What is low grade dysplasia?
In all these patients, the initial high-grade adenoma was > 1 cm in diameter. Initial follow-up colonoscopy was performed on average 7 months following the initial diagnosis. Ten per cent of patients underwent prophylactic segmental resection, and 6% received argon laser therapy.
Are all colon polyps precancerous or worse?
Another way to manage colon dysplasia is by using radiation therapy. This is when powerful energy sources are used to kill cancerous cells that remain after surgery. It can also be used to shrink large tumors before surgery and to relieve symptoms of colon and rectal cancer. In early stages of colon cancer, radiation therapy is not commonly used.
What happens if a polyp is cancerous?
Nov 10, 2020 · The relative risk of polyps with HGD at baseline was 6.87 (95% CI 2.61–18.07) for interval advanced neoplasia in a study by Lieberman, in which 6 of 11 patients with recurrent cancer or high-grade dysplasia had lesions locallized to the resection site .
Is low grade dysplasia cancer?
Mar 07, 2020 · High grade dysplasia (HGD) refers to precancerous changes in the cells of the esophagus. Low grade and then high grade dysplasia can develop.HGD significantly increases a person's risk for esophageal adenocarcinoma and in most cases will progress to …
How is high grade dysplasia in the colon treated?
Resection of a large, flat or sessile lesion, particularly when it is removed in pieces, or a polyp with a focus of high-grade dysplasia or cancer is often followed by repeat endoscopy in 3 months to confirm complete excision.Mar 9, 2020
Does high grade dysplasia in colon mean cancer?
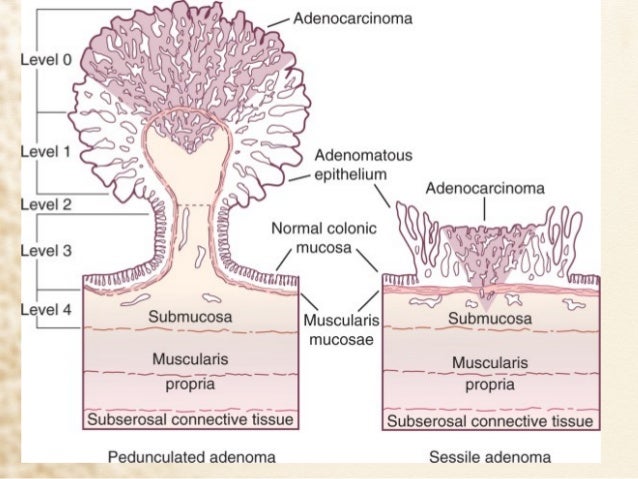
Polyps that are only mildly abnormal (don't look much like cancer) are said to have low-grade (mild or moderate) dysplasia. Polyps that are more abnormal and look more like cancer are said to have high-grade (severe) dysplasia.Feb 27, 2017
How serious is dysplasia in the colon?
Abstract. Colorectal cancer is the most serious complication of chronic inflammatory bowel disease. It is generally accepted that dysplasia in most cases precedes the development of colorectal cancer. Thus, detection of dysplasia through surveillance may allow therapeutic interventions to lower the risk of cancer.Apr 13, 2018
Is high grade dysplasia malignant?
In high-grade dysplasia, the cellular changes are often reminiscent of the changes seen in cells with invasive cancer. However, these cells have not penetrated the muscularis mucosa and, therefore, do not represent a malignancy.
What is the difference between high grade dysplasia and cancer?
A term used to describe the presence of abnormal cells within a tissue or organ. Dysplasia is not cancer, but it may sometimes become cancer. Dysplasia can be mild, moderate, or severe, depending on how abnormal the cells look under a microscope and how much of the tissue or organ is affected.
Can colon dysplasia be reversed?
Patients could be counseled that LGD is reversible and does not always lead to cancer or need for surgery.Jan 14, 2020
What does high grade dysplasia mean?
High grade dysplasia (HGD) refers to precancerous changes in the cells of the esophagus. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can be complicated by Barrett's esophagus (BE), a change in the normal esophageal cells to intestinal-like cells. BE cells can become abnormal or dysplastic.
What causes colon dysplasia?
Anal dysplasia is a pre-cancerous condition that affects the cells of the anus and anal canal. It involves lesions developing within the anus when normal cells change into abnormal cells. The condition is often associated with the human papilloma virus (HPV), which is also a cause of anal warts.Dec 31, 2019
What is dysplasia of the colon?
Dysplasia is an area in the lining of the colon or rectum where the cells look abnormal (but not like true cancer cells) when viewed under a microscope. These cells can change into cancer over time. Dysplasia can also be seen in people who have had diseases such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease for many years.
Is high grade dysplasia curable?
It is documented that BE with HGD or intramucosal adenocarcinoma constitute diseases amenable to cure in most cases.
What is a severe dysplasia?
What is severe dysplasia? If you have severe cervical dysplasia, it means that severely abnormal cells have been found on your cervix. You don't have cancer, and it doesn't necessarily mean you'll develop cancer. Rather, it's a precancerous condition.Dec 17, 2019
What is adenoma with high grade dysplasia?
"Dysplasia" is a term that describes how much your polyp looks like cancer under the microscope. Polyps that are only mildly abnormal are said to have low-grade (mild or moderate) dysplasia, while polyps that are more abnormal and look more like cancer are said to have high-grade (severe) dysplasia.
What is colon dysplasia?
Colon Dysplasia: Diagnosis and Management in Patients. Dysplasia is a term that refers to the abnormal growth or development of organs or cells. In relation to colorectal cancer, dysplasia is the abnormal growth and development of cells in the colon. Generally, colon cancer develops from polyps in the colon. Because polyps start to develop as ...
What is the term for the abnormal growth and development of cells in the colon?
In relation to colorectal cancer, dysplasia is the abnormal growth and development of cells in the colon. Generally, colon cancer develops from polyps in the colon. Because polyps start to develop as a person gets older, colon cancer screening guidelines suggest that everyone 50 years old and above should be screened regularly.
What is the procedure to remove a small polyp?
Polypectomy. When colon dysplasia is discovered, the physician will perform a procedure called a polyepectomy. This is a simple procedure that can be done at the same time as a colonoscopy. Biopsy forceps are used to cut off a small polyp which is removed to test if it has cancerous cells.
What is the treatment for rectal cancer?
It can be used to kill cancer cells after surgery, to control the growth of tumors or to relieve colon cancer symptoms. In cases of rectal cancer, chemotherapy is commonly used together with radiation therapy .
What is the test to see the inner lining of the large intestine?
Diagnosis. Diagnosis can be easily made with a colonoscopy. This is a test conducted to view the inner lining of the large intestine that includes the colon and rectum. The doctor uses a thin, flexible tube called a colonoscope to see the colon. Colonoscopy can also be used to find colon tumors, colon polyps, ulcers and areas ...
What is colon health magazine?
Colon Health Magazine is a free resource for families, providing everything from in-depth product reviews to expert advice. Our articles and guides are written by industry experts and backed by in-depth research and analysis. View all posts by Colon Health Magazine Staff.
Can a polypectomy be followed up?
Polypectomy Follow Up. There is an increased risk of colon dysplasia when a single colonic polyp is found. Although a polypectomy gets rid of a single lesion, other dormant polyps may still exist. In most cases, physicians recommend increasing rate of colonoscopies in order to make sure that all dysplasia are identified and treated accordingly.
What does it mean when a polyp looks like cancer?
Dysplasia is a term that describes how much your polyp looks like cancer under the microscope: Polyps that are only mildly abnormal (don’t look much like cancer) are said to have low-grade (mild or moderate) dysplasia. Polyps that are more abnormal and look more like cancer are said to have high-grade (severe) dysplasia.
What is a tubulovillous adenoma?
Many adenomas have a mixture of both growth patterns, and are called tubulovillous adenomas. Most adenomas that are small (less than ½ inch) have a tubular growth pattern. Larger adenomas may have a villous growth pattern. Larger adenomas more often have cancers developing in them.
What is a polyp made of tissue that looks much like the normal lining of your colon?
An adenoma is a polyp made up of tissue that looks much like the normal lining of your colon, although it is different in several important ways when it is looked at under the microscope. In some cases, a cancer can start in the adenoma.
Why is it important to have a polyp removed?
The most important thing is that your polyp has been completely removed and does not show cancer. The growth pattern is only important because it helps determine when you will need your next colonoscopy to make sure you don’t develop colon cancer in the future.
What is a serrated adenoma?
Serrated polyps (serrated adenomas) have a saw-tooth appearance under the microscope. There are 2 types, which look a little different under the microscope: Sessile serrated adenomas (also called sessile serrated polyps) Traditional serrated adenomas. Both types need to be removed from your colon.
What is the name of the doctor who examines colons?
When your colon was biopsied, the samples taken were studied under the microscope by a specialized doctor with many years of training called a pathologist. The pathologist sends your doctor a report that gives a diagnosis for each sample taken. This report helps manage your care.
Where does the colon end?
The ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, and sigmoid colon are other parts of the colon after the cecum. The colon ends at the rectum, where waste is stored until it exits through the anus.
What are the factors that increase the risk of colon cancer?
Factors associated with increased risk include long duration of colitis, extensive colonic involvement, primary sclerosing cholangitis, a family history of colorectal cancer, and, according to some studies, early disease onset and more severely active inflammation.
How long does it take for a colonoscopy to detect neoplasia?
An initial screening colonoscopy should be performed 7-8 years from disease onset or immediately in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis.
Is biopsy negative or positive?
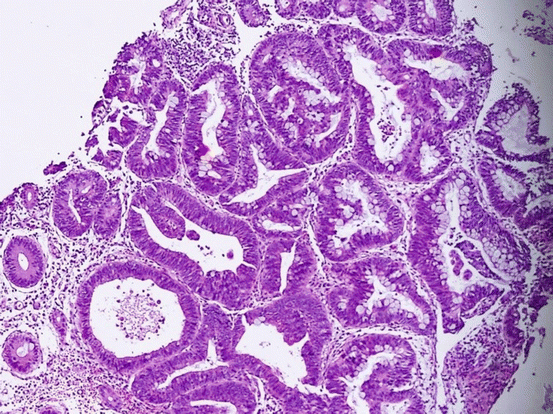
Biopsy specimens are graded pathologically as negative, indefinite for dysplasia, low-grade dysplasia, high-grade dysplasia, or invasive cancer. The diagnosis and grading of dysplasia can be very challenging and should be confirmed by an expert pathologist whenever intervention or a change in management is contemplated.