High grade squamous intraepithelial lesion treatment
| Method | Procedure | Strengths | Limitations |
| Cryotherapy | A highly cooled metal disc is applied to ... | The equipment is simple and relatively i ... | No tissue sample will be available for . ... |
| Loop electrosurgical excision procedure ... | Abnormal areas are removed from the cerv ... | A specimen will be obtained from the pro ... | LEEP requires intensive training. It req ... |
| Cold knife conization (CKC) | A cone-shaped area is removed from the c ... | A single surgical specimen, with “clean” ... | CKC requires spinal or general anaesthes ... |
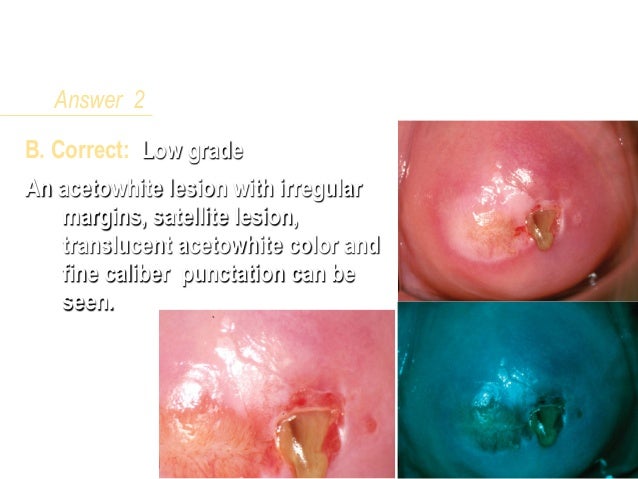
What does low grade squamous mean?
What Does Low Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion Mean? In the simplest terms, low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion indicates slightly abnormal cell formations on the surface of the cervix. The cervix is the lower and the narrow end of the uterus which forms the canal between the uterus and the vagina in females.
What causes HSIL?
High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) is a pre-cancerous, sexually transmitted disease caused by infection with a virus called human papillomavirus (HPV). In addition to the cervix, HSIL commonly involves the vagina and vulva. In both women and men, HSIL may also involve the anal canal and peri-anal skin.
What is a high grade lesion?
Vulval intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN)
- Types of VIN. ...
- High grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) This is the most common type of VIN. ...
- Low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL) VIN 1 is now called low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL). ...
- Differentiated VIN (dVIN) This is an uncommon type of VIN and tends to develop in women between 50 and 60 years of age. ...
What is high grade squamous carcinoma?
Squamous cell carcinoma is a life-threatening type of skin cancer. Squamous cells are small, flat cells in the outer layer of skin. When these cells become cancerous, they typically develop into rounded skin tumors that can be flat or raised. Sometimes the skin around the tumor gets red and swollen.

Is high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion serious?
If not treated, these abnormal cells may become cancer and spread into nearby tissue. A high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion is sometimes called moderate or severe dysplasia.
How long does it take HSIL to turn into cancer?
Types of cervical cell changes LSIL usually disappear without treatment, while HSIL are precancerous. High-grade abnormalities have the potential to develop into early cervical cancer over 10–15 years if they are not found and treated.
What is the treatment for HSIL?
HSIL (CIN2/3) Ablative methods such as CO2 laser ablation are effective but infrequently used in modern practice. Excisional methods such a large loop excision of the TZ (LLETZ), loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) or cold-knife cone biopsy are preferred.
How serious is squamous intraepithelial lesion?
Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions usually go away on their own without treatment, but sometimes they can become cancer and spread into nearby tissue. Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion is sometimes called mild dysplasia. Also called LSIL.
Should I be worried about HSIL?
HSIL is a squamous cell abnormality associated with human papillomavirus (HPV). Though not all HSIL will progress to cancer, HSIL is considered to be a precancerous lesion and therefore is usually treated aggressively.
What are the symptoms of Stage 1 cervical cancer?
Signs and symptoms of stage 1 cervical cancer can include:Watery or bloody vaginal discharge that may be heavy and can have a foul odor.Vaginal bleeding after intercourse, between menstrual periods or after menopause.Menstrual periods may be heavier and last longer than normal.
Why do I need a second LEEP procedure?
In some cases, abnormal cells are found again. If this happens, you may require another LEEP. Following a normal Pap and negative HPV test, patients are required to come back a year later for another screening.
Can high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion go away?
They usually go away on their own without treatment and are less likely to turn into cancer. High-grade: High-grade SILs include moderate dysplasia, severe dysplasia and neoplasia in-situ (the last phase before tissue becomes cancerous).
How long does it take for HSIL to develop?
In some cases, it might take as long as 10 years or more; in other cases, it could happen much more quickly. But with proper diagnosis and management, HSIL does not have to develop into cancer at all.
What does high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion mean?
HSIL ~ High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion This diagnosis means the cells appear very different from normal cells. These precancerous lesions are more severe than with LSIL, but involve cells on the surface of the cervix. They may also be called moderate or severe dysplasia, or CIN 2 or 3.
Can high-grade HPV go away?
High-risk HPV types Infection with HPV is very common. In most people, the body is able to clear the infection on its own. But sometimes, the infection doesn't go away. Chronic, or long-lasting infection, especially when it's caused by certain high-risk HPV types, can cause cancer over time.
Can high-grade dysplasia go away?
On the Pap test report, this will be reported as a low- or high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (SIL) or sometimes as atypical squamous or glandular cells. Dysplasia could go away on its own. Or, rarely, it could develop into cancer.
What is the follow up care for HSIL?
Follow-Up Care After Treatment. Following up after treatment for HSIL is absolutely necessary. Cells can become abnormal again, despite treatment, and may require additional treatment. Follow-up care consists of regular Pap smears and colposcopy exams for an extended period of time.
What is a colposcopy exam?
A colposcopy exam is an in-office procedure that allows a doctor to visually examine the cervix with a lighted instrument called a colposcope. 4 During the exam, the colposcope remains outside of the vagina. It acts like a microscope, allowing an in-depth view of the cervix.
What is AIS in cancer?
AIS is sometimes referred to as stage 0 cancer. When AIS if found or cervical cancer is caught at an early stage, it's easier to treat and the survival rates are highest. 6 Treatments for AIS are often similar to those for severe dysplasia. What to Expect With a Colposcopy Exam.
What is a high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion?
High grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) is a pre-cancerous disease that develops in the cervix. HSIL is caused by a virus called human papillomavirus (HPV). If left untreated, patients with HSIL are at high risk for developing a cancer of the cervix called squamous carcinoma.
What is the procedure for squamous cell carcinoma?
Cold knife cone biopsy – Similar to LEEP (above). Hysterectomy – In this procedure, the entire uterus and cervix are removed. This procedure is usually only performed when squamous cell carcinoma is found and for large tumours. There are many factors to consider when deciding which treatment option is best for you.
What to do after HSIL diagnosis?
After being diagnosed with HSIL your doctor should refer you to a specialist who will perform a colposcopy. A colposcopy allows your doctor to see the entire outer surface of the cervix. During the colposcopy, the doctor will be looking for any areas that look abnormal on the surface of the cervix. If an abnormality is found, ...
What is the movement of abnormal cells from the epithelium into the stroma called?
The movement of abnormal cells from the epithelium into the stroma is called invasion.
How to treat HSIL?
All patients with HSIL should be followed closely or offered treatment to remove the disease. There are several treatment options available:. Laser ablation – A laser is used to remove the abnormal squamous on the surface of the cervix. Loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) – A special type of knife is used to remove the tissue from ...
How many blocks of tissue are positive for HSIL?
Your pathologist will describe the number of pieces (or ‘blocks’ as they are often called) that show HSIL in your report. For example, your report may say “3 out of 14 blocks are positive for high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL)” which means that 3 out of the 14 pieces of tissue examined show the disease.
What is a squamous intraepithelial lesion?
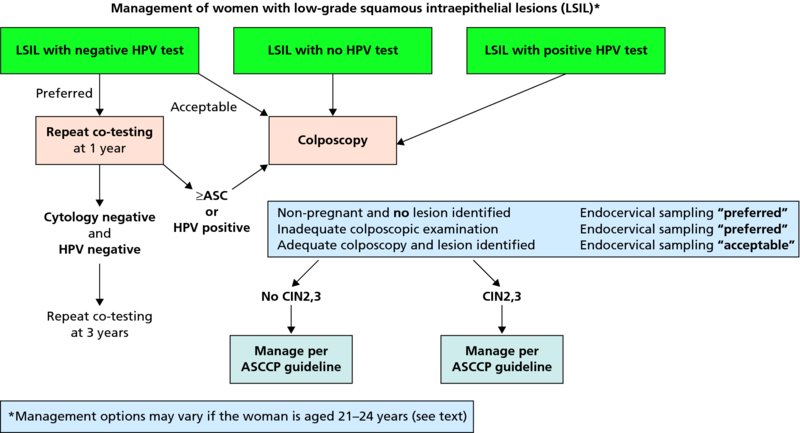
What is squamous intraepithelial lesion. Squamous intraepithelial lesion is used to indicate that the cells collected from the cervical Pap smear may be precancerous. If the changes are low grade (low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion or LSIL), it means the size, shape and other characteristics of the cells suggest that if a precancerous lesion ...
How often should a high grade lesion be analyzed?
If a histologic diagnosis of a high-grade lesion is made, she may have additional cytologic and colposcopic exams up to every 12 weeks. If cytology results are suggestive of invasive cancer or if the colposcopic appearance of the lesions worsens, a repeat biopsy is recommended.
How often should cervical carcinoma be screened?
Screening should be initiated at 21 years of age. Women ages 21 to 29 should be screened by cytology every three years. Women ages 30 to 65 should be screened with cytology and HPV co-testing every five years or by cytology alone every three years. Depending on the HPV test used, the test will provide pooled results for high-risk HPV subtypes and/or individual genotype results for HPV16 and 18. The risk of high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion in a patient with a positive HPV test and an abnormal pap test is approximately 20% and increases to 33% if HPV positive at more than one visit.
What is a loop excision?
Loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) is also called large loop excision of the transformation zone (LLETZ) or loop diathermy, is the removal of abnormal areas from the cervix using a loop made of thin wire powered by an electrosurgical unit. The loop tool cuts and coagulates at the same time, and this is followed by use of a ball electrode to complete the coagulation (see Figure 3). Loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) is the most common treatment for abnormal cervical cells. Loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) aims to remove the lesion and the entire transformation zone. The tissue removed can be sent for examination to the histopathology laboratory, allowing the extent of the lesion to be assessed. Thus, loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) serves a double purpose: it removes the lesion (thus treating the pre-cancer) and it also produces a specimen for pathological examination. The procedure can be performed under local anaesthesia on an outpatient basis and usually takes less than 30 minutes. However, following loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP), a patient should stay at the outpatient facility for a few hours to assure bleeding does not occur.
When to follow up HPV test?
Once the patient is treated, regardless of age, her recommended follow-up is HPV co-testing at 12 and 24 months post-treatment.
What is the major agent in the pathogenesis of cervical dysplasia and cancer of the cervix
Scientific studies have established human papillomavirus (HPV) as the major agent in the pathogenesis of cervical dysplasia and cancer of the cervix. HPV is a non-enveloped double-stranded DNA virus within the Papillomaviridae family. There are over 150 genotypes of HPV with 40 known to infect the anogenital tract.
Can a high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion go away?
If the changes are high grade (high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion or HSIL), the cells look severely abnormal and are less likely than the cells in LSIL to go away without treatment and there’s a greater chance that high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion may develop into cancer much sooner.
What is the best treatment for squamous cell carcinoma?
Topical therapy – A medication (e.g. trichloroacetic acid, imiquimod, 5-fluorouracil) can be applied to specific lesions or to the entire anal canal. Surgery – Removal of the abnormal tissue through surgery may be recommended by your doctor if there is concern that there may also be squamous cell carcinoma.
What is the best treatment for HSIL?
There are several treatment options available for HSIL: Local ablative therapy – Radiofrequency ablation or electrocautery can be used to remove the atypical tissue from the anal canal.
Why is HSIL considered a pre-cancerous disease?
HSIL is called a pre-cancerous disease because over time it can turn into a type of cancer called squamous cell carcinoma. Unlike squamous cell carcinoma, the abnormal cells in HSIL are unable to spread to tissues outside of the anal canal or to other parts of the body such as lymph nodes.
What is the specimen that is collected called?
The specimen that is collected is called a cytology specimen. After tissue samples from the anal canal have been collected, they are examined under a microscope by a pathologist. Unlike normal, healthy squamous cells, the nuclei of HSIL do not become smaller and flatter as they move from the bottom of the epithelium to the surface.
Which zone of the anal canal is made of squamous cells?
The third is the squamous zone. This zone is made entirely of squamous cells. The squamous zone connects with the skin at the very end of the anal canal. Submucosa – The submucosa contains many thick blood vessels that carry blood and lymphatic channels that carry waste and excess fluids away from the tissue.
What are the three zones of the anal canal?
Within the mucosa of the anal canal, there are three zones: 1) colorectal zone, 2) transition zone and 3) squamous zone. The first is called the colorectal zone. It is made of epithelial cells that form glands. The second is the transition zone. In this zone, the epithelium changes from glands to specialized squamous cells.
HSIL Pap Smear Results
Further Testing
- Pap smear screening results, such as HSIL, aren't enough to make a diagnosis and plan treatment (they represent only a sampling of cells). If Pap smear results come back as HSIL, your healthcare provider may recommend a colposcopy examand biopsy. This is true whether or not an HPV test is positive or negative. A colposcopy exam is an in-office procedure that allows a healthcare pro…
Treatment
- When choosing the best treatment for a HSIL Pap smear result, healthcare providers look at the risk of CIN 3 being present. To do so, they look at your current tests, your history of cervical cancer screening, your past medical history, your age, and whether you plan to become pregnant in the future or are pregnant at the current time.
Follow-Up Care After Treatment
- Following up after treatment for HSIL is absolutely necessary. Cells can become abnormal again, despite treatment, and may require additional treatment. Follow-up care consists of regular Pap smears and colposcopy exams for an extended period of time. Your particular schedule of follow up will depend on results of any biopsies you had and treatment...
A Word from Verywell
- If you are feeling anxious after being told that you have an abnormal Pap smear, especially one that shows high-grade changes, keep in mind that cervical cancer is one of the more easily prevented cancers and it is a slow-progressing disease that often takes years to develop. While it can be frustrating to undergo treatments and so many follow-up appointments, you are t…