
Explore
- DCIS accounts for about 20% of breast cancers.
- The condition does not usually cause symptoms but can show up on a mammogram, typically as microcalcification clusters.
- DCIS can be treated with surgery, sometimes with radiation and medicine. Chemotherapy is not needed.
- With timely diagnosis and treatment, patients can expect a good outcome.
What is DCIS, and how is it treated?
This study found that the risk of invasive breast cancer after a diagnosis of low-risk DCIS treated with lumpectomy alone ranged from 7.5% to 13.4%. Some women may find that risk acceptable. Other women may find that risk unacceptable and want more treatments after surgery.
How dangerous is Stage 1 invasive DCIS cancer?
While DCIS isn’t considered life threatening, it does increase the risk of developing invasive breast cancer later in life. DCIS usually is treated with surgery to remove the cancer -- lumpectomy in most cases. After surgery, hormonal therapy may be recommended if the DCIS is hormone-receptor-positive (most are).
Do I need surgery for DCIS?
Some DCIS has microinvasion in it thus it is stage 1 and it can metasize to stage 4. It's not unheard of... but there had to be some kind of invasive component in your DCIS for it to have been staged at a 3. Or there was something else in your pathology report other than the DCIS in order for you to be staged a 3. Do you have an onocologist?
How did DCIS turn into Stage 4 breast cancer?
What is the best treatment for low grade DCIS?
Radiation therapy Treatment of DCIS has a high likelihood of success, in most instances removing the tumor and preventing any recurrence. In most people, treatment options for DCIS include: Breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy) and radiation therapy. Breast-removing surgery (mastectomy)
Is DCIS stage 0 Considered breast cancer?
DCIS is also called intraductal carcinoma or stage 0 breast cancer. DCIS is a non-invasive or pre-invasive breast cancer. This means the cells that line the ducts have changed to cancer cells but they have not spread through the walls of the ducts into the nearby breast tissue.
Do I need a mastectomy for DCIS?
Most women with DCIS or breast cancer can choose to have breast-sparing surgery, usually followed by radiation therapy. Most women with DCIS or breast cancer can choose to have a mastectomy. You have small breasts and a large area of DCIS or cancer. You have DCIS or cancer in more than one part of your breast.
How many radiation treatments are needed for DCIS?
A typical course of radiation treatment for DCIS involves 16 sessions given over three weeks.
Is DCIS really breast cancer?
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is the presence of abnormal cells inside a milk duct in the breast. DCIS is considered the earliest form of breast cancer. DCIS is noninvasive, meaning it hasn't spread out of the milk duct and has a low risk of becoming invasive.
Can DCIS come back after lumpectomy?
A study found that radiation therapy given after DCIS is removed by lumpectomy reduces the risk that the DCIS will come back (recurrence).
Is Tamoxifen necessary for DCIS?
Of the endocrine agents approved for use as adjuvant therapy for invasive breast cancer, only tamoxifen is approved in the United States to prevent invasive breast cancer recurrences in women with DCIS, although data reviewed below indicate that the aromatase inhibitor anastrozole is also an acceptable option.
Does size of DCIS matter?
The larger the area of DCIS, the more likely it is to come back (recur) after surgery. Doctors use information about the size of the DCIS when recommending further treatments.
How long can you wait for DCIS surgery?
In women with a clinical diagnosis of DCIS, greater delay to surgery is associated with lower OS. Although most women with DCIS undergo surgical extirpation within 2 months of diagnosis, longer time to surgery is associated with greater risk of finding invasion and should be limited.
Can I skip radiation after lumpectomy?
If you're having lumpectomy and will be taking hormonal therapy after surgery, it may be possible for you to skip radiation therapy. As you are making your treatment plan, you and your doctor will consider a number of factors, including: your age. the size of the cancer.
How soon after lumpectomy does radiation start?
Radiation after Lumpectomy A course of radiation starts between six and 12 weeks after lumpectomy surgery. Most frequently, we target the entire breast (whole-breast radiation). In some cases, we also treat nearby lymph nodes.
What are the side effects of radiation for DCIS?
Are there risks with radiation therapy for women with DCIS? Many women experience mild acute side effects, such as skin irritation, pain, breast swelling, and fatigue, which generally resolve within several weeks of completing treatment.
How long does DCIS treatment last?
Thus far, we have been focused on reducing that risk at all costs and treating DCIS like an early-stage breast cancer: The first step is surgery—usually lumpectomy—followed by radiation treatment for three to four weeks and finally hormone therapy for five years.
How long does it take to survive DCIS?
It’s important to understand that radiation and hormone treatments do not change survival—the 10-year survival rate for women diagnosed with DCIS is 98% regardless of whether they receive either treatment. These treatments instead reduce the risk of breast cancer down the road.
What is DCIS in breast cancer?
Before the advent of routine mammography, DCIS (ductal carcinoma in situ) was rarely detected. But today, DCIS accounts for 20% of breast cancer diagnoses and would be the fifth most common cancer in women if classified independently. Often called “stage zero breast cancer,” DCIS growths are confined to the inside of the breast’s milk ducts, ...
Where is stage zero breast cancer?
Often called “stage zero breast cancer,” DCIS growths are confined to the inside of the breast’s milk ducts , and many never develop into invasive cancers. Several treatment options are available, and opinions about the optimal treatment for DCIS vary widely among doctors.
Can hormone therapy be used for DCIS?
However, not all treatments for invasive breast cancer may be optimal for DCIS, Gupta says. His study suggests that in most cases of DCIS, the side effects of hormone therapy may outweigh its benefits. The CUIMC Newsroom spoke with Gupta to learn how the study’s findings can help providers and their patients navigate treatment for DCIS.
Is radiation therapy better for DCIS patients?
For patients with low-risk DCIS, though our study found that the benefits of radiation therapy are lower relative to its costs, if a patient is anxio us about the risk of recurrence, it may make sense to pursue radiation—her quality of life will be better because we reduced her anxiety.
Is DCIS a pre-invasive cancer?
“DCIS is considered a pre-invasive cancer, but the current standard of care is to treat it like an early-stage invasive breast cancer,” says Apar Gupta, MD, ...
What is the treatment for DCIS?
In the U.S., most women with DCIS are treated with lumpectomy followed by radiation therapy [ 7 ].
How to treat DCIS?
Surgery is the first step to treat DCIS. It removes the abnormal tissue from the breast. Depending on how far the DCIS has spread within the milk ducts, surgery can be mastectomy or lumpectomy. If DCIS is spread throughout the ducts, affecting a large part of the breast, a total (simple) mastectomy will be done.
What does it mean when a DCIS tumor is estrogen receptor negative?
Hormone receptor-negative (estrogen receptor-negative/progesterone receptor-negative) DCIS tumors do not express hormone receptors. This means they have few or no hormone receptors.
Why is DCIS called in situ?
It’s called “in situ” (which means “in place”) because the cells have not left the milk ducts to invade nearby breast tissue. DCIS is also called intraductal (within the milk ducts) carcinoma. You may hear the terms “pre-invasive” or “pre-cancerous” to describe DCIS. DCIS is treated to try to prevent the development of invasive breast cancer.
What is DCIS in a milk duct?
DCIS is also called intraductal (within the milk ducts) carcinoma . You may hear the terms “pre-invasive” or “pre-cancerous” to describe DCIS.
How do pathologists determine the hormone receptor status of the DCIS?
A pathologist determines the hormone receptor status of the DCIS by testing the tissue removed during a biopsy.
Can DCIS progress to breast cancer?
DCIS is non-invasive, but without treatment, the abnormal cells could progress to invasive cancer over time. Left untreated, it’s estimated 20-50 percent of DCIS cases may progress to invasive breast cancer [ 1-5 ]. Health care providers cannot predict which cases of DCIS will progress to invasive breast cancer ...
What is DCIS on a mammogram?
DCIS is most often discovered during a mammogram used to screen for breast cancer. If your mammogram shows suspicious areas such as bright white specks (microcalcifications) that are in a cluster and have irregular shapes or sizes, your radiologist likely will recommend additional breast imaging. You may have a diagnostic mammogram, which takes ...
What to write down for breast cancer?
Write down your medical history, including any benign breast conditions with which you've been diagnosed. Also mention any radiation therapy you may have received, even years ago. Note any family history of breast cancer, especially in a first-degree relative, such as your mother or a sister.
What is a calcification on a mammogram?
Calcifications are small calcium deposits in the breast that show up as white spots on a mammogram. Large, round or well-defined calcifications (shown left) are more likely to be noncancerous (benign). Tight clusters of tiny, irregularly shaped calcifications (shown right) may indicate cancer.
Does DCIS have a high chance of success?
Treatment of DCIS has a high likelihood of success, in most instances removing the tumor and preventing any recurrence.
Can alternative medicine cure DCIS?
Alternative medicine. No alternative medicine treatments have been found to cure DCIS or to reduce the risk of being diagnosed with an invasive breast cancer. Instead, complementary and alternative medicine treatments may help you cope with your diagnosis and the side effects of your treatment, such as distress.
Is DCIS scary?
A diagnosis of DCIS can be overwhelming and frightening. To better cope with your diagnosis, it may be helpful to:
How to remove DCIS?
DCIS can often be removed via a lumpectomy— a surgery that spares the surrounding breast tissue. (In some cases, if DCIS has infiltrated multiple ducts or a tumor has grown large enough, removing the entire breast via mastectomy may be recommended.)
What is DCIS in situ?
(The words “in situ” mean “in its original place,” indicating that the cancerous cells don’t leave the duct.) RELATED: The 5 Breast Cancer Stages, Explained.
How does DCIS affect breasts?
DCIS occurs when cells in one of those milk ducts have mutated and multiplied to look like cancer cells. About one in five newly diagnosed breast cancers is DCIS.
How many DCIS patients die from breast cancer?
In fact, a 2015 JAMA Oncology study found that, regardless of the type of treatment pursued, only about 3% of DCIS patients died from breast cancer over the next 20 years—a rate similar to that of the general population.
What is stage 0 breast cancer?
About one in five newly diagnosed breast cancers is DCIS. Because those cells usually stay confined to the duct and do not spread to surrounding tissue, DCIS is also known as stage 0 breast cancer or sometimes pre-cancer. (The words "in situ" mean "in its original place," indicating that the cancerous cells don't leave the duct.)
How many DCIS cases were diagnosed in the 1990s?
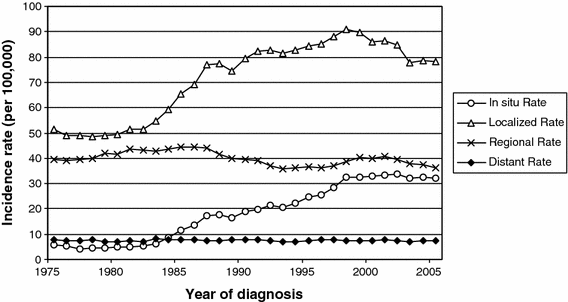
In the 1990s, only about 15,000 to 18,000 DCIS cases were diagnosed per year, she says; now, that number has grown to more than 60,000, according to the American Cancer Society. “That’s because so many women are now getting mammograms, and the technology is so good, that we pick up very small lesions,” says Dr. White.
What happens after a woman is diagnosed with DCIS?
After a woman is diagnosed with DCIS and has the abnormal growth removed via surgery, the next step is to assess her risk of a recurrence or a more invasive cancer.
What is DCIS in situ?
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS) is Stage 0 breast cancer. It is the earliest stage that breast cancer can be detected. This post will share some information about DCIS and offer links to resources to get more information.
What is DCIS in breast cancer?
DCIS is considered Stage 0 breast cancer. On a pathology report, DCIS is reported as Tis (tumor in situ).
What is cancer staging?
Cancer staging identifies where the cancer is in the body and how much of it there is. Staging helps doctors have a shared language to discuss cancer and plan treatment.
What is the stage of cancer?
All cancers, no matter what type, are staged and given a number. These numbers range from 0-IV (0-4). Stage IV cancers have become metastatic or have spread to other locations in the body. At this stage, cancer can be considered terminal.
Where is DCIS located?
DCIS can be located in one location of the breast, or it can be found in many different areas of the breast. In that case, it is usually called multi-focal.
Is stage IV breast cancer curable?
There are treatments available to help slow the progression of MBC and prolong life for patients. Unfortunately, at this time, MBC is not curable .
What grade is DCIS?
DCIS that is high grade, is nuclear grade 3 , or has a high mitotic rate is more likely to come back (recur) after it is removed with surgery.
What is intermediate grade DCIS?
DCIS that is intermediate grade, is nuclear grade 2, or has an intermediate mitotic rate falls in between these two. Patients with higher grade DCIS may need additional treatment.
How to measure DCIS?
If the entire tumor or area of DCIS is removed (such as in an excisional biopsy or breast-conserving surgery ), the pathologist will say how big the DCIS is by measuring how long it is across (in greatest dimension), either by looking at it under the microscope or by gross examination (just looking at it with the naked eye) of the tissue taken out at surgery. Another way to measure DCIS is to note the number of microscopic slides that contain DCIS. For example, the report may say that DCIS was found in 3 slides.
What does it mean when DCIS touches ink?
If DCIS is touching the ink (called positive margins ), it can mean that some DCIS cells were left behind, and more surgery or other treatments may be needed. Sometimes, though, the surgeon has already removed more tissue (at surgery) to help make sure that this isn’t needed.
What is in situ carcinoma?
What is in-situ carcinoma (or carcinoma in situ) of the breast? This term is used for the earliest stage of breast cancer, when it is confined to the layer of cells where it began. The normal breast is made of tiny tubes (ducts) that end in a group of sacs (lobules).
Is LCIS the same as DCIS?
LCIS is discussed on a different page. Sometimes DCIS and LCIS are both found in the same biopsy. In-situ carcinoma with duct and lobular features means that the in-situ carcinoma looks like DCIS in some ways and LCIS in some ways (when looked at under the microscope), and so the pathologist can’t call it one or the other.
Can DCIS come back after treatment?
These terms are used to describe certain ways that the DCIS looks under the microscope. Some of these are linked to a higher chance that the DCIS may come back after treatment, so finding them may change your treatment. Your doctor should discuss this with you.
What is the average age for DCIS?
The study found that the average age of diagnosis for DCIS was 53.8 years. In general the overall breast cancer death rate over a 20 year period was only 3.3%. However, the mortality rate at 20 years increased to 7.8% in women who were diagnosed with DCIS before the age of 35 years old.
How many years does it take for DCIS to recur?
Medical studies of excision of DCIS reported a 20% to 44% local recurrence rate over a 10 year period.
How many grades of ductal carcinoma are there?
There are 3 grades of Ductal Carcinoma In-Situ (DCIS). If you have been diagnosed with DCIS you will be able to find the Grade on your Pathology Report.
How many cases of DCIS are there in 100000?
One recent study estimated that only between 100 to 270 cases of DCIS per 100000 will not progress to invasive breast cancer if left untreated.
How much do you survive ductal cancer?
Indeed, not all of these early changes progress to a more invasive, problematic cancer. The high survival rates of 98% to 99% for Ductal Carcinoma In-Situ, in 2010 reflect the effectiveness of treatment.
Why is ductal cancer called in situ?
The reason ductal cancer is named ‘ in-situ ’ at this early phase, is that the abnormal cells have not yet spread outside of the milk ducts. This explains the reason for the very good prognosis for this type of breast cancer.
What is the term for the duration of preclinical disease?
Sojourn time sometimes formally defined as, the mean duration of pre-clinical disease, has been consistently shown to be longer for older women and for slower-growing breast tumors.
What is DCIS stage?
DCIS also is referred to as stage 0 breast cancer. Women diagnosed with DCIS have very good prognoses. Ten years after DCIS diagnosis, 98% to 99% of women will be alive. Based on this good prognosis, DCIS usually is treated by lumpectomy followed by radiation therapy. If the DCIS is large, a mastectomy may be recommended.
How long after DCIS can you be alive?
Women diagnosed with DCIS were 10% more likely to be alive after 10 years compared to women not diagnosed with breast cancer. Women diagnosed with stage I breast cancer were just as likely to be alive after 10 years compared to women not diagnosed with breast cancer. Women diagnosed with stage II, III, or IV breast cancer were less likely ...
What is the best treatment for breast cancer?
Adjuvant hormonal therapy may be recommended if the cancer is hormone-receptor-positive. The targeted therapy Herceptin (chemical name: trastuzumab) also may be recommended if the cancer is HER2-positive. The researchers compared the health outcomes of two groups of women: 64,894 women diagnosed with either DCIS or invasive breast cancer.
How is breast cancer treated?
Stage I breast cancer is treated by lumpectomy followed by radiation therapy. Depending on the circumstances, a mastectomy may sometimes be recommended. Because stage I breast cancer can come back (recur), chemotherapy is sometimes given after surgery (treatments given after surgery are called adjuvant treatments).
How long did the women follow DCIS?
Half the women were older than 76 and the other half were younger. All the women were older than 67. The women were followed for about 8 years. The researchers projected 10-year survival rates for all the women and compared the projected survival rates of women diagnosed with DCIS or invasive breast cancer to the rates of women not diagnosed with breast cancer.
Can DCIS spread to breasts?
DCIS can be large or small, but it doesn't spread outside the milk duct into the surrounding normal breast tissue or into the lymph nodes or other organs. Still, a woman diagnosed with DCIS is at higher risk of developing invasive breast cancer in the same breast compared to someone who hasn't had DCIS.
Is stage III breast cancer more likely to be alive?
women diagnosed with stage III breast cancer were 55% less likely to be alive. women diagnosed with stage IV breast cancer were 88% less likely to be alive. In this study, the good outcomes of women diagnosed with DCIS or stage I breast cancer are probably because most of the women received the right treatment at the right time.

Diagnosis
Treatment
- Treatment of DCIS has a high likelihood of success, in most instances removing the tumor and preventing any recurrence. In most people, treatment options for DCIS include: 1. Breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy) and radiation therapy 2. Breast-removing surgery (mastectomy) In some cases, treatment options may include: 1. Lumpectomy only 2. Lumpec...
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Alternative Medicine
- No alternative medicine treatments have been found to cure DCIS or to reduce the risk of being diagnosed with an invasive breast cancer. Instead, complementary and alternative medicine treatments may help you cope with your diagnosis and the side effects of your treatment, such as distress. If you're distressed, you may have difficulty sleeping and find yourself constantly thinkin…
Coping and Support
- A diagnosis of DCIS can be overwhelming and frightening. To better cope with your diagnosis, it may be helpful to: 1. Learn enough about DCIS to make decisions about your care. Ask your doctor questions about your diagnosis and your pathology results. Use this information to research your treatment options. Look to reputable sources of information, such as the National …
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Make an appointment with your doctor if you notice a lump or any other unusual changes in your breasts. If you have already had a breast abnormality evaluated by one doctor and are making an appointment for a second opinion, bring your original diagnostic mammogram images and biopsy results to your new appointment. These should include your mammography images, ultrasound …