Procedures
The minimally-invasive, advanced therapy slows down or stops the progression of the corneal deformation of keratoconus, by making collagen bonds in the cornea stronger, allowing it to become stiffer and usually stop bulging out. Learn more about CXL here. Advanced stages Corneal Transplantation
What is keratoconus and how is it treated?
Keratoconus Treatments There are a variety of treatment options for keratoconus, including rigid gas permeable (RGP) contact lenses, scleral contact lenses, intracorneal ring segment implants, and more. Learn about these options below. Eyeglasses or Soft Contact Lenses
How can you prevent keratoconus?
Current treatment for keratoconus includes glasses in the earliest stages to treat nearsightedness and astigmatism. As keratoconus progresses and worsens, glasses are no longer capable of providing clear vision, and patients need to wear a contact lens, usually a hard contact lens. Intermediate Stages
Can keratoconus be corrected?
Other treatment options for more advanced forms of keratoconus include: Intracorneal ring segments Corneal transplant
Is keratoconus a serious condition?
Mar 30, 2022 · Penetrating keratoplasty (PK) is a century-old procedure and the most commonly performed eye transplant. It treats corneal problems that affect visual acuity, such as keratoconus. The PK procedure involves the complete removal of a damaged section of the cornea. This follows replacing it with a healthy one from a donor.
What is the best treatment for keratoconus?
What is the best treatment for keratoconus? Scleral contact lenses are currently the best treatment for keratoconus. Scleral lenses provide excellent vision with great comfort. A local keratoconus contact lens specialist in your area will have the most experience in fitting these specialized lenses.
Can keratoconus be cured permanently?
Keratoconus isn't a condition that can be permanently treated with medications or surgery. It's a chronic eye disorder, which unfortunately means it's for life.Jun 24, 2019
Can keratoconus be corrected?
There is no cure for keratoconus, but you can manage it effectively with treatment. The most effective treatment for this condition depends on its severity. There are several treatments available to help effectively manage keratoconus.Oct 27, 2021
Can you go blind if you have keratoconus?
No, Keratoconus will not cause complete blindness. It can lead to partial blindness or significant visual impairment. It may lead to reduced vision, blurred vision, sensitivity to light, etc.
At what age keratoconus stops?
NEW YORK (Reuters Health) - Although keratoconus is often thought to stop progressing by the time patients are 30 to 40 years old, the corneal degeneration often continues beyond this point, according to researchers from New Zealand. As Dr.Oct 25, 2016
Is keratoconus serious?
Untreated keratoconus can lead to permanent vision loss. The changes to the cornea make it difficult for the eye to focus with or without eyeglasses or standard soft contact lenses.Aug 19, 2019
Is keratoconus surgery painful?
You shouldn't feel any pain during the procedure because your eyes will be numb. The entire treatment takes about 60-90 minutes.May 7, 2020
Is keratoconus painful?
In rare cases, severe keratoconus causes a complication called corneal hydrops. This happens when part of your cornea breaks. This causes the fluid in your eye to flow into your cornea abnormally. This can cause severe pain and swelling.
Can I live a normal life with keratoconus?
The good news is that it does not have to be this way and that patients with keratoconus can go on to live normal lives just like any other person with good sight. You just need the proper treatment in order to get good vision back.Apr 8, 2022
What does a person with keratoconus see?
Individuals with keratoconus often experience near-sightedness, blurry vision, distorted images, and extreme glare when viewing lights, especially at night. The condition is usually not painful, but can have a significant impact on an individual's visual acuity.Oct 21, 2019
Is keratoconus very common?
Keratoconus, a progressive eye condition in which the cornea weakens and thins over time, affects approximately 1 in 2,000 individuals in the US. However, some estimates suggest that the incidence may be as high as 1 in 400 individuals.
Is having keratoconus a disability?
Is Keratoconus a Disability? Keratoconus eye disease could cause loss of visual acuity that is severe enough to be considered a disability. Keratoconus is not a disability, but vision loss caused by keratoconus may be severe enough to qualify as a disability.
How to treat keratoconus?
Generally, there are two approaches to treating keratoconus: slowing the progression of the disease and improving your vision.
How to diagnose keratoconus?
To diagnose keratoconus, your eye doctor (ophthalmologist or optometrist) will review your medical and family history and conduct an eye exam. He or she may conduct other tests to determine more details regarding the shape of your cornea. Tests to diagnose keratoconus include: Eye refraction. In this test your eye doctor uses special equipment ...
What type of contact lens is best for keratoconus?
Hard contact lenses. Hard (rigid, gas permeable) contact lenses are often the next step in treating more-advanced keratoconus. Hard lenses may feel uncomfortable at first, but many people adjust to wearing them and they can provide excellent vision. This type of lens can be made to fit your corneas. Piggyback lenses.
What is a scleral lens?
Scleral lenses. These lenses are useful for very irregular shape changes in your cornea in advanced keratoconus. Instead of resting on the cornea like traditional contact lenses do, scleral lenses sit on the white part of the eye (sclera) and vault over the cornea without touching it.
Can keratoconus be treated with contact lenses?
Improving your vision depends on the severity of keratoconus. Mild to moderate keratoconus can be treated with eyeglasses or contact lenses. This will likely be a long-term treatment, especially if your cornea becomes stable with time or from cross-linking.
What is the protective layer between the eye and contact lens?
Scleral contact lenses cover the white part of the eye and arch over the cornea. A protective layer of saline lies between the eye and contact lens. These lenses are a good alternative to surgery for many patients with keratoconus.
What is the best way to evaluate your eyes?
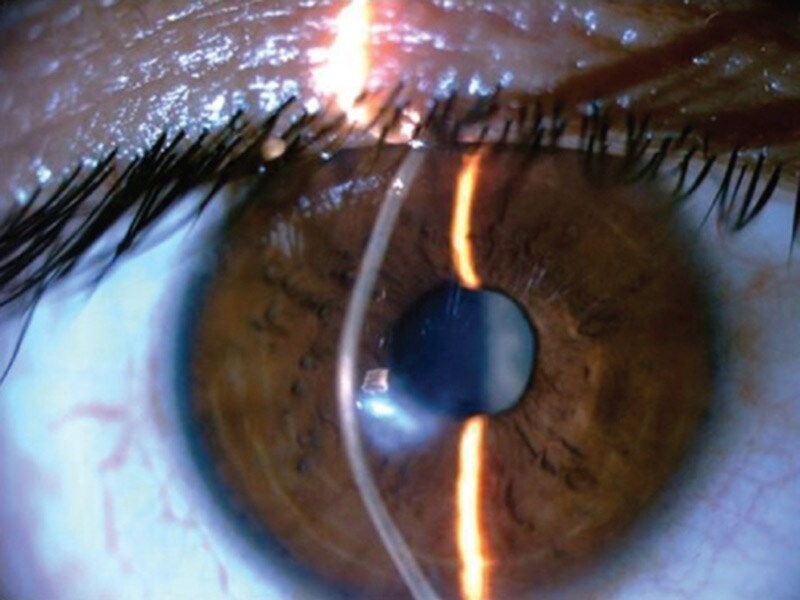
Some doctors may use a hand-held instrument (retinoscope) to evaluate your eyes. Slit-lamp examination. In this test your doctor directs a vertical beam of light on the surface of your eye and uses a low-powered microscope to view your eye. He or she evaluates the shape of your cornea and looks for other potential problems in your eye.
How to treat progressive keratoconus?
This one-time, in-office procedure involves the application of a vitamin B solution to the eye, which is then activated by ultraviolet light for about 30 minutes or less. The solution causes new collagen bonds to form, recovering and preserving some of the cornea’s strength and shape.
What are the risks of keratoconus?
The following may increase the risk of developing keratoconus: 1 Genetics. Patients with a family history of keratoconus or with certain systemic disorders, such as Down syndrome, are at a higher risk of developing keratoconus. 2 Chronic eye inflammation. Constant inflammation from allergies or irritants can contribute to the destruction of corneal tissue that may result in developing keratoconus. 3 Eye rubbing. Chronic eye rubbing is associated with developing keratoconus. It may also be a risk factor for disease progression. 4 Age. Keratoconus is often discovered in the teenage years. Generally, young patients with advanced keratoconus are more likely to need some form of surgical intervention as the disease progresses.
What is collagen cross link?
Corneal collagen cross-linking is a procedure designed to stop the progression of keratoconus or slow it down. Keratoconus is a leading cause of corneal transplantation in the United States. There is no known prevention for keratoconus.
When does keratoconus start?
Keratoconus generally begins at puberty and progresses into the mid-30s. There is no way to predict how quickly the disease will progress, or if it will progress at all. Keratoconus typically affects both eyes, with one being more severely affected than the other.
What is the thickest part of the cornea?
The cornea is the clear, outer layer at the front of your eye. The middle layer is the thickest part of the cornea, mostly made up of water and a protein called collagen. Collagen makes the cornea strong and flexible, and helps keep its regular, ...
Can you wear glasses with keratoconus?
Current treatment for keratoconus includes glasses in the earliest stages to treat nearsightedness and astigmatism . As keratoconus progresses and worsens, glasses are no longer capable of providing clear vision, and patients need to wear a contact lens, usually a hard contact lens.
How long does it take to get a corneal transplant?
The procedure takes about 15 minutes. Corneal transplant. In a corneal transplant, a donor cornea replaces the patient’s damaged cornea. Corneal transplants are often performed on an outpatient basis and take about an hour to complete.
What is the best treatment for keratoconus?
10. Corneal transplant . Some people with keratoconus can't tolerate a rigid contact lens, or they reach the point where contact lenses or other therapies no longer provide acceptable vision. The last remedy to be considered may be a cornea transplant , also called a penetrating keratoplasty (PK or PKP).
How to treat progressive keratoconus?
Treatments for progressive keratoconus include: 1. Corneal crosslinking. This procedure, also called corneal collagen cross-linking or CXL, strengthens corneal tissue to halt bulging of the eye's surface in keratoconus. The aim of corneal cross-linking is to strengthen the cornea by increasing the number of "anchors" that bond collagen fibers ...
What causes keratoconus in the eye?
Keratoconus also is associated with: 1 Overexposure to ultraviolet rays from the sun 2 Eye rubbing 3 A history of poorly fitted contact lenses 4 Chronic eye irritation
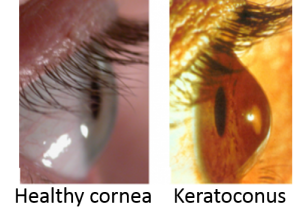
Why does keratoconus bulge forward?
Research suggests the weakening of the corneal tissue that leads to keratoconus may be due to an imbalance of enzymes within the cornea. This imbalance makes the cornea more susceptible to oxidative damage from compounds called free radicals, causing it to weaken and bulge forward.
What is the condition where the cornea is distorted?
Keratoconus is a progressive eye disease in which the normally round cornea thins and begins to bulge into a cone-like shape. This cone shape deflects light as it enters the eye on its way to the light-sensitive retina, causing distorted vision.
What are the symptoms of keratoconus?
Keratoconus signs and symptoms. As the cornea becomes more irregular in shape, it causes progressive myopia and irregular astigmatism to develop, creating additional problems with distorted and blurred vision. Glare and light sensitivity also may occur.
Is keratoconus cross linking FDA approved?
Currently, the only corneal cross-linking platform that is FDA-approved for the treatment of progressive keratoconus in the U.S. is epithelium-off cross-linking performed with a Glaukos KXL System and proprietary Photrexa and Photrexa Viscous riboflavin solutions. (Glaukos recently acquired Avedro.)
What is a keratoconus?
Keratoconus FAQs. Your cornea is the rounded front part of your eye. Keratoconus (also known as KC, bulging cornea, or conical cornea) is a progressive eye disease in which your cornea thins, causing it to bulge into a cone-like shape . A cone-shaped cornea deflects light as it enters your ...
How to tell if you have keratoconus?
Early signs of keratoconus include: 1 Sudden vision change in one eye 2 Double vision when looking with one eye 3 Slightly distorted vision (straight lines appearing bent or wavy) 4 Bright light sensitivity
How many people have keratoconus?
The adverse changes to the shape of the cornea can stop at any time, or continue throughout your lifetime. Keratoconus affects roughly 1 in 2,000 people. It is most common in people aged 10-25.
What causes nearsightedness?
Clouded vision. Poor night vision. Red or swollen eyes. As your cornea thins and bulges, the shape of your eye changes. This is known as irregular astigmatism and causes nearsightedness (myopia). Objects up close are visible, but anything further away is blurry.
How does a keratometer work?
This can be done in several ways. Keratometry is a procedure that measures the anterior curvature of your cornea. The optometrist uses a keratometer to shine a circle of light on your eye. He then measures its reflection to determine the shape of your cornea. The most accurate and common method is corneal topography.
Does rubbing your eyes cause keratoconus?
However, it is unknown whether eye rubbing causes the disorder, or if it is a reaction to the discomfort experienced in the early stages. Either way, it likely worsens the condition. Approximately 30 percent of people with keratoconus have some type of allergic disorder. This is not fully understood either.
What is a slit lamp?
In a slit-lamp examination, your eye doctor will shine a vertical beam of light on your eye and use a low-power microscope to examine the cornea's shape. They can also look for additional problems with your eye.