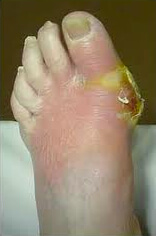
What is the life expectancy of someone with osteomyelitis?
Apr 15, 2017 · TREATMENT OF OSTEOMYELITIS The treatment of DFO remains a hot topic in the field of diabetic foot. Over the years the most debated theories have been surgical or antibiotic therapy as first approach. Nowadays the treatment of osteomyelitis is not completely standardized and evaluated case by case.
How long should osteomyelitis last?
Dec 11, 2008 · Amputation, limited resection, debridement, and antibiotic therapy alone each have a place in the management of diabetic foot osteomyelitis. In cases of extensive bone involvement, deep abscess, necrosis or gangrene, amputation or limited resection is appropriate.
What is the prognosis for osteomyelitis?
Studies have shown that a protocol of 6 weeks of intravenous antibiotics may be appropriate to treat osteomyelitis; however, this is controversial and often not curative. Osteomyelitis is a surgical disease; a subtle balance between medical and surgical therapy is necessary if a potentially curative outcome is to be achieved.
Is there a natural treatment for diabetes?
Feb 11, 2014 · antibiotic therapy was largely considered adjunctive to surgery, but in the past two decades reports appeared of patients with diabetic foot osteomyelitis apparently cured by antibiotic therapy with little or no surgical resection ( 12 ), leading some to reexamine the belief that surgery was almost always needed for this form of chronic …

How serious is a bone infection in a diabetic?
When a foot ulcer becomes infected and the infection spreads to bone, the risk of limb amputation, with its substantial associated morbidity and mortality, is dramatically increased [2]. Furthermore, diabetic foot osteomyelitis often requires surgical therapy and/or prolonged antibiotic therapy.
What is the most effective treatment for osteomyelitis?
The most common treatments for osteomyelitis are surgery to remove portions of bone that are infected or dead, followed by intravenous antibiotics given in the hospital.Nov 14, 2020
Can osteomyelitis be treated without surgery?
Non-Surgical Treatment for Osteomyelitis Non-surgical treatment of osteomyelitis requires a multidisciplinary team approach including primary care, infectious disease specialist care, nutritionist care and wound care. These wounds will require antibiotic therapy for a duration of six to eight weeks.May 6, 2019
Which antibiotic is best for diabetic wound?
Medication Summary Patients with mild infections can be treated in outpatient settings with oral antibiotics that cover skin flora including streptococci and Staphylococcus aureus. Agents such as cephalexin, dicloxacillin, amoxicillin-clavulanate, or clindamycin are effective choices.Jan 16, 2020
What is the drug of choice for osteomyelitis?
For osteomyelitis caused by anaerobic gram-negative bacteria, clindamycin, metronidazole, beta-lactam/beta lactamase inhibitor combinations, or carbapenems are the drugs of choice.
What is the best antibiotic for osteomyelitis?
Oral antibiotics that have been proved to be effective include clindamycin, rifampin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and fluoroquinolones. Clindamycin is given orally after initial intravenous (IV) treatment for 1-2 weeks and has excellent bioavailability.Jul 12, 2020
Does osteomyelitis mean amputation?
Osteomyelitis is usually due to non-healing ulcers and it is associated with high risk of major amputation[13-15].
How long does osteomyelitis take to heal?
You'll usually take antibiotics for 4 to 6 weeks. If you have a severe infection, the course may last up to 12 weeks. It's important to finish a course of antibiotics even if you start to feel better. If the infection is treated quickly (within 3 to 5 days of it starting), it often clears up completely.
Does osteomyelitis require debridement?
The cornerstone of the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis is surgical management (Table 2). This should include an adequate surgical debridement to remove all pathogens along with their biofilms and sequestra (dead bone) that act as a foreign material, reaching down to healthy and viable tissue (Fig.May 31, 2016
Which ointment is best for diabetic wound?
Antibiotics such as Neomycin, Gentamycin, and Mupirocin have good antibacterial coverage when used topically. Silver containing dressings come in different formulations and have very good antibacterial coverage. Silver dressings and polyherbal preparations have shown good results in healing diabetic foot wounds[74].
How can a diabetic wound heal faster?
Tips to help a diabetic wound heal fasterWash your hands with soap and water.Rinse off the wound with warm water.Apply pressure to stop any bleeding.Apply antibiotic cream and cover with a bandage.
Can a diabetic take amoxicillin?
People who have diabetes can take antibiotics. This is important to know, as having diabetes raises the risk of a number of types of infections, including UTIs, skin infections, and infections in the hands and feet.May 3, 2018
How to treat osteomyelitis?
The most common treatments for osteomyelitis are surgery to remove portions of bone that are infected or dead, followed by intravenous antibiotics given in the hospital.
What does it mean when your blood test shows you have osteomyelitis?
Blood tests may reveal elevated levels of white blood cells and other factors that may indicate that your body is fighting an infection. If osteomyelitis is caused by an infection in the blood, tests may reveal which germs are to blame.
How long does it take for a bone biopsy to show infection?
The antibiotics are usually administered through a vein in your arm for about six weeks.
How does an open biopsy work?
In some situations, a surgeon inserts a long needle through your skin and into your bone to take a biopsy. This procedure requires local anesthetics to numb the area where the needle is inserted. X-ray or other imaging scans may be used for guidance.
What is the procedure called when a bone is removed?
In a procedure called debridement, the surgeon removes as much of the diseased bone as possible and takes a small margin of healthy bone to ensure that all the infected areas have been removed. Surrounding tissue that shows signs of infection also may be removed. Restore blood flow to the bone.
Can you amputate a limb?
Amputate the limb. As a last resort, surgeons may amputate the affected limb to stop the infection from spread ing further.
Etiology
Methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus is the most frequently identified pathogen across all types of osteomyelitis, followed by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and methicillin-resistant S. aureus. Hematogenous osteomyelitis is often monomicrobial and can occur from aerobic gram-negative rods or from P.
Clinical Features
The clinical presentation of nonhematogenous osteomyelitis varies and symptoms are often non-specific. Signs and symptoms common to all sub-types may include pain, edema, and erythema. Acute osteomyelitis may present with a more rapid onset of symptoms (development over days) and is more likely to be associated with fever.
Diagnosis
A diagnosis of osteomyelitis should be considered in any patient with acute onset or progressive worsening of musculoskeletal pain accompanied by constitutional symptoms such as fever, malaise, lethargy, and irritability. Constitutional symptoms do not always occur in adults, especially in the setting of immunocompromise.
Treatment
Osteomyelitis treatment requires a multifaceted approach that may include antibiotics, surgical intervention, and other modalities depending on multiple clinical factors, including clinical stage. Clinical staging guides decision-making when choosing specific surgical treatments and limits the need for amputation.
Special Considerations
When selecting treatment strategies for osteomyelitis, several groups of patients require special considerations, such as children and patients who have prosthetic joints, vertebral osteomyelitis, and diabetes. The treatment of these groups is beyond the scope of this article.
What is osteomyelitis of the foot?
Osteomyelitis is a bone infection. It commonly affects the long bones in the legs, causing pain. The prevalence of osteomyelitis in patients with diabetic foot ulcers is about 15%. In patients with diabetic foot infections, it’s 20%.
Osteomyelitis Causes
Osteomyelitis develops due to an open and neglected ulcer that becomes infected. The most common cause is a direct infection of the bone by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus (a type of staph bacteria).
Osteomyelitis Symptoms
Due to the numbness caused by diabetic neuropathy, osteomyelitis can often be completely painless.
How is osteomyelitis diagnosed?
While you may come to the doctor for diabetic foot ulcers or forefoot lesions, it’s always important to run proper diagnostic tests. Because underlying osteomyelitis is present in a large portion of patients with infected foot ulcers, proper testing should always be performed. Undiagnosed osteomyelitis creates a risk of lower extremity amputation.
Treatment of Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis
In the time before antimicrobial therapy, an infected diabetic foot was often treated with major amputation (limb amputation above the knee) to prevent the spread of the infection.
Osteomyelitis Prevention
Proper foot care and examination is the first step in preventing ulceration and infection. Proper foot care includes:
University Foot and Ankle Institute, the Best Choice for Diabetic Foot Treatment
Our doctors and surgeons employ cutting-edge treatment for diabetic foot infection patients. Our aim is to use non-surgical options to heal your wound. But when surgery is indicated we strive to employ the least-invasive approach and get you back to good health.
Who is at risk?
Only 2 out of every 10,000 individuals may get osteomyelitis. This health problem affects adults and children. Various conditions deteriorate immunity. And they increase an individual’s risk for osteomyelitis. These conditions can include:
Causes of Osteomyelitis
Many cases of osteomyelitis occur due to staphylococcus bacteria. These are types of bacteria commonly present in the skin or nose of healthy people. Germs may enter a bone in several ways such as:
Risk Factors of Osteomyelitis
Bones are usually resistant to infection. However, this protection reduces as a person gets older. Other factors that may increase the susceptibility of the bones to osteomyelitis can be:
Prevention of Osteomyelitis
Discussion with the doctor is important in case of an increased risk of infection. He or she discusses different ways of preventing infections from occurring. Lowering the infection risk also helps in reducing the risk of developing osteomyelitis. Usually, exercise precautions to avoid scrapes, cuts, and bites.
Treatment of Osteomyelitis
The most common osteomyelitis treatments are surgery followed by I.V. antibiotics. Surgery removes infected or dead parts of the bone.
FAQs
Osteomyelitis complications can involve bone death. The condition is known as osteonecrosis. Bone infection obstructs the blood circulation within the bone. This leads to bone death.
References
The information included at this site is for educational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional. Because of unique individual needs, the reader should consult their physician to determine the appropriateness of the information for the reader’s situation.
Why is it important to treat osteomyelitis early?
In cases of acute osteomyelitis, early treatment prevents the condition from becoming a chronic problem that requires ongoing treatment . Besides the pain and inconvenience of repeated infections, getting osteomyelitis under control early provides the best chance for recovery.
How to prevent osteomyelitis?
Preventing Osteomyelitis. The best way to prevent osteomyelitis is to keep things clean. If you or your child has a cut, especially a deep cut, wash it completely.
How long does it take for osteomyelitis to develop?
Symptoms of Osteomyelitis. Acute osteomyelitis develops rapidly over a period of seven to 10 days. The symptoms for acute and chronic osteomyelitis are very similar and include: Osteomyelitis in the vertebrae makes itself known through severe back pain, especially at night.
What is the cause of osteomyelitis?
In most cases, a bacteria called Staphylococcus aureus, a type of staph bacteria, causes osteomyelitis. Certain chronic conditions like diabetes may increase your risk for osteomyelitis.
What is the disease of the bone?
Osteomyelitis. By Joanne Barker. Medically Reviewed by Jennifer Robinson, MD on May 11, 2019. Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone, a rare but serious condition. Bones can become infected in a number of ways: Infection in one part of the body may spread through the bloodstream into the bone, or an open fracture or surgery may expose ...
How many people get osteomyelitis?
Only 2 out of every 10,000 people get osteomyelitis. The condition affects children and adults, although in different ways. Certain conditions and behaviors that weaken the immune system increase a person's risk for osteomyelitis, including: Diabetes (most cases of osteomyelitis stem from diabetes) Sickle cell disease.
Can osteomyelitis be chronic?
In adults, osteomyelitis can be either acute or chronic. People with diabetes, HIV, or peripheral vascular disease are more prone to chronic osteomyelitis, which persists or recurs, despite treatment. Whether chronic or acute, osteomyelitis often affects an adult's pelvis or vertebrae of the spine.
