Does a pleural effusion have a cure?
13 rows · Jun 22, 2012 · The specific treatment of pleural effusion depends on the etiology. Treatment of the ...
What is the best treatment for malignant pleural effusions?
Jun 05, 2006 · The standard first-line treatments for joint effusion include rest, ice application, immobilization, and a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) like Advil (ibuprofen) or Aleve (naproxen). 17 If the swelling is especially severe, your healthcare provider may want to aspirate the joint to reduce pressure inside the joint.
What are the effective pleural effusion treatment options?
Treatment of pleural effusion includes: Removing excess fluid from the lungs to prevent infection and alleviate pressure. Treating the symptoms. Treating the underlying cause to prevent fluid from reaccumulating. Draining Fluid A thoracentesis can be …
What is the difference between effusion and infiltrate?
Treatments help heal the swelling by addressing the cause. There are several actions you can take at home to help heal your joint effusion. Your swollen joint might be a sign of an injury, infection, arthritis or other condition. It can be unnerving to look at the puffy skin, especially if you don’t know what caused it.
Does effusion go away?
How long does effusion take to heal?
What is the most common cause of effusion?
Which medicine is best for pleural effusion?
| Drug name | Rating |
|---|---|
| Generic name: doxycycline systemic Drug class: tetracyclines, miscellaneous antimalarials For consumers: dosage, interactions, side effects | |
| View information about Doryx MPC Doryx MPC | Rate |
| Generic name: doxycycline systemic For consumers: dosage, interactions, side effects | |
Can fluid around the heart be treated with medication?
Is pericardial effusion serious?
How serious is fluid on the lungs in elderly?
It's fairly common for seniors to suffer from fluid in the lungs, but getting a good prognosis depends on understanding the underlying cause. Most cases are the result of heart problems, which is why acute pulmonary edema has a one-year mortality rate of about 40% for elderly patients.Apr 25, 2019
What color is fluid in the lungs?
How long can you live with non malignant pleural effusion?
Can antibiotics cure pleural effusion?
Can antibiotics help fluid on the lungs?
What happens if pleural effusion is left untreated?
What to do if you have pericardial effusion?
If your pericardial effusion is discovered as a result of a heart attack or other emergency, you won't have time to prepare for your appointment. Otherwise, you'll likely start by seeing your primary care provider. Or you might be referred immediately to a cardiologist.
What test is done to determine if you have pericardial effusion?
If you have signs or symptoms of pericardial effusion, a series of blood and imaging tests will be done to confirm the diagnosis, identify possible causes and determine treatment.
What is the surgical removal of the pericardium?
The surgical removal of all or part of the pericardium (pericardiectomy) is usually reserved for people who have recurring pericardial effusions despite catheter drainage.
How to drain fluid from pericardial space?
Drain the fluid. Your doctor can enter the pericardial space with a needle and then use a small tube (catheter) to drain fluid — a procedure called pericardiocentesis. The doctor uses echocardiography or a type of X-ray imaging called fluoroscopy to guide the catheter to the right position. In most cases, the catheter will be left in place to drain the area for a few days to help prevent the fluid from building up again.
What to do if you don't have tamponade?
If you don't have tamponade or there's no immediate threat of tamponade, your doctor might prescribe an anti-inflammatory drug to reduce inflammation of the pericardium:
What is the procedure to drain the pericardium?
Open-heart surgery. If there's bleeding into the pericardium, especially due to recent heart surgery or other complications, open-heart surgery may be done to drain the pericardium and repair damage. Occasionally, a surgeon may also create a "passage" that allows fluid to drain as necessary into the abdominal cavity, where it can be absorbed.
What to do if anti-inflammatory treatment doesn't work?
If anti-inflammatory treatments don't correct the problem or you have or are likely to have tamponade, your cardiologist may recommend one of the following procedures to drain fluids or prevent fluids from accumulating again. Drain the fluid.
What is an effusion?
Effusion is a sign of joint inflammation, and can be broadly classified as either infectious (septic) or non-infectious (aseptic). Joint effusion caused by infection is called " septic arthritis .". Aseptic joint effusion can be the result of an injury or arthritis.
How to diagnose joint effusion?
Diagnosing a joint effusion may involve a physical exam, imaging tests, and a lab evaluation of the fluid in your joint. 7 In addition, the healthcare provider will also review your medical history, current health, and other symptoms.
What is the term for a condition in which fluid accumulates in or around a joint?
Joint effusion is a condition in which excess fluid accumulates in or around a joint, usually the knee. It is commonly referred to as water on the knee or fluid on the knee.
What are the symptoms of joint effusion?
Depending on what is causing your joint effusion, you could have other symptoms such as: Bruising and bleeding in the joint space (caused by an injury) Fever, chills, malaise, and weakness (if infection is present) Progressive muscle loss (from long-term arthritis, also called arthrogenic muscle inhibition )
How to relieve pain from swollen joints?
Your healthcare provider may want to drain (aspirate) fluid from your swollen joint. This will help reduce pressure and relieve some pain.
Is joint effusion the same as edema?
It is not the same as edema, a different type of swelling caused by inflammation, allergy, heart failure, and other conditions. Read on to learn more about joint effusion, its causes and symptoms, and what treatments are available. Illustration by Emily Roberts, Verywell.
Can fluid be drained?
In many cases, fluid can be drained, and steps taken to address the cause (such as antibiotics for an infection). Regardless of what is causing your joint effusion, there are steps you can take to avoid future episodes and improve your joint health.
What is the best treatment for pleural effusion?
Types of medication used to treat pleural effusion include steroids, anti-inflammatories, diuretics or antibiotics.
How to treat pleural effusion?
Treatment of pleural effusion includes: 1 Removing excess fluid from the lungs to prevent infection and alleviate pressure. 2 Treating the symptoms. 3 Treating the underlying cause to prevent fluid from reaccumulating.
What is the procedure to drain pleural fluid?
Pleurodesis. If your pleural effusion keep recurring, your doctor may recommend a procedure called pleurodesis. After draining the pleural fluid with surgery or chest tube, your doctor will prescribe a medication that intentionally causes inflammation inside the pleural space. This will seal this area shut.
What is a thoracentesis?
A thoracentesis can be used for both diagnosis and treatment. During a thoracentesis procedure, a thin needle is inserted into the chest cavity , and a syringe is used to remove excess fluid. This can also be done using a chest tube (thoracostomy) if a very large amount of fluid is present. The chest tube is made of flexible plastic and is placed between your ribs. A local painkiller can be used to reduce discomfort.
What is a tunneled pleural catheter?
Tunneled Pleural Catheter. If you have recurrent pleural effusion, or fluid that reaccumulates around the lung, your doctor may recommend a tunneled pleural catheter. This outpatient procedure places a thin silicone tube (catheter) between the ribs, into the space filled with fluid around the lungs.
Overview
Joint effusion (a swollen joint) happens when extra fluids flood the tissues around your joint. The fluids make your joint look larger and puffier compared to your other joints. Your bones form joints when two or more of them connect. Your knee, for example, is made up of three bones:
Possible Causes
There are several reasons why your knee or other joints might swell with fluid. The most common reasons include:
Care and Treatment
The cause of your knee joint effusion determines its care and treatment. Often once the cause of the swollen joint gets treated, the swelling goes away. However, not all causes of a knee joint effusion are curable. For many, treatment consists of managing your symptoms instead of eliminating them.
When to Call the Doctor
You should contact emergency services or go to the emergency department if you have the following symptoms:
Frequently Asked Questions
Pain sometimes goes along with a joint effusion (swollen joint). You might feel a slight tenderness or a deep ache. Talk to your healthcare provider about what you can do to relieve both the pain and swelling.
What are home remedies for knee effusion?
Knee sleeves: Help with swelling and are generally safe to use while engaging for a wide range of activities.
What are medical treatment options for knee effusion?
Osteoarthritis: Draining excess fluid from your knee joint can alleviate pressure. Corticosteroid injections may also help treat inflammation.
When is surgery for knee effusion required?
Surgery may be required when other treatments for knee effusion do not work. Your doctor can evaluate the damage to your knee and determine whether surgery is required. Cases that may require surgery include:
Can knee effusion be prevented?
While you can’t always avoid knee trauma, you can take precautions, such as wearing a knee brace to protect your knee joint during physical activity.
Top How Do You Treat a Knee Effusion Related Articles
If you have knee pain from arthritis you might notice symptoms including stiffness and swelling, increased pain and swelling in the morning or after sitting, increased pain after activity, 'locking' or 'sticking' of the knee, and weakness or buckling in the knee.
What is the best treatment for a knee that doesn't respond to treatment?
Joint aspiration to relieve pressure in the joint. Physiotherapy to build the strength of the supportive muscles and improve flexibility. Arthroscopy. If your knee doesn’t respond well to treatment, removal of the Bursa Sack may be needed or even knee replacement surgery for severe cases.
Can stress cause joint effusion?
Anyone can put their knee joint under stress and cause Joint Effusion. However some are more at risk than others. These high-risk groups include: Older people – Your risk grows as you get older. People who regularly play sports that put stress on your joints such as Soccer, Basketball and Wrestling.
How many incisions are needed for pleural effusion?
A minimally-invasive approach that is completed through 1 to 3 small (approximately ½ -inch) incisions in the chest. Also known as thoracoscopic surgery, this procedure is effective in managing pleural effusions that are difficult to drain or recur due to malignancy. Sterile talc or an antibiotic may be inserted at the time of surgery to prevent the recurrence of fluid build-up.
What causes pleural effusion?
Causes of pleural effusion that can be effectively treated or controlled include an infection due to a virus, pneumonia or heart failure. Two factors that must be considered are treatment for associated mechanical problems as well as treatment of the underlying cause of the pleural effusion.
What is the water on the lungs called?
Pleural effusion, sometimes referred to as “water on the lungs,” is the build-up of excess fluid between the layers of the pleura outside the lungs. The pleura are thin membranes that line the lungs and the inside of the chest cavity and act to lubricate and facilitate breathing. Normally, a small amount of fluid is present in the pleura.
Can pleural effusions be treated?
Pleural effusions that cannot be managed through drainage or pleural sclerosis may require surgical treatment.
Can radiation cause pleural effusion?
Certain medications, abdominal surgery and radiation therapy may also cause pleural effusions. Pleural effusion may occur with several types of cancer including lung cancer, breast cancer and lymphoma. In some cases, the fluid itself may be malignant (cancerous), or may be a direct result of chemotherapy.
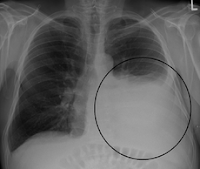
Can pleural effusion be detected on x-ray?
Some patients with pleural effusion have no symptoms, with the condition discovered on a chest x-ray that is performed for another reason. The patient may have unrelated symptoms due to the disease or condition that has caused the effusion.Symptoms of pleural effusion include:
What is pericardial effusion?
Overview. Pericardial effusion is a buildup of fluid in the pericardium, a fibrous sac that surrounds the heart. Normally there is a small amount of fluid between the two thin layers of the pericardium, but certain medical problems like autoimmune diseases, cancer, injuries or infections can cause too much fluid to build up, ...
What is the procedure to drain fluid from the heart?
If the health care team determines that it’s necessary to drain the excess fluid, they may recommend a procedure called pericardiocentesis, which uses a needle and small catheter to drain the fluid. This treatment may need to be repeated if fluid buildup continues.
What is a balloon pericardiotomy?
Percutaneous balloon pericardiotomy is another catheter-guided draining procedure, but it uses a balloon to create a small hole in the pericardium to ease draining.
What is the next step in reducing swelling in knee?
Aspiration is usually the next step when a knee does not reduce on its own, or when the swelling is compromising the joint 1. This is done by a medical professional either at an emergency room or a doctor's office.
How to treat swelling in knee?
The I.C.E. treatment-- (I)ce, (C)ompress, and (E)levate--is often very effective. Get off the injured knee immediately, and apply a cold compress to the joint 1. This can be a bag of ice, or even a bag of frozen vegetables. Place a cloth over the knee and apply the ice to the joint 1. Prop the leg above hip level, and then wrap the ice onto the knee 1.
Can swelling be treated with home remedies?
Sometimes the swelling can become enormous, and immediate treatment is necessary. ** More often, however, the swelling is nominal, and can often be treated with home remedies. This article will give you some options for treating knee effusion.
