What can you do to cure endometrial hyperplasia?
5 rows · Dec 01, 2015 · TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR ENDOMETRIAL HYPERPLASIA. Although there is no bona fide treatment for ...
What is endometrial hyperplasia and how is it treated?
Jan 16, 2019 · Endometrial hyperplasia treatment. Treatment options for endometrial hyperplasia depend on what type you have. The most common treatment is progestin. This can be taken in several forms, including pill, shot, vaginal cream, or intrauterine device. Atypical types of endometrial hyperplasia, especially complex, increase your risk of getting cancer.
What is endometrial hyperplasia and how to cure it?
Endometrial hyperplasia responds well to progestin treatments. Atypical endometrial hyperplasia can lead to endometrial or uterine cancer. Your healthcare provider may recommend more frequent direct (hysteroscopic) assessment or a hysterectomy to eliminate cancer risk.
Does endometrial hyperplasia go away after menopause?
Nov 22, 2017 · Progesterone preparations (medroxyprogesterone acetate, levonorgestrel, megestrol acetate) are effective and lead to the disappearance of hyperplasia for the vast majority of women in a period of 3 – 6 months of treatment. Surgical Intervention
What is the treatment for thickened endometrium?
The most common treatment is progestin. This can be taken in several forms, including pill, shot, vaginal cream, or intrauterine device. Atypical types of endometrial hyperplasia, especially complex, increase your risk of getting cancer. If you have these types, you might consider a hysterectomy.Jan 16, 2019
Is endometrial hyperplasia serious?
Endometrial hyperplasia is a condition of the female reproductive system. The lining of the uterus (endometrium) becomes unusually thick because of having too many cells (hyperplasia). It's not cancer, but in certain women, it raises the risk of developing endometrial cancer, a type of uterine cancer.Aug 28, 2020
Should I have a hysterectomy for endometrial hyperplasia?
If you have atypical endometrial hyperplasia, your specialist will probably recommend you have a hysterectomy. This is an operation to remove the womb. This is to prevent you developing a cancer of the lining of the womb.Aug 22, 2017
Can endometrial hyperplasia go away on its own?
Simple Hyperplasia can go away on its own or with hormonal treatment. Endometrial Hyperplasia is caused by either too much estrogen or not enough progesterone.Jun 1, 2020
When should I worry about endometrial thickness?
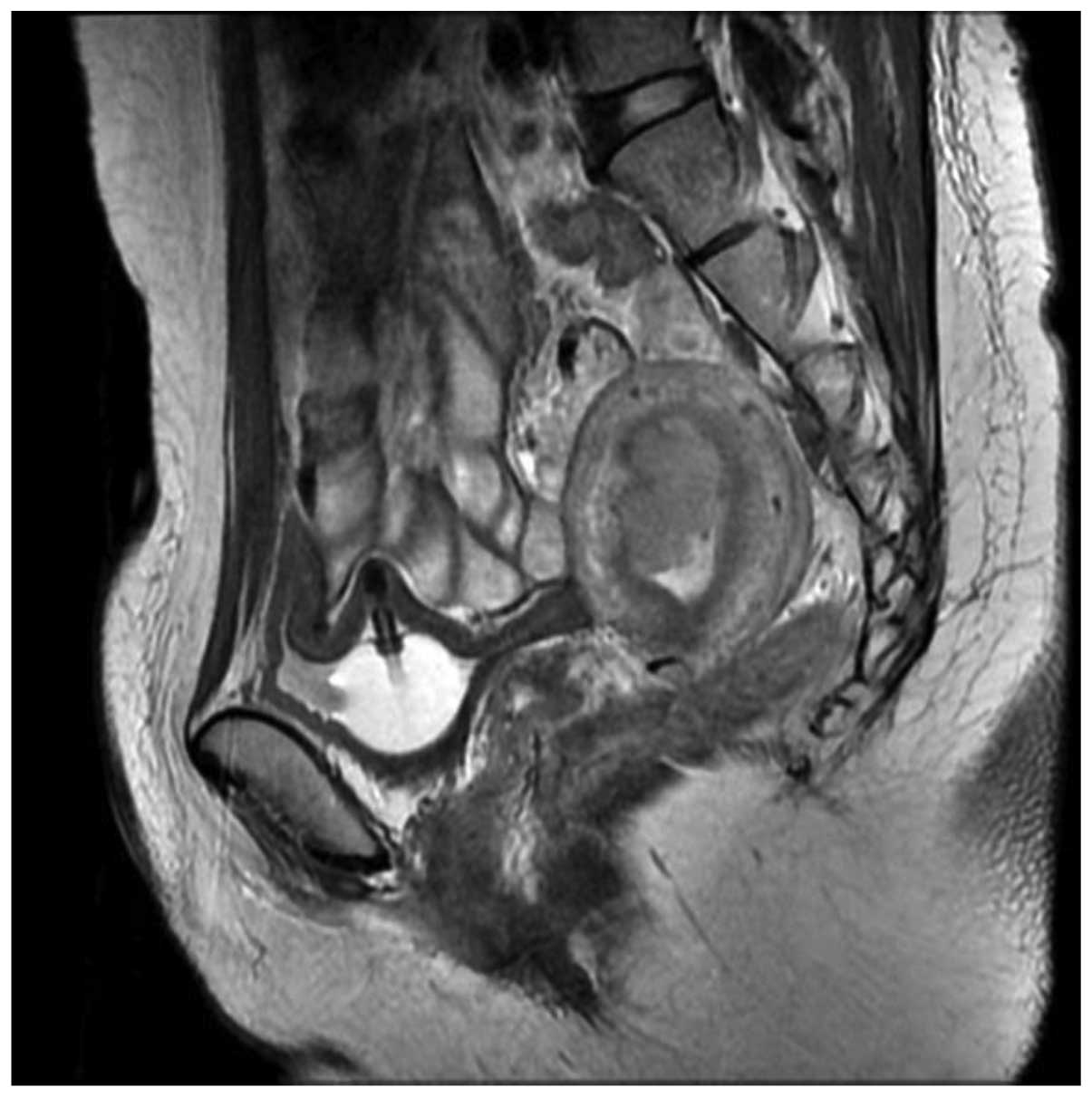
Among postmenopausal women with vaginal bleeding, an endometrial thickness ≤ 5 mm is generally considered normal, while thicknesses > 5 mm are considered abnormal4, 5.Sep 14, 2004
What is the most common cause of endometrial thickening?
The most common cause of endometrial hyperplasia is having too much estrogen and not enough progesterone. That leads to cell overgrowth. There are several reasons you might have a hormonal imbalance: You've reached menopause.Dec 3, 2018
What happens if my endometrial biopsy is abnormal?
Biopsy results may show cell changes linked to hormone levels, or abnormal tissues, such as fibroids or polyps. These can lead to abnormal bleeding.
Is endometrial hyperplasia painful?
Some of the most common symptoms of endometrial hyperplasia include: Abnormal vaginal bleeding between menstrual periods or post-menopause. Abnormally heavy menstrual bleeding. Painful intercourse.
Does an endometrial biopsy hurt?
It may be painful as the tube is passed through your cervix, and you may feel a cramping pain as the sample is being taken from the lining of the womb. It is exactly the same pain as a period, because the pain is caused by the same muscles of the uterus contracting. So for most women this is familiar and bearable.Aug 20, 2018
What is the most common age to get endometrial hyperplasia?
In our study, among women 18–90 years the overall incidence of endometrial hyperplasia was 133 per 100,000 woman-years, was most common in women ages 50–54, and was rarely observed in women under 30. Simple and complex hyperplasia incidences peaked in women ages 50–54.Apr 23, 2009
What are the symptoms of endometrial hyperplasia?
Symptoms of endometrial hyperplasia. The primary symptom of endometrial hyperplasia is abnormal menstrual bleeding. Contact your doctor if you experience: Menstrual bleeding that is heavier or longer lasting than usual. Menstrual cycles (amount of time between periods) that are shorter than 21 days. Menstrual bleeding between menstrual periods.
Why does endometrial hyperplasia occur?
Endometrial hyperplasia is caused by too much estrogen or not enough progesterone. Both of these hormones play roles in the menstrual cycle. Estrogen makes the cells grow, while progesterone signals the shedding of the cells. A hormonal imbalance can produce too many cells or abnormal cells.
What does a transvaginal ultrasound show?
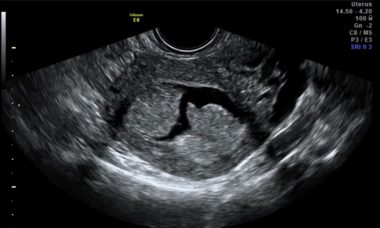
Your doctor can perform an exam and tests to diagnose the main condition. A transvaginal ultrasound measures your endometrium. It uses sound waves to see if the layer is average or too thick. A thick layer can indicate endometrial hyperplasia.
What is the procedure to remove the uterus?
If you have these types, you might consider a hysterectomy. This is a surgery to remove your uterus. Doctors recommend this if you no longer want to become pregnant. There are also a number of more conservative treatments for younger women who do not wish to have a hysterectomy.
Is endometrial hyperplasia a treatable condition?
In most cases, endometrial hyperplasia is very treatable. Work with your doctor to create a treatment plan. If you have a severe type or if the condition is ongoing, you might need to see your doctor more often to monitor any changes.
What is endometrial hyperplasia?
A note from Cleveland Clinic. Endometrial hyperplasia is a condition that causes abnormal uterine bleeding. These symptoms can be uncomfortable and disruptive. Many women find relief through progestin hormone treatments. Women who have atypical endometrial hyperplasia have a higher risk of developing uterine cancer.
What are the risk factors for endometrial hyperplasia?
Other risk factors include: Certain breast cancer treatments ( tamoxifen ). Diabetes. Early age for menstruation or late onset of menopause.
Why is the lining of the uterus thick?
The lining of the uterus (endometrium) becomes unusually thick because of having too many cells (hyperplasia). It’s not cancer, but in certain women, it raises the risk of developing endometrial cancer, a type of uterine cancer. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission.
How many women have uterine cancer?
Endometrial or uterine cancer develops in about 8% of women with untreated simple atypical endometrial hyperplasia. Close to 30% of women with complex atypical endometrial hyperplasia who don’t get treatment develop cancer.
Does obesity increase estrogen levels?
Additionally, obesity contributes to the elevation of estrogen levels . The adipose tissue (fat stores in the abdomen and body) can convert the fat producing hormones to estrogen. This is the how obesity contributes to elevated circulating levels of estrogen and increases the risk of endometrial hyperplasia.
Can you get pregnant after a hysterectomy?
If you’re at increased risk of cancer due to atypical endometrial hyperplasia, your healthcare provider may recommend a hysterectomy to remove the uterus. After a hysterectomy, you won’t be able to get pregnant. Many people see symptoms improve with less invasive progestin treatments. Progestin comes in many forms:
Can endometrial hyperplasia cause cancer?
Atypical endometrial hyperplasia can lead to endometrial or uterine cancer. Your healthcare provider may recommend more frequent direct (hysteroscopic) assessment or a hysterectomy to eliminate cancer risk.
What causes endometrial hyperplasia?
The main cause of endometrial hyperplasia is considered the increase of the estrogen level in the blood , which can be triggered by the following factors of risk: Treatment that involves estrogen, without the opposition of progesterone. The installation of menopause. Polycystic ovary syndrome. Diabetes.
What is hysteroscopy in utero?
Hysteroscopy – allows the examination of the uterus with a special optical system. During the procedure, the doctor may take a small piece of endometrial tissue for a supplementary investigation under the microscope (biopsy) in order to ensure that hyperplasia isn`t cancer.
Can a surgical intervention be done to remove uterus?
In case that the histological examination of the obtained tissue from curettage shows a risk of uterine cancer (), it`s recommended a surgical intervention of removing the uterus. Only a procedure of this type can protect the woman from developing uterine cancer in the future.
Does progesterone affect endometrium?
As already mentioned, progesterone (female sexual hormone, which produces in the second half of the menstrual cycle) has a regulatory influence on the growth of the endometrium. For this reason, progesterone preparations are the main method of treatment for this medical condition.
Does endometrial hyperplasia cause cancer?
Consequences & Complications. As already mentioned, end ometrial hyperplasia increases significantly the risk of uterine cancer. In addition, menstruation is very heavy and abundant, and there may also be severe bleeding if you experience this condition. Heavy, long menstruation and irregular bleeding at women with endometrial hyperplasia may lead ...
How to treat endometrial hyperplasia?
You can reduce your chances of developing endometrial hyperplasia by: 1 Using birth control to regulate your menstrual cycle. 2 Following a healthy diet and exercising regularly as this can help you maintain a moderate weight. It can also reduce your risk of developing diabetes. 3 Avoiding cigarette smoking.
What is the purpose of ultrasound for endometrial hyperplasia?
Endometrial Hyperplasia Ultrasound. We may perform a transvaginal ultrasound exam to measure the density of the endometrium. The endometrial hyperplasia ultrasound uses sound waves to produce images of your uterus. This can help us determine whether you have endometrial hyperplasia if you have a thickened endometrium.
What is atypical hyperplasia?
Atypical hyperplasia: It develops when there is an overgrowth of abnormal cells, and is considered precancerous. According to the American Cancer Society, if a patient has simple atypical hyperplasia, 8% of cases can lead to cancer if left untreated. If they have complex atypical hyperplasia ...
What to do if you have abnormal bleeding?
If you experience abnormal bleeding, we recommend you visit your doctor’s clinic, as they can ask about your medical history, perform diagnostic tests and confirm if you have hyperplasia . You should also contact your doctor if you have vaginal bleeding and have reached menopause.
Does obesity cause endometrial hyperplasia?
Obesity can also increase estrogen levels and your chances of developing endometrial hyperplasia. In the next section, we will discuss the risk factors that can lead to the thickening of the uterus.
What are the two types of endometrial hyperplasia?
There are two main types of endometrial hyperplasia, depending on whether they involve unusual cells, known as atypia. The two types are: Endometrial hyperplasia without atypia. This type doesn’t involve any unusual cells. Atypical endometrial hyperplasia. This type is marked by an overgrowth of unusual cells and is considered precancerous.
How long does it take for endometrial hyperplasia to show?
The following can all be signs of endometrial hyperplasia: Your periods are getting longer and heavier than usual. There are fewer than 21 days from the first day of one period to the first day of the next. You’re experiencing vaginal bleeding even though you’ve reached menopause.
What is the term for the thickening of the endometrium?
Endometrial hyperplasia refers to the thickening of the endometrium. This is the layer of cells that line the inside of your uterus. When your endometrium thickens, it can lead to unusual bleeding.
Is endometrial hyperplasia cancerous?
Endometrial hyperplasia sometimes resolves on its own. And unless you’ve taken hormones, it tends to be slow growing. Most of the time, it isn’t cancerous and responds well to treatment. Follow up is very important to ensure that hyperplasia isn’t progressing into atypical cells.
What hormones are involved in the period?
Your menstrual cycle relies primarily on the hormones estrogen and progesterone. Estrogen helps grow cells on the lining of the uterus. When no pregnancy takes place, a drop in your progesterone level tells your uterus to shed its lining. That gets your period started and the cycle begins again.
Can hyperplasia cause cancer?
Hyperplasia without atypia can eventually develop atypical cells. The main complication is the risk that it will progress to uterine cancer. Atypia is considered precancerous. Various studies. Trusted Source. have estimated the risk of progression from atypical hyperplasia to cancer as high as 52 percent.
What is endometrial hyperplasia?
Endometrial hyperplasia is a disordered proliferation of endometrial glands. It results from the unopposed estrogenic stimulation of the endometrial tissue with a relative deficiency of the counterbalancing effects of progesterone.[1] .
Is estrogen exogenous or endogenous?
This imbalance in the hormonal milieu can be seen in a number of conditions where the cause of estrogen excess is either endogenous or exogenous. The irregular growth of the endometrium results in an abnormal gland-to-stroma ratio and presents in a continuum of the spectrum of changes in the endometrium.
Can estrogen cause endometrial hyperplasia?
Ovarian tumors- granulosa cell tumors. Hormone replacement therapy- estrogen-only therapy can lead to endometrial hyperplasia at even a minimal dose and is contraindicated in women with a uterus. Over the counter/ herbal preparations may have a high amount of estrogen.
Is Lynch syndrome a hereditary cancer?
Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer or Lynch syndrome – women with this condition are at a greatly increased risk of endometrial hyperplasia. [7][8] Epidemiology. Endometrial malignancy is the most common gynecologic cancer in the United States.
Is endometrial hyperplasia a precursor to cancer?
Endometrial hyperplasia is thought to be a precursor to endometrial cancer, and if caught early, prevention to progression fo cancer can be performed.[9] In order to limit the number of cases of endometrial malignancy, it is required to diagnose and treat endometrial hyperplasia appropriately.
Does estrogen affect endometrium?
In the normal menstrual cycle, estrogen leads to proliferative endometrium. After ovulation in the luteal phase, endometrium shows secretory changes under the effect of progesterone. In the follicular phase, normal endometrial tissue shows no glandular crowding, and the ratio of glands to stroma is less than 50%.
Can endometrial cancer be caused by estrogen?
Endometrial hyperplasia is the result of chronic exposure to estrogen along with a relative deficiency of progesterone. The causes of estrogen excess could be endogenous or exogenous.
What are the different types of endometrial hyperplasia?
Types. There are four types of endometrial hyperplasia: complex with atypia – it is most often diagnosed by gynecologists who are evaluating symptoms of abnormal uterine bleeding in premenopausal women. Some doctors call it endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia. It is the most common type of EH. It has about 40 percent important risk ...
How to reduce EH?
daily moderate physical exercise can reduce the risk of EH; in addition, physical exercise reduces stress and enhances cognitive functioning; moderate exercise includes activities like swimming, brisk walking, and mowing the lawn;
What is the term for a thickening of the inner lining of the womb?
Endometrial hyperplasia ( EH) is a thickening of the inner lining of the womb. It is most frequently caused by excess estrogen (a group of hormones which mainly influence the female reproductive tract) without progesterone (a female hormone that regulates the menstrual cycle). The condition has a high risk of malignant transformation and relapses.
Does Frankincense oil help with cancer?
It is used to help decrease the appearance of scars, reduce the signs of aging, prevent dangerous infections, reduce pain, relieve chronic stress, support heightened immunity, and fight disease-causing inflammation. Frankincense essential oil can also reduce tumor growth and cancerous cell production.
Is licorice root a hepatoprotective plant?
The botanical name for licorice root, Glycyrrhiza, comes from “glukos” and “riza.” The compound glycyrrhizic acid, found in the root of this plant, has been shown to be hepatoprotective. Licorice root has an anti-allergenic effect and has an aspirin-like action. Additionally, it is effective in relieving the symptoms of endometrial hyperplasia.
What is EH in medical?
Diagnosis. EH can be established through the following procedures: hysterosalpingography – it is an x-ray examination of a woman’s fallopian tubes and uterus; a detailed medical history evaluation followed by a pelvic and physical exam;
How long does it take for a woman to bleed after menopause?
any bleeding after menopause; menstrual cycles which are shorter than 21 days – counting from the 1st day of the menstrual period to the 1st day of the next menstrual period; bleeding during the menstrual period which is heavier or lasts longer than normal.