Explore
Endocrine therapy (hormonal blockade): “Endocrine therapy is almost always part of the plan for treating lobular cancers,” Tran says. “Invasive lobular carcinomas are usually strongly estrogen receptor-positive, which makes them very responsive …
What are the treatments for papillary carcinoma?
Invasive lobular carcinoma is the second most common type of breast cancer. It usually grows because of estrogen. Treatments include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy and hormonal therapy. Invasive lobular carcinoma has a high survival rate when detected and treated early.
Is there a cure for metastatic adenocarcinoma?
Feb 04, 2022 · Treatments for invasive lobular carcinoma may include: Advertisement surgery : You and your doctor will work together to determine the type of surgery that’s right for you, based on the characteristics of the cancer, your family and medical history, and your preferences.
What is the treatment for intraductal papilloma?
Apr 19, 2022 · Although lobular breast cancer responds to hormone therapies, tumors can become resistant to treatment. Invasive lobular carcinoma has generally been treated like HR-positive invasive ductal carcinoma, but there are marked differences in how the two types of invasive carcinoma respond to hormone therapies.
Are there treatment options for hepatocellular carcinoma?
Invasive lobular carcinoma is known for being a slow growing tumor, usually grade I or II. Slow growing, grade I tumors don’t usually respond well to chemotherapy, so hormonal therapy is key for this type of cancer.

Is chemo needed for invasive lobular carcinoma?
Is invasive lobular breast cancer aggressive?
Where does invasive lobular carcinoma spread to?
Is lobular breast cancer serious?
If you've been diagnosed with LCIS — abnormal cells confined within breast lobules — your risk of developing invasive cancer in either breast is increased. LCIS isn't cancer, but is an indication of increased risk of breast cancer of any type.May 23, 2020
Should I have a mastectomy for LCIS?
Does lobular breast cancer respond chemo?
How long can you live with invasive lobular carcinoma?
Why are lobular cancers sneaky?
Which is worse lobular or ductal carcinoma?
Is lobular breast cancer more likely to recur?
What is the best type of breast cancer to have?
It occurs when cancer cells within the milk duct of the breast produce mucous, which also contains breast cancer cells. The cells and mucous combine to form a tumor. Pure mucinous ductal carcinoma tends to grow slowly, and has a better prognosis than some other types of IDCs.
What is Stage 2 lobular carcinoma?
What You Need to Know
Age increases the risk of invasive lobular carcinoma. According to the American Cancer Society, about two-thirds of women diagnosed with invasive lobular carcinoma are age 55 or older.
ILC Symptoms
Some invasive lobular carcinomas do not cause symptoms. In other cases, you might notice:
What is the difference between lobular carcinoma and lobular carcinoma?
What Is The Difference Between Invasive Lobular Carcinoma (ILC) and Lobular Carcinoma In Situ (LCIS)? LCIS means the cancer is still contained in the milk glands and has not invaded any other area. ILC is cancer that began growing in the lobules and is invading the surrounding tissue.
What is invasive breast cancer?
What Is Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer? Invasive breast cancer that begins in the lobules (milk glands) of the breast and spreads to surrounding normal tissue.
Is invasive lobular carcinoma the second most common type of breast cancer?
Invasive lobular breast cancer is the second most common type of breast cancer. Over 10% of invasive breast cancers are invasive lobular carcinomas. Though mammograms are helpful and important, they are less likely to detect invasive lobular breast cancer than other types of breast cancers. Invasive lobular cancer doesn’t always appear clearly on ...
Where does stage IV breast cancer go?
If it spreads to other organs, becoming Stage IV breast cancer, it typically goes to the colon, uterus, ovary, stomach, lung, bone, and other areas. Materials on this page courtesy of National Cancer Institute.
Is lobular carcinoma grade I or II?
It can be commonly identified as a higher stage cancer. Invasive lobular carcinoma is known for being a slow growing tumor, usually grade I or II. Slow growing, grade I tumors don’t usually respond well to chemotherapy, so hormonal therapy is key for this type of cancer.
Is lobular breast cancer HER2 or ER+?
Over 80% of the time, invasive lobular breast cancer is ER+ and HER2-. Sometimes invasive lobular breast cancer can be larger than it appears to be when reviewing a mammogram because of the way it grows. It can be commonly identified as a higher stage cancer.
What are the factors that increase the risk of invasive lobular carcinoma?
Factors that may increase your risk of invasive lobular carcinoma include: Being female. Women are more likely to develop breast cancer, but men also can develop breast cancer. Older age. Your risk of breast cancer increases as you age.
How does lobular carcinoma spread?
Doctors know that invasive lobular carcinoma begins when cells in one or more milk-producing glands of the breast develop mutations in their DNA. The mutations lead to the inability to control cell growth, which results in the cells dividing and growing rapidly. Depending on the aggressiveness of the cancer type, the cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body.
What tests are needed for breast cancer?
Your doctor will perform an examination and determine whether you need a diagnostic breast X-ray (mammogram) or a breast ultrasound. Ask your doctor when to begin screening tests for breast cancer to help detect cancer early and before you may have any signs or symptoms. Routine screening tests may include a physical exam and a mammogram.
What to do if you have a family history of breast cancer?
If you have a family history of breast cancer or feel you may have an increased risk of breast cancer, discuss it with your health care provider. Preventive medications, surgery and more-frequent screening may be options for women with a high risk of breast cancer. By Mayo Clinic Staff.
What does it mean when cancer is invasive?
Invasive cancer means the cancer cells have broken out of the lobule where they began and have the potential to spread to the lymph nodes and other areas of the body.
Is lobular carcinoma a lump?
Invasive lobular carcinoma is less likely than other forms of breast cancer to cause a firm or distinct breast lump.
Can lobular carcinoma cause dimpling?
At its earliest stages, invasive lobular carcinoma may cause no signs and symptoms. As it grows larger, invasive lobular carcinoma may cause: A change in the texture or appearance of the skin over the breast, such as dimpling or thickening. Invasive lobular carcinoma is less likely than other forms of breast cancer to cause a firm ...
Can lobular carcinoma be treated?
Optimal surgical treatment of invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast. Invasive lobular carcinoma can be safely treated with breast conservation with no difference in local recurrence or survival. In the absence of a suspicious finding on clinical or radiologic examination, routine contralateral breast intervention is not recommended.
Can lobular carcinoma be treated with breast conservation?
Invasive lobular carcinoma can be safely treated with breast conservation with no difference in local recurrence or survival. In the absence of a suspicious finding on clinical or radiologic examination, routine contralateral breast intervention is not recommended.
How long do you live with lobular carcinoma?
Invasive lobular carcinoma survival rates. Survival rates for cancer are typically calculated in terms of how many people live at least 5 years after their diagnosis. The average 5-year survival rate for breast cancer is 90 percent, and the 10-year survival rate is 83 percent. This is an average of all stages and grades.
What is lobular breast cancer?
Lobular breast cancer , also called invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC), occurs in the breast lobes, called lobules. Lobules are the areas of the breast that produce milk. ILC is the second most common type of breast cancer. ILC affects about 10 percent of people with invasive breast cancer. Most people with breast cancer have it in their ducts, ...
How to tell if ILC is a lump?
This thickening can be felt by touch, but it feels different from the classic lump associated with IDC, the more common breast cancer. Other symptoms of ILC may include: swelling or fullness in a part of the breast, or in the whole breast. a change in the skin texture in a part of the breast. dimpling in the breast.
How do ILC cells spread?
They spread through the breast tissue one by one, in line formation, sometimes branching out like the limbs of a tree. The cells tend to look alike, and they have small nuclei that resemble each other.
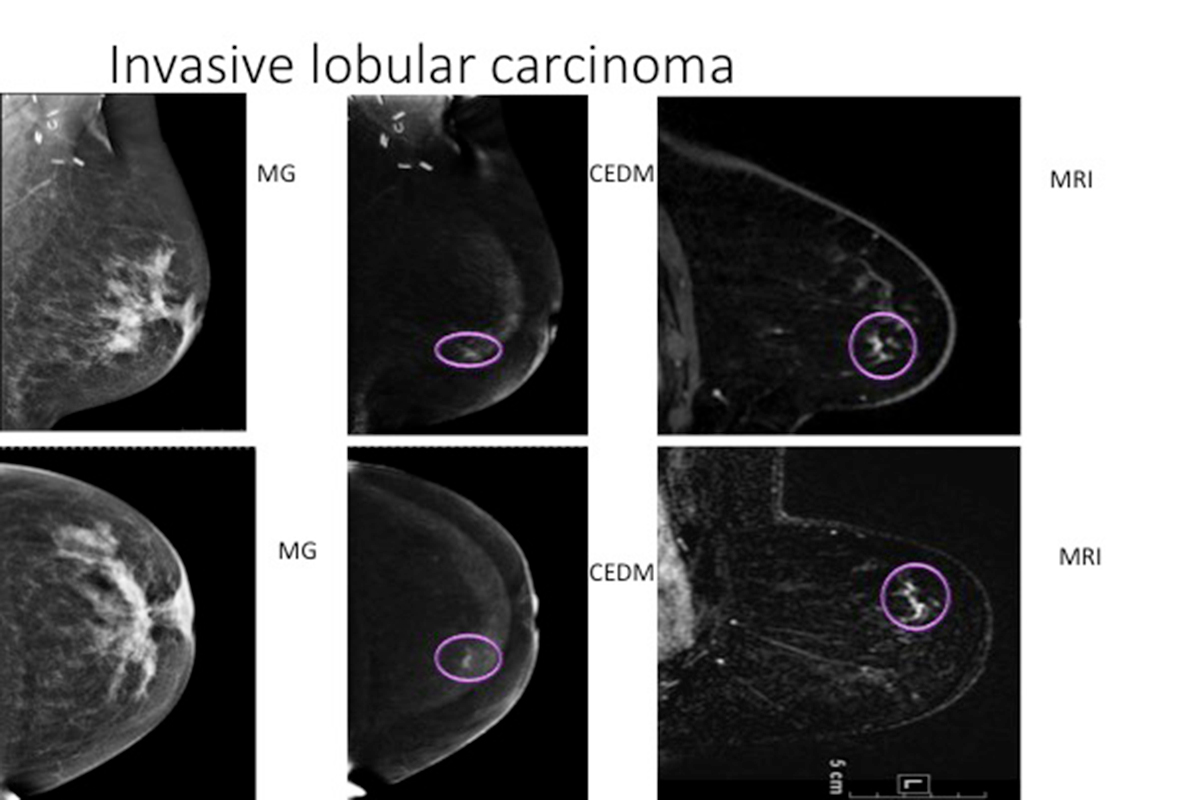
Why is it so hard to see ILC on a mammogram?
Spotting ILC on a mammogram can be difficult because the cancer cells spread in a line rather than in a distinctive lump, as in IDC. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) imaging is reported to provide more sensitive images that may show the cancer better.
What percentage of people with breast cancer have ILC?
ILC affects about 10 percent of people with invasive breast cancer. Most people with breast cancer have it in their ducts, which are the structures that carry milk. This type of cancer is called invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC).
Why is ILC so difficult to diagnose?
ILC can be more difficult to diagnose than other forms of breast cancer because it spreads in a unique pattern that’s not always noticeable in imaging tests. The good news is that it’s a relatively slow-growing cancer, which gives you time to form a treatment plan with your cancer team.
Is Invasive Lobular Carcinoma Aggressive
Over time, invasive lobular carcinoma can spread to the lymph nodes and possibly to other areas of the body. Although invasive lobular carcinoma can affect women at any age, it is more common as women grow older.
Whats New In Ilc Research
While there are challenges to lobular research â itâs a less common cancer so there are fewer sample sizes and cell lines â studies now underway may lead to answers about the cancerâs origins, changes to current treatment and potential therapies.
If Histological Features Of Lcis Are Grade 2 An Excisional Biopsy Is Necessary
Doctors grade;lobular carcinoma in situ on several pathologic features, including nuclear grade, necrosis, and pleomorphism.
When To See A Doctor
Make an appointment with your doctor if you have any signs or symptoms that worry you. Your doctor will perform an examination and determine whether you need a diagnostic breast X-ray or a breast ultrasound.
What If My Report Mentions Margins Or Ink
When an entire tumor is removed, the outside edges of the specimen are coated with ink, sometimes even with different colors of ink on different sides of the specimen. The pathologist looks at slides of the tumor under the microscope to see how close the cancer cells get to the ink .
Invasive Lobular Carcinoma Survival Rates
Survival rates for cancer are typically calculated in terms of how many people live at least 5 years after their diagnosis. The average 5-year survival rate for breast cancer is 90 percent, and the 10-year survival rate is 83 percent. This is an average of all stages and grades.
Patient Characteristics Between Ilc And Idc
The SEER tumor registry database was used to identify 1,097,908 patients diagnosed with ILC and IDC. After selecting patients based on specific inclusion and exclusion criteria, the remaining 318,406 patients were included in our research. Table 1 shows the patient selection process.
