
What are thyroid antibodies and what do they indicate?
| Antibodies | What do they indicate? |
| Thyroid peroxidase antibodies (TPOAb) | Raised in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (or au ... |
| Thyroglobulin antibodies (Tg Ab) – antib ... | May be measured as part of the monitorin ... |
| Thyroid stimulating hormone receptor ant ... | Raised in Graves’ disease |
| Thyroid Stimulating Immunoglobulin (TSI) ... | May be raised in Graves’ disease. This i ... |
How do you lower your thyroid antibodies?
What May Help Lower Thyroid Antibodies?
- Vitamin D. Those prone to thyroid disease are more apt to be deficient in vitamin D than those who are not. ...
- Sleep Apnea. Is your sleep unrefreshing? ...
- Thyroid Medication (If You Need It) If you are already taking thyroid medication, don’t think that stopping it will lower your antibodies.
- Natural Desiccated Thyroid. ...
- Food Categories. ...
Why are my thyroid antibodies still high?
The first reason why your thyroid antibodies can still be high is that you’re still consuming “trigger foods” that cause an immune system reaction in your body. These include: Gluten-containing grains (barley, wheat, and rye) Corn; Dairy products; Eggs; Legumes; Pseudo grains, like quinoa and buckwheat, can still cause a reaction
What does it mean when your thyroid antibodies are high?
The test checks the levels of:
- thyroid-stimulating hormone a hormone produced by the pituitary gland which controls the production of thyroid hormones
- triiodothyronine one of the main thyroid hormones
- thyroxine another of the main thyroid hormones
What are healthy levels for thyroid antibodies?
These antibodies may target:
- Thyroid peroxidase (TPO). This can lead to Hashimoto thyroiditis. This is an autoimmune disorder that causes an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism).
- Thyroglobulin (Tg). This substance in the thyroid plays a role in T3 and T4 production. ...
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) receptor. This can cause Graves disease. ...
See more

How can I lower my thyroid antibodies?
Vitamin D supplementation reduces thyroid peroxidase antibody levels in patients with autoimmune thyroid disease: An open-labeled randomized controlled trial.
Should high thyroid antibodies be treated?
In people under the age of 65 whose TSH falls in this range, treatment with levothyroxine may be helpful if they have symptoms of hypothyroidism, an enlarged thyroid (goiter),14 and/or high levels of TPO antibodies. Treatment usually isn't necessary for those who are 65 years or older.
What happens if thyroid antibodies are high?
In general, the presence of thyroid antibodies suggests the presence of an autoimmune thyroid disorder and the higher the level, the more likely that is. Levels of autoantibody that rise over time may be more significant than stable levels as they may indicate an increase in autoimmune disease activity.
How is high TPO antibodies treated?
The American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists recommends levothyroxine therapy for patients with TSH levels higher than 10 μIU per mL, positive anti-TPO antibodies, or goiter; the recommended starting dose of 25 to 50 mcg daily must be adjusted as necessary after repeating the TSH level in six to eight weeks.
Do thyroid antibodies go away?
Is it possible for thyroid antibodies to go away? It is possible. In Graves' disease patients, antithyroid medication, radioactive iodine (RAI) and surgery all aim to restore the thyroid function to normal.
Does levothyroxine reduce thyroid antibodies?
In our study, a negative correlation between antibody titers and the duration of the disease also suggests that the titer of antibody decreases over time, either with levothyroxine effect or independently of the drug.
What causes elevated thyroid antibodies?
It can be caused by several conditions, including Hashimoto's disease or Graves' disease. Autoimmune disease, like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis. These and other disorders may raise your chance of having a thyroid problem.
Why do I have thyroid antibodies?
The presence of TPO antibodies in your blood suggests that the cause of thyroid disease is an autoimmune disorder, such as Hashimoto's disease or Graves' disease. In autoimmune disorders, your immune system makes antibodies that mistakenly attack normal tissue.
What does it mean when you have antibodies in your thyroid?
Antibody tests are useful in finding the cause of your thyroid disease. They can also help identify subclinical thyroid disease, which is thyroid disease with mild or no symptoms. Positive thyroid antibodies suggest you could have autoimmune thyroid disease.
How do I get rid of TPO antibodies?
Studies show that taking 200 mcg of selenium per day may help reduce antithyroid peroxidase (TPO) antibodies and improve well-being in people with Hashimoto's thyroiditis ( 24 ). Zinc. Zinc is essential for thyroid function.
How high is too high for TPO antibodies?
Anti-Thyroperoxidase Antibody Levels >500 IU/ml Indicate a Moderately Increased Risk for Developing Hypothyroidism in Autoimmune Thyroiditis.
What are the symptoms of high TPO antibodies?
It occurs when your body makes antibodies that attack the cells in your thyroid. Symptoms may include an enlarged thyroid gland (goiter), tiredness, weight gain, and muscle weakness. You don't need treatment if your thyroid hormone levels are normal.
How to get rid of hashimoto?
Try starting a gluten free & antiinflammatory diet. Also walk for 1 hour everyday or any cardio you enjoy but do it every single day . I lost weight and all my symptoms disappeared. I have hashimoto and had ibs and reflux plus brain fog fatigue now I have tons of energy feel great !
What is the recommended TSH range?
Since many labs are using outdated TSH ranges (the "new" recommended range is 0.3-3.0), and many doctors are diagnosing/treating, based solely on TSH, many people are being left undiagnosed. If your doctor is testing only TSH or reacting to TSH levels, you need to find another one, because yours will keep you ill.
What to do if you have hyperthyroidism?
If you've been diagnosed with hyperthyroidism, the most important thing is to receive the necessary medical care. After you and your doctor have decided on a course of action, there are some things you can do that will help you cope with the condition and support your body during its healing process.
How to test thyroid?
During this test, you'll have a radioactive isotope injected into the vein on the inside of your elbow or sometimes into a vein in your hand. You then lie on a table with your head stretched backward while a special camera produces an image of your thyroid gland on a computer screen. This test shows how iodine collects in your thyroid.
Why is radioiodine high?
A high uptake of radioiodine indicates your thyroid gland is producing too much thyroxine. The most likely cause is either Graves' disease or hyperfunctioning thyroid nodules. If you have hyperthyroidism and your radioiodine uptake is low, this indicates that the thyroxine stored in the gland is leaking into the bloodstream, which may mean you have thyroiditis.
Why is TSH important?
The amount of TSH is important because it's the hormone that signals your thyroid gland to produce more thyroxine. These tests are particularly necessary for older adults, who may not have classic symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
What test can you take to check if you have hyperthyroidism?
If blood tests indicate hyperthyroidism, your doctor may recommend one of the following tests to help determine why your thyroid is overactive: Radioiodine uptake test. For this test, you take a small, oral dose of radioactive iodine (radioiodine) to see how much will collect in your thyroid gland.
How to diagnose hyperthyroidism?
Diagnosis. Hyperthyroidism is diagnosed using: Medical history and physical exam. During the exam your doctor may try to detect a slight tremor in your fingers when they're extended, overactive reflexes, eye changes and warm, moist skin. Your doctor will also examine your thyroid gland as you swallow to see if it's enlarged, ...
How long does it take for iodine to disappear?
Symptoms usually subside within several months. Excess radioactive iodine disappears from the body in weeks to months.
Why does thyroid go down?
Thyroid levels go up and they go down in response to the daily triggers and stressors in your life. Your blood work is just a tiny snapshot- a moment in time if you will of what’s happening in your body. Try to keep this in perspective.
Does medication address the immune system?
The answer is IT CANT! – So again medication doesn’t address the Immune system. If you have time, You can check out a video that I did tiled “10 steps to naturally supporting your Thyroid” or here
Can you test for all toxins?
There are so many toxins we’re exposed to, and it’s impossible to not only test for all of them but to understand how each individual reacts to the specific toxin. Two patients being exposed to the same toxins can have a very different response. This is why in my practice, I rely very heavily on testing. Where some Holistic practitioners only look at hormones or the adrenal glands, these areas may not be the primary triggers. They might be secondary or Tertiary problems. Contributing triggers but just not the MAIN ones.
Does Hashimoto's thyroid cause thyroid to shut down?
This indicates that the immune system is destroying the enzyme or the proteins in your body needed to make thyroid hormones and ultimately, if you do what traditional medicine offers- which is just thy roid replacement hormones, your thyroid will slowly but surely burn out and shut down at some point in your life.
Can a leaky gut cause thyroid disease?
A leaky gut can be a major trigger into the development of not only Autoimmune thyroid disease but also Neuroautoimmunity-This is where the immune system begins to attack the neurological tissue ( the spinal cord, the brain, neurotransmitters, nerve synapses, etc) This is where you start seeing the connection between. 1.
Why isn't the thyroid antibody test ordered?
The main reason why the test for thyroid antibodies is not ordered as often as it should be lies in the treatment approach to hypothyroidism. According to conventional medicine, euthyroid Hashimoto’s patients (those who have normal thyroid function) do not require any treatment and most practitioners take a “wait and watch” approach.
Why don't doctors test for thyroid antibodies?
Most doctors do not research why the person became hypothyroid and don’t test for thyroid antibodies because the conventional treatment approach to hypothyroidism remains the same regardless of its cause.
How much is the discount code for thyroid testing?
If it’s something you need and are willing to do, the lab I recommend for thyroid and autoimmune testing is offering 20% off on all lab testing. You just need to use the discount code DISEASE20 at the check out.
What happens if you have TPO antibodies during pregnancy?
Exposure to maternal TPO thyroid antibodies during the third trimester of pregnancy is associated with impaired auditory and hearing development in the child and can also result in hearing loss.
How many women have elevated TPO?
One study estimated that up to 12.5% of women can have elevated TPO thyroid antibodies during the first two trimesters of pregnancy and it can negatively affect development of the fetus and child.
What is the treatment for Hashimoto's disease?
Only when Hashimoto’s disease progresses to hypothyroidism, thyroid hormone replacement therapy is prescribed. The main goal of treatment is to compensate for missing thyroid hormones and manage hypothyroid symptoms.
Why is gliadin a protein?
The reason for this wide spectrum of organs involved is the molecular structure of gliadin which is a protein contained in gluten. For example, gliadin has structure that is close to proteins found in the thyroid gland and also can cross react with thyroid antigens making the thyroid as a target for an autoimmune attack when gluten containing foods are consumed .
What is the abbreviation for thyroid antibodies?
Still, this article will look specifically at thyroglobulin antibodies, known by its abbreviation TgAB or anti-Tg.
How to test for autoimmune thyroiditis?
The most common way to check for autoimmune thyroiditis is to test for the presence of thyroperoxidase antibodies ( TPO antibodies, sometimes known as anti-TPO). Like TgAB, your immune system also creates TPO antibodies to attack your thyroid gland.
What is the T4 hormone?
Thyroxine (T4) is the primary hormone produced by the thyroid gland and circulated throughout the body. Most lab tests measure your free T4 level, which is the amount of T4 not attached to a protein in your blood.
What enzyme is involved in the production of thyroid hormone?
Thyroid peroxidase is a key enzyme involved in the production of thyroid hormone. Specifically, the TPO enzyme facilitates the chemical reaction where iodine bonds to the thyroglobulin protein. This critical step helps to create thyroxine (T4).
Why do doctors check TGAb?
Your doctor may check your TgAB levels if they suspect you have an underlying autoimmune condition causing thyroid dysfunction. A doctor may want to see the results of a TGAb test if they see specific clinical findings on your lab work and physical exam, including:
What happens when your immune system sends out antibodies?
When your immune system sends out antibodies to disrupt this chemical reaction, it prevents thyroid hormones from being made. Over time, it can lead to chronic inflammation and eventual hypothyroidism and organ failure.
What is the T3 test?
Triiodothyronine (T3) is another form of thyroid hormone that circulates in your blood. Testing for free T3 in addition to TSH and free T4 can help inform how well your body is converting thyroid hormone to the active form to be used by the body
How to restore thyroid health?
Finding the right balance for your own body is the best way to restore your thyroid health.
How to reverse thyroid disease?
Phytonutrients to help your thyroid produce enough natural hormones. By supporting your immune system, you can reverse your condition. (True.) So, a plan that involves eating lots of vitamin-rich foods packed with nutrients is vital to your immune system, thyroid gland, and overall health.
What is thyroid autoantibodies?
Thyroid autoantibodies are antibodies that develop when a person’s immune system mistakenly targets the thyroid gland or thyroid proteins. This leads to chronic inflammation of the thyroid (thyroiditis), tissue damage, and/or disruption of thyroid function.
What is the function of the thyroid?
Basically, the thyroid regulates metabolism. The body uses a feedback system in which thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid to produce T4 and T3 as needed. This system helps maintain a relatively stable amount of the thyroid hormones in the blood.
Why is protein important for thyroid?
Protein is needed to transport thyroid hormones throughout the body . Animal meat contains tyrosine which is the precursor amino acid for the thyroid gland hormone thyroxin.
Why does the immune system attack the thyroid gland?
Doctors don’t know what causes the immune system to attack your thyroid gland.
How many people have Hashimoto's disease?
Hashimoto’s disease is the most common thyroid disorder in the United States, affecting over 14 million people.
How to treat Hashimoto's disease?
Treatment for Hashimoto's disease may include observation and use of medications. If there's no evidence of hormone deficiency, and your thyroid is functioning normally, your doctor may suggest a wait-and-see approach. If you need medication, chances are you'll need it for the rest of your life.
Why is my thyroid low?
If your thyroid is underactive, the level of thyroid hormone is low. At the same time, the level of TSH is elevated because your pituitary gland tries to stimulate your thyroid gland to produce more thyroid hormone. An antibody test. Because Hashimoto's disease is an autoimmune disorder, the cause involves production of abnormal antibodies.
What is the name of the hormone that is made by the thyroid gland?
This usually involves daily use of the synthetic thyroid hormone levothyroxine (Levoxyl, Synthroid, others). Synthetic levothyroxine is identical to thyroxine, the natural version of this hormone made by your thyroid gland.
Why do doctors check TSH?
Because the TSH test is the best screening test, your doctor will likely check TSH first and follow with a thyroid hormone test if needed. TSH tests also play an important role in managing hypothyroidism. These tests also help your doctor determine the right dosage of medication, both initially and over time.
What is the diagnosis of Hashimoto's disease?
Diagnosis of Hashimoto's disease is based on your signs and symptoms and the results of blood tests that measure levels of thyroid hormone and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced in the pituitary gland. These may include:
What is the name of the medication that lowers cholesterol?
Cholestyramine (Prevalite), a medication used to lower blood cholesterol levels
Can a TSH test detect Hashimoto's?
In the past, doctors weren't able to detect an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism), the main indicator of Hashimoto's disease, until symptoms were fairly advanced. But by using the sensitive TSH test, doctors can diagnose thyroid disorders much earlier, often before you experience symptoms. Because the TSH test is the best screening test, your ...
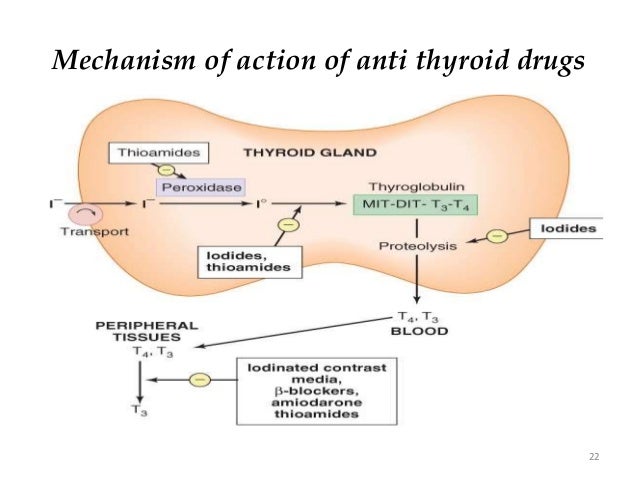
Diagnosis
Treatment
- Several treatments for hyperthyroidism exist. The best approach for you depends on your age, physical condition, the underlying cause of the hyperthyroidism, personal preference and the severity of your disorder. Possible treatments include: 1. Radioactive iodine. Taken by mouth, radioactive iodine is absorbed by your thyroid gland, where it causes...
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Once you begin treatment, symptoms of hyperthyroidism should subside and you should start feeling much better. However, your doctor may recommend that you watch out for iodine in your diet because it can cause hyperthyroidism or make it worse. Kelp, dulse and others types of seaweed contain a lot of iodine. Cough syrup and multivitamins also may contain iodine.
Coping and Support
- If you've been diagnosed with hyperthyroidism, the most important thing is to receive the necessary medical care. After you and your doctor have decided on a course of action, there are some things you can do that will help you cope with the condition and support your body during its healing process. 1. Get regular exercise.Exercise in general will help you feel better and improve …
Preparing For Your Appointment
- You'll likely start by seeing your primary care doctor. However, in some cases, you may be referred immediately to a doctor who specializes in the body's hormone-secreting glands (endocrinologist). If you have eye involvement, you may also be referred to an eye doctor (ophthalmologist). It's good to prepare for your appointment. Here's some information to help yo…