
High grade squamous intraepithelial lesion treatment
| Method | Procedure | Strengths | Limitations |
| Cryotherapy | A highly cooled metal disc is applied to ... | The equipment is simple and relatively i ... | No tissue sample will be available for . ... |
| Loop electrosurgical excision procedure ... | Abnormal areas are removed from the cerv ... | A specimen will be obtained from the pro ... | LEEP requires intensive training. It req ... |
| Cold knife conization (CKC) | A cone-shaped area is removed from the c ... | A single surgical specimen, with “clean” ... | CKC requires spinal or general anaesthes ... |
Full Answer
What does low grade squamous mean?
Jun 10, 2019 · To get rid of high grade squamous intraepithelial lesions, various treatment options are available. The option chosen depends upon the severity of the condition and the changes in the morphology of the cervical tissue. The treatment options include the destruction of the abnormal cells, technically known as ablative therapy, and removal of the affected tissues …
What causes HSIL?
Treatment options for high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions. The introduction of testing for high-risk HPV types and P16 immunostaining of CIN2 histologic specimens allows for determination of the risk of progression versus regression for a woman with a particular cytologic or histologic specimen. Observation with serial cytological or colposcopic …
What is a high grade lesion?
Jan 05, 2022 · If the colposcopy is adequate and HSIL (CIN2, CIN3 or CIN2-3) is confirmed on biopsy, ablation of the transformation zone or excision is considered acceptable. However, only a diagnostic excisional procedure is acceptable if the colposcopy is inadequate or the endocervical curettage shows a high-grade lesion.
What is high grade squamous carcinoma?
Management and Treatment How are squamous intraepithelial lesions treated? Most low-grade lesions go away on their own. High-grade lesions require immediate treatment. Depending on the location of the lesions, your healthcare provider may recommend: Topical treatments: You may apply some medicine directly to your skin.
How to treat HSIL?
Ablative treatments for HSIL include: 1 Cryotherapy: Cryotherapy is a technique that's used to destroy abnormal tissue by freezing it. It is also called cryosurgery. 2 Thermal ablation: Thermal ablation is similar to cryotherapy, but uses heat instead of cold to destroy tissue. 3 Laser ablation: This type of laser therapy uses a tiny beam of light to destroy abnormal cells.
What is abnormal Pap smear?
An abnormal Pap smear result of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) means that cells of the cervix (the narrow neck of a woman's uterus) look somewhat to very abnormal when examined under a microscope. 1 . Before cervical cancer forms, the cells of the cervix undergo abnormal changes called cervical dysplasia.
What is a colposcopy exam?
A colposcopy exam is an in-office procedure that allows a doctor to visually examine the cervix with a lighted instrument called a colposcope. 4 During the exam, the colposcope remains outside of the vagina. It acts like a microscope, allowing an in-depth view of the cervix.
How many cervical cancers are preventable?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, up to 93% of cervical cancers are preventable with regular screening and treatment of abnormalities that arise. 3 This is why women undergo regular Pap smear exams to screen for any abnormal changes to the cervix. JodiJacobson / Getty Images.
Can cervical dysplasia cause cancer?
Although untreated cervical dysplasia can lead to cervical cancer, having it does not mean that a person has cancer or will develop the disease. Additional testing is typically needed for HSIL to confirm cervical dysplasia and to learn more about the severity of the abnormal cells.
What is a cin 3?
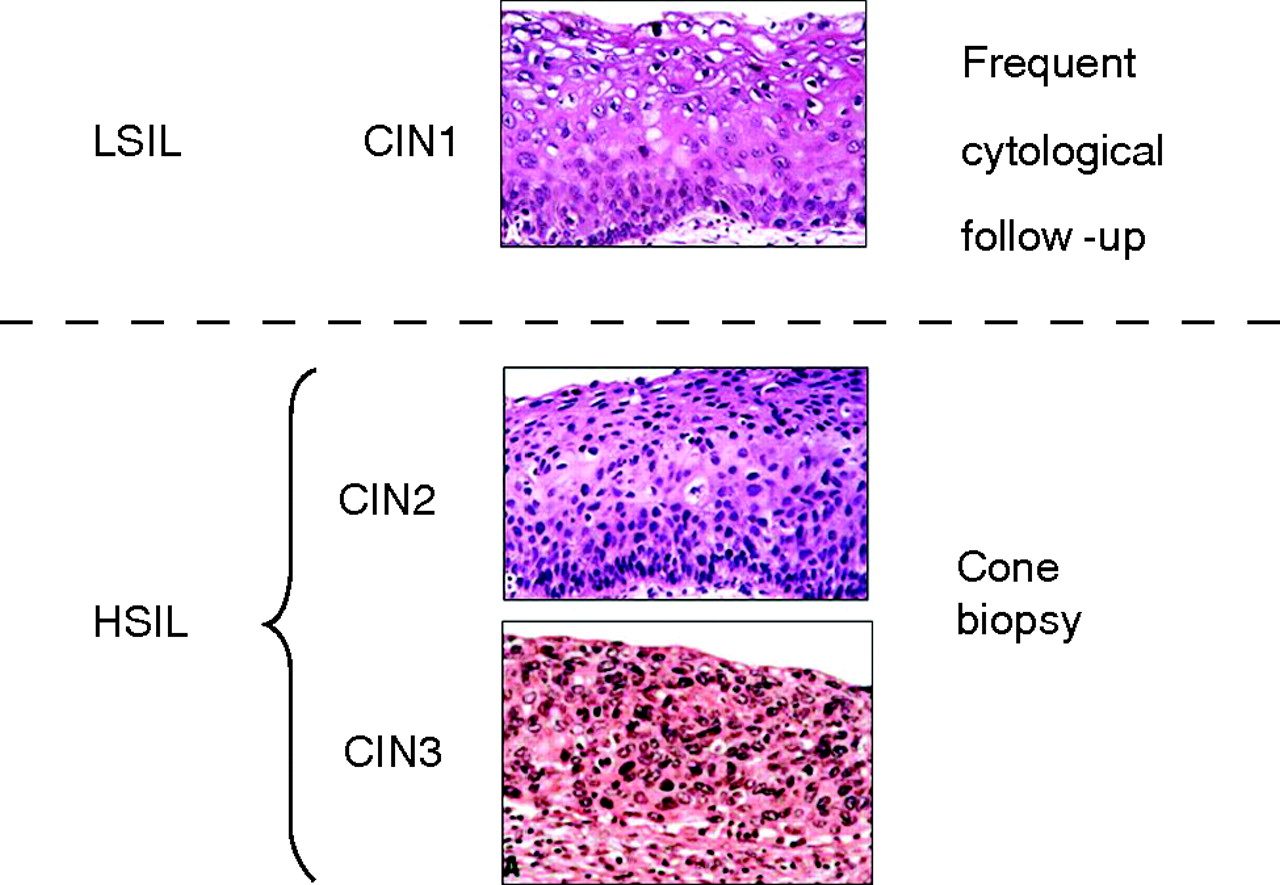
CIN 3 (grade 3): Also called severe or high-grade dysplasia, there are severely abnormal cells found on the cervix. CIN 1 usually goes away on its own without treatment, but in some cases it can spread or turn into cancer. CIN 2 is more likely to spread and turn into cancer than CIN 1 and treatment may be needed.
Can HPV be tested with a Pap smear?
HPV testing is most often done along with a Pap smear, and if it was not done, should be performed on the sample. This testing looks for the high-risk forms of HPV that can lead to cervical cancer, including HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 66, and 68, with HPV 16 and 18 most commonly found.
What is a high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion?
A high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) is a pre-cancerous disease that starts from the squamous cells in the mucosa of the anal canal. HSIL is called a pre-cancerous disease because over time it can turn into a type of cancer called squamous cell carcinoma.
What is the best treatment for HSIL?
There are several treatment options available for HSIL: Local ablative therapy – Radiofrequency ablation or electrocautery can be used to remove the atypical tissue from the anal canal.
What is the best treatment for squamous cell carcinoma?
Topical therapy – A medication (e.g. trichloroacetic acid, imiquimod, 5-fluorouracil) can be applied to specific lesions or to the entire anal canal. Surgery – Removal of the abnormal tissue through surgery may be recommended by your doctor if there is concern that there may also be squamous cell carcinoma.
What is the transition zone?
The second is the transition zone. In this zone, the epithelium changes from glands to specialized squamous cells. The transition point is called the dentate line . The third is the squamous zone. This zone is made entirely of squamous cells.
What is a squamous cell?
Squamous. cells are flat, scale-like types of epithelial cells. Epithelial cells are cells that help absorb, move, and. distribute some of the fluids and nutrients in the body. The cervix is a small, cylinder-shaped organ that forms. the lower part and neck of the uterus. The uterus is a.
What is intraepithelial lesion?
intraepithelial lesions) refers to how abnormal the cells are and how much of the cervix is. affected. A high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion is one in which the cells are very abnormal. and much of the cervix is affected. A low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion.
What is a Pap smear?
with a Pap smear or colposcopy. A Pap smear is a type of test. used to detect abnormal changes in cells. This is done by scraping. away loose cells from the cervix, spreading (smearing) it on a glass. slide, and examining it under a microscope. A colposcopy is a.
What is a squamous intraepithelial lesion?
What is squamous intraepithelial lesion. Squamous intraepithelial lesion is used to indicate that the cells collected from the cervical Pap smear may be precancerous. If the changes are low grade (low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion or LSIL), it means the size, shape and other characteristics of the cells suggest that if a precancerous lesion ...
Can cervical cancer cause squamous intraepithelial lesion?
Women with early cervical cancers and low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion usually have no symptoms. Symptoms often do not begin until the cervical cancer becomes invasive and grows into nearby tissue. When this happens, the most common symptoms are:
What is a CIN2/3?
High grade squamous intraepithelial lesion, classically referred to as CIN2/3 or CIS (carcinoma in situ) usually requires an excisional procedure for treatment. Ablative procedures can be offered, but the majority of clinicians perform excisional procedures to give the pathologist a better specimen to evaluate. Excisional procedures provide assurance that an underlying cancer is identified and adequate treatment for the lesion is provided. A loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) to remove the abnormal tissue with a thin electrified wire that cuts the specimen from the cervix can be performed in the office. A cold knife cone (CKC) typically is performed in the operating room, using a knife to resect a cone shaped portion of cervical tissue. The advantage of a cold knife cone is that the pathologist can identify the margins more clearly and because they are not obscured by the burn artifact created with the electrified wire. Following a complete excision and negative margins, patients require yearly follow-up with a pap smear. If underlying cancer is discovered, treatment plans are expanded, and an oncologist is consulted. If an excisional procedure provides results in positive LEEP (loop electrosurgical excision procedure) margin findings, the decision to re-excise or follow conservatively is based on the patient’s age and fertility status.
What is a loop excision?
Loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) is also called large loop excision of the transformation zone (LLETZ) or loop diathermy, is the removal of abnormal areas from the cervix using a loop made of thin wire powered by an electrosurgical unit. The loop tool cuts and coagulates at the same time, and this is followed by use of a ball electrode to complete the coagulation (see Figure 3). Loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) is the most common treatment for abnormal cervical cells. Loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) aims to remove the lesion and the entire transformation zone. The tissue removed can be sent for examination to the histopathology laboratory, allowing the extent of the lesion to be assessed. Thus, loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) serves a double purpose: it removes the lesion (thus treating the pre-cancer) and it also produces a specimen for pathological examination. The procedure can be performed under local anaesthesia on an outpatient basis and usually takes less than 30 minutes. However, following loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP), a patient should stay at the outpatient facility for a few hours to assure bleeding does not occur.
What is abnormal Pap?
An abnormal Pap test result may mean more testing, sometimes including tests to see if a cancer or a pre-cancer is actually present. The tests that are used include colposcopy (with biopsy), endocervical scraping and cone biopsies.
How old do you have to be to get tested for cervical cancer?
All women should begin cervical cancer testing (screening) at age 21.
What is the pain after cervical biopsies?
Several types of biopsies can be used to diagnose cervical pre-cancers and cancers. After these procedures, patients may feel mild cramping or pain and may also have some light bleeding.
HSIL Pap Smear Results
Further Testing
- Pap smear screening results, such as HSIL, aren't enough to make a diagnosis and plan treatment (they represent only a sampling of cells). If Pap smear results come back as HSIL, your healthcare provider may recommend a colposcopy examand biopsy. This is true whether or not an HPV test is positive or negative. A colposcopy exam is an in-office procedure that allows a healthcare pro…
Treatment
- When choosing the best treatment for a HSIL Pap smear result, healthcare providers look at the risk of CIN 3 being present. To do so, they look at your current tests, your history of cervical cancer screening, your past medical history, your age, and whether you plan to become pregnant in the future or are pregnant at the current time.
Follow-Up Care After Treatment
- Following up after treatment for HSIL is absolutely necessary. Cells can become abnormal again, despite treatment, and may require additional treatment. Follow-up care consists of regular Pap smears and colposcopy exams for an extended period of time. Your particular schedule of follow up will depend on results of any biopsies you had and treatments you have chosen, but is usuall…
A Word from Verywell
- If you are feeling anxious after being told that you have an abnormal Pap smear, especially one that shows high-grade changes, keep in mind that cervical cancer is one of the more easily prevented cancers and it is a slow-progressing disease that often takes years to develop. While it can be frustrating to undergo treatments and so many follow-up appointments, you are t…