Procedures
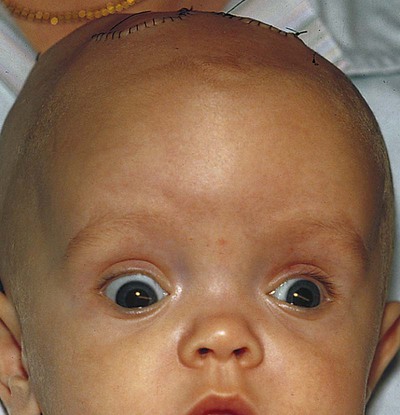
The most common treatment for hydrocephalus is a medical device called a shunt, a flexible tube, which is placed in the ventricular system of the brain that diverts the flow of CSF to another region of the body, most often the abdominal cavity, or heart, where it can be absorbed.
Self-care
Surgery is the only treatment option for hydrocephalus. Surgery outcomes have significantly improved combined with early intervention and advanced diagnostic protocols. Hydrocephalus is most commonly treated with a brain shunt. In some situations, a non-shunt treatment – an endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) – may be sufficient.
Nutrition
Both congenital and acquired hydrocephalus are treated with either shunt surgery or neuroendoscopy. Shunt surgery During shunt surgery, a thin tube called a shunt is implanted in your brain. The excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the brain flows through the shunt to another part of your body, usually your tummy.
Which medications are used in the treatment of hydrocephalus?
May 18, 2021 · In the presence of any of the signs or symptoms mentioned, it is necessary to seek urgent medical attention, to diagnose if you are in the presence of a case of hydrocephalus. Treatment may require surgery to drain excess fluid. Basically, we …
What causes death in untreated hydrocephalus?
Hydrocephalus can be treated in a variety of ways. The problem area may be treated directly (by removing the cause of CSF obstruction) or indirectly (by diverting the fluid to somewhere else, typically to another body cavity). Indirect treatment is performed by implanting a device known as a shunt to divert the excess CSF away from the brain.
What are the possible prevention of hydrocephalus?
Hydrocephalus can be treated in a variety of ways. Based on the underlying etiology, the condition may be treated directly by removing the cause of CSF obstruction or indirectly by diverting the excess fluid. Hydrocephalus is most commonly treated indirectly by implanting a device known as a “shunt” to divert the excess CSF away from the brain.
Is there a cure for acquired hydrocephalus?
Nov 15, 2021 · Hydrocephalus is treated with one of two surgical options: A shunt (tube) is surgically inserted into the brain and connected to a flexible tube placed under the skin to drain the... Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy (ETV) improves the flow of CSF out of the brain. A tiny hole is made at the bottom ...

What is the current treatment for hydrocephalus?
Shunts. The current standard treatment for hydrocephalus is the surgical implantation of a shunt. A shunt redirects cerebrospinal fluid to another part of the body. This lets the brain's enlarged ventricles return to a more normal size in an effort to relieve the symptoms of hydrocephalus.
Can hydrocephalus be treated without surgery?
There is currently no definitive cure. Most patients are managed by shunting using a silicone tube and valve system, where CSF is diverted from the cerebral ventricles to another body site [3].Feb 5, 2016
What is the survival rate of hydrocephalus?
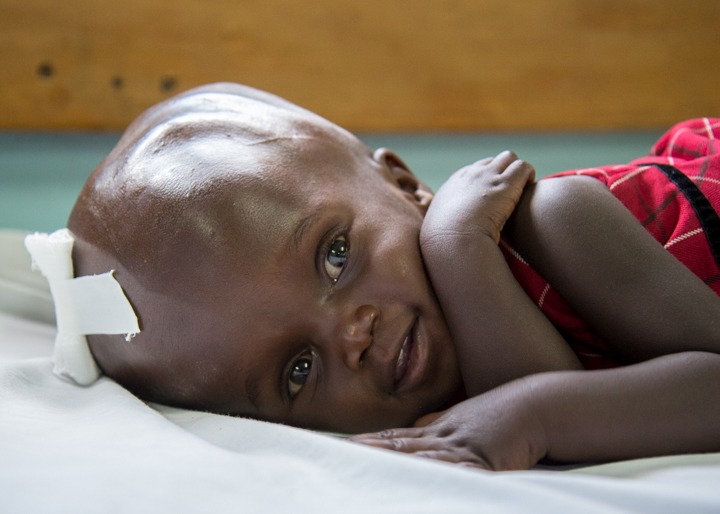
Survival in untreated hydrocephalus is poor. Approximately, 50% of the affected patients die before three years of age and approximately 80% die before reaching adulthood. Treatment markedly improves the outcome for hydrocephalus not associated with tumors, with 89% and 95% survival in two case studies.Oct 27, 2020
What is the main cause of hydrocephalus?
Hydrocephalus is caused by an imbalance between how much cerebrospinal fluid is produced and how much is absorbed into the bloodstream. Cerebrospinal fluid is produced by tissues lining the ventricles of the brain. It flows through the ventricles by way of interconnecting channels.Sep 3, 2021
Can hydrocephalus correct itself?
Hydrocephalus has no cure, but there are treatments that allow those affected to lead fairly normal lives with the condition. In some cases, it is possible for the blockage that is causing the fluid to build in the brain to be surgically removed.
Can hydrocephalus be treated with drugs?
There is little use for medication in hydrocephalus. In some acquired cases, as with tumors and infections, resolving the underlying condition will resolve the hydrocephalus, but most patients still require surgical intervention.Mar 20, 2013
How long can you live with a brain shunt?
The average lifespan of an infant's shunt is two years. Adults and children over the age of 2 may not need a shunt replacement for eight or more years. Shunt systems require frequent monitoring and follow-up.
Is fluid on the brain serious?
Hydrocephalus is a build-up of fluid in the brain. The excess fluid puts pressure on the brain, which can damage it. If left untreated, hydrocephalus can be fatal.
Can you live a normal life with a shunt?
Overview. Many people with normal pressure hydrocephalus enjoy a normal life with the help of a shunt. Regular, ongoing checkups with the neurosurgeon will help ensure that your shunt is working correctly, your progress is on track, and you are free to keep living the way you want.
What are 4 types of hydrocephalus?
The four types of hydrocephalus are communicating, noncommunicating, ex vacuo, and normal pressure. Diagnosis is typically made by physical examination and medical imaging. Hydrocephalus is typically treated by the surgical placement of a shunt system.
How do you detect hydrocephalus?
Diagnosis of Hydrocephalus A diagnosis is made by using brain imaging techniques such as ultrasonography, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and a thorough neurological evaluation during a doctor visit. More tests are often performed in adults in order to diagnose the condition.
What are the complications of hydrocephalus?
What are possible complications of hydrocephalus?Visual changes. Occlusion of posterior cerebral arteries secondary to downward transtentorial herniation. Chronic papilledema injuring the optic disc. Dilatation of the third ventricle with compression of optic chiasm.Cognitive dysfunction.Incontinence.Gait changes.
What is the most common treatment for hydrocephalus?
This surgical treatment is the most common and successful treatment option for those with hydrocephalus. Shunting, which began in the 1950’s, entails the placement of a tube (shunt) in one of the brain’s ventricles or into the space of fluid in the spine.
What is a shunt in hydrocephalus?
The choice of shunt depends on the type and blockage location that results in the hydrocephalus. Most patients undergo shunt placements, including the following types: 1 Ventriculo-peritoneal (VP) shunt#N#This is the most common treatment, which shifts fluid from the brain into the peritoneal cavity (a fluid-filled gap between the walls of the abdomen and the organs in the abdomen). 2 Ventriculo-pleural (VPL) shunt#N#Shifts fluid from the brain into the pleural cavity (space between the two pleura of the lungs) 3 Ventriculo-atrial (VA) shunt or “vascular shunt”#N#Shifts fluid from the brain to the right atrium of the heart
Where does fluid go in the brain?
This is the most common treatment, which shifts fluid from the brain into the peritoneal cavity (a fluid-filled gap between the walls of the abdomen and the organs in the abdomen).
What is ETV treatment?
ETV is a minimally invasive treatment option for hydrocephalus, without involving a shunt. The neurosurgeons at ANA are adept at this procedure, relevant for patients for whom the condition follows certain criteria.
What happens if you don't treat hydrocephalus?
If hydrocephalus is not treated, the increase in pressure will cause brain damage.
What is the procedure called when you have a shunt?
Endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) An alternative procedure to shunt surgery is an endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV). Instead of inserting a shunt, the surgeon makes a hole in the floor of your brain to allow the trapped cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to escape to the brain's surface, where it can be absorbed.
What is the tube called that is implanted in the brain?
During shunt surgery, a thin tube called a shunt is implanted in your brain. The excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the brain flows through the shunt to another part of your body, usually your tummy. From here, it's absorbed into your blood.
How long does it take to recover from a shunt?
Shunt surgery is done by a specialist in brain and nervous system surgery (neurosurgeon). It's done under a general anaesthetic and usually takes 1 to 2 hours. You may need to stay in hospital for a few days after the operation to recover.
How is ETV done?
ETV is done under general anaesthetic. The neurosurgeon makes a small hole in your skull and brain, and uses an endoscope to look inside the chambers of your brain. An endoscope is a long, thin tube with a light and camera at one end.
What is the success rate of hydrocephalus?
The success rate varies from 25 to 74 percent for NPH cases in which its cause is unknown. In general, the earlier hydrocephalus is diagnosed, the better the chance for successful treatment. The longer the symptoms have been present, the less likely it is that treatment will be successful.
What is the meaning of hydrocephalus?
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds up within the ventricles (fluid-containing cavities) of the brain and may increase pressure within the head.
How old do you have to be to get hydrocephalus?
Hydrocephalus can occur at any age, but is most common in infants and adults age 60 and older. It affects adult males and females, as well as people of different races, about equally.
What is the water on the brain called?
Although hydrocephalus often is described as "water on the brain," the "water" is actually CSF — a clear fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord. CSF has three crucial functions: It acts as a "shock absorber" for the brain and spinal cord; It acts as a vehicle for delivering nutrients to the brain and removing waste; and.
What is the cause of hydrocephalus ex-vacuo?
Hydrocephalus ex-vacuo occurs when a stroke or injury damages the brain and brain matter actually shrinks. The brain may shrink in older patients or those with Alzheimer's disease, and CSF volume increases to fill the extra space. In these instances, the ventricles are enlarged, but the pressure usually is normal.
What causes pressure hydrocephalus?
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus results from the gradual blockage of the CSF-draining pathways in the brain. The ventricles enlarge to handle the increased volume of CSF, thus compressing the brain from within and eventually damaging or destroying the brain tissue.
How often do you need to urinate?
Urinary frequency is the need to urinate more than usual, often as frequently as every one to two hours.
What is acquired hydrocephalus?
Acquired Hydrocephalus: This is the type of hydrocephalus that develops at birth or in adulthood and is typically caused by injury or disease. Congenital Hydrocephalus: It is present at birth and may be caused by events that occur during fetal development or as a result of genetic abnormalities.
How do you know if you have hydrocephalus?
The symptoms of hydrocephalus tend to vary greatly from person to person and across different age groups. Infants and young children are more susceptible to symptoms from increased intracranial pressure like vomiting and adults can experience loss of function like walking or thinking.
How common is hydrocephalus in children?
According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), hydrocephalus is believed to affect approximately one to two in every 1,000 children born in the U.S.
What causes a brain to shrink?
Hydrocephalus Ex-vacuo: It primarily affects adults and occurs when a degenerative disease, like Alzheimer’s disease, stroke or trauma, causes damage to the brain that may cause the brain tissue to shrink.
Can pressure hydrocephalus be reversed?
In some instances of normal pressure hydrocephalus, dementia can be reversed by shunt placement. Other symptoms, such as headaches, may disappear almost immediately if the symptoms are related to elevated pressure.
What are the symptoms of a shunt malfunction?
A shunt malfunction may be indicated by headaches, vision problems, irritability, fatigue, personality change, loss of coordination, difficulty in waking up or staying awake, a return of walking difficulties, mild dementia or incontinence.
Can hydrocephalus be inherited?
Some cases of hydrocephalus are present at birth, while others develop in childhood or adulthood. Hydrocephalus can be inherited genetically, may be associated with developmental disorders, like spina bifida or encephalocele, or occur as a result of brain tumors, head injuries, hemorrhage or diseases such as meningitis.
What are the two types of hydrocephalus?
The two major types of hydrocephalus are called communicating hydrocephalus and non-communicating hydrocephalus. Communicating hydrocephalus occurs when the flow of CSF is blocked after it exits the ventricles. This form is called communicating because the CSF can still flow between the ventricles, the passages between which remain open.
What is non-communicating hydrocephalus?
Non-communicating hydrocephalus happens when the flow of CSF is blocked along one or more of the narrow passages connecting the ventricles. Two additional types of hydrocephalus include: Hydrocephalus ex-vacuo results from brain damage caused by stroke or injury.
Why do babies get hydrocephalus?
In these cases, hydrocephalus may be caused by: inherited genetic abnormalities that block the flow of CSF. developmental disorders such as those associated with birth defects in the brain, spine, or spinal cord.
What is the difference between CSF and hydrocephalus?
What is hydrocephalus? Hydrocephalus is an abnormal buildup of fluid in the ventricles (cavities) deep within the brain. This excess fluid causes the ventricles to widen, putting pressure on the brain’s tissues. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is the clear, colorless fluid that protects and cushions the brain and spine.
Is hydrocephalus a congenital condition?
Hydrocephalus may be present at birth (congenital) or may develop over time as a result of injury or disease (acquired). Except for hydrocephalus secondary to physical obstruction of CSF passages within the brain or skull by blood or tumor, the exact causes of hydrocephalus are still not well understood.
Can hydrocephalus be fatal?
If left untreated, hydrocephalus can be fatal. Early diagnosis and successful treatment improve the chance for a good recovery. With the benefits of surgery, rehabilitative therapies, and educational interventions, many people with hydrocephalus live relatively normal lives.
Is hydrocephalus a developmental disorder?
Hydrocephalus is a relatively common developmental abnormality, but its underlying mechanisms are not well understood. NINDS supports a wide range of studies that explore the complex mechanisms of normal and abnormal brain development.