Ethylene glycol poisoning
| Diagnostic method | Calcium oxalate crystals in the urine, a ... |
| Treatment | Antidote, hemodialysis |
| Medication | Fomepizole, ethanol |
| Frequency | > 5,000 cases per year (US) |
Full Answer
What is the treatment for ethylene glycol (EG) toxicity?
14 rows · Sep 01, 2002 · Fomepizole is a new agent with a specific indication by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for ...
What is the role of ethanol in the treatment of ethylene glycol?
Specific treatment for ethylene glycol poisoning may include the following: Sodium bicarbonate to temporarily correct the metabolic acidosis, as indicated. Fomepizole or ethanol to competitively inhibit metabolism of ethylene glycol to its more toxic metabolites (Baud et al. 1988; Brent et …
What happens if you eat ethylene glycol?
7 rows · Aug 24, 2010 · Ethylene glycol (EG) and methanol are responsible for life-threatening poisonings. Fomepizole, a ...
What is the antidote for ethylene glycol and methanol?
Nov 28, 2021 · If ethylene glycol poisoning is suspected, begin antidotal therapy empirically while awaiting confirmation. This is performed with either fomepizole (4-MP) or ethanol. The latter is usually administered intravenously but may be administered orally in remote settings where emergency hospital care is not immediately available.
See more
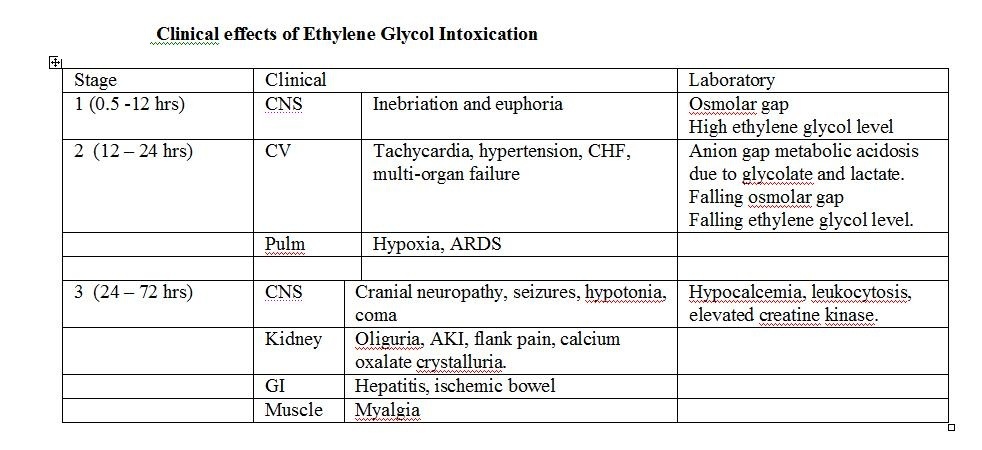
Ethylene glycol poisoning should be suspected in an intoxicated patient with anion gap acidosis, hypocalcemia, urinary crystals, and nontoxic blood alcohol concentration. Fomepizole is a newer agent with a specific indication for the treatment of ethylene glycol poisoning. Metabolic acidosis is resolved within three hours of initiating therapy.
What is the main antidote for ethylene glycol?
What is the best treatment for ethylene glycol toxicity?
What is used as a treatment for ethylene?
How do you reverse ethylene glycol poisoning?
How do you neutralize ethylene glycol?
How do I get rid of ethylene glycol?
How do you treat antifreeze poisoning in dogs?
How do you treat ethylene glycol poisoning in dogs?
What is the antidote for isoniazid?
How ethylene glycol is cleared from the body?
How is propylene glycol toxicity treated?
How long does it take for ethylene glycol to kill you?
3, 5, 9 If untreated, severe ethylene glycol toxicity is usually fatal within 24 to 36 hours. 3, 5 – 8, 10.
What is ethylene glycol?
Ethylene glycol is a solvent found in products ranging from antifreeze fluid and de-icing solutions to carpet and fabric cleaners. 3, 4 According to results from animal studies, 4 the ingested amount of ethylene glycol required to produce toxicity in animals is approximately 1.0 to 1.5 mLper kg, or 100 mL in an adult.
What is fomepizole used for?
Fomepizole is a newer agent with a specific indication for the treatment of ethylene glycol poisoning. Metabolic acidosis is resolved within three hours of initiating therapy. Initiation of fomepizole therapy before the serum creatinine concentration rises can minimize renal impairment. Compared with nervous system and hypoglycemia, ...
Can ethylene glycol cause renal failure?
When treated appropriately, patients have survived much larger ingestions. 4 Ethylene glycol is an important cause of metabolic acidosis of un known source and subsequent acute renal failure. While death and renal failure may occur with delayed diagnosis, death is uncommon in persons who receive prompt diagnosis and treatment.
What is the effect of ethylene glycol on the CNS?
Toxicity results from the depressant effects of ethylene glycol on the central nervous system (CNS). Metabolic acidosis and renal failure are caused by the conversion of ethylene glycol to noxious metabolites.
What is the cause of metabolic acidosis?
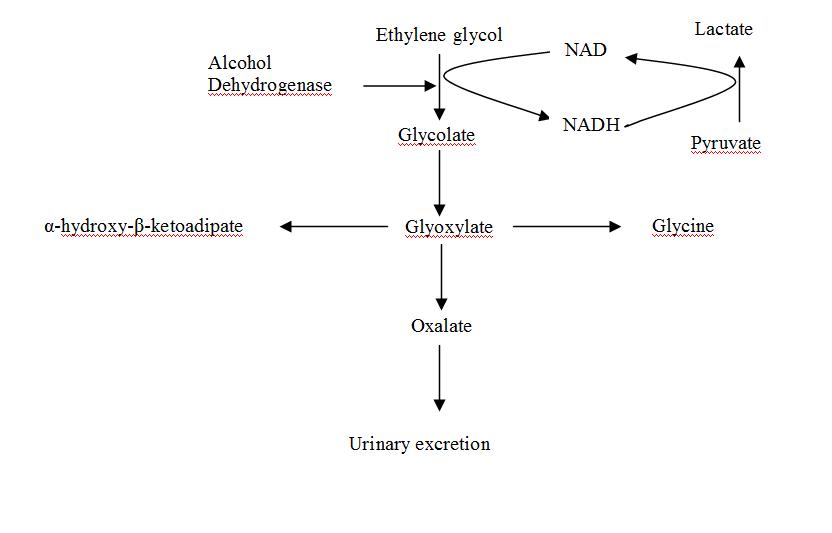
Metabolic acidosis and renal failure are caused by the conversion of ethylene glycol to noxious metabolites. Oxidative reactions convert ethylene glycol to glycoaldehyde, and then to glycolic acid, which is the major cause of metabolic acidosis. 5 – 7 Both of these steps promote the production of lactate from pyruvate.
What is the best treatment for ethylene glycol poisoning?
Fomepizole, an alcohol dehydrogenase enzyme (ADH) antagonist, is the preferred therapy for ethylene glycol poisoning. The American Academy of Clinical Toxicology developed the following criteria for using fomepizole rather than ethanol (Barceloux et al. 1999): Ingestion of multiple substances, resulting in depressed level of consciousness.
Can ethylene glycol be delayed?
Treatment should not be delayed pending results of ethylene glycol serum levels if the patient’s condition or history suggests such poisoning. Treatment advice can be obtained from a regional poison control center or medical specialists such as the following with expertise and experience treating patients exposed to ethylene glycol:
Is thiamine a B complex?
Thiamine and pyridoxine are two water-soluble B-complex vitamins that act as metabolic cofactors in the metabolism of ethylene glycol. The benefits of giving supplemental thiamine (100 mg IV) or pyridoxine (50 mg IV) to patients poisoned with ethylene glycol are unknown. However, both are routinely administered, ...
Do third party sites share information?
Users of third-party sites often share information with the general public, user community, and/or the third-party operating the site. Consequently, you should review the privacy policies of third-party sites before using them and ensure that you understand how your information may be shared and used.
What are the guidelines for ethylene glycol poisoning?
Guidelines on the medical management of ethylene glycol poisoning are available from the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. These include recommendations on prehospital, emergency department, and critical care treatment. [ 1]
What is the treatment for metabolic acidosis?
Hemodialysis. Hemodialysis is used to treat metabolic acidosis or to prevent renal insufficiency. Early in the intoxication, the toxin is present as the parent compound, ethylene glycol. As time passes, toxic metabolites accumulate and the patient develops metabolic acidosis.
Is pyridoxine a cofactor?
Pyridoxine and thiamine are cofactors in ethylene glycol metabolism that promote production of nontoxic metabolites, and are safe adjuncts with no significant disadvantages.They may be administered parenterally. Place symptomatic patients in a monitored setting.
What is Foley catheterization?
Foley catheterization may be considered for patients with altered mental status, to monitor urinary output and to allow serial examination of urine for crystals or fluorescence. If ethylene glycol poisoning is suspected, begin antidotal therapy empirically while awaiting confirmation.
What is the purpose of hemodialysis?
Hemodialysis is used to treat metabolic acidosis or to prevent renal insufficiency. Early in the intoxication, the toxin is present as the parent compound, ethylene glycol. As time passes, toxic metabolites accumulate and the patient develops metabolic acidosis.
What is the number to call for poison control?
The telephone number for certified poison centers anywhere in the United States and Puerto Rico is 1-800-222-1222. If dialysis is considered, consult a nephrologist as early as possible to allow timely treatment of patients with toxic metabolite accumulation.
Where is oxalate deposited?
Eventually, oxalate is deposited in the kidney and elsewhere; renal insufficiency may ensue. Once any of these manifestations occurs, antidotal therapy alone (used to block alcohol dehydrogenase with ethanol or fomepizole) is insufficient to treat the poisoning.
How is ethylene glycol metabolized?
Following ingestion, ethylene glycol is first hepatically metabolised to glycoaldehyde by alcohol dehydrogenase. Glycoaldehyde is then oxidised to glycolic acid, glyoxylic acid and finally oxalic acid.
Is ethylene glycol a solvent?
Ethylene glycol, a common antifreeze, coolant and industrial solvent, is responsible for many instances of accidental and intentional poisoning annually. Following ingestion, ethylene glycol is first hepatically metabolised to glycoaldehyde by alcohol dehydrogenase. Glycoaldehyde is then oxidised to glycolic acid, ...
What is the best treatment for ethylene glycol poisoning?
The antidotes for ethylene glycol poisoning are ethanol and fomepizole. This antidotal treatment forms the mainstay of management of ethylene glycol poisoning. The toxicity of ethylene glycol comes from its metabolism to glycolic acid and oxalic acid.
What are the symptoms of ethylene glycol?
Additionally low calcium concentrations in the blood, overactive muscle reflexes, muscle spasms, QT interval prolongation, and congestive heart failure may occur .
What is the most common source of ethylene glycol?
The most common source of ethylene glycol is automotive antifreeze or radiator coolant, where concentrations are high. Other sources of ethylene glycol include windshield deicing agents, brake fluid, motor oil, developing solutions for hobby photographers, wood stains, solvents, and paints. Some people put antifreeze into their cabin's toilet to prevent it from freezing during the winter, resulting in toxicities when animals drink from the toilet. Small amounts of ethylene glycol may be contained in holiday ornaments such as snow globes.
Is ethylene glycol toxic to humans?
Ethylene glycol has been shown to be toxic to humans and is also toxic to domestic pets such as cats and dogs. A toxic dose requiring medical treatment varies but is considered more than 0.1 mL per kg body weight (mL/kg) of pure substance. That is roughly 16 mL of 50% ethylene glycol for an 80 kg adult and 4 mL for a 20 kg child. Poison control centers often use more than a lick or taste in a child or more than a mouthful in an adult as a dose requiring hospital assessment.
What happens if you drink antifreeze?
Ethylene glycol is a colorless, odorless, sweet liquid, commonly found in antifreeze. It may be drunk accidentally or intentionally in a suicide attempt.
How is serum osmolality measured?
The person' serum osmolality is measured by freezing point depression and then compared with the predicted osmolality based on the person's measured sodium, glucose, blood urea nitrogen, and any ethanol that may have been ingested. The presence of a large osmolal gap supports a diagnosis of ethylene glycol poisoning.
Is antifreeze safe for animals?
Antifreeze products for automotive use containing propylene glycol in place of ethylene glycol are available, and are generally considered safer to use, as it possesses an unpleasant taste in contrast to the perceived "sweet" taste of toxic ethylene glycol-based coolants, and only produces lactic acid in an animal's body, as their muscles do when exercised.
Can ethylene glycol be treated?
All patients with ethylene glycol poisoning should be evaluated and treated without delay. Even patients with no or mild symptoms should undergo appropriate blood and urine tests if they have a history of significant ingestion. Patients requiring ethanol infusions, 4-methylpyrazole, or hemodialysis should be admitted to an intensive care unit.
Can you be discharged for ethylene glycol poisoning?
Patients who have no history suggestive of significant exposure and who have no symptoms or laboratory findings of et hylene glycol poisoning may be discharged with instructions to seek medical care promptly if symptoms develop (see the Ethylene Glycol-Patient Information Sheet below).
What is the synonym for ethylene glycol?
Synonyms include 1,2-dihydroxyethane, 1,2-ethanediol, 2-hydroxyethanol, ethylene alcohol, glycol, glycol alcohol, monoethylene glycol, and ethylene dihydrate. Ethylene glycol is sold under a variety of brand names as automobile radiator antifreeze. It should not be confused with ethylene glycol ethers, which are a different group of chemicals.
Is ethylene glycol a liquid?
Ethylene glycol is a clear, odorless, slightly viscous liquid with a sweet taste. It is combustible and has a low vapor pressure. Ethylene glycol is a very useful industrial compound because of its low freezing point and high boiling point. It is widely available as automotive antifreeze; in that application, it is often mixed with a yellow-green fluorescent.
Is ethylene glycol toxic at room temperature?
Toxic inhalation of ethylene glycol is unlikely at room temperature because of the chemical's low volatility, but can occur when the liquid is heated, agitated, or sprayed. Ethylene glycol is odorless and thus, odor does not provide any warning of hazardous concentrations. Ethylene glycol vapor is lighter than air.
Is ethylene glycol absorbed by the body?
Ethylene glycol is rapidly absorbed following ingestion, which is the predominant route of exposure. Ingestion of ethylene glycol leads to systemic toxicity beginning with CNS effects, followed by cardiopulmonary effects, and finally renal failure.
Can ethylene glycol cause respiratory problems?
Levels higher than 80 ppm produce intolerable respiratory discomfort and cough. Ethylene glycol's CNS effects can cause respiratory depression, and metabolic acidosis can result in hyperventilation and respiratory alkalosis. Aspiration of ethylene glycol following ingestion can result in pulmonary edema.