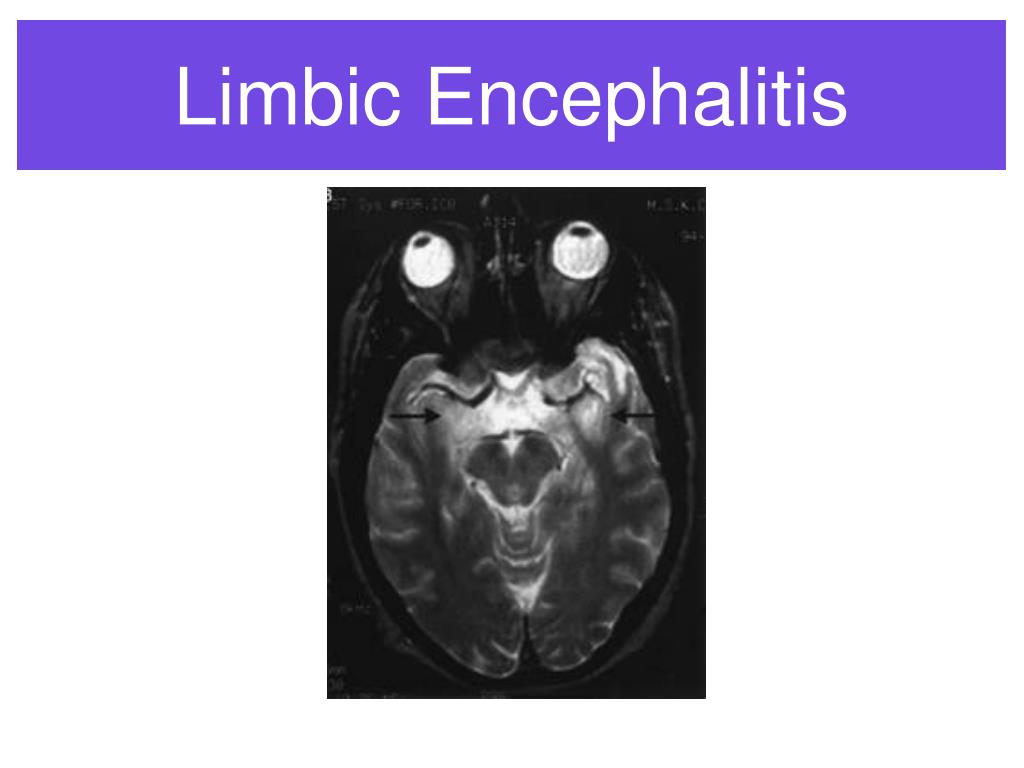
Limbic encephalitis treatment
| 1, 3. | Höftberger R, Titulaer MJ, Sabater L, Do ... |
| 2. | Billinton A, Ige AO, Wise A, White JH, D ... |
| 4. | Benarroch EE. GABAB receptors: Structure ... |
| 5, 31, 32. | Anderson NE, Barber PA. Limbic encephali ... |
| 6, 29, 33, 35. | Asztely F, Kumlien E.. The diagnosis and ... |
Does anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis have a cure?
Fast Treatment Can Reverse Anti-NMDA-Receptor Encephalitis. The researchers suggest that these antibodies reduced the numbers of cell-surface NMDA receptors and receptor clusters in the postsynaptic dendrites of the nervous system. This effect, they say, could be reversed by removing the antibodies.
Is there any natural treatment for encephalitis?
encephalitis lethargica Treatment. Patient stabilization during the early stages of encephalitis lethargica is the best treatment. No evidence of consistent effective treatment for the early stages, but taking steroids has shown improvement. Levodopa and other anti-parkinson drug often show dramatic responses.
Can You recover from encephalitis?
Some people eventually make a full recovery from encephalitis, although this can be a long and frustrating process. Many people never make a full recovery and are left with long-term problems caused by damage to their brain. These problems can have a significant impact on the life of the affected person, as well as their family and friends.
What should you know about limbic encephalitis?
- [1] subacute onset (less than 12 weeks) of the clinical signals and symptoms cited above;
- [2] neuropathologic or radiologic (MRI, or single photon-emission computer tomography (SPECT); positron-emission computed tomography (PET-CT) evidence of limbic involvement;
- [3] exclusion of other possible etiologies;
Can you recover from limbic encephalitis?
Initial recovery may be rapid but usually falls short of complete. Further recovery takes place more slowly over a period of months, even years. People are different. No two cases of encephalitis will have an identical outcome and people recover at different paces.
How long does limbic encephalitis last?
The mean duration of symptoms before presentation was 11 months (range 5 days-2 years). The most common symptom at presentation was short-term memory impairment in 7 patients followed by seizures in 5 and behavioral changes in three.
What causes autoimmune limbic encephalitis?
Cause. Limbic encephalitis is associated with an autoimmune reaction. In non-paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis, this is typically due to infection (commonly herpes simplex virus) or as a systemic autoimmune disorder. Limbic encephalitis associated with cancer or tumors is called paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis.
What is the best treatment for encephalitis?
Encephalitis caused by certain viruses usually requires antiviral treatment....Antiviral medications commonly used to treat encephalitis include:Acyclovir (Zovirax)Ganciclovir (Valcyte, Zirgan, others)Foscarnet (Foscavir)
Can the limbic system be repaired?
Brain retraining programs offer a way to calm an overactive limbic system, rewiring the brain so that it prunes away harmful neural pathways and creates new, healthy pathways.
Can brain damage from encephalitis be reversed?
Doctors can often treat encephalopathy, and many people make a full recovery. With treatment, impaired brain function may be reversed. However, certain types of encephalopathy are life-threatening.
Can autoimmune limbic encephalitis be cured?
It should be noted that the brain imaging and the routine lumbar puncture results may be normal in autoimmune limbic encephalitis. The diagnosis of autoimmune encephalitis is particularly important because the disease is potentially treatable with medicines that dampen down the immune system.
What are the symptoms of autoimmune limbic encephalitis?
What are the clinical features of autoimmune limbic encephalitis? Typical symptoms of ALE reflect dysfunction of the limbic structures of the brain and include short-term memory deficits, behavioural changes, anxiety, depression, psychosis and seizures.
What happens if encephalitis goes untreated?
However, despite improvements in diagnosis and treatment, encephalitis still leads to death in about 10% of patients. Survivors of severe cases of encephalitis can be left with permanent problems such as fatigue, irritability, impaired concentration, seizures, hearing loss, memory loss and blindness.
How long does it take for encephalitis to clear up?
The inflammation of the brain can last from a few days to two or three months. After this, most people find that they make their best recovery from their symptoms within two or three months.
What is the survival rate of encephalitis?
The mortality for EBV encephalitis is 8%, with substantial morbidity found in approximately 12% of survivors. Rabies encephalitis and acute disseminated encephalitis are virtually 100% fatal, although there are rare survivors reported in the medical literature.
Does encephalitis show up on an MRI?
Brain scans A scan of the brain can help show whether you have encephalitis or another problem such as a stroke, brain tumour or brain aneurysm (a swelling in an artery). The 2 main types of scan used are: a CT scan. an MRI scan.
What is the most common form of limbic encephalitis?
Most forms of limbic encephalitis fall into two main categories: Infectious encephalitis – caused by direct invasion of the limbic area of the brain by a bug, usually a virus. Autoimmune encephalitis – caused by the person’s own immune system reacting against parts of the limbic system. 1.
What is the condition of paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis?
Most individuals with paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis have a cancer of the lung, thymus gland, ovary, breast or testes. More rarely, other cancers can initiate the condition. The outcome is very dependent on the underlying tumor and the precise condition, often classified by the antibody.
How is LGI1 CASPR2 treated?
If the antibodies are found in a patient with the recognised clinical features, LGI1/CASPR2-antibody encephalitis can be treated by dampening down the immune reaction that is causing the inflammation using immunosuppression.
How long does it take for limbic encephalitis to develop?
The symptoms typically develop over a few weeks or months, but they may evolve over a few days.
Why does the immune system react with the limbic system?
Sometimes when the immune system starts to react with the limbic areas, this happens because the person has a tumor (neoplasm) in their body which activates the immune system. This activated immune system can, in turn, attack the brain.
What are the limbic areas of the brain?
The limbic areas of the brain control many functions including memory, learning, and emotions such as aggression. In addition, some of these limbic areas are susceptible to seizures, which are a common feature of limbic encephalitis. The cardinal sign of limbic encephalitis is a severe impairment of short-term memory; however, ...
Can paraneoplastic encephalitis cause cancer?
Another antibody that can cause paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis is the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antibody. This disease may be associated with a growth such as a cancer in around 30% of cases. This antibody usually causes encephalitis involving several brain regions, but it can sometimes cause a pure limbic encephalitis. The N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor is a protein in the brain that helps control thoughts, mood and movements, and therefore antibodies against NMDA receptors are likely to have an important role in altering these functions. Anti-NMDAR encephalitis affects the brain more diffusely than purely the limbic system, and therefore it is not classified as a limbic encephalitis.
What is the term for limbic encephalitis?
The term ‘limbic encephalitis ’ (LE) describes the condition when limbic areas of the brain are inflamed (swollen) and consequently not functioning properly. The main regions of the limbic system include the hippocampus and amygdala. The limbic areas of the brain control many functions including memory, learning, and emotions such as aggression.
What are the two receptors that cause limbic encephalitis?
Antibodies against two other receptors in the brain, AMPA and GABA A/B, are less common causes of autoimmune limbic encephalitis. Although the majority of these patients have an underlying tumour, this is a form of Paraneoplastic Limbic Encephalitis that can often respond to treatment relatively well (see above PLE).
What is the difference between autoimmune and infectious encephalitis?
Infectious encephalitis – caused by direct invasion of the limbic area of the brain by a bug, usually a virus. Autoimmune encephalitis – caused by the person’s own immune system reacting against parts of the limbic system. 1.
Why does the immune system react with the limbic system?
Sometimes when the immune system starts to react with the limbic areas, this happens because the person has a tumour in their body which activates the immune system. This activated immune system can, in turn, attack the brain. Doctors call this paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis as the tumour (neoplasm) affects the brain from a distance, ...
What are the limbic areas of the brain?
The limbic areas of the brain control many functions including memory, learning, and emotions such as aggression. In addition, some of these limbic areas are susceptible to seizures, which are a common feature of limbic encephalitis.
Can herpes cause inflammation in the limbic system?
Many infections of the brain can potentially cause inflammation of the limbic areas . A number of viruses, such as the herpes simplex virus (HSV) seem to preferentially target this area. Some people may therefore be given the diagnosis of LE whilst others are given the diagnosis herpes simplex encephalitis for the same condition.
What is the first step in treatment for limbic encephalitis?
In cases of confirmed paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis (PLE), removal or treatment of the tumor is often the first step in treatment. If the cause of limbic encephalitis is a viral infection, an antiviral drug may be prescribed. Immunotherapy is often utilized as a first line or second line treatment.
What are the symptoms of limbic encephalitis?
A variety of symptoms may be associated with limbic encephalitis such as anterograde amnesia (the inability to store new memories after the onset of the condition), anxiety, depression, irritability, personality change, acute confusional state, hallucinations and seizures.
What is the Encephalitis Society?
Where to Start. The Encephalitis Society offers a factsheet on Limbic encephalitis. The International Autoimmune Encephalitis Society offers patients and families detailed information on diagnosis and treatment.
What is the term for a group of autoimmune conditions characterized by inflammation of the limbic system and other parts
Limbic encephalitis represents a group of autoimmune conditions characterized by inflammation of the limbic system and other parts of the brain. The cardinal sign of limbic encephalitis is a severe impairment of short-term memory; however, symptoms may also include confusion, psychiatric symptoms, and seizures .
How long does it take for a limbic encephalitis to develop?
The symptoms typically develop over a few weeks or months, but they may evolve over a few days. Limbic encephalitis is often associated with an underlying neoplasm (paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis); however some cases never have a neoplasm identified (non-paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis).
What is the presenting sign of limbic encephalitis?
Although the symptoms of the condition may vary from person to person, the presenting sign of limbic encephalitis is severe impairment of short-term memory, with most patients having difficulties in recall. Epileptic seizures are common and may occur prior to symptoms of memory loss. [2] .
What are the criteria for encephalitis?
Diagnosis of limbic encephalitis can be made when all three of the following criteria have been met: [14588]#N#1. Subacute onset (rapid progression of less than 3 months) of working memory deficits (short-term memory loss), altered mental status, or psychiatric symptoms#N#2. At least one of the following:#N#• New focal CNS findings#N#• Seizures not explained by a previously known seizure disorder#N#• CSF pleocytosis ( white blood cell count of more than five cells per mm3)#N#• MRI features suggestive of encephalitis#N#3. Reasonable exclusion of alternative causes#N#Examples of conditions that must be ruled out before a diagnosis of limbic encephalitis can be made, include: [5]
What is limbic encephalitis?
Limbic encephalitis is a type of autoimmune encephalitis (AE) that targets the brain’s limbic system. The limbic system is a group of brain structures that underlie memory and emotion (Fig. 1). The term limbic encephalitis is slightly misleading, however. The disease does not affect all areas of the limbic system and frequently involves non-limbic ...
What causes non-viral encephalitis?
Non-viral causes result from an autoimmune response involving either cytotoxic T-cells or antibodies. Cytotoxic T-cells arise as a result of a cancerous tumor. In limbic encephalitis, these T-cells target proteins inside neurons (common proteins targeted are Hu and Ma2) 2,4. In contrast, limbic encephalitis caused by antibodies rather ...
What are the major brain structures of the limbic system?
The major brain structures of the limbic system include the amygdala and the hippocampus (Fig. 1). The amygdala is critical in regulating emotion while the hippocampus is primarily responsible ...
What is an EEG?
An electroencephalogram (EEG) is administered to measure electrical brain activity. EEG electrodes are placed throughout the scalp, allowing doctors to pick up seizure-like activity in the brain and often isolate where in the brain the seizures originate. EEGs from patients with limbic encephalitis frequently suggest involvement ...
Where is the limbic system located?
The Limbic System. The temporal lobes (green, left) are located on the sides of the head, behind the ears. The image to the right shows the inside of the brain. The temporal lobe houses the hippocampus (blue, right), and the amygdala (purple, right) which are two of the major brain structures that make up the limbic system.
What is the best treatment for cell surface proteins?
In cases where antibodies against cell-surface proteins were present, removing the root cause along with a course of steroids and immunotherapy to restore the immune system can be an extremely successful treatment.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for seizures?
The temporal lobe houses the amygdala and hippocampus and is therefore often the source of seizures in limbic encephalitis. A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is also performed which gives doctors an image of the brain. Differences in contrast can indicate that the blood brain barrier is compromised in the temporal lobe, ...
What is needed for encephalitis?
People who are hospitalized with severe encephalitis might need: Breathing assistance, as well as careful monitoring of breathing and heart function. Intravenous fluids to ensure proper hydration and levels of essential minerals. Anti-inflammatory drugs, such as corticosteroids, to reduce swelling and pressure within the skull.
What is the emergency team for encephalitis?
The emergency care team will likely include specialists in infectious diseases and in the brain and nervous system (neurologist).
What test can be done to detect encephalitis?
Samples of blood, urine or excretions from the back of the throat can be tested for viruses or other infectious agents. Electroencephalogram (EEG). Electrodes affixed to your scalp record the brain's electrical activity. Certain abnormal patterns may indicate a diagnosis of encephalitis. Brain biopsy.
Can encephalitis be diagnosed with brain biopsy?
Certain abnormal patterns may indicate a diagnosis of en cephalitis. Brain biopsy. Rarely, a small sample of brain tissue might be removed for testing. A brain biopsy is usually done only if symptoms are worsening and treatments are having no effect.

Pathophysiology
Symptoms
- The cardinal sign of limbic encephalitis is a severe impairment of short-term memory; however, symptoms may also include confusion, psychiatric symptoms, and seizures. The symptoms typically develop over a few weeks or months, but they may evolve over a few days. Limbic encephalitis is often associated with an underlying neoplasm (paraneoplastic limbic encephaliti…
Epidemiology
- Initially limbic encephalitis was considered a rare disorder in association with cancer (paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis); most commonly associated with small cell lung cancer (SCLC), breast cancer, testicular tumors, teratomas, Hodgkins lymphoma and thymomas but can occur in the absence of malignancy also 1). About 60-75% of patients neurological symptoms pr…
Diagnosis
- Limbic encephalitis can have varied presentation and delayed diagnosis is common, but improvements are being made to assist in early detection. The improvements in neuroimaging studies (MRI, PET) and identification of antineuronal antibodies in patients (CSF analysis) and tests that measure the electrical activity of the brain (EEG) have facilitated to confi…
Treatment
- Treatment of limbic encephalitis includes removal of the neoplasm (if identified) and immunotherapy 5), 6), 7). It is becoming increasingly clear that non-paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis is caused, at least in part, by specific antibodies in the patients blood that target the patients brain, particularly the hippocampus and other limbic areas. M...
Function
- The limbic system is sometimes called the emotional brain because it plays a primary role in a range of emotions, including pain, pleasure, docility, affection, and anger. It also is involved in olfaction (smell), learning and memory. Together with parts of the cerebrum, the limbic system also functions in memory; damage to the limbic system causes memory impairment. One portio…
Structure
- The limbic system is a ring of cortex on the medial side of each hemisphere, encircling the corpus callosum and thalamus. The main components of the limbic system are as follows: Its most anatomically prominent components are the cingulate gyrus, which arches over the top of the corpus callosum in the frontal and parietal lobes; the hippocampus in the medial temporal lobe; …
Components
- Other components include the mammillary bodies and other hypothalamic nuclei, some thalamic nuclei, parts of the basal nuclei, and parts of the frontal lobe called prefrontal and orbitofrontal cortex. Limbic system components are interconnected through a complex loop of fiber tracts allowing for somewhat circular patterns of feedback among its nuclei and cortical neurons. All o…
Features
- Note: Mesial temporal lobes (yellow arrows), cingulate gyrus (red arrow), and insulae (blues arrows) involvement with asymmetric (right>left) cortical thickening and FLAIR hyperintensity.
Classification
- There are broadly two forms of autoimmune limbic encephalitis: paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis and non-paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis.
Causes
- Sometimes when the immune system starts to react with the limbic areas, this happens because the person has a tumor (neoplasm) in their body which activates the immune system. This activated immune system can, in turn, attack the brain. Doctors call this paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis as the tumor affects the brain from a distance, via the immune system. These two f…
Research
- As these autoimmune diseases have only been recently described, there is still much to be done to raise awareness amongst clinicians. Future research aims to understand the biological mechanisms by which this antibody affects the excitability of the brain, and hence causes disease. Researchers also hope to discover further antibodies which may allow other autoimmu…
Types
- A number of specific brain protein targets for these antibodies have been discovered over the last years and this variety may explain why people have different symptoms. The main established antibodies and their associated features are described below:
Prognosis
- As this disease was only relatively recently described, there is still much to learn about what happens to patients in the long-term. Almost all patients make some improvements but very few patients are left with no residual problems after treatments. Patients are left with problems in memory, seizures and behaviour which may require medical and psychological input and, occasi…