Which medications are used in the treatment of fat embolism?
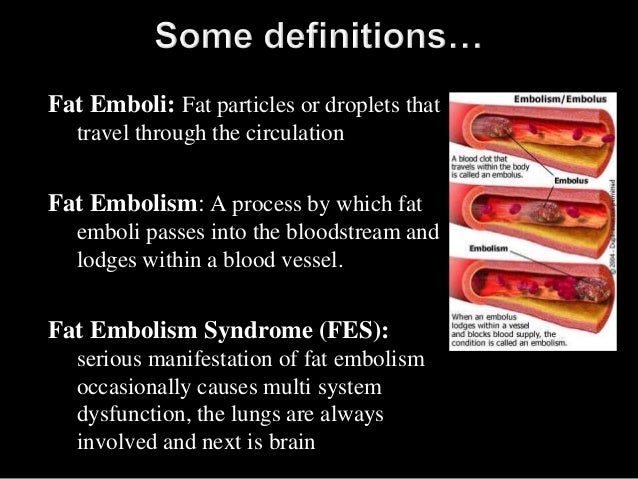
The fat embolism syndrome (FES) is a rare clinical condition in which circulating fat emboli or fat macroglobules lead to multisystem dysfunction. In 1862, Zenker first described this syndrome at autopsy. In 1873, Von Bergmann clinically diagnosed FES for the first time. [ 1] Fat embolism occurs in all patients with long-bone fractures after ...
What are the treatment options for fat embolism?
Mar 08, 2014 · Supportive Medical Care. Specific medical therapy for fat embolism and fat embolism syndrome (FES) does not exist at this time, and supportive measures have not been tested in adequate randomized,...
How to get rid of fat embolism?
Nov 03, 2021 · There is no specific treatment for fat embolism or fat embolism syndrome. Based on experimental studies, an attempt was made to use dextrose infusion to decrease FFA mobilization. Ethanol also was used as an agent to inhibit lipolysis.
What are the risks of a fat embolism?
Treatment of fat embolism syndrome Treatment for FES generally revolves around supportive care. You’ll be admitted to the hospital, most likely to …

Can a fat embolism be treated?
There is no specific treatment for a fat embolism. That is why prevention can reduce the length of hospital stays and lower the risk of complications and death.May 17, 2021
What is the most common cause of fat embolism?
Fat embolism is most commonly associated with trauma. Long bone and pelvic fractures are the most frequent causes, followed by orthopedic surgery—particularly total hip arthroplasty—and multiple traumatic injuries. Soft tissue damage and burns can cause fat embolisms, although far less frequently than fracture.
How long does it take to recover from a fat embolism?
Complete neurological recovery has been reported in many case reports at 3 weeks to 4 months after the initial insult. Our two patients also had delayed, but complete recovery after 5 and 6 months respectively.
Is a fat embolism fatal?
It is usually associated with neurological, hematological and respiratory involvement, the latter being the major cause of death. We present a case of severe fat embolism syndrome occurring 3 hours after a long bone injury, leading to permanent vegetative state and death without any respiratory signs.
What is one of the earliest signs of fat embolism syndrome?
Fat embolism syndrome occurs when fat enters the blood stream (fat embolism) and results in symptoms. Symptoms generally begin within a day. This may include a petechial rash, decreased level of consciousness, and shortness of breath. Other symptoms may include fever and decreased urine output.
What is the difference between fat embolism and pulmonary embolism?
Fat particles enter the circulation and cause damage to capillary beds. While the pulmonary system is most frequently affected, fat embolism can occur in the microcirculation of the brain, skin, eyes, and heart can be involved.
How do you detect a fat embolism?
Your doctor will do an exam and blood tests to look for specific conditions to diagnose fat embolism syndrome. Some of the indicators they look for include: Low oxygen saturation in your blood. Retinal changes, such as evidence of bleeding or fat globules in your eyes.May 20, 2021
How to treat fat embolism syndrome?
Treatment for FES generally revolves around supportive care. You’ll be admitted to the hospital, most likely to the intensive care unit. Your oxygen levels will be monitored and you may be given oxygen, if needed. Some people will need help breathing with mechanical ventilation.
What is a fat embolism?
A fat embolism (FE) is a piece of intravascular fat that lodges within a blood vessel and causes a blockage of blood flow. Fat emboli commonly occur after fractures to the long bones of the lower body, particularly the femur (thighbone), tibia (shinbone), and pelvis. While fat emboli are common and generally resolve on their own, ...
How does the body respond to fat emboli?
It’s thought that the body responds to the fat emboli by secreting chemicals which cause the formation of free fatty acids, glycerol, and other substances which, in turn, damage cells and organs. Regardless of its cause, researchers do know that certain people are more at risk for FES than others. Risk factors include:
Why is FES more likely?
While theoretically this can happen with smaller bones, larger ones have more fat tissue, making FES more likely. Although rare, FES can also be due to other bodily trauma, including joint replacement surgery, and liposuction. FES can even occur when soft tissue is damaged due to burns.
How long does it take for a fat embolism to show?
Symptoms of fat embolism syndrome. Signs of FES generally appear 12 to 72 hours. Trusted Source. after trauma. Symptoms tend to occur throughout the body and include: rapid breathing. shortness of breath. mental confusion. lethargy.
How many people with FES will not recover?
FES is a serious condition. Roughly 10 to 20 percent of people with the syndrome will not recover. However, when treatment is prompt and careful, most people with FES will fully recover with no lasting side effects.
What is the best way to remove fatty acids from the body?
You may also receive intravenous fluids and drugs that will increase blood volume. This helps remove damaging free fatty acids from the body. Your doctor may prescribe steroids and the blood thinner heparin, but these drugs have not been proven to be highly effective. Their use has to be carefully monitored.
What are the effects of fat embolism?
That leads to low blood volume and the risk of shock. IV fluids will help replace your blood volume. . Oxygen. Low blood oxygen saturation is another common effect of fat embolism syndrome. The blockages in some blood vessels keep your blood from circulating well.
What are the symptoms of fat embolism syndrome?
Neurologic changes such as confusion, headache, or seizures. Petechial rash (a red dotted rash often seen in the eyes, under the arms, or on the chest) Racing heart rate. Fever. Jaundice of the skin or eyes. Your doctor will do an exam and blood tests to look for specific conditions to diagnose fat embolism syndrome.
What is the name of the condition where fat particles get into the bloodstream?
What Is Fat Embolism Syndrome? An embolism is anything that blocks a blood vessel and makes it difficult or impossible for your blood to flow normally. One type of embolism is a “fat” embolism. These happen when fat particles get into your bloodstream and create blockages.
How does an embolism affect the body?
But the embolism can become a significant obstruction in certain cases and affect your whole body. Your body mounts an immune system response to try and clear fat cells when they get into your blood. Platelets and fibrin are substances that help with blood clotting and attack the invading fat cells.
What are the substances that help with blood clotting and attack the invading fat cells?
Platelets and fibrin are substances that help with blood clotting and attack the invading fat cells. They can actually increase the size of your obstruction and make it more dangerous. Other causes. There are other less common reasons that fat embolisms develop.
How do you know if you have fat embolism?
Symptoms of Fat Embolism Syndrome. The symptoms of fat embolism syndrome are easy to confuse with other health issues. . You may already be feeling tired or weak if you are recovering from surgery or an injury. You may not recognize these early symptoms of fat embolism syndrome as a cause for concern.
Can you clear a fat embolism?
Your body can clear it out without any help. You will probably not notice any symptoms in this case. . Certain cases of fat embolisms can be very serious. They have the potential to block blood and oxygen from getting to your heart, lungs, or brain. This can cause a severe condition called fat embolism syndrome (FES).
How to keep a person alive with fat embolism?
The aim is to keep the person with fat embolism syndrome alive and well until the fat is re-absorbed. Most people with fat embolism syndrome will have oxygen therapy to make sure all of the tissues of the body get enough oxygen. If the condition is severe, the person might need, mechanical ventilation in the ICU.
What is fat embolism syndrome?
What is a fat embolism syndrome? Fat embolism syndrome is a rare condition that can develop after trauma (injury) or surgery to the legs.
What is the cause of fat embolism?
However, it can also occasionally happen as a result of another type of injury, illness or treatment during which fat droplets have been able to enter the bloodstream.
What tests are done to confirm fat embolism?
To confirm fat embolism syndrome, doctors may do a number of tests such as chest x-rays, blood tests and CT scans. If there are any heart-related symptoms, investigations such as an electrocardiogram (ECG) and echocardiography may also be done.
How long does it take for fat embolism to show?
When someone has fat embolism syndrome, signs and symptoms usually start to show within one to three days. a rash on the skin, usually around the upper torso, and/or small pin-point blood spots in the eye. To confirm fat embolism syndrome, doctors may do a number of tests such as chest x-rays, blood tests and CT scans.
Can fat embolism cause a blockage in the lungs?
In rare cases, these emboli can block small blood vessels in the lungs, skin, or brain, triggering a series of events that lead to the much more serious condition of fat embolism syndrome. Some people with fat embolism syndrome find their lungs can no longer absorb oxygen properly. When this happens, the person affected needs to be admitted ...
How many symptoms are there for a fat embolism?
Possible symptoms can occur throughout the body, and sometimes, fat embolisms are difficult to diagnose. Typically, either two of three major symptoms must be present or one major symptom and at least four minor symptoms. These major symptoms include: Lung impairment. Cerebral (brain) impairment.
What is the difference between embolism and fat embolism?
First off, an embolus is an intravascular mass that gets stuck when traveling through the bloodstream and causes a blockage. A fat embolism is an embolus made up of fatty acids. So basically, it's a glob of fat that gets into the bloodstream and lodged in a blood vessel.
How long does it take for a fat embolism to show?
Symptoms of Fat Embolisms. The time frame for an embolism is anywhere from 12-72 hours after the trauma, and the symptoms vary based on where the blockage occurs. The most problematic embolisms occur in the brain, lungs, or skin, and fat embolisms are fatal approximately 10-20% of the time.
Can broken bones cause embolism?
In fact, most broken bones cause some fat to enter the blood stream, but not all of this fat causes a blockage; closed fractures (the bone doesn't break through the skin) cause more embolisms than open fractures.
What is the diagnosis of a fat embolism?
Diagnosis. specific diagnostic criteria for a fat embolism. Instead, diagnosis depends on a person’s symptoms and laboratory tests, as well as tests to rule out other issues. A doctor may monitor blood oxygen, because drops in blood oxygen may indicate a fat embolism.
What do doctors do for embolism patients?
Instead, doctors provide supportive care to ensure a person can breathe until the embolism clears. A person may need to be on oxygen and, in some cases, may need to use a ventilator. A doctor may also give a person the drug albumin or electrolytes to bind to fat and help maintain normal blood volume.
What is an embolism in the body?
An embolism is a blockage due to an object in the bloodstream that is not supposed to be there. Fat does not usually travel in the bloodstream. However, it can enter it following an injury, especially to the bones.
What is the name of the condition where fat is deposited in the circulatory system?
Pulmonary embolism. Symptoms. Diagnosis. Outlook. Treatment. Prevention. Summary. A fat embolism happens when there is fat in the circulatory system, including the veins or arteries. It usually happens after a bone injury, when fat surrounding the bone and muscle gets into broken blood vessels.
How many people have fat embolism?
In most, though, there are no symptoms, and the embolism goes away on its own. However, about 10% of people develop fat embolism syndrome, which means the embolism produces symptoms.
Why does a blood clot in the leg cause pulmonary embolism?
For example, a person who breaks a leg may suffer a fat embolism, then later develop a blood clot in the leg because they do not move around much due to their injury. The leg blood clot can then cause a pulmonary embolism.
Can a fat embolism cause a pulmonary embolism?
A fat embolism can cause a pulmonary embolism. Even when it does not, a person may experience breathing difficulties similar to those accompanying a blockage in the pulmonary artery. In some cases. Trusted Source. , a pulmonary embolism may also occur at the same time as a fat embolism.
