
Medication
· Treatment for diabetic gastroparesis The first, and perhaps most challenging, aspect of treating and managing gastroparesis is what and how you eat. The NIDDK recommends the following guidelines to reduce your symptoms and overall discomfort: Eat a low-fiber diet Eat a low-fat diet Eat small meals (5 or 6 a day) instead of 2 or 3 larger meals
Procedures
Domperidone (Motilium) manages problems in your upper digestive system that are linked to gastroparesis. Erythromycin , an antibiotic, also helps your stomach to move food out.
Therapy
Treating Gastroparesis by stimulating Muscle Activity There are drugs that can be giving that increase the motility of the stomach. These include Propulsid (cisapride), erythromycin, Reglan (metoclopramide), and domperidone. The act to treat gastroparesis by allowing for increased muscle contractions so that stomach emptying can be increased.
Self-care
When you have diabetes, one of the most effective ways to manage gastroparesis symptoms is to vary your eating schedule. Instead of three meals each day, eat six small meals instead. You won’t feel as full since there will be less food in your stomach. The food will also be easier to pass through your body.
Nutrition
Metoclopramide: This medicine increases the movements in your digestive system, helping the food to pass through more quickly and efficiently. This is the only medication in the United States that is FDA approved to treat gastroparesis. However, in some patients it …
How is gastroparesis due to diabetes treated?
How Does Gastroparesis Affect People with Diabetes? limiting fat intake to 25% to 30% of total calories. limiting fiber intake to 15 grams for every 1,000 calories consumed. eating foods like mashed potatoes that are easy to mash with a fork into small particles.
Do we have a cure for gastroparesis?
The initial studies show that oral levosulpiride 25 mg three times a day is superior to placebo, 24 and may be as effective as cisapride in relieving nausea and vomiting in patients with gastroparesis. 25, 26 Further studies are needed to see whether sulpiride is superior to metoclopramide and domperidone for these gastrointestinal indications.
Is Bentyl good for diabetic gastroparesis?
Does gastroparesis have a cure?
How do you control diabetic gastroparesis?
How do doctors treat gastroparesis?eat foods low in fat and fiber.eat five or six small, nutritious meals a day instead of two or three large meals.chew your food thoroughly.eat soft, well-cooked foods.avoid carbonated, or fizzy, beverages.avoid alcohol.More items...
Is diabetic gastroparesis curable?
There is no cure for gastroparesis, but you can lessen symptoms with the following actions: Keep your blood sugar levels as close to their target range as possible. Eat frequent, small meals that are low in fat and fiber. Fat, fiber, and large meals can delay stomach emptying and make symptoms worse.
Can diabetic gastroparesis reversed?
There's no cure for gastroparesis. It's a chronic, long-term condition that can't be reversed.
What is the latest treatment for gastroparesis?
Metoclopramide is currently the only drug approved by the FDA for the treatment of gastroparesis, yet numerous other treatment options are available and utilized by physicians.
What is the life expectancy of a person with gastroparesis?
[8] Diabetic patients with gastroparesis have a normal life expectancy after adjustment for other disorders.
Is gastroparesis serious?
Gastroparesis is generally non-life-threatening, but the complications can be serious. They include malnutrition, dehydration, or a bezoar completely blocking the flow of food out of the stomach.
What is the best medication for gastroparesis?
Medications to treat gastroparesis may include:Medications to stimulate the stomach muscles. These medications include metoclopramide (Reglan) and erythromycin. ... Medications to control nausea and vomiting. Drugs that help ease nausea and vomiting include diphenhydramine (Benadryl, others) and ondansetron (Zofran).
What foods should be avoided with gastroparesis?
What to AvoidRaw and dried fruits (such as apples, berries, coconuts, figs, oranges, and persimmons)Raw vegetables (such as Brussels sprouts, corn, green beans, lettuce, potato skins, and sauerkraut)Whole-grain cereal.Nuts and seeds (including chunky nut butters and popcorn)More items...•
What foods should you avoid with gastroparesis?
Foods to avoid if you have gastroparesiscarbonated beverages.alcohol.beans and legumes.corn.seeds and nuts.broccoli and cauliflower.cheese.heavy cream.More items...
What medications make gastroparesis worse?
Medicines that may delay gastric emptying or make symptoms worse include the following: narcotic pain medicines, such as codeine link , hydrocodone link , morphine link , oxycodone link , and tapentadol link. some antidepressants link , such as amitriptyline link , nortriptyline link , and venlafaxine link.
What are the symptoms of diabetic gastroparesis?
Signs and symptoms of gastroparesis include:Vomiting.Nausea.Abdominal bloating.Abdominal pain.A feeling of fullness after eating just a few bites.Vomiting undigested food eaten a few hours earlier.Acid reflux.Changes in blood sugar levels.More items...•
Do you poop with gastroparesis?
The delayed stomach emptying and reduced digestive motility associated with gastroparesis can have a significant impact on bowel function. Just as changes in bowel motility can lead to things like diarrhea and constipation, so also changes in stomach motility can cause a number of symptoms: nausea. vomiting.
Can diabetes cause gastric emptying?
The severity of DGP symptoms does not always correlate with the rate of gastric emptying.
What is the first line of treatment for DGP?
The first-line medical therapy for patients with DGP is generally a combination of an antiemetic agent and a promotility drug (Table 1). Unfortunately, data from adequately powered clinical trials in patients with gastroparesis are limited, and no study has adequately stratified patients by etiologic subtypes.
What is the cause of bloating and nausea?
Gastroparesis, or chronic delayed gastric emptying without mechanical obstruction, affects about 40% of patients with type 1 diabetes and up to 30% of patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetic gastroparesis (DGP) typically causes nausea, vomiting, early satiety, bloating, and postprandial fullness. These symptoms can be extremely troubling ...
How many people have GERD?
GERD affects 14% of all Americans, yet the overall prevalence of GERD symptoms in diabetic patients is twice that (30%) of people without diabetes.9Neuropathy appears to play a key role. Heartburn has been identified in 42% of patients with neuropathy compared to 24% of patients without neuropathy.
What is the best medicine for gastroparesis?
Medications to treat gastroparesis may include: Medications to stimulate the stomach muscles. These medications include metoclopramide (Reglan) and erythromycin. Metoclopramide has a risk of serious side effects. Erythromycin may lose its effectiveness over time, and can cause side effects, such as diarrhea.
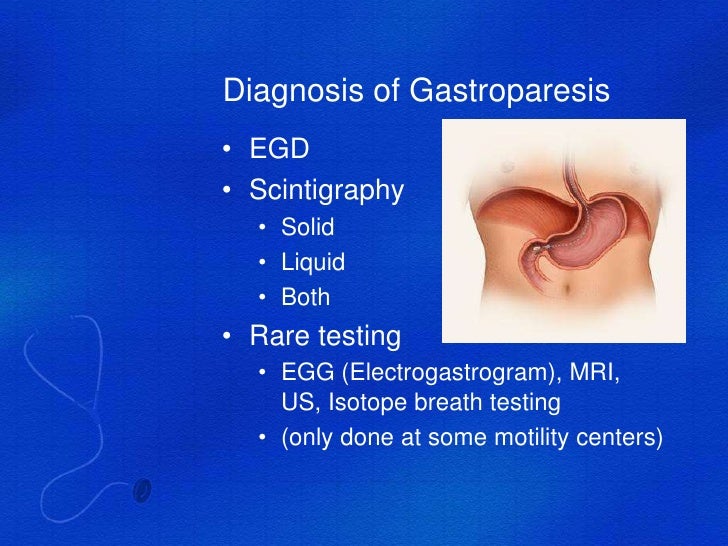
What is the most important test for gastroparesis?
Scintigraphy. This is the most important test used in making a diagnosis of gastroparesis. It involves eating a light meal, such as eggs and toast, that contains a small amount of radioactive material. A scanner that detects the movement of the radioactive material is placed over your abdomen to monitor the rate at which food leaves your stomach.
How to get rid of bezoars?
Chew food thoroughly. Eat well-cooked fruits and vegetables rather than raw fruits and vegetables. Avoid fibrous fruits and vegetables, such as oranges and broccoli, which may cause bezoars. Choose mostly low-fat foods, but if you can tolerate fat, add small servings of fatty foods to your diet.
How to get rid of a swollen intestine?
Exercise gently after you eat, such as going for a walk. Avoid carbonated drinks, alcohol and smoking. Try to avoid lying down for two hours after a meal.
What is the best medication for nausea and vomiting?
Medications to control nausea and vomiting. Drugs that help ease nausea and vomiting include diphenhydramine ( Benadryl, others) and ondansetron (Zofran). Prochlorperazine (Compro) is used if nausea and vomiting persist.
Where do feeding tubes go?
Feeding tubes can be passed through your nose or mouth or directly into your small intestine through your skin . The tube is usually temporary and is only used when gastroparesis is severe or when blood sugar levels can't be controlled by any other method.
What is gastric electrical stimulation?
In gastric electrical stimulation, a surgically implanted device provides electrical stimulation to the stomach muscles to move food more efficiently. Study results have been mixed. However, the device seems to be most helpful for people with diabetic gastroparesis.
How to treat gastroparesis?
The NIDDK recommends the following guidelines to reduce your symptoms and overall discomfort: Eat a low-fiber diet. Eat a low-fat diet. Eat small meals (5 or 6 a day) instead of 2 or 3 larger meals.
Can diabetes cause gastroparesis?
Gastroparesis in people with diabetes despite healthy blood sugar levels. While it’s usually associated with high blood sugar levels, diabetic gastroparesis can sometimes develop even if your HbA1c is in a healthy range and blood sugars are in your goal range. Generally, a person who develops complications of diabetes despite healthy blood sugar ...
How many people with diabetes have gastroparesis?
It’s estimated that up to 50% of people living with diabetes develop some level of gastroparesis during their lifetime, but the symptoms can vary a lot from person to person and ...
Is gastroparesis a complication?
The symptoms of gastroparesis are much more complicated than straight-forward digestion troubles. And like any complication in diabetes, it develops gradually which means the earlier signs and symptoms may go unnoticed until they are severe enough and genuinely disrupting your overall wellbeing.
What happens if you don't digest food?
When your body isn’t able to properly digest food, a variety of complications can develop–even before you’ve been properly diagnosed with gastroparesis . Dehydration due to frequent vomiting. Malnutrition due to poor absorption of nutrients in the food you eat. Difficulty managing your blood sugar levels after eating .
How long does it take for a stomach to empty after eating?
A healthy stomach will empty completely if it’s been at least 12 hours since eating food. If your X-ray still shows remnants or food, that is a very clear indication that your stomach is not digesting and emptying properly. However, an empty stomach doesn’t necessarily mean you don’t have gastroparesis.
How long does it take for a breath sample to come out of your stomach after eating?
Your doctor will then get a sample of your breath about 4 hours after eating to see how much of the substance is still present. This will reveal how quickly or slowly your stomach is digesting and emptying its contents.
What is the best medicine for gastroparesis?
For some people with gastroparesis, medications can help: Dimenhydrinate ( Dramamine ), an over-the-counter antihistamine, helps prevent nausea and vomiting. Domperidone ( Motilium) manages problems in your upper digestive system that are linked to gastroparesis.
How to control gastroparesis?
Diet Changes. When you have diabetes, one of the best ways to help control the symptoms of gastroparesis is to vary when and how you eat. Instead of three times a day, you can have six small meals. You'll have less food in your stomach, so you won't feel as full. It'll be easier for the food to leave your system, too.
Is gastroparesis bad for you?
It can make you feel queasy and vomit. It's also bad for your blood sugar levels. Although it's more common in people with type 1 diabetes, people with type 2 can also get it. Most people with gastroparesis have had diabetes for at least 10 years and also have other complications related to the disease.
What happens when you have diabetes?
When it's damaged, your digestion slows down and food stays in your body longer than it should. This is a condition called gastroparesis. It can make you feel queasy and vomit.
What happens if you eat too much food in your stomach?
Food that stays in your stomach too long can spoil and lead to the growth of bacteria. Undigested food can harden and form a lump called a bezoar. It can block your stomach and keep what you eat from moving into the small intestine. Gastroparesis can make it hard to control diabetes.
What is the tube called that shows the lining of the stomach?
Upper endoscopy: Your doctor will pass a thin tube (called an endoscope ) down your throat to view the lining of your stomach. Stomach or small intestine biopsy: Your doctor may need to take a small sample of tissue to confirm the diagnosis. Treatment.
How does diabetes affect the body?
Over time, diabetes can affect many parts of your body. One of those is the vagus nerve, which controls how quickly your stomach empties. When it's damaged , your digestion slows down and food stays in your body longer than it should.
How to treat gastroparesis?
The main goals of the treatment of gastroparesis include the following: 1 To allow for maximal nutrition. 2 To enhance muscle activity inside the stomach so that the food can be ground properly and then emptied from the stomach into the duodenum. 3 To relieve the typical symptoms of gastroparesis, including abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. 4 To control the underlying medical conditions that make gastroparesis worse. 5 To provide the diabetic patient with a diet that includes food that can be more easily digested and emptied through the pylorus into the duodenum.
What is the best medicine for gastroparesis?
Sometimes serotonin blockers like Zofran, the scopolamine patch, and Marinol (medial marijuana) are used to treat gastroparesis.
What drugs can increase stomach motility?
There are drugs that can be giving that increase the motility of the stomach. These include Propulsid (cisapride), erythromycin, Reglan (metoclopramide), and domperidone. The act to treat gastroparesis by allowing for increased muscle contractions so that stomach emptying can be increased. Zelnorm (tegaserod) is usually used for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome but has also been found to improve gastric emptying.
Dietary Changes
Many patients who suffer from gastroparesis are not absorbing enough nutrition. Dietary changes can relieve symptoms while maintaining proper nutrition. Dietary modifications include:
Medication
There are a number of medications available to treat gastroparesis. Your doctor will discuss with you the benefits and risks of each one before deciding on a medication regimen.
Endoscopic Therapy
If dietary changes and medication did not improve your symptoms, your doctor may perform an endoscopic procedure.
Experimental Therapies
Doctors at Johns Hopkins are at the forefront of novel therapies for patients with gastroparesis. In fact, we are the only health care center in Maryland to offer gastric pacing, a new approach to treating gastroparesis.
Is gastroparesis common in diabetes?
In gastrointestinal (GI) practice, gastroparesis is common among patients with diabetes mellitus, and is reported to occur in 30–50% of the patients.5Another large group comprises patients with idiopathic gastroparesis in whom no underlying cause of the disorder can be found.
What are the symptoms of gastroparesis?
A wide range of dyspeptic symptoms are common in patients with gastroparesis—for example, nausea, vomiting, upper abdominal pain, abdominal distension and bloating. The individual symptoms have, in general, a low specificity to predict delayed emptying.
What is a macrolide?
Macrolides are a group of substances, some of which have antibiotic properties and/or motilin receptor stimulation action in the GI tract, and thereby exert prokinetic effects. The first macrolide clinically explored was erythromycin, which, in early experiments, showed motility‐stimulating properties in dogs.
How long before meals can you take erythromycin?
If the patient responds favourably, treatment is then continued with erythromycin suspension given orally in due time, preferably 30–45 min before meals.
What is sulpiride used for?
Sulpiride is a dopamine blocker used for some psychotic and other psychiatric disorders. This drug has prokinetic properties, but a pharmacological profile that is somewhat different from metoclopramide and domperidone, and has been studied in patients with dyspeptic symptoms.
What is the term for a weakness of movement?
The term “gastroparesis” is a Greek word that means “a weakness of movement”. In this article, some basic facts about gastroparesis are briefly mentioned before aspects on therapy are discussed.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Specialist to consult
Alternative Medicine
Preparing For Your Appointment