How do you treat Stage 1 breast cancer?
Nov 03, 2021 · Treatment for early breast cancer (including invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma) usually involves some combination of surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, HER2-targeted therapy and/or other drug therapies. Surgery and radiation therapy Surgery
How should we treat Stage 0 breast cancer?
Dec 09, 2020 · Systemic adjuvant therapy is routinely used in early-stage breast cancer to reduce the risk of cancer recurrence throughout the body and may consist of chemotherapy or precision cancer medicines used alone or in combination. Systemic therapy can be administered through a vein or delivered orally in the form of a pill.
How soon after diagnosis should breast cancer treatment begin?
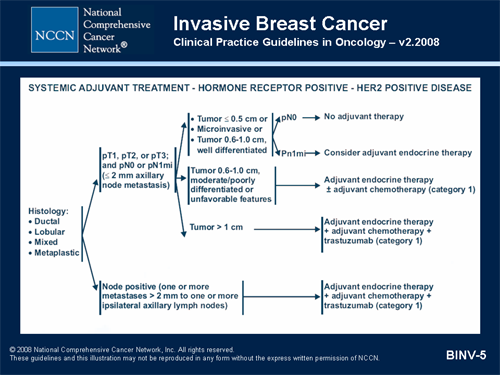
Targeted drug therapy: For women with early-stage breast cancer that is hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative, has cancer in the lymph nodes, and has a high chance of coming back, the targeted drug abemaciclib can be given after surgery along with tamoxifen or an AI. It is a pill typically given for 2 years twice a day.
Is Chemo necessary for early stage breast cancer?
Surgery is standard treatment for this stage. Since the tumor is small, you may have a lumpectomy -- just the tumor and some of the tissue around it are removed. Some women get a mastectomy, in...
What treatment do you have for stage 1 breast cancer?
Surgery is the main treatment for stage I breast cancer. The nearby lymph nodes will also need to be checked, either with a sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) or an axillary lymph node dissection (ALND). Some women can have breast reconstruction at the same time as the surgery to remove the cancer.
Can breast cancer be cured if caught early?
Left untreated, early stage breast cancer can continue to grow and eventually spread to other areas of the body. Early detection and treatment can help prevent the cancer from progressing, and, in many cases, cure or get rid of it entirely.Oct 29, 2021
How long does it take to treat Stage 1 breast cancer?
If you're lucky and catch your condition early on, then your breast cancer treatment will generally last between three and six months. This assumes there is no further growth while you are undergoing treatment. In more advanced cases, you should typically expect a minimum of six months of treatment.Mar 9, 2020
Is early stage breast cancer painful?
The most common symptom of breast cancer is a new lump or mass (although most breast lumps are not cancer). A painless, hard mass that has irregular edges is more likely to be cancer, but breast cancers can be also soft, round, tender, or even painful.Jan 14, 2022
What are the symptoms of stage 1 breast cancer?
Symptoms of stage 1 breast cancer include skin irritation or dimpling, swelling/redness/scaling/flaking/thickening of the nipple or breast skin, change in the size or the shape of the breast, nipple turning inward, change in the appearance of a nipple, nipple discharge that is not breast milk, breast pain, nipple pain, ...Aug 24, 2021
Is chemo needed for stage 1 breast cancer?
Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is not usually offered for stage 1 breast tumours. It may be offered after surgery (called adjuvant therapy) for these tumours if there is a high risk that the cancer will come back (recur). Find out more about the risk of breast cancer recurrence and adjuvant therapy.
How soon after diagnosis of breast cancer is surgery?
Overall, the optional time for surgery after diagnosis is less than 90 days. Lumpectomy, mastectomy and lymph node removal are three common surgical procedures to treat breast cancer.Oct 25, 2021
Can breast cancer be treated without chemo?
A federally funded study has found that many women with the most common type of early stage breast cancer likely do not need chemotherapy after surgery.Jun 4, 2018
What is clinical trial?
Clinical trials are studies that evaluate the effectiveness of new drugs or treatment strategies. Areas of active investigation aimed at improving the treatment of early stage breast cancers include the following:
What is the Oncotype DX test?
The Oncotype DX Breast Recurrence Score test provides a genomic-based, individualized risk assessment for invasive breast cancer that individuals can use to personalize a treatment plan. The test measures the expression of 21 genes: 16 cancer-related genes and five reference genes - in a breast tumor sample after it has been removed by surgery or biopsy to calculate a Recurrence Score that can predict the likely benefit of chemotherapy as well as the risk of distant recurrence in women with ER positive breast cancers. 36,37,42
What is the name of the cell that contains estrogen?
The breasts, uterus and other female organs are composed of cells that contain estrogen receptors. When cells that have estrogen receptors become cancerous, exposure to estrogen increases the cancer’s growth. Cancer cells that have estrogen receptors are referred to as estrogen receptor-positive (ER-positive) cancers.
How does chemotherapy help with cancer?
Chemotherapy is the standard treatment to reduce cancer recurrence risk and prolong survival for the majority of patients who do not have a specific biomarker identified that can be targeted with a precision cancer medicine. A pivotal National Cancer Institute sponsored clinical trial illustrates the benefit of adjuvant chemotherapy treatment of women with node-negative breast cancer. In this study, 536 women were treated with surgical mastectomy alone or with surgical mastectomy plus adjuvant chemotherapy. Ten years following treatment, 73% of women treated with mastectomy and chemotherapy were alive without evidence of cancer recurrence, compared to only 58% of women treated with mastectomy alone. Chemotherapy reduced the risk of recurrence by 37% and the chance of dying from breast cancer by 34%. 21
What is ESBC surgery?
Surgery for ESBC also involves the evaluation of underarm (axillary) lymph nodes in order to determine whether cancer has spread outside the breast and establish the stage of the cancer. Involvement of lymph nodes with cancer is an important determinant of recurrence risk and whether additional systemic treatment is beneficial.
Why is adjuvant therapy used for breast cancer?
Adjuvant therapy is typically administered after surgery and before radiation because this sequence produces superior survival when compared to giving radiation first. It is much easier to treat a local recurrence of cancer than a systemic recurrence and this may explain why patients ...
Does ESBC have a dose response?
Multiple studies and long-term follow-up data confirm the benefit of dose dense therapy for treatment of ESBC. Breast cancer is known to have a “dose response” effect meaning that higher doses of chemotherapy tend to destroy more breast cancer cells than lower doses.
What are the stages of breast cancer?
Most women with breast cancer in stages I to III will get some kind of drug therapy as part of their treatment. This may include: 1 Chemotherapy 2 Hormone therapy (tamoxifen, an aromatase inhibitor, or one followed by the other) 3 HER2 targeted drugs, such as trastuzumab (Herceptin) and pertuzumab (Perjeta) 4 Some combination of these
What is the treatment for BCS?
Women who have BCS are treated with radiation therapy after surgery. Women who have a mastectomy are typically treated with radiation if the cancer is found in the lymph nodes.
How big is a stage 3 breast tumor?
In stage III breast cancer, the tumor is large (more than 5 cm or about 2 inches across) or growing into nearby tissues (the skin over the breast or the muscle underneath), or the cancer has spread to many nearby lymph nodes.
What is the treatment for stage 1 breast cancer?
Local therapy (surgery and radiation therapy) Surgery is the main treatment for stage I breast cancer. These cancers can be treated with either breast-conserving surgery (BCS; sometimes called lumpectomy or partial mastectomy) or mastectomy.
Does radiation help with lymph nodes?
None of the lymph nodes removed contained cancer. The cancer is ER-positive or PR-positive, and hormone therapy is given. Radiation therapy in this set of women still lowers the chance of the cancer coming back, but it has not been shown to help them live longer.
Can stage 3 breast cancer spread to lymph nodes?
If you have inflammatory breast cancer: Stage III cancers also include some inflammatory breast cancers that have not spread beyond near by lymph nodes. Treatment of these cancers can be slightly different from the treatment of other stage III breast cancers.
Can you get radiation therapy before mastectomy?
If you were initially diagnosed with stage II breast cancer and were given treatment such as chemotherapy or hormone therapy before surgery, radiation therapy might be recommended if cancer is found in the lymph nodes at the time of the mastectomy.
What is the best medicine for a tumor?
These drugs include tamoxifen for all women, and anastrozole ( Arimidex ), exemestane ( Aromasin ), and letrozole ( Femara) for postmenopausal women .
Why do women have to have their ovaries removed?
Women who haven't reached menopause may consider having their ovaries removed to stop making hormones that help cancer grow. Targeted therapy is a newer treatment. About 20% of women with breast cancer have too much of a protein known as HER2 that sometimes makes the cancer spread quickly.
What is the best treatment for cancer after surgery?
The treatment is usually given in cycles that allow your body breaks in between. Hormone therapy is a good option after surgery for women who have tumors that use hormones to grow, called hormone receptor -positive cancer. Medication can help prevent tumors from getting hormones.
What is stage 4 breast cancer?
Breast Cancer Recurrence. In this early stage, the cancer either hasn't spread beyond the breast or has spread in a very small amount to a lymph node. You have a number of treatments to choose from. Women usually do well with a combination of treatments.
Can you have a lumpectomy on a breast?
Since the tumor is small, you may have a lumpectomy -- just the tumor and some of the tissue around it are removed. Some women get a mastectomy, in which the whole breast is removed. In either case, the surgeon will likely take out one or more lymph nodes.
Can you get chemo after surgery?
Chemotherapy after surgery can lower the risk of the cancer coming back. The drugs attack cancer cells. Women who had larger tumors removed are more likely to get chemo. You can get chemo several ways. You may take pills or liquids, but often the drugs are put right into your veins.
Can you have breast reconstruction after a mastectomy?
After a mastectomy, you might choose to have breast reconstruction surgery. Radiation therapy can kill cancer cells that were missed. It’s usually given after a lumpectomy. Women with stage I cancer who get a mastectomy sometimes need radiation, too. Chemotherapy after surgery can lower the risk of the cancer coming back.
How many doctors are on the breast cancer team?
Dr. Mayer: There usually are at least three doctors who are on the breast cancer treatment team. This includes a surgeon who does breast surgery, a radiation oncologist who may or may not be necessary on the team, and then a medical oncologist who provides what's called systemic therapy, so therapy that goes throughout the body.
What is the most important thing to know about breast cancer?
Dr. Mayer: One of the most important things to know is what kind of breast cancer is it. The entire treatment plan depends on which category of breast cancer someone's diagnosed with. So sitting down with one of the doctors and going through the pathology report to really understand what is the diagnosis and what type of breast cancer is it.
What is early stage breast cancer?
Early Stage Breast Cancer: An Introduction. Erica L. Mayer, MD, MPH, Member, American Society of Clinical Oncology: Breast cancer is a cancer that originates in the breast. What's important to know about breast cancer is that even though all breast cancer comes out of one part of the body, it's actually three different diseases.
What is the second category of breast cancer?
The second category is the chemotherapy category . Most of the time that's intravenous treatment. And then the third category, what we sometimes think of as the most exciting category in breast cancer, is what we call targeted or biologic therapy.
What is the treatment for cancer?
We have what's called hormone therapies, also known as endocrine therapies. And these are the medicines that block the body's hormones from stimulating cancer cells. This includes pill medicines such as tamoxifen or the aromatase inhibitors. The second category is the chemotherapy category.
Which type of breast cancer has no estrogen receptors?
Therefore, it has none of those three receptors. We call it triple negative breast cancer.
Is breast cancer HER2 positive or triple negative?
This has to do with those categories of breast cancer, hormone receptor positive, HER2 positive, or triple negative and some other features about the growth pattern of the cancer. And then the third category is who is the person with the breast cancer diagnosis.
What is the treatment for stage IV breast cancer?
Treatment for stage IV breast cancer is usually a systemic (drug) therapy.
What is stage 0 breast cancer?
Stage 0 means that the cancer is limited to the inside of the milk duct and is non-invasive. Treatment for this non-invasive breast tumor is often different from the treatment of invasive breast cancer. Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a stage 0 breast tumor. Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) used to be categorized as stage 0, ...
What is the difference between stage 2 and stage 3 breast cancer?
Stage II: These breast cancers are larger than stage I cancers and/or have spread to a few nearby lymph nodes. Stage III: These tumors are larger or are growing into nearby tissues (the skin over the breast or the muscle underneath), or they have spread to many nearby lymph nodes. Treatment of Breast Cancer Stages I-III.
Is lobular carcinoma in situ a stage 0 tumor?
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a stage 0 breast tumor. Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) used to be categorized as stage 0, but this has been changed because it is not cancer. Still, it does indicate a higher risk of breast cancer. See Lobular Carcinoma in Situ (LCIS) for more information.
How big is a stage 1B breast tumor?
The tumor is less than 20 mm (2 cm) in size and there is no spread to lymph nodes. Stage 1B: T1N1miM0. The tumor is less than 20 mm (2 cm) in size and there are micrometastases in a nearby lymph node. Stage 1B: T0N1miM 0. There is no evidence of a primary tumor in the breast but there are micrometastases in a lymph node (usually in the armpit).
What does N mean in cancer?
N = Nodes: All stage 1 cancer is N-0 or N-1mi. N-0 means it has not spread to any lymph nodes. N-1 means that it has spread to lymph nodes nearby. The "mi" means micrometastases, which can only be seen under the microscope. Micrometastases measure between 0.2 millimeters (mm) and 2 mm (0.2 cm) in diameter. 3.
What does M mean in TNM?
M = Metastases: M-0 means that cancer has not metastas ized (spread to other areas of the body). Verywell / Gary Ferster. Thus, using the TNM system, stage 1 cancers are defined as follows: Stage 1 Breast Cancers. Stage 1A: T1N0M0. The tumor is less than 20 mm (2 cm) in size and there is no spread to lymph nodes.
What is stage 1 breast cancer?
Stage 1 breast cancer is the earliest stage of what's considered invasive breast cancer. "Invasive" does not mean that the cancer has invaded other areas of your body. Rather, it simply means that the cells in your tumor have infiltrated the area past what's called the basement membrane. When a tumor first begins, ...
What is the best treatment for stage 1 cancer?
Surgery. Surgery is recommended for the majority of stage 1 cancers. 10 Options include either a lumpectomy or a mastectomy. People choose one over the other for a number of reasons, and it can be a very personal choice. If you choose a lumpectomy, following up with radiation therapy is usually recommended.
What is systemic therapy for stage 1 breast cancer?
With stage 1 breast cancers, the use of systemic therapy is considered adjuvant (add-on) therapy. 9 The goal is to eliminate any cancer cells that may have spread beyond the breast but are too small to be detected. In consultation with your doctor, weigh the pros and cons of each option in relation to your case.
How long does it take for breast cancer to progress?
It is not possible to determine exactly how long it will take for newly diagnosed breast cancer to progress from stage 1 to stage 2. It can happen within months if it is an aggressive high-grade tumor, or it can take longer.
