Intravascular volume expansion by RL infusion increased cardiac output, SV, and RVEDPTM and decreased HR and PVR. The results of this study indicate that volume loading may be the treatment of choice to restore cardiac output in the face of acute PHN. NE and NTG may be effective as an adjunct therapy.
What does cardiac output do if the heart rate decrease?
When your cardiac output is low, your adrenal glands also release more norepinephrine (adrenaline), which travels in the bloodstream and stimulates your heart to beat faster.
What causes increased cardiac output?
They include:
- Obesity
- Liver disease
- Anemia
- Hyperthyroidism
- Pregnancy
- Lung disease
- Septic shock
- Paget's disease
- Arteriovenous fistula
- Beriberi heart disease
Does decreased peripheral resistance increase cardiac output?
Neurogenic shock is from alterations in the autonomic nervous system that also results in decreased cardiac output and a decrease in SVR from a loss of the sympathetic innervation. Distributive shock reduces systemic vascular resistance from anaphylaxis or septic mediators, with an increase in cardiac output.
What are symptoms of low cardiac output?
Low-output symptoms, which are caused by the inability of the heart to generate enough cardiac output, leading to reduced blood flow to the brain and other vital organs. These symptoms may include lightheadedness, fatigue, and low urine output. If the cardiac output is very low, this can damage organs, particularly the kidneys.
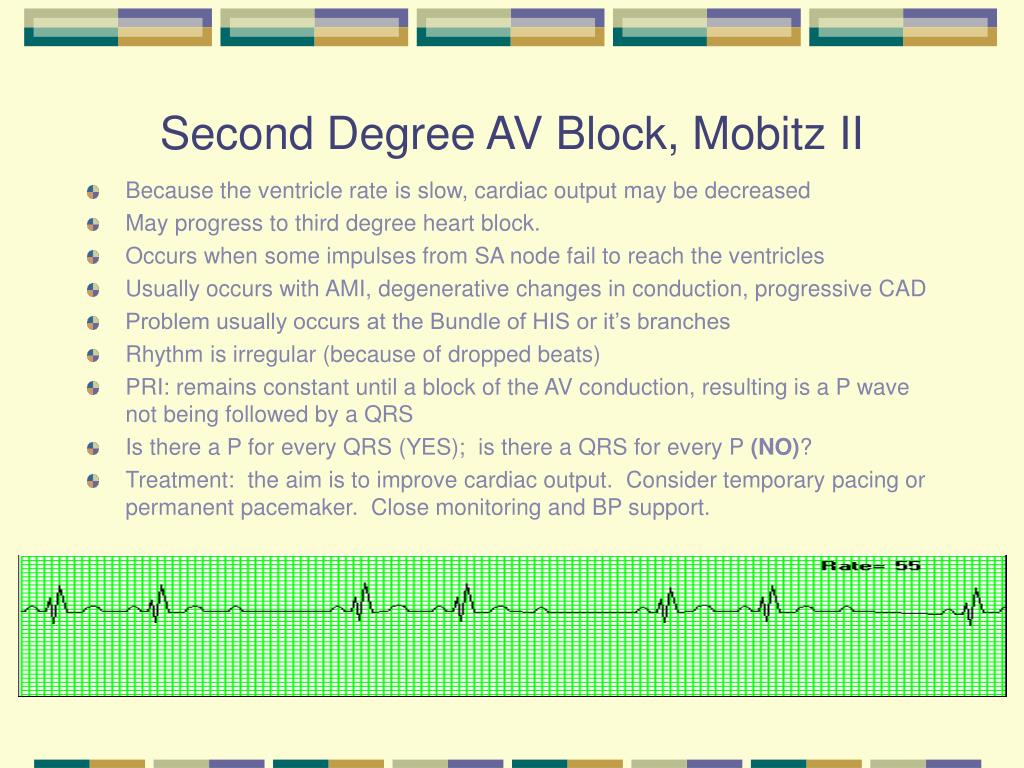
What happens if you have high cardiac output?
High Output. Sometimes, sepsis, your body's response to blood infections that can lead to a dangerous drop in blood pressure and organ failure, can cause high cardiac output. High output also can happen when your body lacks enough oxygen-carrying red blood cells, a condition called anemia.
How do you fix cardiac output?
Common nursing interventions for decreased cardiac output include:Provide supplemental oxygen (if needed)Monitor fluid intake, including IVs if necessary.Monitor the patient's heart rate.Monitor blood pressure.Record heart sounds.Record pulse.More items...•
What medication improves cardiac output?
Inotropic agents such as milrinone, digoxin, dopamine, and dobutamine are used to increase the force of cardiac contractions.
How is cardiac output controlled?
Cardiac output is controlled and affected by many different factors, including the atrial and ventricular reflexes, the autonomic nervous system, hormones, blood ion concentrations, and emotions.
What drugs decrease cardiac output?
Diuretics, beta-blockers, and central adrenergic inhibitors decrease cardiac output.
What causes increased cardiac output?
Cardiac output can be increased by a variety of signaling methods including enhancement of sympathetic tone, catecholamine secretion, and circulation of thyroid hormone.
Do ACE inhibitors decrease cardiac output?
Hemodynamic Effects ACE inhibitors decrease systemic vascular resistance but cause little change in heart rate. In normotensive and hypertensive subjects with normal left ventricular function, ACE inhibitors have little effect on cardiac output or pulmonary capillary wedge pressure.
What are the 5 types of diuretics?
Let's take a closer look at the classes of diuretics and how they work, and what nurses need to know.Loop Diuretics. ... Thiazides and Thiazide-Like Diuretics. ... Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors. ... Potassium-Sparing Diuretics. ... Osmotic Diuretics. ... Nursing Considerations.
Do beta-blockers reduce preload?
Beta-blocker therapy results in the improvement of the left ventricular systolic and diastolic function, reversal remodeling, heart rate control, effective prevention of the malignant arrhythmias, and lowering of the both cardiac afterload and preload in patients with chronic heart failure.
Does increased cardiac output increase BP?
Blood pressure increases with increased cardiac output, peripheral vascular resistance, volume of blood, viscosity of blood and rigidity of vessel walls. Blood pressure decreases with decreased cardiac output, peripheral vascular resistance, volume of blood, viscosity of blood and elasticity of vessel walls.
Which of the following is the main control of cardiac output?
Cardiac output is primarily controlled by the oxygen requirement of tissues in the body. In contrast to other pump systems, the heart is a demand pump that does not regulate its own output.
How does heart regulate cardiac output?
The body's demand for oxygen changes, such as during exercise, and the cardiac output is altered by modulating both heart rate (HR) and stroke volume (SV). As a result, the regulation of cardiac output is subject to a complex mechanism involving the autonomic nervous system, endocrine, and paracrine signaling pathways.
What tests show if you have an enlarged heart?
Electrocardiogram ( EKG ): This records the electrical activity of your heart. Chest X-ray: It will let your doctor know if you have an enlarged heart. It can also show congestion.
What is the test that measures the heart response?
Echocardiogram: This uses sound waves to make a video image of your heart. Exercise test: You may hear this called a stress test. It measures how your heart responds when it has to work hard. Heart catheterization: In this test, you get dye injected through a small tube into a blood vessel.
How to tell if you have heart failure?
To figure out if you have heart failure, your doctor will: 1 Examine you 2 Ask about your medical history 3 Run some tests
Is high output heart failure rare?
High-output heart failure is rare. It's also very different from other types of the disorder. Usually, if you have heart failure, your heart isn't pumping enough blood through your body to help it work the way it should. With the high-output version, it's pumping a normal amount of blood -- or even more than normal.
What is cardiac output?
Cardiac output is the amount of blood the heart pumps in 1 minute, and it is dependent on the heart rate, contractility, preload, and afterload. Understanding of the applicability and practical relevance of each of these four components is important when interpreting cardiac output values. In the present article, we use a simple analogy comparing ...
What are the four determinants of cardiac output?
Although most clinicians should/will be able to recite the four determinants of cardiac output – heart rate, contractility, preload, and afterload – understanding of the applicability and practical relevance of each of these four components is all too often less well ingrained. To try to clarify the individual roles and the combined roles ...
Why is afterload reduced in sepsis?
Because of the simultaneous tachycardia and reduced vascular tone, however, afterload is reduced – and cardiac output can therefore be maintained or even increased. In addition, the hyperkinetic state seen in sepsis is typically preceded by fluid therapy.
Is preload a component of cardiac output?
Venous return therefore equals cardiac output, whereas preload is only one component of cardiac output. Afterload. Afterload is the force against which the ventricles must act in order to eject blood, and is largely dependent on the arterial blood pressure and vascular tone.
Does preload increase cardiac output?
An increase in the distension of the ventricle will therefore result in an increase in the force of contraction, which will increase cardiac output. In our analogy, preload can be compared with a tailwind allowing the cyclist to move faster without any additional muscular effort.
Does pedal power reduce cardiac output?
Too little pedal power, or impaired contractility, will reduce cardiac output; however, too much effort will result in fatigue, sometimes leading to a complete collapse, with the need to slow down substantially or even to stop. This may occur with excessive inotropic support, resulting in increased mortality rates.
Does vasopressor affect cardiac output?
In contrast to the beneficial effects of vasodilator drugs, the administration of strong vasopressors may decrease cardiac output by increasing afterload, even in individuals with normal cardiac function. This effect is seen, for example, with phenylephrine, which has almost pure α-adrenergic effects.
What is the nursing care plan for decreased cardiac output?
The nursing care plan for decreased cardiac output will be tailored to each patient, and it may include monitoring the patient's heart rate, blood pressure, and fluid intake. The patient may also be recommended to make lifestyle changes such as reducing sodium intake and cutting back calories.
How to determine if a patient has decreased cardiac output?
In order to determine if a patient has decreased cardiac output, a medical professional may check the patient's pulse, monitor their heart rate, check their blood pressure, and listen to the heart with a stethoscope, among other assessments . The nursing care plan for decreased cardiac output will be tailored to each patient, ...
How much does cardiac output vary?
Normal cardiac output is typically between 4 and 8 liters per minute , and decreased cardiac output means the output is lower than 4 liters/minute. Cardiac output depends primarily on four factors: Preload: How much the ventricles stretch when the heart muscle relaxes and allows the chambers to fill with blood.
Why is cardiac output decreased?
Decreased cardiac output means that there is not enough blood being pumped and distributed by the heart to meet the needs of the body. This can be a serious problem because the body is not getting enough blood and oxygen to perform normal metabolic functions ...
What is cardiac output?
Cardiac output is the amount of blood that the heart pumps in one minute. It's the product of heart rate (the number of heartbeats per minute) and stroke volume (the amount of blood pumped per beat), and it's usually given in a value of liters/minute. Normal cardiac output is typically between 4 and 8 liters per minute, ...
What causes a decrease in cardiac output?
It can be caused by multiple factors, some of which include heart disease, congenital heart defects, and low blood pressure.
Can cardiac output be returned to normal?
For some people, their cardiac output can be returned to a normal, healthy level, while for others the issue is chronic and they will need to make lifestyle changes in order to manage their decreased cardiac output.