and most delicate vertebrae. 2 The thoracic region (vertebrae T1-T12) is composed of 12 small bones in the upper chest. Thoracic vertebrae are the only ones that support the ribs. Muscle tension from poor posture, arthritis, and osteoporosis are common sources of pain in this region. 3 The lumbar region (vertebrae L1-L5) features vertebrae that are much larger to absorb the stress of lifting and carrying heavy objects. Injuries to the lumbar region can result in some loss of function in the hips, legs, and bladder control. 4 The sacral region (vertebrae S1-S5) includes a large bone at the bottom of the spine. The sacrum is triangular-shaped and consists of five fused bones that protect the pelvic organs.
What is the pain caused by a herniated disc?
Herniated disks can cause nerve pain known as sciatica, which travels along the sciatic nerve running from the lower back down the length of each leg.
What is the function of the cervical vertebrae?
Their main function is to support the weight of the head, which averages 10 pounds. The cervical vertebrae are more mobile than other areas, with the atlas and axis vertebra facilitating a wide range of motion in the neck. Openings in these vertebrae allow arteries to carry blood to the brain and permit the spinal cord to pass through. They are the thinnest and most delicate vertebrae.
How do you know if you have spondylosis?
Our spine specialists diagnose spondylosis based on your history of symptoms, a physical exam, and imaging tests that may include X-rays, CT scan, or MRI.
Which vertebrae are the thinnest?
They are the thinnest and most delicate vertebrae. The thoracic region (vertebrae T1-T12) is composed of 12 small bones in the upper chest. Thoracic vertebrae are the only ones that support the ribs.
What is the treatment for chronic lower back pain?
We will briefly describe these treatment options for the management of chronic low back pain syndromes within each of the four primary categories: physical therapy (and associated modalities and behavioral techniques), pharmacotherapy, injection therapy, and surgical intervention.
What is spinal stenosis?
These degenerative anatomical changes may culminate in a clinical presentation of spinal stenosis, or narrowing within the spinal canal [30] through progressive ingrowth of osteophytes, hypertrophy of the inferior articular process [31], disk herniation, bulging of the ligamentum flavum [17], or spondylolisthesis. The clinical result: a constellation of pain symptoms encompassed in the term neurogenic claudication(NC). NC may include (to varying extents) lower back pain, leg pain, as well as numbness and motor weakness to lower extremities that worsen with upright stance and walking, and improve with sitting and supine positioning [30].
How common are degenerative spine changes?
Degenerative spine changes are remarkably common in population studies. Symmons’ et al. [19] study of individuals aged 45–64 years identified 85.5% of participants to demonstrate osteophytes within the lumbar spine. O’Neill et al. [20] explored osteophytosis within a UK adult population over age 50 years, finding 84% of men and 74% of women to demonstrate at least one vertebral osteophyte, with increased incidence among individuals with more physical activity, self reported back pain, or higher BMI scores. Despite marked variability within the population, men appear to have more significant degenerative changes than women, both with regard to number and severity of osteophyte formation [20].
What is spinal osteoarthritis?
Spinal osteoarthritis(OA) is a degenerative process defined radiologically by joint space narrowing, osteophytosis, subchondral sclerosis, and cyst formation [13, 14]. Osteophytes included within this definition fall into one of the two primary clinical categories [14]. The first, spondylosis deformansdescribes bony outgrowths arising primarily along the anterior and lateral perimeters of the vertebral end-plate apophyses. These hypertrophic changes are believed to develop at sites of stress to the annular ligament and most commonly occur at thoracic T9–10 and lumbar L3 levels [15]. These osteophytes have minimal effect on intervertebral disk height [16] and are frequently asymptomatic, with only rare complications arising from their close anatomic relationship to organs anterior to the spine [15].
What is intervertebral osteochondrosis?
By contrast, intervertebral osteochondrosisdescribes the formation of more pathological end-plate osteophytes, associated with disk space narrowing, vacuum phenomenon, and vertebral body reactive changes [16]. If protruding within the spinal canal or intervertebral foramina, these bony growths may compress nerves with resulting radiculopathy or spinal stenosis. Moreover, these bony projections may limit joint mobility and invade other organs or tissues [14]. The term “osteoarthritis” suggests pathology limited to bone. Nevertheless, in this context, it has clear implications for the health of neighboring disks and nerve roots.
How long does it take for low back pain to subside?
Fortunately, for the large majority of individuals, symptoms are mild and transient, with 90% subsiding within 6 weeks [4]. Chronic low back pain, defined as pain symptoms persisting beyond 3 months, affects an estimated 15–45% of the population [5, 6]. For the minority with intractable symptoms, the impact on quality of life and economic implications are considerable [7].
How long does low back pain last?
Chronic low back pain, defined as pain symptoms persisting beyond 3 months, affects an estimated 15–45% of the population. For the minority with intractable symptoms, the impact on quality of life and economic implications are considerable. Despite the high prevalence of low back pain within the general population, the diagnostic approach and therapeutic options are diverse and often inconsistent, resulting in rising costs and variability in management throughout the country. In part, this is due to the difficulty establishing a clear etiology for most patients, with known nociceptive pain generators identified throughout the axial spine. Back pain has been termed as “an illness in search of a disease.” Indeed, once “red flag” diagnoses such as cancer and fracture have been ruled out, the differential sources of low back pain remain broad, including the extensive realm of degenerative changes within the axial spine for which radiological evaluation is nonspecific and causal relationships are tentative. We will elaborate on these degenerative processes and their clinical implications. We will further discuss diagnostic approaches and the efficacy of existing treatment options.
How to treat spondylosis?
Conservative spondylosis treatment options can often effectively address mild cases of the condition. A conservative treatment is any form of therapy that does not involve surgery. This classification ranges from yoga to medication. There are several forms of effective conservative spondylosis treatment, including: 1 Physical therapy. A physical therapist can guide you through exercises that will strengthen the muscles surrounding your spine. As your muscles strengthen, they will better hold your spine in place and help take some of the pressure off of your vertebrae and joints. While this spondylosis treatment won’t reverse the condition, it can slow spinal degeneration down and prevent it from worsening. 2 Restorative yoga. Restorative yoga is designed to restore the muscle strength in the core. Similar to physical therapy, restorative yoga develops the muscles which will help your spine stay aligned and slow natural wear. 3 Lifestyle changes. Some people may benefit from a lifestyle change, such as a weight loss plan. Losing weight can help relieve the pressure from the spine and slow down the deterioration of its components. Additionally, weight loss programs usually include strength training, which will enhance the muscles surrounding your spine and help hold everything in its proper place. 4 Pain medication. Pain medication can be prescribed to help alleviate the discomfort caused by spondylosis, if that happens to be a symptom you experience. This spondylosis treatment can either be prescribed as daily pills or epidural shots that you have injected every month or every three months.
What type of surgery is used for spondylosis?
We offer two types of surgery to treat spondylosis: minimally invasive stabilization surgery and minimally invasive decompression surgery. The type of surgery you have depends on the severity of your spondylosis and whether or not you have developed any correlating spine conditions due to your spondylosis. Our surgeons and physicians can determine the type of surgery you need.
What is conservative spondylosis?
Conservative spondylosis treatment options can often effectively address mild cases of the condition. A conservative treatment is any form of therapy that does not involve surgery. This classification ranges from yoga to medication. There are several forms of effective conservative spondylosis treatment, including:
How to help your spine?
Lifestyle changes. Some people may benefit from a lifestyle change, such as a weight loss plan. Losing weight can help relieve the pressure from the spine and slow down the deterioration of its components. Additionally, weight loss programs usually include strength training, which will enhance the muscles surrounding your spine and help hold everything in its proper place.
Can spondylosis be treated?
If you have been diagnosed with spondylosis, you are most likely searching for a treatment option to help e ase your symptoms and prevent new conditions from developing. Most mild forms of spondylosis respond to conservative (nonsurgical) treatment methods. However, more advanced forms of spondylosis might require surgical treatment to restore the components of the spine.
Can aging cause spondylosis?
Spondylosis is a spine condition that describes the natural deterioration of the spine, typically due to the aging process. Since aging cannot be completely stopped or reversed , spondylosis treatment focuses on providing patients with relief from the symptoms of the condition. Even if spondylosis does not show symptoms, if left untreated, it could lead to the development of other spine conditions and weakness in the spine.
Is USA Spine Care a good alternative to open back surgery?
At USA Spine Care, we understand your need to find a spondylosis treatment that provides sufficient pain relief without having to undergo traditional open back surgery. We offer a safer and effective alternative to traditional open back surgery.^ Our minimally invasive surgeries help patients find relief from spondylosis and lead to no lengthy recovery.^
How to treat lumbar spondylosis?
Resume your daily tasks as soon as you can. 1 The best way to treat lumbar spondylosis is to get up and move more. That will help strengthen your back and core. [5]#N#X Expert Source Tracy Zollinger Dipl. OM, L.Ac., FABORM#N#Licensed Herbalist & Acupuncturist Expert Interview. 6 October 2020. 2 Exercises like Tai Chi and Qi Gong can help strengthen your lower back as well. [6]#N#X Expert Source Tracy Zollinger Dipl. OM, L.Ac., FABORM#N#Licensed Herbalist & Acupuncturist Expert Interview. 6 October 2020. 3 If you can’t do any daily tasks because the pain is so bad, then you should see a doctor right away.
How to treat spondylosis pain?
By applying heat or cold to the affected area and staying active, you can improve the pain significantly. If this doesn’t work, then taking an NSAID pain reliever can also relieve the pain. If your condition doesn’t improve after a week of treatment at home, then you should visit a doctor for more treatment options.
What is the best cream for back pain?
Rub cayenne pepper cream onto the affected area. Cayenne pepper creams are effective for arthritis pain and could help relieve some of your back pain too. [24]
How to treat a sharp pain?
If your pain acts up suddenly, then ice is the best treatment. Wrap an ice pack in a towel and hold it on the painful spot for 15-20 minutes at a time. Repeat this 2-3 times per day.
What to do if your pain is acting up?
If your pain is acting up, you could stretch instead of exercising.
How to fix a back injury?
However, most doctors prefer a more natural approach first. They’ll probably recommend an exercise, stretching, rest, and physical therapy regimen to build strength and flexibility in your back.
How to help spondylosis?
You can learn a few simple exercises to do at home, or consult a physical therapist for more guidance . Either way, make sure you stay active to build strength and flexibility in your back. This can help improve your condition.
How to treat spondylolysis?
The recommended treatment program for active spondylolysis is usually a combination of the following: 1 Bracing to immobilize the spine for a short period (e.g. four months) to allow the pars defect to heal 2 Pain medications and/or anti-inflammatory medication, as needed 3 Stretching, beginning with gentle hamstring stretching and progressing with additional stretches over time 4 Exercise that is controlled and builds gradually over time.
What is the best treatment for inactive spondylolysis?
For discomfort or pain associated with chronic inactive spondylolysis, there are several treatment options available, including pain medications, chiropractic or osteopathic manipulation, physical therapy and exercise.
What is the procedure for spinal fusion?
Usually, two procedures are performed as part of the same surgery: A decompressive laminectomy, which reduces irritation and inflammation in the area (but increases spinal instability) A spinal fusion to provide stabilization of the affected area. See more: Spinal Fusion Surgery for Isthmic Spondylolisthesis.
Is bracing necessary for inactive spondylolysis?
For inactive spondylolysis, bracing is usually not necessary. In many cases, however, the spondylolysis will be discovered long after the pars defect has already healed. This condition is often referred to as chronic inactive spondylolysis and may produce symptoms of chronic or recurring lower back pain or discomfort.
Is spondylolysis unstable?
However, it is important to note that any therapeutic approach must take into account that spondylolysis means that there is a potentially unstable area of the spine, so caution and the skill of the treating spine specialist are very important considerations.
Can spondylolysis cause lower back pain?
This is because appropriate manipulation treatment can relieve many of the side effects of spondylolysis, such as lower back pain caused by stresses on various spinal structures, including the facet joints.
Does a slippage require surgery?
Medical literature indicates that once the lesion has healed and becomes inactive, the likelihood of significant progression is minimal, and only rarely does the slippage require surgical intervention.
What is lumbar spondylosis?
Lumbar spondylosis is a degenerative condition which affects the lower spine. In a patient with lumbar spondylosis, the spine is compromised by a narrowing of the space between the vertebrae, causing a variety of health problems ranging from back pain to neurological issues. This condition is usually caused by old age, as the spine undergoes changes as people grow older, and many of these changes contribute to degeneration of the vertebrae. Spondylosis, which can appear in the cervical and thoracic vertebrae as well, is also known as spinal osteoarthritis.
How to diagnose lumbar spondylosis?
This condition is usually diagnosed with a manual exam and x-ray imaging of the spine. A neurological exam may also be administered to determine whether or not the lumbar spondylosis has caused problems in the spinal canal. Once a doctor has assessed the situation, he or she can work with the patient to develop an approach to treatment. Treatments are based on the severity of the lumbar spondylosis, along with the age of the patient; in a 90 year old patient, for example, surgery would not be advised, but in a 60 year old, surgery to correct the problem might be well worth the risk.
What happens when lumbar spondylosis is allowed to progress?
These symptoms are the result of pressure on the nerves as they exit the spinal cord. If the spondylosis is allowed to progress, it can lead to a narrowing of the spinal canal, resulting in impingement of the spinal cord, which can cause poor bladder control, unsteady gait, and other severe neurological problems.
Can lumbar spondylosis cause unsteady gait?
Untreated lumbar spondylosis may result in an unsteady gait .
What is lumbar spondylosis?
Lumbosacral spondylosis is spondylosis that affects both the lumbar spine and the sacral spine (below the lumbar spine, in the midline between the butto cks). Multilevel spondylosis means that these changes affect multiple vertebrae in the spine.
What is spondylosis of the lumbar spine?
For example, the phrase "spondylosis of the lumbar spine" means degenerative changes such as osteoarthritis of the vertebral joints and degenerating intervertebral discs (degenerative disc disease) in the low back. Spondylosis can occur in the cervical spine (neck), thoracic spine (upper and mid back), or lumbar spine (low back).
What is the growth of bone spurs around a degenerating intervertebral disc in the spine?
Spondylosis deformans is growth of bone spurs (osteophytes) or bony bridges around a degenerating intervertebral disc in the spine. Spinal stenosis is narrowing of the spinal canal. This narrowing of the spinal canal limits the amount of space for the spinal cord and nerves.
How long does it take for spondylosis to heal?
Home treatment is important in pain caused by spondylosis because pain may frequently improve or resolve after several days. Experts have found that bed rest prolongs the time to recovery. Therefore, it is recommended to continue normal or near normal activities. However, do not do anything that could exacerbate the problem, such as heavy lifting.
What is the term for degenerative changes in the spine such as bone spurs and degenerating intervertebral?
Spondylosis refers to degenerative changes in the spine such as bone spurs and degenerating intervertebral discs between the vertebrae.
How old do you have to be to have spondylosis?
Symptoms are often first reported between the ages of 20 and 50. Over 80% of people over the age of 40 have evidence of spondylosis on X-ray studies. The rate at which spondylosis occurs is partly related to genetic predisposition as well as injury history. Genetics is another risk factor for spondylosis.
Why do doctors re-evaluate spondylosis?
Because the diagnosis of spondylosis is made with images by plain film X-ray, CT scan, or MRI scan, most people with this diagnosis have already seen their doctor. Reasons for re-evaluation by a health-care professional include the following: If your pain is not manageable with the prescribed treatment.
