Can erythroblastosis fetalis be treated during pregnancy?
Erythroblastosis Fetalis can be treated during pregnancy or after the baby is born. Erythroblastosis Fetalis treatment was first identified in 1932 at Boston Children’s Hospital by Dr. Louis Diamond.
How is erythroblastosis fetalis diagnosed?
Erythroblastosis fetalis diagnosis. Ultrasound is a diagnostic imaging technique which uses high-frequency sound waves and a computer to create images of blood vessels, tissues, and organs. Ultrasound is used to view internal organs as they function, and to assess blood flow through various vessels.
What blood type causes erythroblastosis fetalis?
A, B, and O are the 3 major blood types. Erythroblastosis fetalis is most common when the mother's blood type is O and the baby's blood type is A or B. The differences in blood type causes your immune system to react by making antibodies. The antibodies can cross over to your baby through the placenta.
What is the incidence of erythroblastosis fetalis?
The incidence of erythroblastosis fetalis has decreased greatly since the introduction of RhoGAM in the 1960’s. RhoGAM is a shot given to the mother during pregnancy to keep her body from attacking her baby’s body. Every person has a blood type (O, A, B, or AB) and an Rh factor, either positive (Rh+) or negative (Rh-).

What is erythroblastosis fetalis and its treatment?
Erythroblastosis fetalis is a preventable condition. A medication called Rh immunoglobulin (Rhig), also known as RhoGAM, can help prevent Rh sensitization. This medication prevents the pregnant woman from developing Rh-positive antibodies. However, this will not help women who have already undergone Rh sensitization.
How do you treat erythroblastosis?
Injections of a medicine called Rh immune globulin can keep your body from making Rh antibodies. It helps prevent the problems of Rh incompatibility. If treatment is needed for the baby, it can include supplements to help the body to make red blood cells and blood transfusions.
What is the treatment for Rh incompatibility?
Rh incompatibility can be prevented with the use of RhoGAM. Therefore, prevention remains the best treatment. Treatment of an infant who is already affected depends on the severity of the condition. Infants with mild Rh incompatibility may be treated with phototherapy using bilirubin lights.
What is erythroblastosis fetalis What is the cause who is at risk How is it treated?
Erythroblastosis fetalis is hemolytic anemia in the fetus (or neonate, as erythroblastosis neonatorum) caused by transplacental transmission of maternal antibodies to fetal red blood cells. The disorder usually results from incompatibility between maternal and fetal blood groups, often Rho(D) antigens.
Why are RhoGAM injections given?
Getting a RhoGAM shot is the best way to prevent any possible complications from Rh incompatibility. It protects your baby's red blood cells from attack if her blood comes into contact with yours during labor and delivery and helps prevent Rh-related complications from happening in later pregnancies.
When is RhoGAM given?
To offset problems, your doctor can give you a shot of RhoGAM — generic: Rho(D) immune globulin — at about 28 weeks of pregnancy and whenever your blood may mix with your baby's, like during prenatal tests or delivery.
How is a Rh-negative mother treated?
If the mother is RhD negative, she'll be offered injections of anti-D immunoglobulin at certain points in her pregnancy when she may be exposed to the baby's red blood cells. This anti-D immunoglobulin helps to remove the RhD foetal blood cells before they can cause sensitisation.
What is given to Rh-negative mothers?
Special immune globulins, called RhoGAM, are now used to prevent RH incompatibility in mothers who are Rh-negative. If the father of the infant is Rh-positive or if his blood type is not known, the mother is given an injection of RhoGAM during the second trimester.
What happens if mother is Rh-positive and baby is Rh-negative?
If she is ever carrying another Rh-positive child, her Rh antibodies will recognize the Rh proteins on the surface of the baby's blood cells as foreign. Her antibodies will pass into the baby's bloodstream and attack those cells. This can make the baby's red blood cells swell and rupture.
What happens in erythroblastosis fetalis?
erythroblastosis fetalis, also called hemolytic disease of the newborn, type of anemia in which the red blood cells (erythrocytes) of a fetus are destroyed in a maternal immune reaction resulting from a blood group incompatibility between the fetus and its mother.
What is the main cause of erythroblastosis fetalis?
Hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDFN), also known as alloimmune HDFN or erythroblastosis fetalis, is caused by the destruction of red blood cells (RBCs) of the neonate or fetus by maternal immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies.
What happens if mom and baby have different blood types?
If a baby's and mother's blood are incompatible, it can lead to fetal anemia, immune hydrops (erythroblastosis fetalis) and other complications. The most common type of blood type incompatibility is Rh disease (also known as Rh incompatibility). The Rh factor is a protein on the covering of red blood cells.
What is the condition where the mother's blood type isn't compatible with the baby's blood type?
ABO incompatibility. Another type of blood type mismatch that can cause maternal antibodies against her baby’s blood cells is ABO incompatibility. This occurs when the mother’s blood type of A, B, or O isn’t compatible with the baby’s. This condition is almost always less harmful or threatening to the baby than Rh incompatibility.
Why do you give blood transfusions to a baby?
If a baby experiences erythroblastosis fetalis in the womb, they may be given intrauterine blood transfusions to reduce anemia. When the baby’s lungs and heart mature enough for delivery, a doctor may recommend delivering the baby early. After a baby is born, further blood transfusions may be necessary.
How to detect ABO incompatibility?
ABO incompatibility can be detected via a blood test known as a Coombs test . This test, along with a test to determine the baby’s blood type, is performed after the baby is born. It can indicate why the baby may appear jaundiced or anemic. These tests are usually done for all babies whose mothers have type O blood.
What causes erythroblastosis fetalis?
There are two main causes of erythroblastosis fetalis: Rh incompatibility and ABO incompatibility. Both causes are associated with blood type. There are four blood types: In addition, blood can be either Rh positive or Rh negative. For example, if you’re type A and Rh positive, you have A antigens and Rh factor antigens on the surface of your RBCs.
Why is my baby jaundiced after birth?
If your baby is jaundiced after birth, but Rh incompatibility isn’t a concern, the baby may be experiencing problems due to ABO incompatibility. ABO incompatibility occurs most frequently when a mother with an O blood type gives birth to a baby who has an A, B, or AB blood type. Because O blood types may produce both A and B antibodies, the mother’s blood can attack the baby’s. However, these symptoms are generally much milder than a Rh incompatibility. ABO incompatibility can be detected via a blood test known as a Coombs test. This test, along with a test to determine the baby’s blood type, is performed after the baby is born. It can indicate why the baby may appear jaundiced or anemic. These tests are usually done for all babies whose mothers have type O blood.
Why is it bad for a baby to have fluid in the fetus?
This includes spaces in the: This symptom can be harmful because the extra fluid places pressure on the heart and affects its ability to pump.
What are antigens in blood?
Antigens are substances that trigger an immune response in your body. If you have AB negative blood, then you have both A and B antigens without the Rh factor antigen.
What is bilirubin in babies?
Bilirubin is made when RBCs break down. It is usually removed from the body through bowel movements. A high bilirubin level in your baby can be a sign of erythroblastosis fetalis. Your baby may need more blood tests after he or she is born. Amniocentesis is a procedure done during pregnancy.
What is the condition that causes the RBCs to break down?
Erythroblastosis fetalis is a condition that causes your unborn baby's red blood cells (RBCs) to break down. This may cause severe anemia (low RBC count). Anemia makes it difficult for the RBCs in your baby's blood to carry enough oxygen to his or her body. This condition is also called hemolytic disease of the newborn.
What blood type causes erythroblastosis?
Another type happens because you and your baby have different major blood types. A, B, and O are the 3 major blood types. Erythroblastosis fetalis is most common when the mother's blood type is O and ...
Why is rh factor given?
You may be given Rh factor immune globulin if you and your baby have different Rh blood types. This medicine is given to prevent erythroblastosis fetalis. This medicine may be given while you are pregnant and after you give birth.
What are the three blood types?
A, B, and O are the 3 major blood types. Erythroblastosis fetalis is most common when the mother's blood type is O and the baby's blood type is A or B. The differences in blood type causes your immune system to react by making antibodies. The antibodies can cross over to your baby through the placenta.
What blood test is used to check a baby's blood type?
You or your baby may need any of the following tests: Blood tests are used to check your blood type and Rh type, and to look for antibodies. Providers may want to test the blood of the baby's father for ABO and Rh type. Your baby's blood type, RBCs, Rh type, and bilirubin levels may also be checked. Bilirubin is made when RBCs break down.
How does phototherapy work?
After your baby is born: Phototherapy uses light to turn bilirubin into a form that your newborn's body can remove.
What is the name of the disease when a mother has Rh negative blood?
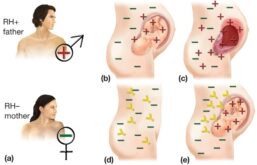
Erythroblastosis Fetalis most frequently occurs when a mother with Rh-negative blood becomes pregnant by a Rh-positive father, resulting in a Rh-positive baby. This type of Erythroblastosis Fetalis is often called Rh disease.
What is erythroblastosis fetalis?
It is a blood disorder that occurs when the blood types of a mother and baby are incompatible. It is also called as hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN).
Is erythroblastosis fetalis preventable?
Erythroblastosis Fetalis is very preventable. Erythroblastosis Fetalis prevention is easy. Today, nearly all women with Rh-negative blood are identified in early pregnancy through blood tests. If a mother is Rh-negative and has not been sensitized, she is usually given a drug called Rh immunoglobulin, or RhoGAM. This specially developed blood product prevents a Rh-negative mother’s antibodies from reacting to her baby’s Rh-positive red blood cells. Mothers are typically given RhoGAM around the 28th week of pregnancy and again within 72 hours of giving birth.
What is the term for a baby with an immune system that attacks the blood cells of the Rh positive baby?
Erythroblastosis fetalis also called immune hydrops or Rh disease during pregnancy, that occurs when Rh-negative mother’s immune system attacks the blood cells of the Rh-positive baby. For example, a mother who has an Rh-negative blood type who is carrying a baby with an Rh-positive blood type may have an immune response ...
What happens to the baby when the mother's antibodies cross the placenta?
As the antibodies destroy the red blood cells, the baby can become sick. This is called erythroblastosis fetalis during pregnancy. In the newborn, the condition is called hemolytic disease of the newborn.
What are the complications of Rh?
Some of the more common complications of Rh disease for the fetus and newborn baby include the following: Anemia (in some cases, the anemia is severe with enlargement of the liver and spleen) Jaundice. This is a yellowing of the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Hydrops fetalis.
What is the condition of a newborn called?
In the newborn, the resulting condition is called hemolytic disease of the new born (HDN). Babies affected by erythroblastosis fetalis are usually in a mother’s second or higher pregnancy, after she has become sensitized with a first baby.
Why do antibodies cross the placenta?
During that pregnancy, the mother’s antibodies cross the placenta to fight the Rh positive cells in the baby’s body. As the antibodies destroy the red blood cells, the baby can become anemic. The anemia can lead to other complications including jaundice, heart failure, and organ enlargement.
What is the term for a newborn's blood cells that are not able to do the work of mature red
The blood cells produced in these other organs are usually immature and are not able to do the work of mature red blood cells and are referred to as erythroblasts . This causes erythroblastosis fetalis. In the newborn, the resulting condition is called hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN).
What does ultrasound show in a fetus?
Ultrasound of the fetus shows enlarged liver, spleen, or heart and fluid buildup in the fetus’s abdomen, around the lungs, or in the scalp. The symptoms of Rh disease may resemble other conditions or medical problems. Always consult your doctor for a diagnosis.
What are the clinical features of erythroblastosis fetalis?
The clinical features of erythroblastosis fetalis result from destruction of fetal RBCs by maternal antibodies against them. They can range from mild anemia and jaundice to fetal death in utero. The major symptoms of erythroblastosis fetalis are briefly discussed below:
What is the term for a newborn with hemolytic disease?
Erythroblastosis fetalis, also called hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN), usually occurs in the fetus, but can also occur in the neonate (erythroblastosis neonatorum). It is a type of anemia in which the red blood cells (RBC) of the fetus are destroyed by maternal antibodies in an immune response targeted against the fetus.
What happens if a mother becomes pregnant again?
If the mother again becomes pregnant with an Rh + fetus, her antibodies can cross the placenta and attack the fetal RBCs, thereby causing severe hemolytic anemia.
Why does a baby die from anemia?
This occurs due to incompatibility of the blood groups of the mother and fetus, which arises when the fetus inherits a certain blood group factor from the father that is absent in the mother. As a result, the baby can suffer from severe anemia, brain damage, or even death.
What is the cause of enlarged liver and/or spleen?
Hemolytic Anemia: This occurs due to the destruction of RBCs. Untreated anemia can cause heart failure, enlarged liver and/or spleen, generalized swelling and respiratory distress. Kernicterus: This occurs due to the deposition of bilirubin in the brain and spinal cord.
What blood groups are incompatibility?
These blood groups include Kell, Duffy, Kidd, Lutheran, Diego, Xg, P, Ee, Cc and MNS.
What is the purpose of light treatment for bilirubin?
The light treatment helps to convert the bilirubin in the baby’s skin to a form that can be excreted by the baby. The baby is usually placed on its back and illuminated from above by a special light. Nowadays, flexible light pads are also available that wrap around the baby.
Erythroblastosis fetalis
is a condition that causes your unborn baby's red blood cells (RBCs) to break down. This may cause severe anemia (low RBC count). Anemia makes it difficult for the RBCs in your baby's blood to carry enough oxygen to his or her body. This condition is also called hemolytic disease of the newborn. Hemolysis means breaking down RBCs.
Treatment
Blood transfusions may be given to your baby through the umbilical cord.
Blood tests
Your baby's bilirubin and RBC levels may need to be checked after he or she leaves the hospital. You may need to bring your baby to your pediatrician's office or a lab to have this done. Your baby's bilirubin level may reach a very high level after he or she leaves the hospital.
Follow up with your baby's doctor as directed
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your child's visits.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.