
Differential Diagnosis of Kidney Diseases
| Normal echogenicity with normal or incre ... | Normal or increased echogenicity with in ... |
| Early diabetic nephropathy | Normal or increased echogenicity with in ... |
| GN | |
| Normal echogenicity with increased kidne ... | Vasculitis |
| Normal echogenicity with increased kidne ... | Tubulointerstitial disease ( e.g ., acut ... |
Full Answer
Does increased renal cortical echogenicity always indicate chronic kidney disease?
Apr 10, 2022 · While increased echogenicity is a subjective assessment, kidneys that are brighter than liver are considered to be echogenic. This becomes a potential indicator of fetal disease because of the association of this finding with chromosomal abnormality, adult and infantile polycystic kidney disease, Pearlman syndrome, Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome ...
What is echogenic kidney?
Sep 19, 2020 · Increased cortical echogenicity is a marker of renal disease that correlates to severity of interstitial histological changes in renal parenchymal disease [5]. Normally, the renal cortical echoes are lower in amplitude than either the …
What causes echogenicity to increase in fetal kidney disease?
Jun 28, 2018 · Echogenicity of kidneys means ability of various anatomical parts of kidney to generate echo signals on ultrasound examination. There is increased correlation between increased echogenicity of the...
What does slight increased echogenicity of renal pyramids bilaterally mean?
Dr. Michael Gabor answered. Diagnostic Radiology 34 years experience. "Slightly": increased echogenicity is a hedge. It means that the kidney tissue may be marginally brighter looking than normal on US. It could be normal.
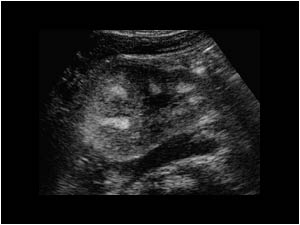
What does increased echogenicity of the kidney mean?
Increased echogenicity of the kidney parenchyma results from the increased presence of material that can reflect sound waves back, thus increasing its brightness on the ultrasonography image.Nov 14, 2013
Can echogenic kidneys be normal?
Echogenic kidneys can be a normal variant but are also seen in association with renal dysplasia, chromosomal abnormality, adult and fetal polycystic disease, Pearlman syndrome, Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome, and CMV infection. The incidence of echogenic kidneys has been estimated at 1.6 cases per 1000 sonograms.
Can dehydration cause echogenic kidneys?
Transient Hyperechoic Renal Cortex Caused by Dehydration and Induced Acute Renal Failure in Two Patients with Intra-Abdominal Infection. Increased renal cortical echogenicity can be seen in patients with various underlying renal abnormalities.
How is abnormal kidney function treated?
Treatment for end-stage kidney disease At that point, you need dialysis or a kidney transplant. Dialysis. Dialysis artificially removes waste products and extra fluid from your blood when your kidneys can no longer do this. In hemodialysis, a machine filters waste and excess fluids from your blood.Sep 3, 2021
What is increased echogenicity?
An echogenic liver is defined as increased echogenicity of the liver parenchyma compared with the renal cortex. The prevalence of echogenic liver is approximately 13% to 20%. In most clinical settings, increased liver echogenicity is simply attributed to hepatic steatosis.Sep 21, 2020
What causes echogenicity?
These are the causes of echogenic bowel: Fetal aneuploidy, especially Trisomy 21 and less frequently trisomy 18 or 13, Turner's syndrome and triploidy. The cause of echogenic bowel in aneuploidy is less clear. It is thought to be due to decreased bowel motility with increased water absorption from the meconium.
What is Grade 1 increased echogenicity?
Renal echogenicity was graded from 0 to 2 by comparing renal echogenicity to the adjacent liver echogenicity; grade 0: the renal echogenicity was less than that of the liver; grade 1: the renal echogenicity equaled that of the liver; grade 2: the renal echogenicity was greater than that of the liver (Fig.Oct 30, 2017
What does echogenicity mean in medical terms?
Medical Definition of echogenic : reflecting ultrasound waves the normal thyroid gland is uniformly echogenic— Catherine Cole-Beuglet.
What does normal echogenicity mean?
Normal liver echogenicity is homogeneous, with fine echoes. 1 One of the main causes of heterogeneous echogenicity of the liver is chronic liver disease/cirrhosis (Figure 1 of the supplementary material). Other common conditions leading to heterogeneous echogenicity are patchy steatosis and diffuse tumor infiltration.
What does term slightly increased cortical echogenicity of both kidneys means in an ultrasound test?
"Slightly": increased echogenicity is a hedge. It means that the kidney tissue may be marginally brighter looking than normal on US. It could be normal. Truly ... Read More
Can a high-protein ketogenic diet cause slightly increased bilateral echogenicity on a kidney ultrasound?
Not likely : If you use this diet, you have some medical problems required this kind of diet. Diet can not do this. You have to discus all this questions with you... Read More
Increased echogenicity of the pancreas?
Pancreas Lesion : A hyper echo genic lesion can represent a cyst or a tumor, as well as a localized area of scarring or inflammation. At your age, the lesion is more t... Read More
What causes increased echogenicity of the medullary pyramids?
Several things: Calcifications in the renal pyramids can cause increased echogenicity. This can be caused by abnormal calcium metabolism related to renal osteodystro... Read More
Slight increased echogenicity of the renal pyramids bilaterally?
Likely inflammation: Increased echogenicity of a tissue, usually indicates inflammation. It does not indicate why its there but its likely there. Given that the echogen... Read More
Diffuse increased echogenicity and coarsening of hepatic echotexture?
Non-Specific: These are not normal findings but they are non-specific. That is they do not give a "Diagnosis" Do you have an alcohol problem?? Have you ever had H... Read More
What does this mean? mixed echogenicity in right ovary, areas of increased echogenicity also some cystic changes but no abnormal vasclarity
Not cancer: The mixed echogenicity means a variety of densities of tissue and the cystic changes can be nothing more than normal follicles. The vascularity is imp... Read More
What is increased echogenicity?
Increased cortical echogenicity is commonly attributed to chronic kidney disease (CKD) and has been correlated with interstitial fibrosis, tubular atrophy, and glomerulosclerosis in histologic studies. However, increased echogenicity can also be seen in acute kidney injury (AKI) where inflammatory infiltrates and proteinaceous casts reflect sound ...
How thick is the kidney?
The normal pole-to-pole kidney length in adults is 10-12 cm, and varies with body size. Cortical thickness is measured from the base of the medullary pyramid to the outer margin of the kidney. It is generally around 7-11 mm, being thicker at the poles.
What is the normal length of a kidney?
The normal pole-to-pole kidney length in adults is 10-12 cm, and varies with body size.
