Key Points to Remember
- Jaw deformities occur when one or both jaws grow too much or too little.
- Children with these conditions may have trouble speaking and chewing, and they sometimes develop long-term problems with the teeth and gums.
- The most effective treatment approach for jaw deformities is often a combination of surgery and braces or other orthodontic appliances.
What are the most common types of jaw deformities?
Jaw deformities are a common condition, ranging from mild abnormalities to more severe defects that can be surgically corrected. In some instances, the upper or lower jaw — or both — may grow too little or too much, resulting in malocclusion, the improper alignment of the teeth in relation to the first molars.
What causes a child to have a short lower jaw?
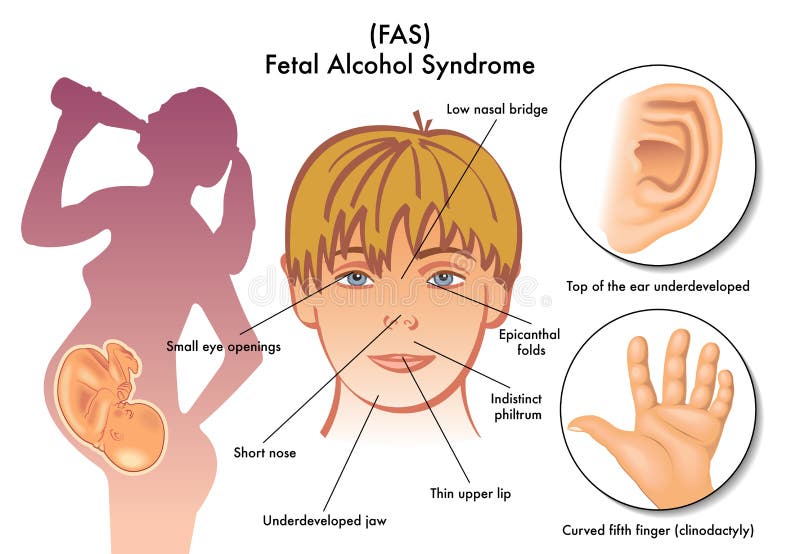
A child with micrognathia has a lower jaw that’s much shorter or smaller than the rest of their face. Children may be born with this problem, or it can develop later in life. It mainly occurs in children who are born with certain genetic conditions, such as trisomy 13 and progeria. It can also be the result of fetal alcohol syndrome.
What is jaw distraction surgery for breathing problems?
Jaw distraction surgery (mandibular distraction) A small or recessed jaw can cause severe or ongoing breathing difficulties. Jaw distraction involves the surgical insertion of distraction (lengthening) devices into the jaw. These devices lengthen the jaw bone, which allows the airway to open up and the child to breathe clearly.
Why does my child have a bump on his jaw?
Children may be born with this problem, or it can develop later in life. It mainly occurs in children who are born with certain genetic conditions, such as trisomy 13 and progeria. It can also be the result of fetal alcohol syndrome. In some cases, this problem goes away as the child’s jaw grows with age.

How do you fix jaw deformity?
Jaw Surgery In some severe cases, your dental professional may recommend orthognathic surgery of your jaw. This procedure involves adjusting or repositioning your upper or lower jaw and is often used in combination with orthodontic correction like braces.
What causes jaw abnormalities?
Some jaw deformities occur in utero and are present at birth, while others are acquired later in life. They originate from many causes: genetic abnormalities, deformations, intrauterine disruptions, diseases, injuries, or abnormal function.
Can an uneven jaw be fixed?
Uneven jaws can be fixed. Working together with a maxillofacial oral surgeon, your orthodontist will align your dental arches and teeth with braces or Invisalign to prepare you for orthognathic jaw surgery. Your uneven jaws will be repositioned and your smile, teeth, and bite form and function will be improved forever.
Can jaw deviation be fixed?
There are two major methods for the treatment of mandibular deviation: nonsurgical treatment (fixed and removable orthodontic appliances) and surgical treatment (orthopedic surgery and orthognathic surgery).
Are jaw deformities hereditary?
Besides growth differences between your upper and lower jaws, jaw deformities may be caused by genetic factors, trauma and certain birth defects, such as cleft lip and cleft palate.
What causes uneven jaw growth?
Summary. Uneven jaw occurs when the upper jaw, or maxilla, does not properly line up with the lower jaw, or mandible. This arises due to a range of factors, including misalignment of the teeth, disorders of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) connecting these bones, trauma, as well as birth defects.
Can I fix an uneven jaw without surgery?
TMJ issues can cause facial asymmetry with or without pain. Most often these issues for uneven jaws can be treated non-surgically. However, many orthodontist and Oral Surgeons may tell you the only way to fix this is to do orthognathic surgery.
Can jaw alignment be done without surgery?
Braces and clear aligners can fix an underbite. There are several non-surgical options for fixing an underbite. “For mild cases, a dentist may recommend metal braces or clear aligners to move teeth into the correct position. In some cases, a dentist may use a grinding device to shave down larger teeth,” Ataii says.
Can jaw asymmetry be fixed without surgery?
Fillers — By inserting a “soft filler” directly into the face via a small injection, it is possible to correct facial asymmetry. Such fillers often include Botox, which is popular to help raise the eyebrows or smooth the wrinkles on one side of the face.
What is jaw deviation?
Jaw-deviation dystonia is characterized by the lateral shift of the mandible due to involuntary masticatory muscle contraction, causing difficulties in speech or mastication.
What is jaw surgery called?
Jaw surgery, also known as orthognathic (or-thog-NATH-ik) surgery, corrects irregularities of the jaw bones and realigns the jaws and teeth to improve the way they work. Making these corrections may also improve your facial appearance.
How do you put your jaw back in place?
After wrapping their fingers with gauze, doctors or dentists place their thumbs inside the mouth on the lower back teeth. They place their other fingers around the bottom of the lower jaw. They press down on the back teeth and push the chin up until the jaw joints return to their normal location.
What is the procedure to fix a child's jaw?
This surgery, called orthognathic surgery, creates a cut or osteotomy in the affected jaw, and the bones are repositioned so that they align better. Generally, the bones are held in their new positions with plates, screws and wires. The child may also need arch bars, a type of temporary braces, placed on the teeth to hold the jaws together and add stability (a procedure called fixation). This procedure realigns the upper and lower jaws so that, when they are brought together, the child's bite is aligned.
What type of surgery is used to correct jaw deformities?
Another kind of surgery that can be done to correct jaw deformities is bone positioning by distraction ( separating). This surgery was originally developed for lengthening uneven limbs, but it has now been adapted to meet the needs of children with congenital or acquired skull and jaw deformities.
What Causes Jaw Deformities?
For reasons that are not well understood, a child’s upper or lower jaw may not grow and develop proportionately.
What is jaw surgery?
Jaw surgery is also used when the jaw is out of proportion to the rest of the face such as may occur in the following conditions: Cleft lip and palate. Treacher Collins syndrome. Hemifacial microsomia.
What is it called when your child's jaw is not aligned properly?
They can cause chewing and eating problems, abnormal speech and eventually lead to the early loss of the child’s teeth. When the upper and lower teeth do not meet properly, this condition is called malocclusion. Very often, an orthodontist is consulted, and if the child’s poor bite alignment is primarily due to dental issues, the orthodontist may recommend therapy to correct it.
What do you put on your teeth to hold your jaws together?
Generally, the bones are held in their new positions with plates, screws and wires. The child may also need arch bars, a type of temporary braces, placed on the teeth to hold the jaws together and add stability (a procedure called fixation).
Is distraction osteogenesis surgery safe?
Some plastic surgeons believe that distraction osteogenesis may be safer than other methods of reconstruction, since it may involve less blood loss.
What are the symptoms of jaw deformities?
Among the symptoms of jaw deformities, the first place is usually the dissatisfaction of the patient (and often - and the people around him) with the appearance of the face. Especially persistently express this complaint of the girl and the young man: they ask to eliminate the "disfigurement" of their person.
Why do my jaws deform?
In childhood and adolescence, as well as in adults, deformations of the jaws can occur under the influence of accidental trauma, coarse Scarring concretions, surgical intervention and pathological processes (osteomyelitis, ankylosis, nome, etc.). The latter can lead to excessive bone regeneration or, conversely, to resorption and its atrophy.
What causes anomalies and deformations of the jaws?
The causes of tooth-maxillofacial deformations are very diverse. Thus, the organo- and morphogenesis of the jaws in the fetus may be affected by the hereditary effect on the embryo, the parents borne diseases (including endocrine and metabolic disorders in the mother's body, infectious diseases ), radioactive irradiation, and also due to physiological and anatomical disorders of the genital organs of the mother and the wrong position of the fetus.
What are the causes of jaw growth?
In early childhood, the development of the jaws can be affected by endogenous factors (heredity, endocrine disorders, various infectious diseases, metabolic disorders) and exogenous effects (inflammation in the areas of jaw growth, trauma, including birth, radiation damage, mechanical pressure, harmful habits - sucking a finger, pacifiers, lower lip or putting a cam under the cheek during sleep, pushing the lower jaw forward during the eruption of wisdom teeth, while playing the children's violin and t etc., dysfunction of the masticatory apparatus, violation of the act of swallowing, nasal breathing, etc.).
What is the pathogenesis of the combined deformities of the bones of the face?
The pathogenesis of the combined deformities of the bones of the face is closely related to the impairment of the function of the synchondrosis of the base of the skull. Micro- and macrognathia are caused either by oppression or irritation of the growth zones, localized in the heads of the mandibular bone.
What causes unilateral underdevelopment of the lower jaw?
Quite often, the acquired unilateral underdevelopment of the lower jaw is caused by osteomyelitis, a purulent inflammation of the temporomandibular joint and mechanical damage to the condylar process in the first decade of the patient's life.
What is the second criterion for the presence of deformation of the jaw?
The second criterion for the presence of deformation of the jaw is a violation of chewing function and speech.
What are the causes of Pediatric Dentofacial Deformities ?
Pediatric dentofacial deformities can occur because of many different conditions, including:
What are some examples of jaw problems?
Problems can occur in primary teeth and permanent teeth. Facial asymmetries – Can cause problems with jaw development. Craniofacial microsomia, for example, occurs when one side of the face and skull develops smaller than the other side.
Why do my teeth grow over my jaw?
It can also result from facial paralysis. Excess gums – Some conditions can cause gums to grow over the teeth more than usual. Jaw disorders – Jaw disorders can cause “malocclusions,” or misalignment of the teeth, including: Underbite – Occurs when the lower jaw (mandible) sticks out farther than the upper jaw.
Why does my lower jaw stick out?
Underbite – Occurs when the lower jaw (mandible) sticks out farther than the upper jaw. This can be caused by a genetic condition, or it can be a symptom of other syndromes or conditions. Overbite – Occurs when the upper jaw grows too large, or the lower jaw doesn’t grow enough.
What causes crowded teeth in babies?
It can affect primary (baby) and permanent (adult) teeth. Apert syndrome and Crouzon syndrome – These syndromes occur when skull bones fuse too soon while the baby is developing in the womb, affecting the appearance of the face. Both can cause an underdeveloped jaw and crowded teeth.
What causes a child's face to look abnormal?
Congenital conditions can affect the appearance of a child’s face and teeth. Some abnormalities may be evident at birth, and some may not be noticeable until later.
Can a child have a cleft lip?
Cleft lip and palate – A child can have a cleft lip, cleft palate or both. A cleft palate occurs when the roof of the mouth doesn’t fuse completely as a baby is developing in the first trimester of pregnancy. A cleft lip occurs when the upper lip doesn’t completely join and leaves a gap.
Why is my baby's jaw so small?
Call your child’s doctor if your child’s jaw looks very small or if your baby is having trouble eating or feeding. Some of the genetic conditions that cause a small lower jaw are serious and need a diagnosis as soon as possible so that treatment can begin. Some cases of micrognathia may be diagnosed before birth with ultrasound.
What causes a baby's jaw to fall backwards?
Pierre Robin syndrome causes your baby’s jaw to form slowly in the womb, which results in a very small lower jaw. It also causes the baby’s tongue to fall backward into the throat, which can block the airways and make breathing difficult.
What are the treatment options for micrognathia?
Your child’s lower jaw may grow long enough on its own, especially during puberty. In this case, no treatment is necessary.
Why do children with progeria have a narrow face?
It’s due to a genetic mutation, but it’s not passed down through families. In addition to a small jaw, children with progeria may also have a slow growth rate, hair loss, and a very narrow face.
What is a child with a small jaw called?
Micrognathia, or mandibular hypoplasia, is a condition in which a child has a very small lower jaw. A child with micrognathia has a lower jaw that’s much shorter or smaller than the rest of their face.
How many babies are born with cleft palate?
These babies may also be born with an opening in the roof of their mouth (or cleft palate). It occurs in about 1 in 8,500 to 14,000 births.
How to treat a child's underlying condition?
Treatment methods can range from medications and close monitoring to major surgery and supportive care.
Why does my child need a jaw distraction?
This is mostly due to the tongue moving back into the throat when the child breathes in, blocking the airway. This is known as upper airway obstruction, and can cause serious disruption to breathing and feeding.
How long does a child need to stay in hospital after jaw surgery?
This involves another surgery, and your child will need to stay in hospital for another one or two nights.
What is jaw distraction?
Jaw distraction is the name for a surgical method of lengthening a small or recessed (hollow or indented) jaw. The medical term for jaw distraction is mandibular distraction osteogenesis ( man-dib-u-lar dis-track-shon osti-oh-jen-esis ). A small or recessed jaw can cause severe or ongoing breathing difficulties.
What is a small recessed jaw?
A small or recessed jaw can cause severe or ongoing breathing difficulties. Jaw distraction involves the surgical insertion of distraction (lengthening) devices into the jaw. These devices lengthen the jaw bone, which allows the airway to open up and the child to breathe clearly. This procedure is only used in cases of severe, ...
What to do if your child has an upper airway obstruction?
If your child has an upper airway obstruction, they will need to stay in hospital for a period of time so their breathing can be monitored and assessed. During this time, non-surgical methods of improving the airway obstruction will be tried, such as the insertion of a nasopharyngeal ( nay-zo-far-an-jeel ) tube (a tube down the nose that improves air flow to the breathing tubes and lungs).
How long does it take for a distractor arm to turn?
After surgery. The day after surgery, each distractor arm will be turned a full 360 degrees. This procedure is repeated every eight hours for about 10 days. During the eight hours between turns, your child's jawbone will grow to fill the space.
How long does it take to get a jaw surgery?
The surgery takes about two to three hours. An incision (cut) is made through the skin under the jaw line, and then the jaw bone is carefully separated so a distraction device can be attached to the bone. This happens on each side of the jaw.
When can a child extend their thumb?
It is usually seen in the thumb. It may take some time in the child's development before it is noted that the child can't extend the thumb. Some of these cases improve on their own. Surgery is usually not done until the second year of life, but preferably before the age of 3. ViewMedica 8.
What are congenital hand deformities?
Congenital anomalies are hand or finger deformities that are present at birth. Any type of deformity in a newborn can become a challenge for the child as he or she grows. Hand deformities can be particularly disabling as the child learns to interact with the environment through the use of his or her hands. The degree of deformity varies from a minor deformity, such as unequal or uneven fingers or thumb deformity, to a severe deformity, such as total absence of a bone.
What is the degree of deformity of a child's hand?
The degree of deformity varies from a minor deformity, such as unequal or uneven fingers or thumb deformity, to a severe deformity, such as total absence of a bone. Early consultation with a hand surgeon is an important part of the treatment process for the child born with a hand deformity.
What causes a child's hand to not separate?
Another example of failure of the hand to separate is seen in contractures of the hand. Contractures of the hand may also develop as a result of a problem with the cells in the womb. A contracture is an abnormal pulling forward of the fingers of the hand. It is usually caused by problems with the muscles or skin. One of the common types of this classification includes congenital triggering. Congenital triggering occurs when one of the fingers is unable to extend. It is usually seen in the thumb. It may take some time in the child's development before it is noted that the child can't extend the thumb. Some of these cases improve on their own. Surgery is usually not done until the second year of life, but preferably before the age of 3.
What is the congenital band syndrome?
Congenital constriction band syndrome. This occurs when a tissue band forms around a finger or arm, causing problems that can affect blood flow and normal growth. Ring constrictions are congenital (present at birth).
When to use prosthetics?
Prosthetics. These may be used when surgery is not an option, or in addition to surgical correction.
What is the term for the failure of parts of the hand to separate?
The most common type of this classification is syndactyly . Syndactyly is when 2 or more fingers are fused together.
How to reshaped a baby's ears?
It can be reshaped using ear molding, a treatment in which a custom-fit, soft plastic mold—in a “corrected” shape—is temporarily attached to the infant’s ear using adhesive strips and compounds. Over time, the ear conforms to this corrected shape. Ear molding works well in the treatment of protruding ears, Stahl’s ears, constricted ears, lop ears, and cryptotia. Usually this treatment takes between two and four weeks.
How long does it take to cure a congenital ear deformity?
Usually this treatment takes between two and four weeks. Surgical Treatment. Surgery may be an option for people whose congenital outer ear deformity cannot be or was not treated with ear molding. However, some ear deformities can only be addressed using surgical correction.
What is a congenital ear deformity?
The ear is made up of three main sections—the outer, middle, and inner ear. The outer ear represents the external, visible ear—called the auricle or pinna—and the external auditory canal. It is more complex than you might guess, containing many structures, curves, and folds—all of which work in concert to collect sound waves and direct them to the middle and inner ear, which work together with the brain to allow us to hear sound.
What are the types of outer ear congenital deformities?
There are many varieties of congenital deformities of the outer ear , including:
How are congenital ear deformities diagnosed?
Congenital deformities of the outer ear are typically diagnosed at birth during a physical exam. Your doctor will closely examine your baby to assess symmetry and proportionality, as well as to check for facial and jaw defects. They will also look into the ears using an otoscope, a device that allows for the visual examination of ear canal and tympanic membrane, or ear drum.
What causes ear deformities?
Because outer ear deformities are present from birth, a number of factors may contribute to their development: 1 Environment. Congenital ear deformities can occur when a developing baby is exposed to certain conditions in the uterus. Prenatal exposure to particular drugs, including isotretinoin (Accutane, for example), thalidomide, mycophenolate, and alcohol have been linked to the development of outer ear deformities. 2 Fetus positioning. In some cases, deformities arise due to how a baby is positioned in the uterus or during birth. For instance, a reduction in blood supply to the outer ear can lead to abnormal development.
How common are congenital deformities of the outer ear?
Congenital deformities of the outer ear—that is, deformities of the visible ear and ear canal that are present from birth—are common. Approximately 1 in every 6,000 newborns has an outer ear deformity. In general, treatments result in good outcomes, and if they are undertaken when your child is still young, they may help avoid social stigmatization altogether.
How old is a baby when it has a head deformity?
The outlook for babies with positional head deformity is excellent. Most deformities are self-corrected by the time the child is 1 year old. A persistent deformity can be corrected with reconstructive surgery between 12 and 18 months of age, but very few cases require this.
Why are premature babies more vulnerable to positional head deformities?
Premature babies are more vulnerable to positional head deformities because their skulls are softer than those of full-term babies and because their medical needs sometimes result in spending a great deal of time on their backs without being moved or picked up.
How to diagnose positional plagiocephaly?
A child’s physician usually makes a diagnosis of positional plagiocephaly simply by examining the child's head. The doctor will also note whether regular repositioning of your child's head during sleep successfully reshapes the growing skull over time. X-rays or a CT scan of may be necessary to confirm diagnosis or clarify if the skull bones are normally separated or if they fused together too soon. If the bones aren't fused, the doctor will rule out craniosynostosis and confirm that the child has positional head deformity.
Why is my baby's head flat?
Because infants' heads are soft to allow for the incredible brain growth that occurs in the first year of life, they're susceptible to being "molded" into a flat shape. Fortunately, positional plagiocephaly usually is easy to treat, and with appropriate intervention will correct itself by the time a child is 1 year old.
When to start wearing a helmet for a child with positional head deformity?
These work best if started between the ages of 4 and 6 months, when a child grows the fastest, and are usually less helpful after 10 months of age.
Why does my baby have a flat spot on the side of his head?
When a baby develops a flat spot, either in the back or on one side of the head, it could be a sign of a positional head deformity. Also referred to as positional plagiocephaly or flattened head syndrome, this can occur when a baby sleeps in the same position repeatedly or because of problems with the neck muscles (torticollis).
