
Medication
Self-care
Nutrition
What is the best treatment to treat diphtheria?
TreatmentAntibiotics. Antibiotics, such as penicillin or erythromycin, help kill bacteria in the body, clearing up infections. ... An antitoxin. If a doctor suspects diphtheria, he or she will request a medication that counteracts the diphtheria toxin in the body.
What antibiotics treat diphtheria?
Antibiotics. The recommended antibiotics for respiratory or cutaneous diphtheria is either erythromycin or penicillin.
What are the treatment and prevention of diphtheria?
In the United States, there are four vaccines used to prevent diphtheria: DTaP, Tdap, DT, and Td. Each of these vaccines prevents diphtheria and tetanus; DTaP and Tdap also help prevent pertussis (whooping cough). Learn more about diphtheria vaccination, including who should get which vaccine(s).
Is diphtheria easily treated?
Before antibiotics were available, diphtheria was a common illness in young children. Today, the disease is not only treatable but also preventable with a vaccine.
Does penicillin cure diphtheria?
Erythromycin and penicillin are both recommended for the treatment of diphtheria.
What is the main cause of diphtheria?
Diphtheria is a serious infection caused by strains of bacteria called Corynebacterium diphtheriae that make a toxin (poison). It is the toxin that can cause people to get very sick. Diphtheria bacteria spread from person to person, usually through respiratory droplets, like from coughing or sneezing.
How was diphtheria treated in the 1900's?
Beginning in the early 1900s, prophylaxis was attempted with combinations of toxin and antitoxin. Diphtheria toxoid was developed in the early 1920s but was not widely used until the early 1930s. It was incorporated with tetanus toxoid and pertussis vaccine and became routinely used in the 1940s.
How did they treat diphtheria in 1925?
A 1925 outbreak of diphtheria in Nome, Alaska, brought national attention to the country's need for diphtheria antitoxin. With the town snowed in, a sled dog team rushed diphtheria antitoxin 674 miles from Nenana to Nome in five days and quelled the epidemic.
What vaccine is used for diphtheria?
DTaP vaccine — protects against diphtheria, tetanus, and whooping cough (for infants and children) Tdap vaccine — protects against diphtheria, tetanus, and whooping cough (for preteens, teens, and adults) Td vaccine — protects against diphtheria and tetanus (for preteens, teens, and adults)
Is diphtheria a virus or disease?
Diphtheria is a highly contagious and potentially life-threatening bacterial disease caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae. There are two types of diphtheria: respiratory and cutaneous. Respiratory diphtheria involves the nose, throat and tonsils, and cutaneous diphtheria involves the skin.
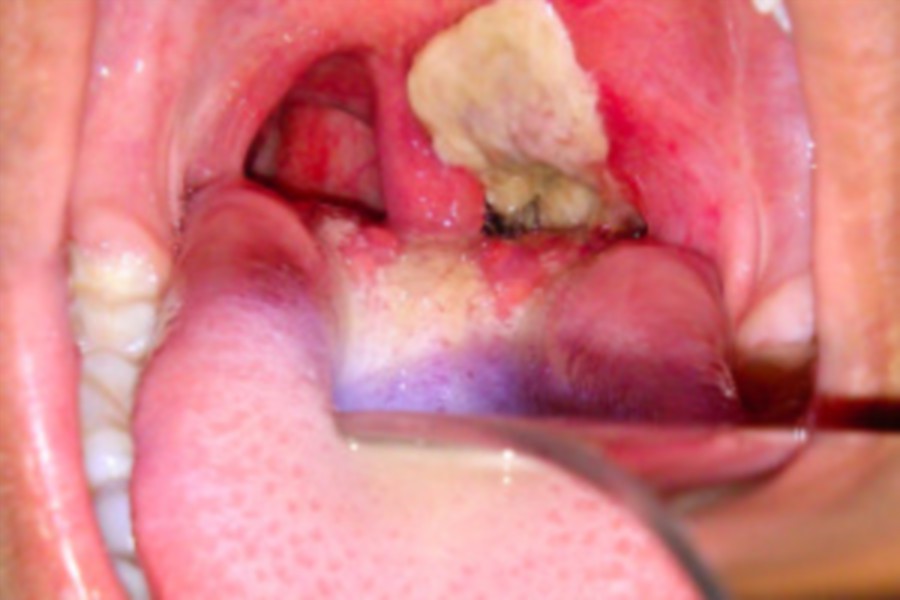
Why is the back of my throat GREY?
Within two to three days, the dead tissue forms a thick, gray coating that can build up in the throat or nose. Medical experts call this thick, gray coating a “pseudomembrane.” It can cover tissues in the nose, tonsils, voice box, and throat, making it very hard to breathe and swallow.
When was the last case of diphtheria in the US?
Diphtheria is rare in the United States, with only two cases reported between 2004 and 2015. In recent years, diphtheria has been in the headlines in three countries where the disease had been virtually eliminated — Venezuela, Yemen and Bangladesh.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Preparing For Your Appointment