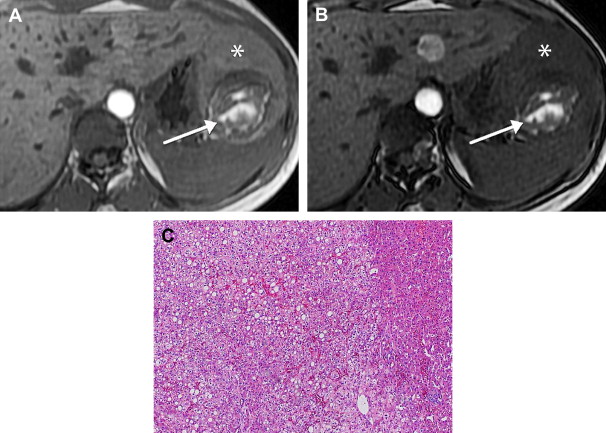
How do you unblock your liver bile duct?
Can a blocked bile duct be treated without surgery?
How serious is a blocked liver duct?
How do doctors clear a blocked bile duct?
How long can you live with a blocked bile duct?
How do you know if you have a bile duct obstruction?
How long does bile duct surgery take?
What will happen if bile duct is blocked?
Will a CT scan show blocked bile ducts?
Can you live without bile duct?
How complicated is bile duct removal surgery?
Removing part of the liver is called a partial hepatectomy. Sometimes this means that a whole lobe (right or left part) of the liver must be removed. This is called hepatic lobectomy and is a complicated operation that requires an experienced surgical team.Jul 3, 2018
What happens if you block bile ducts?
If untreated, a blockage of the bile ducts can cause severe infection. The liver produces a liquid called bile. Bile contains cholesterol and bile salts that help the gut to digest fats. It also contains a waste product called bilirubin. Bile passes through the bile ducts from the liver to the gallbladder, which stores it.
What is bile duct obstruction?
A bile duct obstruction, also known as biliary obstruction, is when one of the ducts that carry bile from the liver to the intestine via the gallbladder becomes blocked. If left untreated, this blockage can lead to serious complications, including severe infection. This article explores some of the leading causes of bile duct obstruction, ...
What is bile duct cancer?
Bile duct or pancreatic cancer. Bile duct cancer refers to all cancers that develop within the biliary system. The resulting tumors may block a bile duct. Pancreatic cancers can cause a bile duct obstruction if the tumor enters the intestine.
Can pancreatic cancer cause obstruction of the bile duct?
Pancreatic cancers can cause a bile duct obstruction if the tumor enters the intestine. Cancers that have started elsewhere in the body may also spread to the biliary system where they can cause an obstruction.
Can choledochal cysts cause obstruction?
Choledochal cysts. Choledochal cysts can sometimes cause bile duct obstructions. These cysts, which are sections of an enlarged bile duct, are congenital, meaning some people are born with them. They are also rare.
What is the best imaging for biliary obstruction?
If blood tests suggest a biliary obstruction, the doctor may recommend one of the following imaging methods to confirm the diagnosis: abdominal ultrasound. abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan.
Can you live without a gallbladder?
This will stop the problem of gallstones reoccurring. People can lead healthy lives without a gallbladder. If the cause is found to be cancer, the ducts may need to be stretched and drained.
What causes a blockage in the bile duct?
Gallstones form inside the gallbladder and can move into the common bile duct, blocking it. Cysts, tumors, inflammation and scarring are other bile duct obstruction causes. Bile duct obstructions are more common in people ...
What happens when bile ducts are blocked?
When a blockage occurs in any of the bile ducts, bile accumulates within nearby structures. As bile builds up in the liver, it causes jaundice and other symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, and upper abdominal pain. Depending on the cause, these symptoms can develop abruptly or slowly with time.
What is bile duct obstruction?
A bile duct obstruction is a blockage in one of the tubes that carries bile. Bile is a product of the liver. It contains cholesterol, bile salts to help digest fats, and waste products, such as bilirubin. After the liver makes bile, it travels through a network of microscopic tubes called hepatic ducts. These small ducts meet to form one large ...
Where does bile go?
Bile from the gallbladder flows through a different pathway, called the cystic duct.
Can a bile duct obstruction cause life threatening complications?
In some cases, a bile duct obstruction can lead to life-threatening complications . Seek immediate medical care ( call 911) if you, or someone you are with, have any of these life-threatening symptoms, including:
What are the symptoms of jaundice?
Call your doctor right away if you notice symptoms of jaundice, such as yellow skin or eyes, dark urine, or pale stools. Seek immediate medical care for severe abdominal pain, high fever and chills, or persistent nausea and vomiting.
What to do if you have jaundice?
Call your doctor right away if you notice symptoms of jaundice, such as yellow skin or eyes, dark urine, or pale stools. Seek immediate medical care for severe abdominal pain, high fever and chills, or persistent nausea and vomiting.
Can bile duct cancer be removed?
Bile duct cancer is usually found after it has spread and can rarely be completely removed by surgery. Palliative therapy may relieve symptoms and improve the patient's quality of life.
What is the intrahepatic bile duct?
Anatomy of the intrahepatic bile ducts. Intrahepatic bile ducts are a network of small tubes that carry bile inside the liver. The smallest ducts, called ductules, come together to form the right hepatic bile duct and the left hepatic bile duct, which drain bile from the liver.
What is bile duct cancer?
Bile duct cancer is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the bile ducts. Having colitis or certain liver diseases can increase the risk of bile duct cancer. Signs of bile duct cancer include jaundice and pain in the abdomen. Tests that examine the bile ducts and nearby organs are used to diagnose and stage bile duct cancer.
What are the ducts in the liver?
A network of tubes, called ducts, connects the liver, gallbladder, and small intestine. This network begins in the liver where many small ducts collect bile (a fluid made by the liver to break down fats during digestion ). The small ducts come together to form the right and left hepatic ducts, which lead out of the liver. The two ducts join outside the liver and form the common hepatic duct. The cystic duct connects the gallbladder to the common hepatic duct. Bile from the liver passes through the hepatic ducts, common hepatic duct, and cystic duct and is stored in the gallbladder.
Where is bile stored?
Bile is stored in the gallbladder and is released when food is being digested. Extrahepatic bile duct cancer: This type of cancer forms in the bile ducts outside the liver. The extrahepatic bile duct is made up of the hilum region and the distal region. Cancer can form in either region:
What is the purpose of liver function test?
Liver function tests: A procedure in which a blood sample is checked to measure the amounts of bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase released into the blood by the liver. A higher than normal amount of these substances can be a sign of liver disease that may be caused by bile duct cancer.
Why are cells removed during a biopsy?
Cells and tissues are removed during a biopsy so they can be viewed under a microscope by a pathologist to check for signs of cancer. Different procedures may be used to obtain the sample of cells and tissue. The type of procedure used depends on whether the patient is well enough to have surgery.
Can a cholecystectomy narrow the bile duct?
If you have suffered a bile duct injury, often caused during a laparoscopic cholecystectomy, it is not atypical to have a narrowing of the bile duct immediately afterwards. Luckily, most experienced biliary surgeons notice the injury right away and resolve it during the surgical procedure already taking place.
What causes bile duct obstruction?
Liver Cancer. Some liver cancers that metastasize into the biliary system can cause bile duct obstructions. Moreover, if you have cancer in your bile ducts near the liver, tumor growth can travel down the bile ducts and obstruct the pathway leading to the small intestine. Pancreatic Cancer. Since the pancreas is located near ...
Why is my bile duct narrowing?
In addition, if you have ever had bile duct inflammation or irritation, the chances of your bile ducts narrowing and becoming restricted increase. Liver Cancer. Some liver cancers that metastasize into the biliary system can cause bile duct obstructions.
How to diagnose biliary obstruction?
How to Diagnose a Biliary Obstruction. In order to treat a biliary obstruction, you must be seen and diagnosed by a doctor who treats them. However, before making the appointment to see your specialist, chances are you will experience some of the following symptoms, thus prompting you to make a trip to the doctor:
What is the procedure to remove gallstones?
Biliary surgery to remove tumors, gallstones, or other blockages. Stent insertion to inflate a collapsing bile duct and allow for bile to flow through naturally. Bile duct bypass to avoid the blockage and redirect the flow of bile into the small intestine.
What is the bile tree?
By Dr. Mark Fraiman on April 27, 2017 in Bile Duct Cancer, Bile Duct Disease. The biliary tree is a key component in your digestive system. Delivering bile that is produced in your liver and stored in your gallbladder until it is needed, the bile ducts are the bile’s pathway to the small intestine where fats you consume are broken down ...
Can a blocked bile duct be prevented?
Be aware of any risk factors you have, so that you can get prompt diagnosis and treatment if a bile duct becomes blocked. The blockage itself may not be preventable.
What is bile duct obstruction?
Biliary obstruction. Share. Bile duct obstruction is a blockage in the tubes that carry bile from the liver to the gallbladder and small intestine. The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down ...
Which organs release hormones into the bloodstream?
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted. Endocrine glands release hormones (chemical messengers) into the bloodstream to be transported to various organs ...
Which glands release hormones into the bloodstream to be transported to various organs and tissues throughout the body?
Endocrine glands release hormones (chemical messengers) into the bloodstream to be transported to various organs and tissues throughout the body. For instance, the pancreas secretes insulin, which allows the body to regulate levels of sugar in the blood. The thyroid gets instructions from the pituitary to secrete hormones which determine ...
Which organs are responsible for releasing bile into the duodenum?
Includes the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts (named the cystic, hepatic, common, and pancreatic duct).
Where is bile stored?
Bile is a digestive fluid secreted by the liver and stored in the gallbladder which normally is released into the duodenum portion of the small intestine through the sphincter of Oddi. Bile, released after a meal containing fats, aids in absorption and digestion of the fat.
What is the purpose of bile salts?
Bile is a liquid released by the liver. It contains cholesterol, bile salts, and waste products such as bilirubin. Bile salts help your body break down (digest) fats. Bile passes out of the liver through the bile ducts and is stored in the gallbladder.
What is bile duct obstruction?
Bile duct obstruction refers to a blockage in the ducts or tubes that transport bile from the liver to the gall bladder and the small intestine.
Which specialist should be consulted in case of signs and symptoms?
A person should consult a doctor if s/he notices any of the above symptoms. S/he will then be referred to a gastroenterologist.
What treatment modalities are available for management of the disorder?
This is commonly carried out through an endoscopic procedure known as Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography or ERCP.
How can the disorder be prevented from happening or recurring?
It is advisable to know one’s risk factors towards developing a bile duct blockage, which can enable quick diagnosis and early treatment. Occurrence of blockage, however, cannot be prevented.
What is the procedure to drain bile ducts?
For bile duct obstruction caused by cancer, your doctor will widen and drain your bile ducts using endoscopy or by inserting a needle through your skin.
Why is my bile duct blocked?
Other causes. Your bile duct can become blocked if you get an injury in your abdomen. It may also occur due to infections, especially if you are taking drugs to suppress your immune system.
What are the symptoms of a syringe?
You may also experience: 1 Pruritus — or itchy skin 2 Pain in your upper right abdomen 3 Fever 4 Nausea and vomiting 5 Tiredness and fatigue 6 Weight loss 7 Loss of appetite
What is biliary obstruction?
Bile Duct Obstruction. Bile duct or biliary obstruction is blockage of one or more bile ducts in your body. If your bile duct is blocked, it can’t transport bile or pancreatic juice to your intestines for digestion. This causes bile to build up in your liver and increases bilirubin levels in your blood. Causes of Biliary Obstruction.
What is bile made of?
Bile is made of cholesterol, bile salts, and water. It gets its color from bilirubin, which is formed when your blood cells break down. . Bile or pancreatic ducts are a network of tubes connecting your liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and intestine. They transport bile and digestive juices from the liver and pancreas to your small intestine ...
Where does bile come from?
It gets its color from bilirubin, which is formed when your blood cells break down. . Bile or pancreatic ducts are a network of tubes connecting your liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and intestine. They transport bile and digestive juices from the liver and pancreas to your small intestine to break down your food.
What causes bile to build up in the liver?
This causes bile to build up in your liver and increases bilirubin levels in your blood. Causes of Biliary Obstruction. Here are some of the common causes of biliary obstruction. . Cholelithiasis — or gallstones. Bile can solidify in your gallbladder if you have high blood cholesterol levels.
How to remove gallstones from bile duct?
Gallstones may be removed from the bile duct using endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). The doctor may even recommend a cholecystectomy to remove the gallbladder to prevent recurring blockages in the future. If the obstruction is formed because of cancer, surgical procedures may be suggested to stretch and drain the ducts.
What is biliary obstruction?
Also known as bile duct obstruction, biliary obstruction is a blockage in one of the ducts that transport bile from the liver to the small intestine through the gallbladder. Bile is a liquid produced by the liver that contains bile salts, cholesterol, and waste products like bilirubin ...
Where does bile accumulate?
From the liver, the bile passes via a network of bile ducts (also referred to as biliary tree) and accumulates in the gallbladder.
Where does bile go after eating?
From the liver, the bile passes via a network of bile ducts (also referred to as biliary tree) and accumulates in the gallbladder. After you have eaten a meal, the bile is released from the gallbladder into the small intestine to help digest food and break down fat.
What are the symptoms of bilirubin?
Common symptoms experienced by patients include: Jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes) due to the build-up of bilirubin in the bloodstream. Itching. Weight loss. Fatigue or lethargy. Fever. Abdominal pain. Vomiting and nausea. Loss of appetite.
How to prevent gallstones?
Add more fiber to your diet, and lower your intake of saturated fats, cholesterol, and sugar, to prevent gallstones. With the help of exercise and a nutritious diet, work towards achieving a healthy weight. To learn more about biliary obstructions and its preventive measures, contact us. Contact us Call Now.
Where does bile come from?
Bile is a liquid produced by the liver that contains bile salts, cholesterol, and waste products like bilirubin that help digest fats. From the liver, the bile passes via a network of bile ducts (also referred to as biliary tree) and accumulates in the gallbladder. After you have eaten a meal, the bile is released from the gallbladder into ...
What is the procedure called for a bile duct?
In a few cases, a procedure called ERCP ( endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography) is needed. In this procedure, the doctor uses a special endoscope (a long, flexible tube with a light and camera at the end) to examine the bile duct.
What is the purpose of bile?
Bile is a substance that helps in digestion of fatty food and excreting (getting rid of) harmful substances. When the bile duct becomes narrow, it makes it difficult for bile to pass from the liver to the small bowel. This reduction in bile to the small bowel leads to difficulty in digesting food, especially fatty food.
What causes biliary strictures?
Biliary strictures can be caused by: 1 Any damage done to the bile duct (for example, after gallbladder removal surgery) 2 Passage of gallstones to the bile duct 3 Infection of the bile ducts 4 Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) 5 Intestinal (small bowel) injuries 6 Cancer in the bile duct or pancreas
What is contrast agent?
The contrast agent allows the doctors to see the ducts of the bile system, gallbladder, and pancreas on the X-rays. This procedure not only helps diagnose small biliary strictures, but can also treat the biliary stricture.
Why is it difficult to digest food?
When the bile duct becomes narrow, it makes it difficult for bile to pass from the liver to the small bowel. This reduction in bile to the small bowel leads to difficulty in digesting food, especially fatty food. When bile is not excreted, it builds up in the body and causes several symptoms.