Medication
Oct 25, 2021 · How is Kawasaki disease treated? Once diagnosed, patients are treated in the hospital. The stay is usually a few days to a few weeks. The standard initial treatment is intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) and aspirin. When given early in the illness, IVIG can reduce the risk of coronary artery problems.
Procedures
It's used to treat Kawasaki disease because: it can ease pain and discomfort it can help reduce a high temperature at high doses, aspirin is an anti-inflammatory (it reduces swelling) at low doses, aspirin is an antiplatelet (it prevents blood clots forming)
How do you cure Kawasaki disease?
Treatment for Kawasaki Disease These medicines help reduce the swelling and inflammation in the blood vessels. IVIG can decrease, but NOT eliminate,... The infusion is most effective if given within the first 10 days of the illness. The risk of developing coronary changes...
What are the long term effects of Kawasaki syndrome?
Kawasaki Disease Treatment Your child may have a lot of pain from the fever, swelling, and skin problems . Their doctor might prescribe medication to …
What are the side effects of Kawasaki disease?
Kawasaki disease is diagnosed by having certain symptoms. For example, a fever lasting at least 5 days. Your child’s healthcare provider will treat Kawasaki with aspirin, intravenous immune globulin (IVIG), or other medicines.
What is the prognosis of Kawasaki disease?
Nov 18, 2021 · Abdominal pain. Diarrhea. Irritability. Joint pain. Vomiting. Children with a high fever for five or more days who have fewer than four of the above signs and symptoms might have what's known as incomplete Kawasaki disease. Children with incomplete Kawasaki disease are still at risk of coronary artery injury and still require treatment within ...
See more
Kawasaki disease (KD), also known as Kawasaki syndrome, is an acute febrile illness of unknown cause that primarily affects children younger than 5 years of age. The disease was first described in Japan by Tomisaku Kawasaki in 1967, and the first cases outside of Japan were reported in Hawaii in 1976. Clinical signs include fever, rash ...

Can you fully recover from Kawasaki disease?
What triggers Kawasaki disease?
What is the first line of treatment for Kawasaki disease?
Does Kawasaki disease stay with you forever?
Can adults get Kawasaki disease?
Is Kawasaki disease serious?
Why do you give aspirin for Kawasaki?
What kind of doctor treats Kawasaki disease?
How is Kawasaki disease prevented?
What is the death rate of Kawasaki disease?
Is Kawasaki disease painful?
Can Kawasaki cause heart failure?
How to treat Kawasaki disease in children?
Their risk of developing complications will also be increased. The 2 main treatments for Kawasaki disease are: aspirin. intravenous immunoglobulin.
What is IVIG in medicine?
Immunoglobulin is a solution of antibodies taken from healthy donors. Intravenous means it's injected directly into a vein. Antibodies are proteins the immune system produces to fight disease-carrying organisms. Research has shown IVIG can reduce fever and the risk of heart problems.
Can I give my child aspirin?
This is one of the few occasions where aspirin may be recommended for a child under 16 years old. Never give your child aspirin, unless it's prescribed by a healthcare professional. It can cause side effects, including Reye's syndrome.
Does aspirin cause Reye's syndrome?
It can cause side effects, including Reye's syndrome. Aspirin is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It's used to treat Kawasaki disease because: it can ease pain and discomfort. it can help reduce a high temperature (fever) at high doses, aspirin is an anti-inflammatory (it reduces swelling)
Is aspirin a NSAID?
Aspirin is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It's used to treat Kawasaki disease because: The dose of aspirin your child is prescribed and how long they need to take it for depends on their symptoms. They'll probably be given high-dose aspirin until their fever subsides.
Does aspirin help with fever?
it can help reduce a high temperature (fever) at high doses, aspirin is an anti-inflammatory (it reduces swelling) at low doses, aspirin is an antiplatelet (it prevents blood clots forming) The dose of aspirin your child is prescribed and how long they need to take it for depends on their symptoms.
Can you take aspirin at 16?
Aspirin isn't usually given to children under the age of 16 because it can cause side effects, including Reye's syndrome. Reye's syndrome is rare, but it can cause serious liver and brain damage, and be fatal if not treated quickly. The symptoms of Reye's syndrome include persistent vomiting and a lack of energy.
Is Kawasaki disease contagious?
The disease is not contagious. The symptoms of Kawasaki disease often go away on their own, and the child recovers. Without medical evaluation and treatment however, serious complications may develop and not be initially recognized. Kawasaki disease more commonly affects children younger than 5 years old, with the majority ...
How to tell if a child has Kawasaki disease?
To determine if a child has Kawasaki disease, the doctor may order blood tests to look for: Recent strep or viral infection. Body’s immune response. Sometimes a urine sample is also collected.
How old is too old to get Kawasaki?
Kawasaki disease more commonly affects children younger than 5 years old, with the majority of children being less than 2 years old. Kawasaki disease, however, can affect older children as well.
What is the most common cause of heart disease in children?
Kawasaki disease is the leading cause of acquired heart disease in children. In as many as 25 percent of children with Kawasaki disease , the heart becomes affected without proper treatment. Aneurysms of the coronary arteries, the blood vessels that supply oxygen to the heart itself, are the most important complication of Kawasaki disease .
How long should I take aspirin for Kawasaki?
Children continue taking a low-dose aspirin every day for usually six to eight weeks or more. Your child will continue to be followed by a cardiologist after Kawasaki disease resolves. Parents are often concerned about using aspirin in children due to the concern over the link of aspirin use and Reye syndrome.
How often should a child go to the cardiology department for Kawasaki?
If after one year from the diagnosis of Kawasaki disease there is no heart involvement, your child’s cardiology visits are spaced out to annual visits or even every few years.
Can an aneurysm cause a heart attack?
Due to the vessel wall irregularity, a coronary artery aneurysm can become a site of blood clot. If a large enough blood clot forms, it can block the blood flow, and the heart tissue becomes deprived of needed oxygen, and in rare cases, could lead to a heart attack.
What are the risks of Kawasaki disease?
Other things can raise a child’s risk of Kawasaki disease, including: Age. It usually affects children who are 5 or younger. Sex. Boys are 1.5 times more likely to get it than girls. Ethnicity. Children of Asian descent are more likely to have Kawasaki disease.
Is Kawasaki disease contagious?
The disease probably isn’t contagious, but it sometimes happens in clusters in a community. Kids are more likely to get it in the winter and spring. Other things can raise a child’s risk of Kawasaki disease, including: Age. It usually affects children who are 5 or younger.
How long does it take for kawasaki to go away?
Symptoms tend to go away slowly in the third phase. It might last as long as 8 weeks. Call your doctor if your child has these symptoms, including a fever between 101 and 103 F that lasts more than 4 days.
How long does kawasaki last?
It might last as long as 8 weeks. Call your doctor if your child has these symptoms, including a fever between 101 and 103 F that lasts more than 4 days. Early treatment can help lower their risk of lasting effects. Kawasaki Disease Diagnosis. Your doctor will do a physical exam and ask about your child’s symptoms.
How to tell if a child has Kawasaki disease?
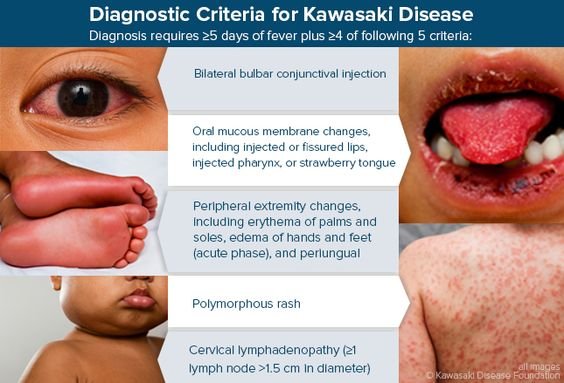
Early treatment can help lower their risk of lasting effects. Kawasaki Disease Diagnosis. Your doctor will do a physical exam and ask about your child’s symptoms. They’ll look for a long-lasting fever and at least four of these five signs: Red eyes. Red lips and mouth. Red, swollen limbs. Rash. Swollen lymph nodes.
Do children need surgery?
In severe cases, a child might need surgery . Infants have a higher risk of serious complications. In the U.S., fewer than 1% of children die during the early illness. After the early symptoms go away, follow up with your child’s doctor to be sure their heart is working the way it should.
Can an echocardiogram show a heart attack?
They could raise a child’s risk of artery blockages , which can cause internal bleeding and heart attacks. An echocardiogram can show many of these complications. In severe cases, a child might need surgery. Infants have a higher risk of serious complications.
What age can you get Kawasaki disease?
Kawasaki disease is a rare illness that most commonly affects children ages 0 to 5, but can sometimes affect children up to the age of 13. It is a type of vasculitis. Vasculitis means inflammation of the blood vessels. It can affect the whole body, including the blood vessels of the heart (coronary arteries).
What causes Kawasaki disease in children?
The cause of Kawasaki disease is unknown. Without treatment, affected children are at higher risk of developing problems with the coronary arteries. Other areas of the heart may also be affected. With timely treatment, most children recover with no lasting problems.
How long does kawasaki last?
What are the symptoms of Kawasaki disease? These are common symptoms of Kawasaki disease: Fever of 102.0° F to 104.0° F (38.8°C to 40.0°C) that lasts for at least 5 days. Red rash. A swollen lymph node, usually in the neck. Swollen hands and feet.
How long does a fever last in Kawasaki?
These are common symptoms of Kawasaki disease: Fever of 102.0° F to 104.0° F (38.8°C to 40.0°C) that lasts for at least 5 days. Red tongue with white spots (called “strawberry tongue”) The symptoms of Kawasaki disease can look like other health conditions.
How long does a child need to stay in the hospital?
Treatment typically starts as soon as the problem is suspected. Your child may need to stay in the hospital for a few days or longer.
Can you give a child aspirin?
Do not give your child aspirin without first talking with the child's healthcare provider. If your child develops heart problems, the provider may send you to a pediatric cardiologist. This is a doctor with special training to treat children’s heart problems. Your child may need medicine, procedures, or surgery.
What is EKG in medical terms?
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG). This test records the electrical activity of the heart through small, sticky patches on the child's chest. The patches are connected to a machine with wires. The machine records the electrical activity. This helps check for problems with heart rhythm and heart structure.
What are the complications of Kawasaki disease?
However, with effective treatment, only a few children have lasting damage. Heart complications include: Inflammation of blood vessels, usually the coronary arteries, that supply blood to the heart. Inflammation of the heart muscle.
Is Kawasaki disease contagious?
No one knows what causes Kawasaki disease, but scientists don't believe the disease is contagious from person to person. A number of theories link the disease to bacteria, viruses or other environmental factors, but none has been proved. Certain genes may make your child more likely to get Kawasaki disease.
What causes swelling in the walls of medium sized arteries?
Kawasaki disease causes swelling (inflammation) in the walls of medium-sized arteries throughout the body. It primarily affects children. The inflammation tends to affect the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle.
How long does it take for a symtom to go away?
In the third phase of the disease, signs and symptoms slowly go away unless complications develop. It may be as long as eight weeks before energy levels seem normal again.
How to know if your child has a fever?
If your child has a fever that lasts more than three days, contact your child's doctor. Also, see your child's doctor if your child has a fever along with four or more of the following signs and symptoms: Redness in both eyes. A very red, swollen tongue. Redness of the palms or soles.
How long does a fever last in a child?
If your child has a fever that lasts more than three days, contact your child's doctor. Also, see your child's doctor if your child has a fever along with four or more of the following signs and symptoms: Treating Kawasaki disease within 10 days of when it began may greatly reduce the chances of lasting damage.
Can an aneurysm cause a heart attack?
Inflammation of the coronary arteries can lead to weakening and bulging of the artery wall (aneurysm). Aneurysms increase the risk of blood clots, which could lead to a heart attack or cause life-threatening internal bleeding.
What is the Kawasaki disease?
Kawasaki disease (KD), also known as Kawasaki syndrome, is an acute febrile illness of unknown cause that primarily affects children younger than 5 years of age. The disease was first described in Japan by Tomisaku Kawasaki in 1967, and the first cases outside of Japan were reported in Hawaii in 1976. Clinical signs include fever, rash, swelling of ...
What is MIS C?
CDC is investigating reports of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) associated with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), which may present with Kawasaki disease-like features. Please visit the CDC MIS-C website for information for healthcare providers, parents, and to find out what CDC is doing to respond to MIS-C.
How to treat Kawasaki disease?
Kawasaki disease treatment. Treatment includes either aspirin or an infusion of an immune protein called gamma globulin through a vein, which can lower the risk of coronary artery problems, Krilov says. For coronavirus patients with the Kawasaki-like illness, the treatment shows promise.
What is strawberry tongue?
One of the symptoms of the disease is a swollen or bumpy tongue colloquially called strawberry tongue. “The tongue turns almost a beefy red, and the taste buds stick through it,” Krilov says.