Stylecraze.com
1. Green Tea...
2. Grape Seed Extract...
3. Juniper Oil...
4. Olive Leaf Extract...
5. Cranberry Juice...
6. Celery Seed Extract...
7. Horse Chestnut Seed Extract...
8. Pineapple Juice...
Learn More...Top10homeremedies.com
1. Apple Cider Vinegar...
2. Epsom Salt Bath...
3. Tea Tree Oil...
4. Massage...
5. Parsley...
6. Dandelion...
7. Coriander Seeds...
8. Flaxseeds...
Learn More...Homeremedyshop.com
1. Flaxseeds...
2. Lower Salt Intake...
3. Exercise...
4. Potassium...
5. Apple Cider Vinegar...
6. Elevating Limbs...
7. Tea Tree Oil...
8. Massage...
Learn More...Tinyqualityhomes.org
1. Apple Cider Vinegar...
2. Grape Seed Extract...
3. Nettle Tea...
4. Juniper Oil...
5. Cranberry Juice...
6. Horse Chestnut Seed Extract...
7. Pineapple Juice...
8. Crushed Flax Seeds...
Learn More...What are the treatments for bone marrow edema?
Bone marrow edema is seen on MRI with a reduced density of the bone, or bone mineral density. According to Osteoporosis International, current available treatments are "limited and ineffective." Treatment is usually rest and physiotherapy. In difficult cases, a type of surgery called core decompression is used.
What causes bone marrow edema?
Bone marrow edema causes. This can occur due to physical activity such as running, competitive dancing, or weightlifting. The fractures are characterized by bone edema and fracture lines. Arthritis. Bone edemas are relatively common in those who have both inflammatory and noninflammatory arthritis.
Can bone marrow edema go away on its own?
Bone marrow edema can be painful, but there are treatments for it. In some cases, it goes away on its own. Bone marrow edema can happen for many reasons, including: Injury. A few different ones can lead to bone marrow edema. They include: Arthritis. Many types, including osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, cause bone marrow edema.
How is a bone marrow lesion treated?
A common procedure for bone marrow lesions or edemas is core decompression. This involves holes being drilled into your bone. Once the holes are drilled, the surgeon may insert bone graft material or bone marrow stem cells — to fill the cavity. This stimulates normal bone marrow growth.

Can bone marrow edema be cured?
Current treatment of bone marrow edema does not cure the condition, but only helps in alleviating the associated symptoms.
How long does it take for bone marrow edema to heal?
Bone marrow edema affects people in different ways. It tends to resolve in four to 12 months following an injury. But in around 15% of cases, the problem lasts two years or more, even if you're in otherwise perfect health.
What is degenerative bone marrow edema?
A bone marrow edema — often referred to as bone marrow lesion — occurs when fluid builds up in the bone marrow. Bone marrow edema is typically a response to an injury such as a fracture or conditions such as osteoarthritis. Bone marrow edema usually resolves itself with rest and physical therapy.
What kind of doctor treats bone marrow edema?
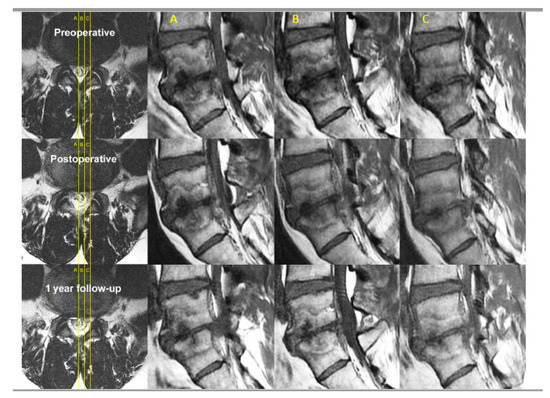
In case of an acute trauma or recent surgical intervention, the patient should be referred to an orthopedic surgeon (Figure 1). Clinical examination should include vital signs, signs of local infection (erythema, warmth, swelling, pain) and joint effusion.
Is walking good for bone marrow edema?
Exercise does not seem to increase bone marrow edema in healthy people. A recent study published in Rheumatology finds that osteitis/bone marrow edema as measured by magnetic resonance imaging was present in healthy people. However, it did not significantly increase due to intense physical activity.
What does marrow edema mean on MRI?
Bone marrow edema is the term given to abnormal fluid signal seen within the bone marrow on MRI. It is a non-specific, yet important imaging finding, usually indicating the presence of underlying pathology.
How do you reduce bone swelling?
resting the affected bone or joint. reducing swelling by raising the injured area above heart level. applying ice to the injury several times a day. taking analgesic drugs, such as acetaminophen, to reduce pain and inflammation.
Does exercise make bone marrow edema worse?
"Bone Marrow Edema does not get worse due to Exercise".
What causes abnormal bone marrow signal on MRI?
The myriad causes of bone marrow signal alteration include variants of normal, marrow reconversion, tumor (myeloproliferative disorders, metastatic, or primary), radiation, fracture, degenerative change, infection, inflammatory arthritis, and osteonecrosis.
Which medication is given to reduce the activity of the cells that cause bone loss?
Fosamax (alendronate): Fosamax has also been shown to reduce bone loss and the risk of spine fractures. This medication is available in both daily and weekly doses.
What is bone marrow edema syndrome?
Bone marrow edema syndrome, sometimes called BME, is a rare and painful transient condition that affects the bones of the lower extremities and for which treatment is limited 1.
What is bone marrow?
Treatment for Bone Marrow Edema. Bone marrow is the sponge like substance inside your bones responsible for making blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets.
How long does it take for bone marrow to heal?
It usually resolves itself within six to 12 months. Conditions such as avascular necrosis, osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can give rise to bone marrow edema as can cases of acute trauma or injury to the bone.
What is the treatment for a bone fracture?
Treatment is usually rest and physiotherapy. In difficult cases, a type of surgery called core decompression is used. In core decompression, a surgeon drills a hole into the affected part of the bone to allow increased blood flow, the formation of new blood vessels and healing to take place.
Why does bone marrow edema occur?
Bone marrow edema can happen for many reasons, including: Injury. A few different ones can lead to bone marrow edema. They include: Stress fractures. Bone bruises. Plantar fasciitis ( inflammation between the bottom of your foot and your heel) Tendinitis (inflammation of a tendon) Arthritis.
What is the difference between bone marrow and edema?
Bone marrow is soft, spongy tissue that' s in the middle of most of your bones. It contains blood stem cells. Those are special cells that can eventually become red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets. Edema is swelling that happens when fluid builds up in your body.
How long does bone marrow edema last?
You may have to rest for several months to feel better. In more serious cases, your doctor may suggest other medicines and surgery.
Why do bones edema?
Bone tumors. Some cancers can cause extra fluid to show up in bones. This can trigger edema in the marrow. Radiation treatment for cancer can also make bone marrow edema more likely. Bone infections. When your body fights a bone infection (your doctor may call it osteomyelitis ), your tissues tend to swell.
Can bone marrow edema show up on X-ray?
Also, you’ll probably have blood tests to look for heavy inflammation in your body. Bone marrow edema doesn’t show up on an X-ray or CT scan.
Does osteoarthritis cause bone marrow edema?
In the case of osteoarthritis, the edema usually appears -- along with loss of cartilage -- as the disease gets worse. Osteoporosis. As bones become weak and start to break easily, bone marrow edema is more likely. It’s particularly common when osteoporosis affects the knee and hip. Bone tumors.
Can bone marrow edema cause pain?
If you have bone marrow edema, you may or may not have symptoms. Pain is usually the main sign that something is wrong. You might also notice swollen joints. Your doctor might call this joint effusion. It's common when you have edema around your knees. Your knees also might be swollen, warm, and painful.
What causes bone marrow edema?
Some of the causes of bone marrow edema include: 4 1 Stress fractures of the foot, hip, ankle, or knee in which repetitive impact places undue strain on a weight-bearing joint 2 Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears, usually complex rather than simple, which manifest with bruising and synovitis 5 3 Vertebral compression fractures, often associated with advanced age, where the bones of the spine begin to crumble and collapse 4 Bone tumors in which the accumulation of fluid can help undermine the structural integrity of a bone and increase the risk of a fracture 5 Bone infection ( osteomyelitis) 6 Very rarely, dislocation of the hip in which the diminished blood supply to the bone can cause osteonecrosis (bone death) 6
How long does bone marrow edema last?
Bone marrow edema can be a confusing condition, affecting some people differently than others. While it tends to resolve within four to 12 months following an injury, up to 15 percent of cases will persist for two years or more, even among those in otherwise perfect health.
What causes a bone to rub against bone?
Subchondral cysts occur is when the damage done to the cartilage begins to harden and form fluid-filled sacs (cysts) within the joint. This causes the joint space to narrow and the cartilage to further wear away, causing a bone to rub against bone .
Can osteoarthritis cause bone marrow edema?
The development of bone marrow edema in osteoarthritis is usually indicative of a worsening condition. In addition to the accumulation of fluid, subchondral cysts can often be spotted on an MRI. 2
How to diagnose bone marrow edema?
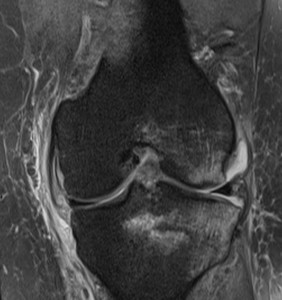
The most effective way to diagnose bone marrow edema is through MRI, which produces an image of bones showing significant contrast in intensity between cells with differing fat and water content. Fluid-containing tissues will appear dark grey or black on T1-weighted (T1W) imaging and bright white on T2-weighted (T2W) imaging.
Why does bone marrow edema hurt?
Bone marrow edema in the knee can occur from a variety of causes through physical stress, inflammation, or decreased blood supply to the bone marrow. If left untreated, bone marrow edema can progress and cause further bone damage that can be very painful and significantly impact your functional abilities.
What is the most common symptom of bone marrow edema in the knee?
The most common symptom of bone marrow edema in the knee is pain. Bone marrow edema can stimulate nerve fibers in the periosteum, a membrane surrounding the outside of bones, that transmit pain signals. This pain often increases with weight-bearing of the knee joint—with standing, walking, and going up and down stairs—and can limit ...
What is bone marrow?
Treatment. Bone marrow is a fatty substance found in the center of bones that helps produce new blood cells. Bone marrow edema, also referred to as a bone marrow lesion, is a condition where the normal fatty bone marrow is replaced with a watery material when there is damage to normal bone structure. 1. This abnormal watery material within the bone ...
Where is fluid most likely to accumulate in the bone marrow?
Fluid is more likely to accumulate in the bone marrow when there is also damage to the cortical bone that surrounds the bone marrow cavity. 1. While bone marrow edema can occur in any bone, it is most frequently observed in the lower limbs, especially within the bones that form the knee joint. Bone marrow edema of the knee can be asymptomatic ...
What causes swelling in the knee?
Fracture of the underlying bones causes increased fluid levels within the knee joint from inflammation and swelling that result from injury as well as damage to the surrounding blood vessels. 2 This excess fluid can replace the normal fatty bone marrow tissue within the leg bones. Dislocation of the kneecap or injuries to ...
Can a dislocated knee cause bone marrow edema?
Dislocation of the kneecap or injuries to the menisci or ligaments of the knee can also increase the risk of developing bone marrow edema in the knee. Mechanical or degenerative: Mechanical or degenerative bone marrow edema results from physical changes that damage the bones that form the knee joint and underlying bone marrow.
How to stop edema from coming back?
Lifestyle and home remedies. Compression stockings, also called support stockings, compress your legs, promoting circulation. A stocking butler may help you put on the stockings. The following may help decrease edema and keep it from coming back.
How to stop edema on feet?
Dry, cracked skin is more prone to scrapes, cuts and infection. Always wear protection on your feet if that's where the swelling typically occurs. Reduce salt intake. Follow your doctor's suggestions about limiting how much salt you consume. Salt can increase fluid retention and worsen edema.
What to wear when swelling goes down?
If one of your limbs is affected by edema, your doctor may recommend you wear compression stockings, sleeves or gloves, usually worn after your swelling has gone down, to prevent further swelling from occurring. These garments keep pressure on your limbs to prevent fluid from collecting in the tissue. Protection.
Does edema go away on its own?
Mild edema usually goes away on its own, particularly if you help things along by raising the affected limb higher than your heart. More-severe edema may be treated with drugs that help your body expel excess fluid in the form of urine (diuretics). One of the most common diuretics is furosemide (Lasix).
Diagnosis
Osteoarthritis
- If you have osteoarthritis, bone marrow edema may be a sign that your condition has gotten worse. You may have developed subchondral cysts along with the fluid buildup. They can often be spotted on an MRI.2 These cysts occur in places where the cartilage has been damaged. The cartilage hardens and forms fluid-filled sacs (cysts) in the joint. The cysts take up space in the jo…
Injury
- Bone marrow edema can happen with fractures and other serious bone or joint injuries. This is especially true when the injury involves the spine, hip, knees, or ankle. After an injury, different types of fluid can build up in a bone. It could be blood or fluids released from fibrosis (scarred tissue) or necrosis (tissue death).2
Other Causes
- Some more causes of bone marrow edema include:4 1. Stress fracturesof the foot, hip, ankle, or knee from repeated impact and strain on a weight-bearing joint 2. Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears, which involve a key ligament that gives the knee joint stability and can cause bruising and inflammation of connective tissue, called synovitis.5 3. Vertebral compression fractures, which …
Treatment
- Some types of bone marrow edema are harder to treat than others. If the problem is related to a trauma or repetitive motion, it often heals with rest, nonsteroidal pain relievers, and physical therapy. Severe cases may need steroid injections or surgery.7 Bone marrow edema affects people in different ways. It tends to resolve in four to 12 months f...
Summary
- Bone marrow edema is a buildup of fluid inside your bones. It can happen because of an injury such as a fracture. Or it can be related to a health condition like osteoarthritis, an infection, or a tumor. Your healthcare provider can usually diagnose the problem using ultrasound or an MRI scan. Rest, pain medication, and physical therapy helps many people recover. How long it takes …