
8 Natural Treatments For Glaucoma In Dogs
- Natural Treatment For Glaucoma In Dogs. Spinach is full of carotenoids which can strengthen the ocular tissue and prevent further degeneration of the eye.
- Homeopathy. Aconitum Napellus 30c. ...
- Reducing The Risk. If you have not seen any signs of glaucoma in your dog, start protecting his eyes right away. ...
How to treat glaucoma in dogs naturally?
Jan 13, 2020 · The higher the pressure is within the eye the more pain a dog is typically in. Treatment Eye medications are typically used to lower the pressure in the eye. If the pressure is not able to be controlled with medications then surgery to remove the eye is done in order to relieve your dog of the chronic pain from the high pressure.
Does marijuana help treat glaucoma in dogs?
The most effective method for preventing blindness due to glaucoma in dogs is surgery, which is done with a procedure known as endolaser cyclophotocoagulation. This procedure uses a laser beam to actually destroy the cells of the eye which produce aqueous humor, thereby eliminating pressure buildup in the eye.
Can dogs live with glaucoma?
Long-term medical therapy may involve drugs such as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (e.g., dorzolamide 2%, brand names Trusopt® and Cosopt®) or beta-adrenergic blocking agents (e.g., 0.5% timolol, brand names Timoptic® and Betimol®). Medical treatment often must be combined with surgery in severe or advanced cases.
Does glaucoma in dogs always affect both eyes?
Your veterinarian will likely refer your dog to a veterinary ophthalmologist. Eye pressures above 40-50mm require emergency treatment. Latanoprost (Xalatan), a prostaglandin (PG) analogue eye drop, can be effective in bringing pressures down to normal, as it increases the flow of aqueous humor.
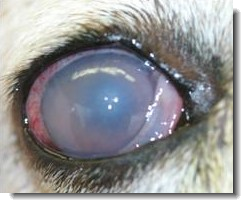
Can glaucoma in dogs be treated?
Treatment of POAG is with anti-glaucoma eye drops. Lifelong treatment is necessary and regular intraocular pressure checks are required in order to ensure optimum control. However, in some advanced cases of POAG it is not possible to reduce pressure and in these cases surgical treatment may be required.
How long does glaucoma take to cause blindness in dogs?
Glaucoma can be painful and approximately 40 percent of cases lead to blindness within one year. If treatment is not started within hours of pressure increase, vision will likely be lost.
Can a dog live with glaucoma?
Dogs diagnosed with glaucoma can and do go on to live long and happy lives, but prompt treatment is the key to reducing the risk of any vision loss for your pooch.Apr 6, 2018
What is the prognosis for a dog with glaucoma?
Unfortunately, the prognosis for dogs affected by primary glaucoma is typically poor and many affected dogs will be blinded by the disease. In cases of secondary glaucoma, the prognosis may be better if the underlying cause can be promptly corrected.
Is glaucoma painful for dogs?
Glaucoma is a painful condition charaterized by increased intraocular pressure within the eye, caused by inadequate fluid drainage. Glaucoma can progress very quickly, and often leads to optical nerve and retinal damage in dogs.Oct 6, 2020
How do I know if my dog is in pain from glaucoma?
Signs and symptoms of glaucoma in dogsEye pain: Rubbing up against the floor or another object or with the paw.Redness of the eye.Cloudy cornea.Squinting.Tearing.Avoidance of light.Weak blink response.Fluttering eyelid.More items...
How much does it cost for glaucoma surgery for dogs?
Diode Laser (for glaucoma treatment) This procedure must be performed under general anesthesia for safety purposes. The cost is approximately $1,400 (one eye) to $1,800 (both eyes).
At what age do dogs get glaucoma?
"Dogs usually develop glaucoma by the time they are 6 years old," he added. "By that age, they may have had three or four litters, if they are breeding dogs." The litters born before the parents show signs of glaucoma will likely inherit the possibility of getting the disease.Mar 2, 2010
What do dogs with glaucoma see?
Cloudy eyes in dogs, foggy eye or hazy with a bluish cloud. Red, cloudy eye, possibly with a dilated pupil. Loss of vision (the dog may be bumping into things) A lethargic dog who is sleeping more and exhibits one of the eye signs above.Aug 8, 2018
How do vets test for glaucoma?
To detect early glaucoma, a veterinarian uses an instrument called a tonometer to measure the pressure within the eye. This is often done for high-risk breeds of dogs as part of the general physical examination.
What causes glaucoma in dogs eyes?
Causes of Glaucoma in Dogs Primary glaucoma is caused by increased IOP in an otherwise healthy eye. It is often due to genetic, inherited abnormalities of the eye's drainage angle. Goniodysgenesis is an inherited risk factor for closed-angle glaucoma and puts affected dogs at a higher risk of glaucoma in the future.Apr 12, 2022
What is secondary glaucoma in dogs?
Secondary glaucoma in dogs develops when a primary eye condition affects the amount of aqueous humor drained within the eye. This type of glaucoma can result from: All of these eye conditions impair the method of fluid drainage within the eye, eventually leading to excessive pressure when not properly treated.
How to prevent blindness in dogs?
The most effective method for preventing blindness due to glaucoma in dogs is surgery, which is done with a procedure known as endolaser cyclophotocoagulation. This procedure uses a laser beam to actually destroy the cells of the eye which produce aqueous humor, thereby eliminating pressure buildup in the eye.
What is the fluid in a dog's eye called?
In dogs, there is a clear liquid within the eyeball that helps to maintain shape and sustain the internal structures of the eye. This fluid is known as aqueous humor.
Can glaucoma cause blindness in dogs?
All of these eye conditions impair the method of fluid drainage within the eye, eventually leading to excessive pressure when not properly treated. Seconda ry glaucoma is by far the most common type of glaucoma in dogs, but primary glaucoma tends to result in blindness more often than seconda ry glaucoma.
Do dogs need to be identified for glaucoma?
In order to find the most effective treatment option, the type of glaucoma the dog has needs to be identified. Cases of primary and secondary glaucoma do not necessarily respond to the same types of treatment, so the original cause of glaucoma must be identified before treatment can begin.
Can a dog have glaucoma?
This particular type of glaucoma in dogs appears to occur more commonly in Bassett Hounds, Shar Peis, Siberian Huskies, and Cocker Spaniels. With primary glaucoma, the dog usually presents with only affected eye initially, but the condition quickly progresses to encompass both eyes.
What causes glaucoma in dogs?
This is the most common cause of glaucoma in dogs. Causes include: 1 Uveitis (inflammation of the interior of the eye) or severe intra-ocular infections, resulting in debris and scar tissue blocking the drainage angle. 2 Anterior dislocation of lens. The lens falls forward and physically blocks the drainage angle or pupil so that fluid is trapped behind the dislocated lens. 3 Tumors can cause physical blockage of the iridocorneal angle. 4 Intra-ocular bleeding. If there is bleeding in the eye, a blood clot can prevent drainage of the aqueous humor. 5 Damage to the lens. Lens proteins leaking into the eye as a result of a ruptured lens can cause an inflammatory reaction resulting in swelling and blockage of the drainage angle.
What happens if you have a blood clot in your eye?
If there is bleeding in the eye, a blood clot can prevent drainage of the aqueous humor. Damage to the lens. Lens proteins leaking into the eye as a result of a ruptured lens can cause an inflammatory reaction resulting in swelling and blockage of the drainage angle.
What is the name of the instrument used to measure intraocular pressure?
Intraocular pressure is measured using an instrument called a tonometer.
Can glaucoma cause blindness?
The cornea or clear part of the eye may become cloudy or bluish in color. Blindness can occur very quickly unless the increased IOP is reduced. All of these signs can occur very suddenly with acute glaucoma. In chronic glaucoma they develop more slowly.
What is aqueous humor?
Aqueous humor contains nutrients and oxygen that are used by the structures within the eye. The excess fluid is constantly drained from the eye between the cornea and the iris. This area is called the iridocorneal angle, or the filtration, or the drainage angle. The intra-ocular pressure remains constant as long as the production ...
Is glaucoma a secondary disease?
Glaucoma is further classified as primary or secondary glaucoma. Primary glaucoma results in increased intra-ocular pressure in a healthy eye. Some breeds are more prone than others (see below).
How do you know if your dog has glaucoma?
Common clinical signs of canine glaucoma include: Mild to severe eye pain that causes your pet to partially close or rub their eye. The appearance of blood vessels in the white of the eye, or “red-eye”. Impaired vision as demonstrated by issues finding things, bumping into objects, or walking cautiously.
What is the best treatment for glaucoma?
Most glaucoma prescriptions come in the form of ointments, topicals, or eye drops, all of which require a vet’s authorization. The vet might also prescribe oral pain relievers to help with the discomfort.
What causes intraocular pressure to increase?
Secondary glaucoma results in increased intraocular pressure caused by eye diseases or injuries to the eye. Common triggers include eye inflammation, tumors, infections, retinal detachment, and advanced cataracts.
How does glaucoma affect the eye?
When the normal outflow of this aqueous fluid is impaired, the pressure in the eye will increase, causing damage to the optic nerve and the retina. If glaucoma becomes chronic or is left untreated, it can cause permanent damage and result in vision loss.
Can a dog have glaucoma in one eye?
The dog might also exhibit signs not directly related to the eyes , such as loss of appetite, lethargy, and even unresponsiveness. In cases of acute glaucoma, all of these symptoms can occur suddenly, compared to chronic glaucoma that develops more slowly over time. As your pet ages, these signs might occur in one eye and then the other.
Can glaucoma be prevented?
Secondary glaucoma is preventable by maintaining pets’ optimal health, avoiding trauma to their orbital area, and seeking timely treatment for infections (especially those related to the eyes). Primary glaucoma, on the other hand, can’t be prevented because it’s the result of genetics.
Can a dog go blind with glaucoma?
Many dogs with glaucoma will end up blind, even with treatment, but early detection can help them keep their sight for as long as possible. There is no cure for glaucoma, but most cases can be managed with eye drops and medication prescribed by a veterinarian . If your dog has symptoms of glaucoma, be sure to see your veterinarian right away .
How to treat glaucoma in dogs?
Some of the best ways to prevent glaucoma in your dog include: 1 Only purchase dogs from responsible breeders that offer medical paperwork clearing both parents of any hereditary disease 2 Trying your best to avoid pressure to your dogs neck such as making sure their collars are not too tight, as well as using appropriate leashes 3 Reducing stress in your dog’s life 4 Watch your dog’s eyes closely for any changes, especially as they age 5 Make sure your veterinarian performs an eye exam at each yearly physical
Why do dogs get glaucoma?
Glaucoma can be brought on due to inflammation within the eye, as well as other conditions that impact the eye . Some of the most common causes of secondary glaucoma include: Though these are the most common causes of secondary glaucoma in dogs, virtually any damage to the eye can result in increased intraocular pressure.
What is primary glaucoma?
Primary glaucoma refers to the presence of glaucoma in an otherwise healthy dog. This could refer to a dog that is among the breeds that are prone to the disease, or a sudden onset of the disease without any relation to illness or injury. Secondary glaucoma refers to the diagnosis of high eye pressure due to another cause.
What is intraocular pressure?
This space within the eye is called the intraocular space, and the intraocular pressure is the measurement that is checked during an eye examination. Whenever the intraocular pressure is above 25 mmHg, this warrants a concern of glaucoma.
How to tell if your eye is hurting?
Signs of eye pain such as pawing at their eyes, rubbing their eyes on the floor, squirting, and more. Redness of the sclera (the white portion of the eye) Cloudy appearance to the eye. Avoidance of light or squinting in the sunlight. Different sized pupils.
Can glaucoma cause blindness in dogs?
Like we mentioned above, glaucoma in dogs can lead to severe pain and blindness when left untreated. Not only is there a chance of blindness, but your dog also runs the risk of needing the eye removed if the pressure within their eye becomes too high.
How to treat glaucoma in dogs?
Key Points in Canine Glaucoma Therapy 1 The cause of glaucoma (primary vs. secondary) is imperative for an appropriate treatment plan as well as prognosis for the affected and unaffected eye. 2 Medical therapy for primary glaucoma involves carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and prostaglandin analogues. 3 Never prescribe a prostaglandin analogue (i.e., latanoprost) if you cannot guarantee there is no lens luxation. 4 When end stage glaucoma sets in and enucleation is pursued, always submit the globe for histopathology with microscopic description of the iridocorneal angle. The cause of glaucoma can be verified and the prognosis for the other eye determined if primary glaucoma is diagnosed.
What is the anterior iris?
The anterior iris face is lined by a more or less contiguous band of melanocytes (except in blue eyed animals), which can aid in identification of these membranes. In this case, the membrane has reflected onto the peripheral cornea, forming a synechiae, leading to impaired aqueous drainage, increased IOP and glaucoma.
