Heparin is typically given by IV. The most commonly used injectable blood thinners for DVT
Deep Vein Thrombosis
A condition in which the blood clots form in veins located deep inside the body.
Full Answer
Are D-dimer levels always elevated after total hip or knee arthroplasty?
D-dimer level was sharply elevated and peaked to 4.5 μg/dl at postoperative day 1. At postoperative day 2, it decreased to baseline level. After then, it slowly elevated again and reached a second peak at postoperative week 2. Conclusion: D-dimer showed a more rapid rise and fall than ESR and CRP in very early postoperative period. The D-dimer ...
What is the normal range of D dimer after surgery?
Background: Serum d-dimer is a common screening test for symptomatic deep venous thrombosis (DVT) after total joint arthroplasty. This study characterized the longitudinal resolution of d-dimer measurements after total hip and knee arthroplasty (THA/TKA) over a …
How much ibuprofen should I take after hip replacement surgery?
Although most patients undergoing total hip replacement are postoperatively treated with antithrombotic agents such as enoxaparin according to the guidelines regardless of D-dimer …
What is the peak level of D-dimer after breast augmentation?
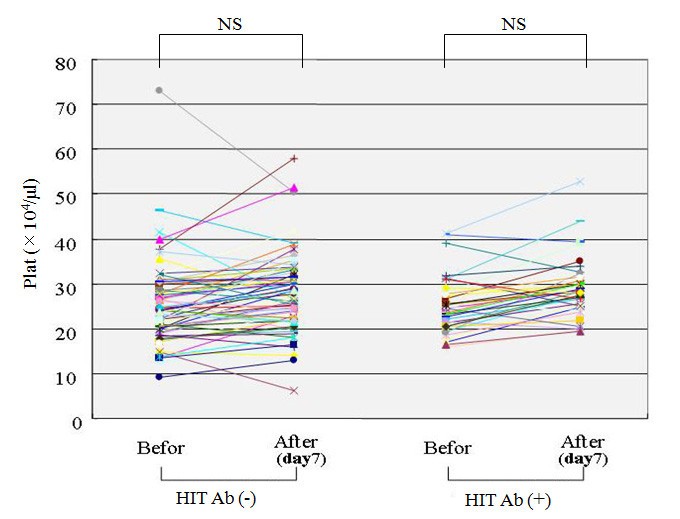
patient developed post-operative symptomatic DVT, but D-dimer levels were elevated in all patients post-operatively (Figure 1). Postoperative heparin was used in 2 patients for a couple …

How long does D-dimer stay elevated after hip surgery?
The results of our study suggest that serum D-dimer remains raised for at least 28 days and possibly considerably longer. Therefore, serum D-dimer should not be used in patients with clinically suspected VTE within this period, due to an unacceptably low specificity of 4.44% and a positive predictive value of 10.42%.
How do you prevent blood clots after hip replacement?
Prevention and Treatment of Blood Clots after Hip and Knee Replacement SurgeryExercise/physical therapy beginning the first day after surgery and continuing for several months.Compression stockings.Anti-clotting medicine to reduce the body's ability to form blood clots.
How long does it take for D-dimer to normalize after surgery?
D-dimer levels increased postoperatively reaching a peak on day 7. After type I surgery, peak D-dimer levels did not exceed normal range (300 ng/ml, 100-500). After type II procedures, peak D-dimer level was 1500 ng/ml (200-7800) and returned to normal values after 25 days (+/-14).
How is elevated D-dimer treated?
Statins have proven antithrombotic properties, as suggested by the reduction of several prothrombotic markers, including D-dimer, in patients at high risk of arterial thrombosis.
How long do you have to worry about blood clots after hip replacement?
Citing several published studies, Heit says the risk period for clots in the deep veins, for instance, can be up to 12 weeks after hip replacement and up to six weeks after knee surgery. These long-term risks are the most important for patients to know about, he says.
How do they treat blood clots after surgery?
Blood thinner medicines. These are also called anticoagulants. They make it harder for your blood cells to stick together and form clots. You take them by mouth, shot, or through an IV.
Is elevated D-dimer serious?
Blood clotting conditions can be serious and life-threatening. Having a high D-dimer level in your blood can be a sign of a blood clotting disorder since the level of D-dimer can rise greatly when there's significant formation and breakdown of blood clots in your body.
Can elevated D-dimer mean nothing?
An elevated D-dimer level is not normal. It's usually found after a clot has formed and is in the process of breaking down. If you are having significant formation and breakdown of a blood clot in your body, your D-dimer may be elevated. A negative D-dimer test means that a blood clot is highly unlikely.
What conditions cause elevated D-dimer?
Also, high D-dimer levels are not always caused by clotting problems. Other conditions that can cause high D-dimer levels include pregnancy, heart disease, and recent surgery. If your D-dimer results were not normal, your provider will probably order more tests to make a diagnosis.
Can aspirin Lower D-dimer?
Introduction of ultra-low-dose warfarin (1 mg) or aspirin 300 mg does not significantly alter these markers, although conventional warfarin therapy reduces beta-TG and fibrin D-dimer levels.
How can I lower my D-dimer naturally?
Natural blood thinners are substances that reduce the blood's ability to form clots....Some foods and other substances that may act as natural blood thinners and help reduce the risk of clots include the following list:Turmeric. ... Ginger. ... Cayenne peppers. ... Vitamin E. ... Garlic. ... Cassia cinnamon. ... Ginkgo biloba.More items...
What type of inflammation causes high D-dimer?
Vasculitis seems to be a common pathophysiologic link between the other reports of inflammatory conditions and elevated D-dimer levels. These reports include Henoch-Schönlein purpura, Kawasaki disease, eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss syndrome), and Behçet syndrome.
Does stretching prevent blood clots?
Another important way to prevent DVT is simply to move more — even if it's just working some simple leg exercises and stretches into your day.
What causes blood clots after hip surgery?
Most people who have one of these major surgeries are less active for several days or weeks after the surgery. This can cause blood flow to slow down, which increases the risk for a blood clot. People with a DVT may not have any symptoms and may not know they have one.
What are the symptoms of a blood clot in the hip?
Symptoms and ComplicationsBulging veins.Discolored, red or tight skin.Edema or swelling.Tenderness and pain.Thickening of veins called "cords"Warmth in the affected area.
How long after hip replacement do I need to take aspirin?
Recent NICE guidelines (2018) on reducing risk of hospital-acquired venous thromboembolism recommend aspirin as an option, though not the switching strategy from rivaroxaban. Recommended options after hip replacement are: Low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) for 10 days followed by aspirin (75 to 150mg) for 28 days; or.
What is the D-dimer test used for?
It was assumed that this test would be used effectively in diagnosing early postoperative infection with the combination of the ESR and CRP. This natural progress can serve as a baseline for early diagnosis of infection.
What is PJI after hip arthroplasty?
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) after total hip arthroplasty (THA) or total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most dreadful complications and it has extremely negative effects on the physical, emotional, social, and economic aspects of a patient’s life [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ]. To eradicate the infection, a diagnosis of PJI in its early stage is very important [ 4, 5, 6, 7 ]. Serum erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) have been generally used as a screening test for infection because of their simplicity and cost-effectiveness [ 8 ]. However, they have low sensitivity and specificity and these may increase under several conditions in addition to infection [ 8, 9, 10, 11 ]. Therefore, there have been some trials to establish a new single reference standard [ 6, 9 ].
Is D-dimer test effective?
The D-dimer test might be effective in early detection of PJI, if combined with levels of ESR and CRP. The postoperative change of D-dimer in our study can serve as a baseline for early diagnosis of PJI.
What is the first line of treatment for venous thromboembolism?
Direct oral anticoagulants should be used as first-line agents for the treatment of venous thromboembolism and the prevention of stroke in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation and a CHA2DS2-VASc score of 2 or higher in men and 3 or higher in women. 20
How often should INR be monitored?
Monitoring should then be decreased to twice weekly until the INR is within the therapeutic range, then decreased to weekly, every other week, and finally monthly. 4 The ACCP guidelines recommend INR monitoring once every 12 weeks for patients who are stable (defined as at least three months of consistent results with no required adjustment of vitamin K antagonist dosing).
What are D-dimers in a venous thromboembolism test?
D-dimers are used in conjunction with clinical probability scores in the assessment of venous thromboembolism (VTE), and they are elevated in other conditions, including malignancy, infection and arrhythmias. High levels of D-dimers in VTE are associated with adverse outcomes, including increased mortality. Their significance in patients without VTE has not previously been established. To establish the clinical significance of elevated D-dimer levels in patients without VTE. This prospective study included 2263 patient episodes of suspected deep vein thrombosis, which were excluded radiologically. Patients were followed up for survival and adverse events for a median of 22 months. D-dimer levels greater than 4000 ng FEU/ml (4.9% of patients), and greater than 8000 ng FEU/ml (1.8%) were associated with a reduced overall survival. D-dimer levels greater than 8000 ng FEU/ml and age over 60 years were independent poor prognostic factors for overall survival (p<0.001.). D-dimer levels greater than 8000 ng FEU/ml were associated with an increased incidence of malignancy (p=0.003). This study provides evidence of very high D-dimer levels in patients with cancer who do not have VTE. This suggests that elevated D-dimer levels in patients with VTE and malignancy are not solely due to presence of thrombus. High D-dimer levels in malignancy are likely to reflect the biology of the underlying tumour, with higher levels observed in breast, prostate and bowel cancers.
What is EMPD in surgery?
Extramammary Paget's disease (EMPD) is an adenocarcinoma of the apocrine glands with unknown exact prevalence and obscure etiology. It has been divided into primary EMPD and secondary EMPD, in which an internal malignancy is usually associated. Treatment for primary EMPD usually consists of wide lesion excision with negative margins. Multiple methods have been proposed to obtain free-margin status of the disease. These include visible border lesion excision, punch biopsies, and micrographic and frozen-section surgery, with different results but still high recurrence rates. The investigators propose a method consisting of a staged contoured marginal excision using "en face" permanent pathologic analysis preceding the steps of central excision of the lesion and the final reconstruction of the surgical defect. Advantages of this method include adequate margin control allowing final reconstruction and tissue preservation, while minimizing patient discomfort. The staged contoured marginal and central excision technique offers a new alternative to the armamentarium for surgical oncologists for the management of EMPD in which margin control is imperative for control of recurrence rates.
