If you have Barrett’s esophagus and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), your doctor will treat you with acid-suppressing medicines called proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). These medicines can prevent further damage to your esophagus and, in some cases, heal existing damage. All of these medicines are available by prescription.
How does Gerd affect the esophagus?
This may lead to such problems as:
- Esophagitis. Long-term inflammation of the esophagus that can cause ulcers.
- Esophageal stricture. Narrowing of the esophagus that may lead to problems with swallowing.
- Barrett’s esophagus. Development of abnormal cells in the esophagus that may result in esophageal cancer.
How to cure Barrett's esophagus naturally?
Treatment often involves lifestyle modifications and medications. In severe cases, surgery may be required. Dietary changes, such as avoiding foods that cause esophageal irritation and eating smaller meals, can be helpful in treating esophagitis caused by chronic acid reflux.
What are the chances of getting Barrett's esophagus?
Between 10 and 15 percent of people with GERD develop Barrett's esophagus. 4. Obesity-specifically high levels of belly fat-and smoking also increase your chances of developing Barrett's esophagus. Some studies suggest that your genetics, or inherited genes, may play a role in whether or not you develop Barrett's esophagus. What factors decrease a person's chances of developing Barrett's esophagus? Having a Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection may decrease your chances of ...
What is Barrett's esophagus and what are the treatment?
How do doctors treat Barrett’s esophagus?
- Periodic surveillance endoscopy. Your doctor may use upper gastrointestinal endoscopy with a biopsy periodically to watch for signs of cancer development.
- Medicines. ...
- Endoscopic ablative therapies. ...
- Endoscopic mucosal resection. ...
- Surgery. ...

Is Barrett's esophagus and GERD the same?
Barrett's esophagus is a change in your cells lining your esophagus (food tube). It's more common in people with acid reflux (GERD), but can develop without having GERD. Management ranges from monitoring your esophageal lining with endoscopies to treatments to remove damaged tissue.
How long does it take for GERD to turn into Barrett's esophagus?
If you have GERD symptoms for longer than 10 years, you have an increased risk of developing Barrett's esophagus.
Does GERD always cause Barrett's?
Not everyone with GERD develops Barrett's esophagus. And not everyone with Barrett's esophagus has GERD. But long-term GERD is the primary risk factor. Anyone can develop Barrett's esophagus, but white males who have had long-term GERD are more likely than others to develop it.
What is the best treatment for Barrett's esophagus?
Preferred treatments include: Endoscopic resection, which uses an endoscope to remove damaged cells to aid in the detection of dysplasia and cancer. Radiofrequency ablation, which uses heat to remove abnormal esophagus tissue. Radiofrequency ablation may be recommended after endoscopic resection.
What are the four stages of Barrett's esophagus?
The stages, or grades, of Barrett's are: Non-dysplastic, Indefinite, Low grade Dysplasia, and High Grade Dysplasia, which can lead to Intramucosal Carcinoma.
Should I worry if I have Barrett's esophagus?
Barrett's esophagus is associated with an increased risk of developing esophageal cancer. Although the risk of developing esophageal cancer is small, it's important to have regular checkups with careful imaging and extensive biopsies of the esophagus to check for precancerous cells (dysplasia).
How do you prevent Barrett's esophagus from progressing?
Getting plenty of fiber in your daily diet is good for your overall health. Medical research shows that it may also help prevent Barrett's esophagus from worsening and lower your risk of cancer in the esophagus. Add these and other fiber-rich foods to your daily diet: fresh, frozen, and dried fruit.
What foods should you avoid if you have Barrett's esophagus?
Avoiding trigger foods—such as chocolate, coffee, fried foods, peppermint, spicy foods, and carbonated beverages—can help reduce symptoms. These foods increase acid levels in the stomach. Doctors also recommend eating multiple small, frequent meals instead of a few large ones.
How long should you take omeprazole for Barrett's esophagus?
Continuous treatment with omeprazole 20 mg daily for up to 6 years in Barrett's oesophagus.
Can Barrett esophagus be cured?
Having Barrett's esophagus may raise your risk of getting esophageal cancer. There is no cure for Barrett's esophagus. Your care plan will try to stop any more damage by keeping acid reflux out of your esophagus.
What is the survival rate for Barrett's esophagus?
During the 1960s and 1970s, only about 5% of patients survived at least 5 years after being diagnosed. Now, about 20% of patients survive at least 5 years after diagnosis.
Is esophageal ablation painful?
The procedure itself is not usually painful, as the patient is sedated during the procedure. It is, however, common for the patient to feel chest pain and discomfort swallowing for no longer than seven days after the procedure.
What is the treatment for Barrett's esophagus?
Gastroenterologists at Johns Hopkins developed the use of cryoablation therapy, an effective treatment for Barrett's esophagus. Ablation therapy may cause Barrett's esophagus to regress. Medications will be given to suppress your stomach acid. Then, during an endoscopy, thermal injury is administered to the abnormal mucous lining.
What is the name of the doctor who treats Barrett's esophagus?
Doctors at Johns Hopkins are at the forefront of diagnosing and treating Barrett's esophagus. In fact, gastroenterologists at Hopkins pioneered the use of cryoablation, a revolutionary new therapy, to treat Barrett's esophagus.
Why do people with high grade dysplasia need an esophagectomy?
Patients with high-grade dysplasia may need to undergo an esophagectomy (removal of the esophagus) because of the increased risk of cancer.
What is the procedure called when you have a stomach wrap?
During a procedure known as a Nissen fundoplication, your surgeon wraps the upper part of your stomach around the lower esophagus. This enhances the anti-reflux barrier and can provide permanent relief for reflux. Your surgeon may perform this surgery laparoscopically, which means the procedure is less invasive and recovery is faster.
What foods affect peristalsis?
Avoiding foods that affect peristalsis (the muscle movements in your digestive tract), such as coffee, alcohol and acidic liquids
What foods increase acidity in stomach?
Avoiding foods that increase the level of acid in your stomach, including caffeinated beverages
Can you have surgery for reflux?
If you did not find relief from your symptoms from lifestyle changes or drug therapy, then you may be a candidate for surgery. Some patients prefer a surgical approach as an alternative to a lifetime of taking medications. The goal of surgery for reflux disease is to strengthen the anti-reflux barrier.
What is the treatment for Barrett's esophagus?
If you have Barrett’s esophagus and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), your doctor will treat you with acid-suppressing medicines called proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). These medicines can prevent further damage to your esophagus and, in some cases, heal existing damage.
How does Barrett's mucosal resection work?
In endoscopic mucosal resection, your doctor lifts the Barrett’s tissue, injects a solution underneath or applies suction to the tissue, and then cuts the tissue off. The doctor then removes the tissue with an endoscope. Gastroenterologists perform this procedure at certain hospitals and outpatient centers. You will receive local anesthesia to numb your throat and a sedative to help you relax and stay comfortable.
What is the alternative to endoscopic surgery?
Surgery called esophagectomy is an alternative to endoscopic therapies. Many doctors prefer endoscopic therapies because these procedures have fewer complications.
What is endoscopic ablative therapy?
Endoscopic ablative therapies use different techniques to destroy the dysplasia in your esophagus. After the therapies, your body should begin making normal esophageal cells. A doctor, usually a gastroenterologist or surgeon, performs these procedures at certain hospitals and outpatient centers.
What is the procedure to numb your throat?
You will receive local anesthesia to numb your throat and a sedative to help you relax and stay comfortable. Before performing an endoscopic mucosal resection for cancer, your doctor will do an endoscopic ultrasound. Complications can include bleeding or tearing of your esophagus.
How long does it take to recover from esophageal surgery?
The surgery is performed at a hospital. You’ll receive general anesthesia, and you’ll stay in the hospital for 7 to 14 days after the surgery to recover.
Can you have anti-reflux surgery for GERD?
Your doctor may consider anti-reflux surgery if you have GERD symptoms and don’t respond to medicines. However, research has not shown that medicines or surgery for GERD and Barrett’s esophagus lower your chances of developing dysplasia or esophageal adenocarcinoma. .
What is Barrett's esophagus?
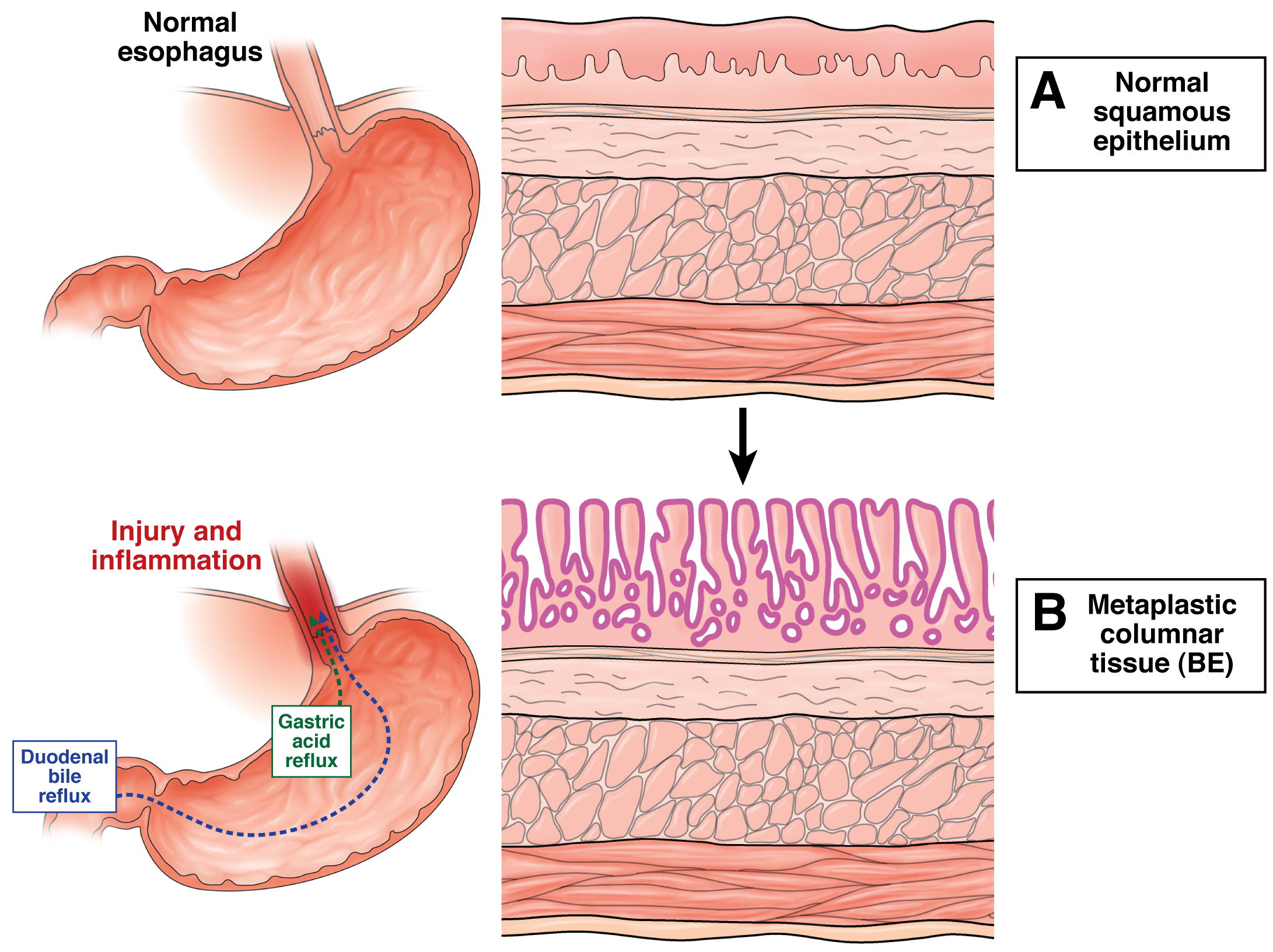
Barrett’s esophagus is a change in the tissue lining your esophagus, the tube in your throat that carries food to your stomach. For reasons no one understands completely, cells in the esophageal lining sometimes become more like intestinal cells. Researchers suspect that having acid reflux or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) ...
How to diagnose Barrett's esophagus?
How is Barrett's esophagus diagnosed? The only way to confirm the diagnosis of Barrett's esophagus is with a test called an upper endoscopy. This involves inserting a small lighted tube (endoscope) through the throat and into the esophagus to look for a change in the lining of the esophagus.
How to keep esophagus healthy?
The best way to keep the lining of your esophagus healthy is to address heartburn or GERD symptoms. People with ongoing, untreated heartburn are much more likely to develop Barrett’s esophagus. Untreated heartburn raises the risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma by 64 times.
What is the procedure to remove a spot on the esophagus?
Surgery: If you have severe dysplasia or esophageal cancer, your provider may recommend an esophagectomy, a surgery to remove all or part of the esophagus.
Why does Barrett's esophagus irritate?
This chronic (ongoing) condition occurs when stomach contents flow backward into the esophagus. Experts believe the acidic liquid irritates the lining of the esophagus, leading to changes in the tissue. But you can also have Barrett’s esophagus without having GERD.
What is the most common procedure for esophageal sloughing?
Radiofrequency ablation: This is the most common procedure. It burns off abnormal tissue using radio waves, which generate heat. Cryotherapy: Healthcare providers use liquid nitrogen to freeze diseased parts of the esophagus lining so it will slough off (shed).
How to treat GERD?
If you have GERD, your healthcare provider may prescribe medications to treat GERD. These medicines decrease stomach acid, which can protect your esophagus from damage. Lifestyle changes, like sleeping slightly inclined and avoiding eating dinner late, often help, too.
What is Barrett's esophagus attributed to?
The development of Barrett's esophagus is most often attributed to long-standing GERD, which may include these signs and symptoms:
What are the factors that increase the risk of Barrett's esophagus?
Factors that increase your risk of Barrett's esophagus include: Family history. Your odds of having Barrett's esophagus increase if you have a family history of Barrett's esophagus or esophageal cancer. Being male. Men are far more likely to develop Barrett's esophagus. Being white.
What is the valve between the esophagus and the stomach called?
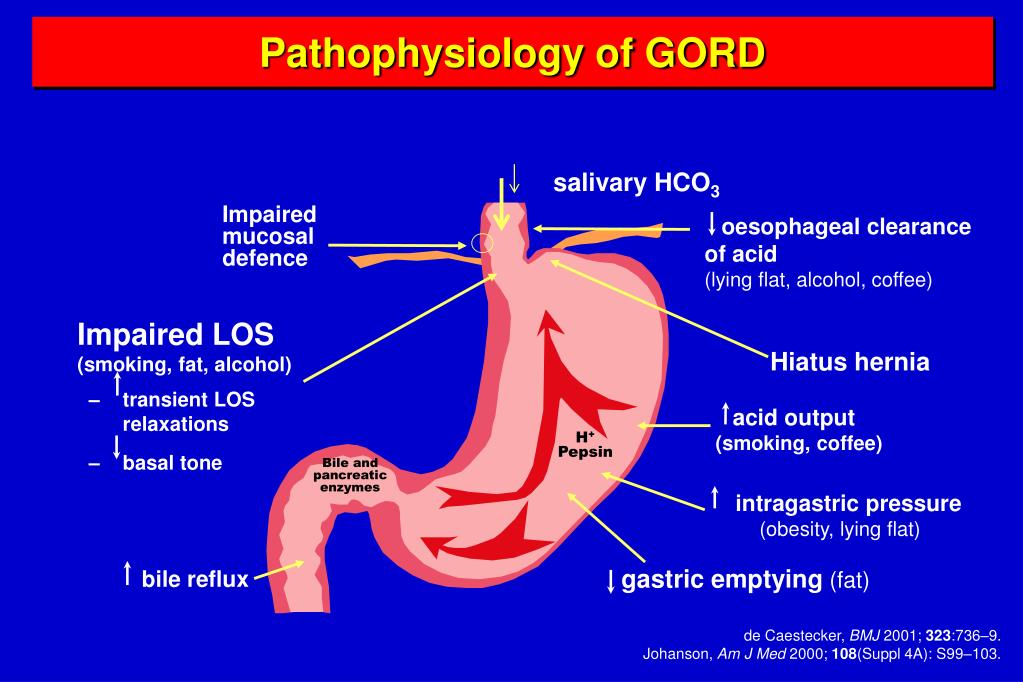
Between the esophagus and the stomach is a critically important valve, the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). Over time, the LES may begin to fail, leading to acid and chemical damage of the esophagus, a condition called gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). GERD is often accompanied by symptoms such as heartburn or regurgitation.
What causes the lining of the esophagus to thicken?
Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the flat pink lining of the swallowing tube that connects the mouth to the stomach (esophagus) becomes damaged by acid reflux, which causes the lining to thicken and become red. Between the esophagus and the stomach is a critically important valve, the lower esophageal sphincter (LES).
How long do you have to wait to see a doctor about Barrett's esophagus?
If you've had trouble with heartburn, regurgitation and acid reflux for more than five years, then you should ask your doctor about your risk of Barrett's esophagus.
Can GERD cause heartburn?
GERD is often accompanied by symptoms such as heartburn or regurgitation. In some people, this GERD may trigger a change in the cells lining the lower esophagus, causing Barrett's esophagus. Barrett's esophagus is associated with an increased risk of developing esophageal cancer. Although the risk of developing esophageal cancer is small, ...
Can Barrett's esophagus cause cancer?
Fortunately, most people with Barrett's esophagus will never develop esophageal cancer. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Barrett's esophagus care at Mayo Clinic.
How old is the average person with Barrett's esophagus?
Age - Barrett's esophagus is most commonly diagnosed in middle-aged and older adults; the average age at diagnosis is 55 years. Children can develop Barrett's esophagus, but rarely before the age of 5 years.
Is it normal to have gas reflux?
Having occasional liquid or gas reflux is considered normal. When it happens frequently, particularly when not trying to belch, and causes other symptoms, it is considered a medical problem or disease and can increase your chances of developing esophageal cancer.
Can GERD cause stricture?
GERD that is untreated over a long period of time can lead to complications, such as an ulcer in the esophagus that could cause bleeding. Another common complication is scar tissue that blocks the movement of swallowed food and drink through the esophagus; this condition is called stricture. Barrett's esophagus, a condition in which the normal esophageal lining is replaced by a new lining, is another complication of GERD.
Can Barrett's esophagus be caused by heartburn?
The exact causes of Barrett's esophagus are not known, but it is thought to be caused in part by the same factors that cause GERD. Although people who do not have heartburn can have Barrett's esophagus, it is found about three to five times more often in people with this condition.
Is Barrett's esophagus common in white people?
Ethnic background - Barrett's esophagus is equally common in white and Hispanic populations and is uncommon in black and Asian populations.
Can GERD be treated?
In most people, GERD symptoms last only a short time and require no treatment at all. More persistent symptoms are often quickly relieved by over-the-counter acid-reducing agents such as antacids.
Can esophageal reflux cause asthma?
Esophageal reflux may also cause certain less common symptoms, such as hoarseness or chronic cough, and sometimes provokes conditions such as asthma. While most patients find that lifestyle modifications and acid-blocking drugs relieve their symptoms, doctors occasionally recommend surgery. Overall, more than 60 million American adults experience GERD, making it one of the most common medical conditions.
What is endoscopic treatment for GERD?
Endoscopic treatment of GERD using a variety of techniques, such as radiofrequency ablation, suturing, and injection, among others, has been reported with variable results. Two interesting abstracts were presented during this year's meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology that addressed this issue.
How common is gastroesophageal reflux disease?
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) symptoms are extremely common in the US adult population, with at least 7% to 8% experiencing GERD on a daily basis; the majority of these patients (ie, between 50% and 75%) will be found to have nonerosive reflux disease (NERD). [1,2]
When was Enteryx recalled?
Please note: The following announcement supercedes any information contained in this article. On September 23, 2005, Boston Scientific issued a recall of all Enteryx Procedure Kits and Enteryx Injector Single Packs from commercial distribution. Serious adverse events, including death, occurred in patients treated with Enteryx, a liquid chemical polymer which is intended to be injected into the lower esophageal sphincter for treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. The serious adverse events involve unrecognized transmural injections of Enteryx into structures surrounding the esophagus.
Does GERD affect sleep?
Patients with GERD symptoms and sleep disturbances can have a significantly decreased QOL, and higher levels of daytime reflux are associated with more sleep complaints. Effective GERD therapy provides a significant improvement in subjective sleep patterns in these patients.
Does GERD cause sleep disturbance?
Sleep disturb ance has been associated with GERD, especially nocturnal reflux, which can lead to arousal from sleep and increased wakefulness. However, data regarding objective and subjective sleep measures in GERD patients are lacking, and effect of treatment on improvement of sleep in not known.
Does acid suppressive therapy help with GERD?
Acid suppressive therapy can reduce asthma exacerbations and improve general well-being of asthma patients with GERD symptoms, and treatment is more effective in patients with difficult-to-control asthma . The results of this study also confirm that high-dose, long-term PPI therapy is required for the management of extraesophageal GERD symptoms.
Is GERD a pulmonary disease?
A variety of extraesophageal symptoms, including pulmonary symptoms of asthma, have been associated with GERD. Epidemiologic studies have shown that pulmonary manifestations are common in patients with both frequent and infrequent GERD. [8] Trials of GERD medical treatment for pulmonary manifestations are largely uncontrolled, and a meta-analysis of 8 randomized controlled trials found some improvement in asthma symptoms and asthma medication use but not in other parameters or pulmonary symptoms. [9]
What percentage of GERD patients develop Barrett's esophagus?
10% of patients with GERD develop Barrett's esophagus, a risk factor for cancer of the esophagus.
What is Barrett's esophagus?
Barrett's esophagus is a complication of chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), primarily in white men . GERD is a disease in which there is reflux of acidic fluid from the stomach into the esophagus (the swallowing tube). GERD most commonly causes heartburn. There are two requirements for the diagnosis of Barrett's esophagus.
How to treat GERD without esophagus?
GERD, with or without the presence of Barrett's esophagus, sometimes is treated by anti-reflux surgery. This operation, called fundoplication, is done to stop the reflux of acid. Fundoplication is not done for Barrett's esophagus itself. The operation involves wrapping the upper stomach (the fundus) around the lower end of the esophagus. The purpose of the wrap is to tighten the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) in order to prevent the reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus. There is no evidence that anti-reflux surgery, or for that matter, acid suppression therapy with drugs, decreases the risk of esophageal cancer among patients with Barrett's. This doesn't mean that the possibility is not affected, but it would take long-term studies to prove that either medical or surgical treatment decreases the risk of cancer, and such studies are not likely to be done.
What type of cells are in Barrett's esophagus?
They pointed out that Barrett's esophagus consisted of a metaplasia in which the normal cells lining the esophagus were replaced by a mixture of gastric and intestinal lining cells. The intestinal-type lining cells also are called specialized columnar cells which include goblet cells.
Why does my esophagus narrow?
A stricture or narrowing is due to scarring (fibrosis) of the esophagus that may cause difficulty in swallowing ( dysphagia ). The dysphagia is sensed as a sticking (stopping) of solid food in the chest (in the esophagus), and liquids when the narrowing is severe.
Why is Barrett's esophagus a protective response?
This transformation, called metaplasia, is believed to be a protective response because the specialized columnar epithelium (epithelium means lining) in Barrett's esophagus is more resistant to injury from acid than the squamous epithelium.
How far up the esophagus is the pink lining?
The diagnosis of Barrett's esophagus rests upon seeing (at endoscopy) a pink esophageal lining that extends a short distance (usually less than 2.5 inches) up the esophagus from the gastroesophageal junction and finding intestinal type cells (goblet cells) on biopsy of the lining.