
Treatment
- Medications. Pain relievers. ...
- Physical therapy. It's common for people who have spinal stenosis to become less active, in an effort to reduce pain. ...
- Steroid injections. Your nerve roots may become irritated and swollen at the spots where they are being pinched. ...
- Decompression procedure. ...
- Surgery. ...
- Potential future treatments. ...
- Alternative medicine. ...
How serious is foraminal stenosis?
How serious is severe foraminal stenosis? The nerve roots that exit the spinal column through the neural foramina may become compressed, leading to pain, numbness, or weakness. For some people, the condition doesn't cause any symptoms and doesn't require treatment.
What do you need to know about foraminal stenosis?
What is Foraminal Stenosis?
- Foraminal Stenosis – An Overview. Foraminal stenosis is a spinal condition characterized by tightening or narrowing of the openings present between the vertebrae.
- Types of Foraminal Stenosis. ...
- Causes of Foraminal Stenosis
- Symptoms of Foraminal Stenosis
- Diagnosis of Foraminal Stenosis. ...
- Treatment Options for Foraminal Stenosis. ...
What are the symptoms of L4 and L5 nerve damage?
These are some of the more common symptoms of compressed nerves:
- Pain in the area of compression, such as the neck or low back.
- Radiating pain, such as sciatica or radicular pain.
- Numbness or tingling.
- "Pins and needles" or a burning sensation.
- Weakness, especially with certain activities.
How to relieve spinal stenosis with exercise?
Spinal Stenosis Exercises
- Back Flexion. This exercise will increase the open spacing between the vertebrae to alleviate pain. ...
- Child’s Pose. Position yourself on all fours with hands placed in line with the shoulders and knees with the hips.
- Cat/Cow. ...
- Abdominal Work. ...
- Curl-Ups. ...
- Tiger Pose. ...
- Lower Back Stretch. ...
- Front/Side Plank. ...
- Chin Tucks. ...
- Knees to Chest. ...
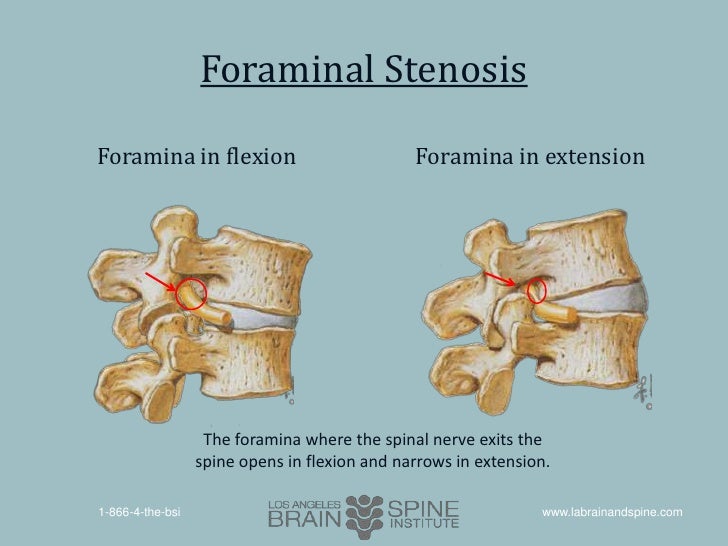
How is lumbar foraminal stenosis treated?
How Is Neural Foraminal Stenosis Treated?Medicines. This may include prescription or over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), prescription pain medicines, muscle relaxers, and steroids.Correcting your posture. ... Modifying your activities. ... Physical therapy. ... Braces. ... Surgery.
Can foraminal stenosis be cured?
Most cases of neural foraminal stenosis improve on their own or with conservative at-home treatments, like painkillers, gentle yoga, and physical therapy. Surgery isn't usually necessary, but it is considered a definitive solution for a case of neural foraminal stenosis.
Do you need surgery for foraminal stenosis?
When neurological deficits, such as numbness or weakness that goes into the arm or hand, continues to worsen despite nonsurgical treatments, surgery may be considered. The goal of surgery for cervical foraminal stenosis is to decompress the inflamed nerve root in order to give it more space to heal and function better.
What surgery is done for foraminal stenosis?
Foraminotomy is surgery that widens the opening in your spine where nerve roots leave your spinal canal. You may have a narrowing of the nerve opening (foraminal stenosis).
What kind of doctor treats foraminal stenosis?
Preparing for your appointment If your primary care doctor thinks you have spinal stenosis, he or she may refer you to a doctor who specializes in disorders of the nervous system (neurologist). Depending on the severity of your symptoms, you may also need to see a spinal surgeon (neurosurgeon, orthopedic surgeon).
Is walking good for foraminal stenosis?
Walking is a good exercise for spinal stenosis. It's low impact, and you control the pace and distance. However, if walking triggers your symptoms, choose a different type of exercise. Discuss alternative movement options with your doctor.
How successful is a lumbar foraminotomy?
6 The success rates reported for open paraspinal foraminotomy are as high as 72% to 83%,4,7-14 and this technique has been considered the gold standard for the surgical treatment of lumbar foraminal or far lateral stenosis.
Is lumbar foraminal stenosis serious?
Foraminal stenosis is one of many serious conditions that affects the spinal column; a nerve center that runs all the way from the base of the brain to the backbone, including the vertebral canal. The brain and spine together form the central nervous system.
What is the difference between spinal stenosis and foraminal stenosis?
Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of the canals through which the spinal cord travels, foraminal stenosis is the narrowing through which the spinal nerves travel before exiting the spine.
What causes neural foraminal stenosis?
Most causes of neural foraminal stenosis are degenerative, which means they happen over time as you age. It can also be caused by injuries. Some causes of foraminal stenosis include: Osteoarthritis, which can cause bone spurs to grow into the foramen. Paget's disease, which also causes bone overgrowth.
Where does neural foraminal stenosis occur?
Neural foraminal stenosis can happen anywhere along your spine. It's a type of spinal stenosis. Your spinal cord is a bundle of nerves that runs down the center of your spine. Nerves branch off of your spinal cord and connect to your arms, legs, and other body parts. Cervical foraminal stenosis.
What is the name of the bone that narrows the neck?
Cervical foraminal stenosis. This occurs in your cervical vertebrae, which are the spinal bones in your neck. Your neck is one of the most mobile parts of your spine and has to support your head, so it's a common place for foraminal narrowing to occur. Thoracic foraminal stenosis.
What is it called when the spinal cord is blocked?
When these openings, called neural foramen, narrow or get blocked, they can press on your nerves. This is called neural foraminal stenosis.
What are the symptoms of a stenosis in the hand?
Trouble using your hands. Numbness or tingling in the hand, arm, foot, or leg. Weakness in the hand, arm, leg, or foot . Thoracic foraminal stenosis. Symptoms can include: Problems with balance. Numbness or tingling at or below the level of the abdomen. Weakness or pain at or below the level of the abdomen .
Where is the thoracic spine located?
Your thoracic spine is located in your upper back area. Thoracic foraminal stenosis can affect your shoulders and ribcage. . Lumbar foraminal stenosis. This is another common type of foraminal stenosis. The lumbar spine is located in your lower back. This is another very mobile area of your spine.
What tests are needed to diagnose spinal cord disease?
They may need to run some tests as well, including an X-ray, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and computed tomography (CT) myelogram, which uses dye to outline the spinal cord and nerves.
What is the best medication for spinal stenosis?
Pain relievers. Pain medications such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others), naproxen (Aleve, others) and acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) may be used temporarily to ease the discomfort of spinal stenosis. They are typically recommended for a short time only, as there's little evidence of benefit from long-term use. Antidepressants.
How to diagnose spinal stenosis?
To diagnose spinal stenosis, your doctor may ask you about signs and symptoms, discuss your medical history, and conduct a physical examination. He or she may order several imaging tests to help pinpoint the cause of your signs and symptoms.
What is lumbar laminectomy?
Lumbar laminectomy. A lumbar laminectomy involves the removal of the back portion of a vertebra in your lower back to create more room within the spinal canal. Cervical laminectomy. Open pop-up dialog box.
How to reduce back pain?
If you're overweight or obese, your doctor may recommend that you lose weight. Losing excess weight can reduce pain by taking some stress off the back, particularly the lumbar portion of the spine.
How does metal hardware work in the spine?
It opens up the space within the spinal canal by creating a hinge on the lamina. Metal hardware bridges the gap in the opened section of the spine. Minimally invasive surgery. This approach to surgery removes bone or lamina in a way that reduces the damage to nearby healthy tissue.
Where is laminoplasty performed?
While shown here on the neck, it can also be performed in the lumbar spine. Laminoplasty is performed only on the vertebrae in the neck (cervical spine). It opens up the space within the spinal canal by creating a hinge on the lamina. Metal hardware bridges the gap in the opened section of the spine.
What is the procedure to remove a portion of the lamina?
This procedure removes only a portion of the lamina, typically carving a hole just big enough to relieve the pressure in a particular spot. Laminoplasty. This procedure is performed only on the vertebrae in the neck (cervical spine). It opens up the space within the spinal canal by creating a hinge on the lamina.
What causes foraminal stenosis?
For example, one cause of foraminal stenosis is a bulging or herniated disk. These cushioning disks between your spinal bones can slip out of place or become damaged. The bulging disk presses on the foramen and nerve root. This is most likely to happen in your lower back.
What is the least common area to be affected by foraminal stenosis?
This is the least common area to be affected by foraminal stenosis. Lumbar stenosis develops when the foramen of your low back narrow. The lower back is the section of your spine most likely to be affected by foraminal stenosis. This can be felt as pain, tingling, numbness, and weakness in the buttock, leg, and sometimes the foot.
What to do if stenosis is pinching nerve root?
The type of surgery will depend on the location of the stenosis and what’s causing it. If a herniated disk is pinching your nerve root, then surgery to remove the bulging disk may be the solution .
What is the narrowing of the bones in the spine called?
Foraminal stenosis is the narrowing or tightening of the openings between the bones in your spine. These small openings are called the foramen. Foraminal stenosis is a specific type of spinal stenosis. Nerves pass though the foramen from your spinal cord out to the rest of your body.
How to prevent back pain?
Using good posture and technique when sitting, playing sports, exercising, and lifting heavy objects can also help prevent injury to your back. Injuries can lead to stenosis and pinched nerves. Keep reading to learn about the symptoms, treatment options, and more.
Can pinched nerves cause foramen stenosis?
You’re more likely to develop foraminal stenosis and pinched nerves as you age. Arthritis and the wear and tear of daily living often lead to changes in your spine that narrow the foramen. But injury can cause stenosis as well, especially in younger people.
Can foraminal stenosis cause spinal cord compression?
Sometimes foraminal stenosis can be accompanied by stenosis of the spinal column itself. When the spinal cord is compressed, the symptoms may be more severe than when the nerve roots are pinched. These symptoms can include: clumsiness.
What is the best treatment for foraminal stenosis in NJ?
Nonsurgical Treatment. Nonsurgical treatments are usually recommended first for foraminal stenosis pain relief in NJ, and they include the following: Pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain medication, such as anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics, can help relieve pain.
How to tell if you have foraminal stenosis?
What symptoms you experience will depend on how compressed the nerves are and how narrow the foramen has become, as well as in what area of your back the condition is manifesting. If it is a foramen in the neck that is affected, you might experience symptoms in your arms, shoulders, fingers, and neck. If the condition is in the lumbar region of the spine, you might experience symptoms in the knee, thighs, feet, buttocks, toes, and back. These symptoms can include:
How successful is lumbar laminectomy?
The success rate reported for surgical treatment like lumbar laminectomy to relieve pain from foraminal stenosis is quite high. After a laminectomy , about 80 percent of the patients will have a marked improvement in their ability to perform their normal daily activities.
What is the condition where the foramina gets narrow?
Foraminal stenosis is a condition in which the foramina get narrow. The foramina are the passages on each side of the vertebrae through which the spinal nerve roots pass. When the spine is healthy, there’s sufficient space for the nerve roots to pass and then move out to various body parts.
How many vertebrae are there in the spine?
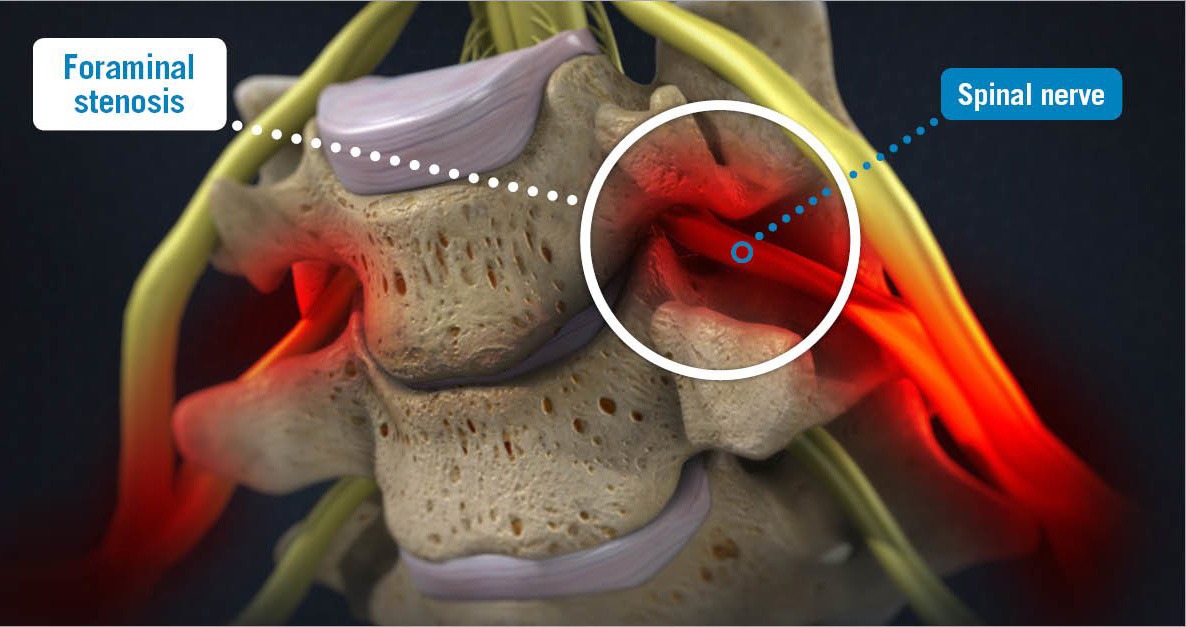
Your spine has 33 vertebral bones. In the middle and on the sides of these bones are openings that allow nerves to enter and exit. These nerves travel out to your legs, arms, and other parts of your body. The spaces where the nerves enter and exit are called foramina (singular foramen). Each foramen is formed by the facet joint (the space between two discs). Sometimes, the foramen can become too narrow and start to compress the nerves entering and exiting. This can cause symptoms such as numbness, pain, or weakness. This is called foraminal stenosis.
What is it called when the foramen is too narrow?
This can cause symptoms such as numbness, pain, or weakness. This is called foraminal stenosis.
What is the red circle on the MRI of the foramen?
The red circles highlight the foramen and show severe impingment of the exiting nerve.
How to relieve foraminal stenosis pain?
Bending forward or sitting may temporarily alleviate foraminal stenosis pain because the space between the vertebrae increases in these positions. It is also common for people to walk in a “hunched over” position because it helps decompress the nerves.
What causes foraminal stenosis in the spine?
Injury to the spinal joints will result in progressive degeneration or arthritis of the joints. Arthritis of the facet joints and degenerative disc disease cause foraminal stenosis in affected areas of the spine by causing bone spurs to form (bone spurs are also known as osteophytes and are bony projections that form along joint margins as ...
What is the name of the joint that surrounds the foramen?
Neuro foramen are surrounded by two moving spinal joints: the facet joint and spinal disc. When this foraminal opening is narrowed, it results in foraminal stenosis and causes symptoms such as numbness, tingling, or burning sensations in the extremities and most commonly, the legs. Bending forward or sitting may temporarily alleviate foraminal ...
What is the name of the hole in the spine that leads to the nerve roots?
Nerve roots exit the spine through small holes on both sides of the spine called neuro foramen. Neuro foramen are surrounded by two moving spinal joints: the facet joint and spinal disc. When this foraminal opening is narrowed, it results in foraminal stenosis and causes symptoms such as numbness, tingling, or burning sensations in ...
What is the name of the condition where nerve roots exit the spinal column?
Foraminal stenosis is one of the three forms of spinal stenosis. Spinal stenosis is defined as a narrowing of the opening from which the nerves exit the spinal column and is the primary cause of pinched nerves or nerve compression. Nerve roots exit the spine through small holes on both sides of the spine called neuro foramen.
Where is foraminal stenosis most common?
Foraminal stenosis is very common in the lower lumbar region of the back. Failure to treat foraminal stenosis or other types of spinal stenosis can result in permanent nerve damage and loss of feeling. Deuk Spine Institute offers one of the safest and most effective neural foraminal stenosis treatments in the world.
What is the term for a nerve that is not functioning properly?
Foraminal stenosis is treated when it causes pain or radiculopathy, which is when the nerves are not functioning properly as a result of being compressed or damaged and causing symptoms such as pain, tingling, or numbness in the hands or feet. Asymptomatic foraminal stenosis does not need treatment.
What is the best treatment for spinal stenosis?
In mild, moderate, and sometimes even severe cases of spinal or foraminal stenosis, exercise therapy and behavioral modification are the best forms of treatment.
What is the narrowing of the spinal canals?
Spinal stenosis and foraminal stenosis describe the narrowing of the canals in your spine. Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of the canals through which the spinal cord travels , foraminal stenosis is the narrowing through which the spinal nerves travel before exiting the spine. This narrowing is caused by the degenerative process ...
How does pressure affect the spine?
Years and years of pressure dehydrate the discs, causing them to shrink and wear down. As a result, the holes through which the spinal nerves travel get smaller. It is here where the process of stenosis begins. Once one part of the spine deteriorates, it directly affects other nearby regions, setting off a chain reaction.
How many vertebrae are in the spine?
The Spine and Stenosis. The spine, or vertebral column, is made up of 33 vertebrae (individual bone segments) that are stacked one on top of the other and spaced apart by small, shock-absorbing, sponge-like structures called intervertebral discs.
What is the purpose of the spine?
The purpose of the spine is to support the body’s weight, protect the spinal cord, and support us in standing , sitting , walking, and all other activities of daily life . The spinal cord runs the length of the spine down to the upper portion of the low back and is encased within the hollow sections of these vertebrae.
Where do spinal nerves exit?
Spinal nerves branch off of the spinal cord at each level and exit the spinal column through holes between each pair of vertebrae called “foramen.”. It is in these two areas—the hollow part of the vertebrae where the spinal cord runs down our backs and the holes between the vertebrae where the spinal nerves exit the vertebral column—that stenosis ...
Why do my canals narrow?
This narrowing is caused by the degenerative process that unfortunately occurs as we age, and can be associated with bulging discs, arthritic bone spurs, or the thickening of tissues such as ligaments. When the canals get too narrow, pain and/or loss of function can occur.
Diagnosis
Treatment
- Treatment for spinal stenosis depends on the location of the stenosis and the severity of your signs and symptoms. Talk to your doctor about the treatment that's best for your situation. If your symptoms are mild or you aren't experiencing any, your doctor may monitor your condition with regular follow-up appointments. He or she may offer some self-care tips that you can do at hom…
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- You'll have regular follow-up appointments with your doctor to monitor your condition. He or she may suggest that you incorporate several home treatments into your life, including: 1. Trying pain relievers.Over-the-counter medications such as aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others), naproxen (Aleve, others) and acetaminophen (Tylenol, others)...
Preparing For Your Appointment
- If your primary care doctor thinks you have spinal stenosis, he or she may refer you to a doctor who specializes in disorders of the nervous system (neurologist). Depending on the severity of your symptoms, you may also need to see a spinal surgeon (neurosurgeon, orthopedic surgeon).