
Table 6
| MORBIDITY | PATHOGENESIS/PATHOPHYSIOLOGY | PREVENTION/TREATMENT |
| Intrauterine fetal death | Usually result of Placental insufficienc ... | Needs regular antepartum and intrapartum ... |
| Neonatal Mortality | Antepartum, intrapartum and postpartum n ... | Tertiary level neonatal care |
| Perinatal/Neonatal Asphyxia | Chronic fetal hypoxia superadded with ac ... | Needs regular Antepartum and Intrapartum ... |
| Hypothermia | Poor thermoregulation mechanism Increase ... | Warm delivery room with temperature from ... |
How is intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) treated?
Treatment for intrauterine growth restriction depends on how far along the pregnancy is and how the baby is doing. Doctors will watch a baby with IUGR closely during prenatal visits. They'll do ultrasounds, keep track of growth, and watch for other problems. If the baby's mother has a condition, doctors will help her manage it.
How is IUGR diagnosed?
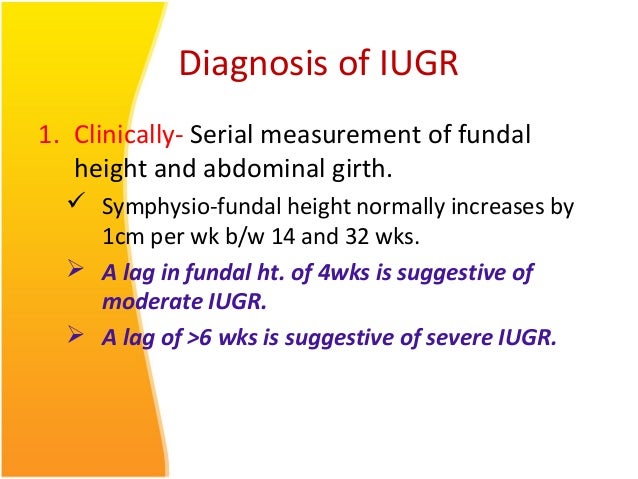
Watching growth is done in several ways. A measurement called the uterine fundal height helps estimate a baby's size by measuring a mother's belly from the top of the pubic bone to the top of the uterus. Another way is to use ultrasounds. In fact, IUGR is usually diagnosed through an ultrasound examination.
What is an example of an IUGR?
For example, some are healthy babies who are just born smaller than average because their parents are small in stature. The two types of IUGR are: Symmetrical IUGR, in which a baby's body is proportionally small (meaning all parts of the baby's body are similarly small in size).
What happens to babies with IUGR?
Babies with IUGR are more at risk for some kinds of health problems. Those born early or who are very small at birth are more likely to need to stay in the hospital for a longer time. They also might need special care in the neonatal intensive care unit (the NICU).
What is the best treatment for IUGR?
If the baby's mother has a condition, doctors will help her manage it. This might include making sure she eats a healthy and nutritious diet and gains the right amount of weight during her pregnancy. Some women might go on bed rest to try to improve blood flow to the baby.
Can a baby with IUGR survive?
Survival and longer term outcome of either SGA or IUGR infants born before 31 weeks is considerably poorer than that of AGA preterm infants. Data of IUGR infants born before 26 weeks show a very poor neonatal outcome and the same holds for the outcome at 2 years of age of infants born at 26 weeks.
Can IUGR be treated?
Sometimes a mother can take steps to improve the growth of her unborn baby, such as by stopping smoking or by eating more nutritious foods. In most cases, however, the mother is unable to affect the growth of the baby. Prenatal treatment for IUGR focuses, therefore, on close monitoring of the pregnancy.
How do I help my baby grow with IUGR?
You can do five important things to help your baby grow big enough before it's born:If you smoke—quit now. ... If you drink alcohol—quit now. ... If you use illegal drugs—quit now. ... Eat a good diet. ... Keep all your appointments for doctor visits and tests.
What causes IUGR baby?
IUGR has various causes. The most common cause is a problem in the placenta (the tissue that carries food and blood to the baby). Birth defects and genetic disorders can cause IUGR. If the mother has an infection, high blood pressure, is smoking, or drinking too much alcohol or abusing drugs, her baby might have IUGR.
How fast do IUGR babies gain weight?
The IUGR babies of mothers with toxaemia of pregnancy demonstrated a catch up growth for all three parameters. The IUGR babies of idiopathic group showed a spurt in weight gain around 3 to 6 months and a similar spurt for crown heel length and head circumference was observed between 6 to 9 months of age.
How serious is IUGR?
IUGR must be taken seriously because a fetus not growing normally could end up with serious health complications. IUGR can even lead to the baby's death either in the womb or shortly after birth.
How can I increase fetal weight?
0:454:03How to Increase Fetal Weight During Pregnancy - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou may eat almonds apricots figs walnuts and other nuts and dry fruits tip number three prenatalMoreYou may eat almonds apricots figs walnuts and other nuts and dry fruits tip number three prenatal vitamins prenatal vitamins help your baby gain weight.
Does bed rest help with IUGR?
Once IUGR is diagnosed, various treatments such as bed rest, increased or supplemental food intake to increase the baby's weight, and treatment of any medical condition, may be recommended. Bed rest may improve circulation to the baby in some cases, though evidence is weak.
Do all IUGR babies need NICU?
Treatment After Birth Treatment at birth varies depending on the cause of IUGR, including the presence of any associated birth defects or genetic conditions, and the gestational age at delivery. In severe cases, IUGR babies may require lengthy stays in the NICU and the highest level of respiratory support.
Do IUGR babies move less?
In the 25-36th week of gestation there was a significant decrease of FM rate in both groups of IUGR which was more pronounced in the symmetrical group. Also shown, was a gradual trend of increase of the FM rate with advancing gestational age in both groups of IUGR.
Can IUGR babies be delivered naturally?
THURSDAY, Feb. 4 (HealthDay News) -- Waiting for natural birth is as effective as inducing labor in pregnant women with intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), a new study shows.
What is IUGR in pregnancy?
Intrauterine growth restriction, or IUGR, is when a baby in the womb (a fetus) does not grow as expected. The baby is not as big as would be expected for the stage of the mother's pregnancy. This timing is known as an unborn baby's "gestational age.". The two types of IUGR are:
What tests are done to check for IUGR?
Doctors will also use ultrasounds to check the blood flow to the placenta and through the umbilical cord. If they think a baby has IUGR, doctors also might do such tests as: fetal monitoring to track the baby's heart rate and movements. screening the mother for infections that could affect the baby.
Why does IUGR happen?
Often, IUGR happens because the fetus doesn't get enough nutrients and nourishment. This can happen if there is a problem with: the placenta, the tissue that brings nutrients and oxygen to the developing baby. the blood flow in the umbilical cord, which connects the baby to the placenta. Intrauterine growth restriction also can happen ...
How to check if a baby has iugr?
Before babies are born, doctors check their growth by measuring the mother's belly from the top of the pubic bone to the top of the uterus. This is called the uterine fundal height. They also can do a prenatal ultrasound, which is how IUGR often is diagnosed.
What are the problems with intrauterine growth restriction?
Other problems that can be related to intrauterine growth restriction include: problems with breathing and feeding.
What do doctors do for a baby?
They'll do ultrasounds, keep track of growth, and watch for other problems. If the baby's mother has a condition, doctors will help her manage it. This might include making sure she eats a healthy and nutritious diet and gains the right amount of weight during her pregnancy.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of IUGR can be made before birth by ultrasound measurements that identify a fetus that is smaller than expected. Sometimes the diagnosis is made after birth when a newborn baby is smaller than expected. The baby’s expected growth depends on the height of the parents.
What causes IUGR?
The list of causes for IUGR is quite long, but the vast majority are due to one of the following:
Treatment Options
There are limited treatment options for IUGR. Currently all treatment options depend on the underlying cause of IUGR. If a mother has a poorly controlled chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes or hypertension, these conditions may be improved with help from her medical provider.
Surveillance and Delivery
Pregnancy surveillance of a fetus with IUGR is performed by ultrasounds assessing fetal growth, amniotic fluid, and blood flow in the fetus and umbilical cord.
What is IUGR in pregnancy?
The most common definition of Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR) is a fetal weight that is below the 10th percentile for gestational age as determined through an ultrasound. Intrauterine Growth Restriction is also known as Small-for-Gestational-Age (SGA) or fetal growth restriction.
What is a primary iugr?
There are basically two different types of IUGR: Symmetric or primary IUGR is characterized by all internal organs being reduced in size. Symmetric IUGR accounts for 20% to 25% of all cases of IUGR.
What are the risks of developing IUGR?
Pregnancies that have any of the following conditions may be at a greater risk at developing IUGR: Maternal weight less than 100 pounds. Poor nutrition during pregnancy. Birth defects or chromosomal abnormalities. Use of drugs, cigarettes, and/or alcohol. Pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH) Placental abnormalities.
How to determine gestational age?
Gestational age can be calculated by using the first day of your last menstrual period (LMP) and also by early ultrasound calculations. Once gestational age has been established, the following methods can be used to diagnose IUGR: A fundal height that does not coincide with gestational age.
What is IUGR in pregnancy?
Babies are diagnosed with intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) if they appear to be smaller than expected. This would happen if an ultrasound indicates that the baby's weight is below the 10th percentile for their gestational age (weeks of pregnancy). It's also called fetal growth restriction (FGR). There are lots of reasons why ...
What causes IUGR in a baby?
Other than having a small parent, here are the most common causes of IUGR: 1 Abnormalities in the umbilical cord or placenta, the organ that delivers oxygen and nutrients to your baby in the womb. The placenta may not be functioning properly if it's too small, improperly formed, or starting to detach from the uterus ( placental abruption ). A placenta that's too low in the uterus ( placenta previa) may slightly increase the risk of IUGR. 2 Medical conditions you may have, such as chronic hypertension or preeclampsia (particularly if the preeclampsia is severe and diagnosed in your second trimester or if you have both chronic hypertension and preeclampsia), kidney or heart disease, certain anemias (like sickle cell disease), advanced diabetes, blood clotting disorders, autoimmune disease, antiphospholipid antibody syndrome, or serious lung disease. 3 Chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome, or structural birth defects, such as anencephaly (in which part of the brain is missing) or defects in the kidneys or abdominal wall. 4 Carrying twins or higher order multiples. 5 Smoking, drinking, or abusing drugs. 6 Certain infections your baby may have gotten from you, such as toxoplasmosis , CMV , syphilis, or rubella. 7 Certain medications, such as some anticonvulsants. 8 Severe malnutrition.
What percentage of gestational age is IUGR?
If they're consistent and your baby is measuring less than the 10th percentile for gestational age, then your baby will be diagnosed with IUGR.
How do growth restricted babies do in the long run?
How a growth-restricted baby will do in the long run depends partly on what caused the growth problem in the first place. Most growth-restricted babies who are otherwise normal do eventually catch up with their peers, although some – particularly those born prematurely – have developmental problems.
Can bedrest be used for IUGR?
Some caregivers will prescribe bedrest, but there's no evidence that it helps. In fact, the American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology (ACOG) recommends against bedrest for IUGR, as it can cause harm—including blood clots, weakening of your bones, and even depression —without any benefit.
Can you deliver IUGR at term?
Timing of your delivery will depend on how you and your baby are doing. For otherwise uncomplicated IUGR, delivery is at term. But if your baby isn't doing well or you're very sick – with severe preeclampsia, for example – you may have to deliver early.
Is a baby with IUGR normal?
In many cases, a baby who's diagnosed with IUGR just happens to be small (perhaps like one of his parents). And sometimes , a baby who seems small in the womb turns out to be a normal size at birth. But in some cases, something is keeping the baby from growing properly, and the prenatal caregiver will try to figure out if there's a problem ...
What is IUGR in pregnancy?
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) is a common complication of pregnancy in developing countries, and carries an increased risk of perinatal mortality and morbidity. IUGR refers to a condition in which foetus (an unborn baby) is smaller or less developed than normal for the baby’s gender and gestational age.
What is considered IUGR?
At term, the birth weight less than 2,500 g (5lb, or 8oz) is considered as IUGR. Small for gestational age or fetal growth restriction are the other terms used for IUGR. The term intrauterine growth restriction has largely replaced the term intrauterine growth retardation. IUGR is classified into two types-.
How to tell if a baby has IUGR?
The main symptom of IUGR is a small for gestational age baby. During the antenatal checkup, a doctor measures the height of the uterus from the pubic bone to estimate the size of the fetus. After about the 20th week, uterine fundal height in centimeters is usually equal to the number of weeks of the pregnancy.
What causes iugr?
Symmetric or primary IUGR is due to genetic or chromosomal causes, early gestational intrauterine infections (TORCH) and maternal alcohol use. Asymmetric IUGR is more commonly due to extrinsic influences that affect the foetus later in gestation, such as preeclampsia, chronic hypertension, and uterine anomalies.
How to determine gestational age?
Gestational age can be calculated by using the first day of last menstrual period (LMP) and also by early ultrasound calculations. Once the gestational age is known the following methods can be used to diagnose IUGR. Fundal height: It is the simplest and most common method to diagnose IUGR.
Is asymmetric iugr normal?
Asymmetric or secondary IUGR: In this condition the head and brain are normal in size, but the abdomen is smaller. It is evident mostly in the 3 rd trimester. It is more common and found in 70% to 80% of total IUGR cases. Intrauterine growth restriction is observed in about 24% of newborns.

Diagnosis
- The diagnosis of IUGR can be made before birth by ultrasound measurements that identify a fetus that is smaller than expected. Sometimes the diagnosis is made after birth when a newborn baby is smaller than expected. The baby’s expected growth depends on the height of the parents. For example, short parents are expected to have a smaller baby than tall parents.
What Causes IUGR?
- The list of causes for IUGR is quite long, but the vast majority are due to one of the following: 1. Medical conditions affecting pregnancy, such as preeclampsia and pregnancy-induced hypertension 2. Chronic medical conditions in the mother, such as chronic kidney disease and chronic hypertension 3. A problem with the development of the placenta 4. Risky social habits, s…
Treatment Options
- There are limited treatment options for IUGR. Currently all treatment options depend on the underlying cause of IUGR. If a mother has a poorly controlled chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes or hypertension, these conditions may be improved with help from her medical provider. Cessation of substance abuse has been shown to be beneficial and...
Surveillance and Delivery
- Pregnancy surveillance of a fetus with IUGR is performed by ultrasounds assessing fetal growth, amniotic fluid, and blood flow in the fetus and umbilical cord. In the third trimester, generally after 30 weeks of pregnancy, additional surveillance of the fetus is often performed once or twice per week, but some mothers require hospitalization for twice daily surveillance. This additional surv…