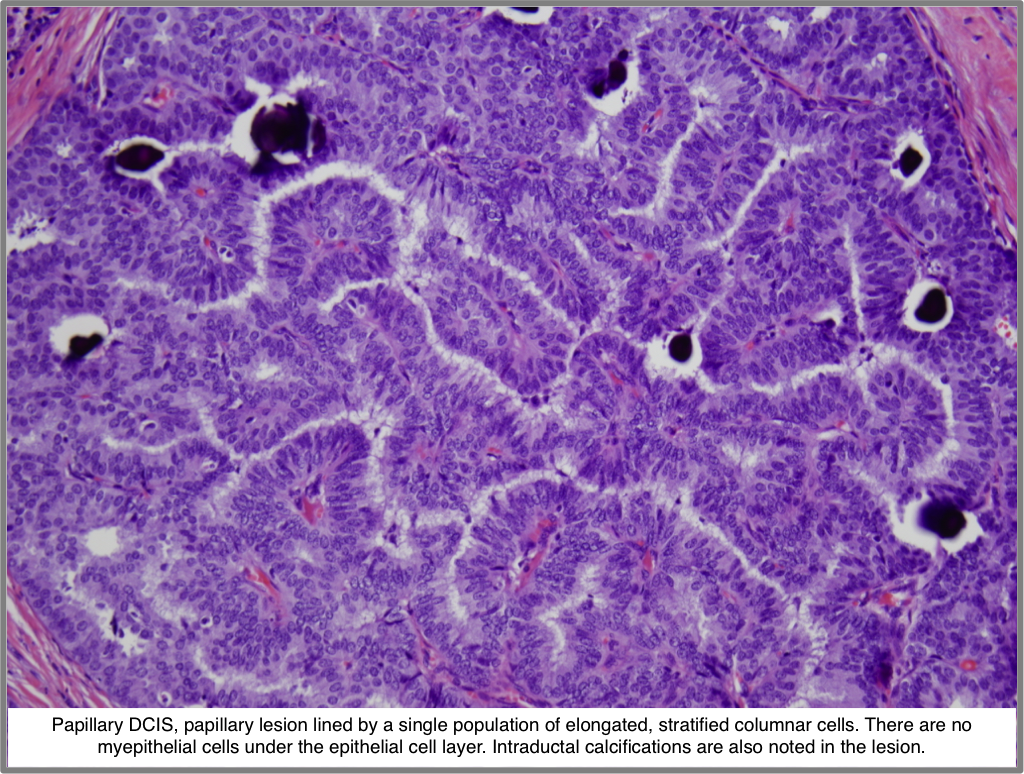
Do I need surgery for DCIS?
Jul 13, 2021 · Hormone therapy after breast surgery If the DCIS is hormone receptor-positive (estrogen or progesterone), treatment with tamoxifen (for any woman) or an aromatase inhibitor, such as exemestane or anastrozole, (for women past menopause) for 5 years after surgery can lower the risk of another DCIS or invasive cancer developing in either breast.
Should tamoxifen be taken for DCIs in breast?
Because DCIS might progress to invasive breast cancer, almost all cases of DCIS are treated. Surgery (with or without radiation therapy ) is recommended to treat DCIS. After surgery and radiation therapy, some people take hormone therapy .
What is the prognosis of DCIS breast cancer?
Jun 09, 2021 · Opinions vary about how to treat DCIS (ductal carcinoma in situ), but a new study suggests the optimal treatment for most women with …
Should I have a mastectomy for DCIS?
DCIS accounts for about 20% of breast cancers. The condition does not usually cause symptoms but can show up on a mammogram, typically as microcalcification clusters. DCIS can be treated with surgery, sometimes with radiation and medicine. Chemotherapy is not needed. With timely diagnosis and treatment, patients can expect a good outcome.
What is the current best treatment for ductal carcinoma in situ DCIS?
Radiation therapy Treatment of DCIS has a high likelihood of success, in most instances removing the tumor and preventing any recurrence. In most people, treatment options for DCIS include: Breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy) and radiation therapy. Breast-removing surgery (mastectomy)May 20, 2020
Is DCIS breast cancer curable?
Women diagnosed with DCIS have very good prognoses. Ten years after DCIS diagnosis, 98% to 99% of women will be alive. Based on this good prognosis, DCIS usually is treated by lumpectomy followed by radiation therapy. If the DCIS is large, a mastectomy may be recommended.Mar 16, 2011
Does DCIS ever require chemo?
Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is not needed for DCIS since the disease is noninvasive. Hormonal (endocrine) therapy. Hormonal (endocrine) therapy may be appropriate for those whose ductal carcinoma in situ is hormone receptor positive.
How aggressive is DCIS breast cancer?
DCIS is a noninvasive form of early breast cancer in which abnormal cells are localized to milk ducts in the breast. In some cases, however, DCIS may become aggressive and spread to surrounding tissue, but until now pathologists have not had a way to identify which cases may become invasive.Oct 25, 2016
Should I have a mastectomy for DCIS?
If the DCIS is large, a mastectomy may be recommended. Removing the opposite breast usually isn't recommended; chemotherapy usually isn't recommended either. Hormonal therapy may be recommended if the DCIS is hormone-receptor-positive. DCIS is NOT invasive cancer.Apr 10, 2009
Should I worry about DCIS?
A new study suggests that women who are diagnosed with abnormal cells in the lining of a breast duct—a noninvasive condition called ductal carcinoma in situ, or DCIS—generally have a low risk of dying from breast cancer.Aug 26, 2015
Do I need tamoxifen for DCIS?
Tamoxifen is the only hormonal therapy currently approved for adjuvant therapy in patients treated with breast-conserving surgery and radiation for DCIS. A retrospective study found that patients with ER-positive DCIS who were treated with tamoxifen showed significant decreases in subsequent breast cancer at 10 years.
Does having DCIS make you tired?
Fatigue. You may feel tired during and after treatment. Radiation therapy, chemotherapy, surgery and other treatments may cause you to have less energy.
How long can you wait for DCIS surgery?
The researchers assessed overall survival using five time intervals representing delays to surgery: less than 30 days, 31-60 days, 61-90 days, 91-120 days, or 121-365 days. Overall survival was 95.8 percent, with a median delay from diagnosis to surgery of 38 days.Oct 21, 2019
Why did I get DCIS?
DCIS forms when genetic mutations occur in the DNA of breast duct cells. The genetic mutations cause the cells to appear abnormal, but the cells don't yet have the ability to break out of the breast duct. Researchers don't know exactly what triggers the abnormal cell growth that leads to DCIS.May 20, 2020
What happens if DCIS is left untreated?
The cells in DCIS are cancer cells. If left untreated, they may spread out of the milk duct into the breast tissue. If this happens, DCIS has become invasive (or infiltrating) cancer, which in turn can spread to lymph nodes or to other parts of the body.
Can DCIS spread to lungs?
They die the conventional way from breast cancer — because it spreads to the bones, liver and lungs. The women who die of DCIS died because their breast cancer already spread by the time they received treatment,” says Narod.Aug 20, 2015
How to treat DCIS?
Surgery is the first step to treat DCIS. It removes the abnormal tissue from the breast. Depending on how far the DCIS has spread within the milk ducts, surgery can be mastectomy or lumpectomy. If DCIS is spread throughout the ducts, affecting a large part of the breast, a total (simple) mastectomy will be done.
How can we improve cancer care?
The report identified key ways to improve quality of care: 1 Ensure cancer patients understand their diagnoses so they can make informed treatment decisions with their health care providers 2 Develop a trained and coordinated workforce of cancer professionals 3 Focus on evidence-based care 4 Focus on quality measures 5 Provide accessible and affordable care for all
What is the National Comprehensive Cancer Network?
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) and the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) are respected organizations that regularly review and update their guidelines. In addition, the National Cancer Institute (NCI) provides treatment overviews.
What is sentinel node biopsy?
A sentinel node biopsy is a procedure used to check whether or not invasive breast cancer has spread to the lymph nodes in the underarm area (axillary nodes). The surgeon removes 1-5 nodes.
Can axillary dissection cause lymphedema?
Because it disrupts more of the normal tissue in the underarm area, axillary dissection is more likely to affect arm function and cause lymphedema. So, even though a sentinel node biopsy may not be needed with DCIS, most people who have a mastectomy for DCIS will have a sentinel node biopsy done at the same time.
Can hormone therapy be used for DCIS?
Hormone therapy isn’t recommended for women who have a mastectomy for DCIS. These women have an excellent prognosis with a very low risk of DCIS recurrence or developing breast cancer in the opposite breast.
Is DCIS invasive or noninvasive?
DCIS is non-invasive, but without treatment, the abnormal cells could progress to invasive cancer over time. Left untreated, it’s estimated 20-50 percent of DCIS cases may progress to invasive breast cancer [ 1-5 ]. Health care providers cannot predict which cases of DCIS will progress to invasive breast cancer and which will not.
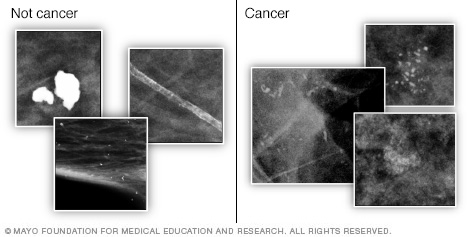
What is a calcification on a mammogram?
Calcifications are small calcium deposits in the breast that show up as white spots on a mammogram. Large, round or well-defined calcifications (shown left) are more likely to be noncancerous (benign). Tight clusters of tiny, irregularly shaped calcifications (shown right) may indicate cancer.
What is radiation therapy after lumpectomy?
Radiation therapy after lumpectomy reduces the chance that DCIS will come back (recur) or that it will progress to invasive cancer.
What is a mammogram?
You may have a diagnostic mammogram, which takes views at higher magnification from more angles. This examination evaluates both breasts and takes a closer look at the microcalcifications to be able to determine whether they are a cause for concern.
What is lumpectomy surgery?
A lumpectomy involves removing the cancer and some of the healthy tissue that surrounds it. This illustration shows one possible incision that can be used for this procedure, though your surgeon will determine the approach that's best for your particular situation.
What is clinical trial?
Clinical trials are studying new strategies for managing DCIS, such as close monitoring rather than surgery after diagnosis. Whether you're eligible to participate in a clinical trial depends on your specific situation. Talk with your doctor about your options.
Can you have a mastectomy with DCIS?
Most women with DCIS are candidates for lumpectomy. However, mastectomy may be recommended if: You have a large area of DCIS.
What is DCIS in mammography?
Before the advent of routine mammography, DCIS (ductal carcinoma in situ) was rarely detected. But today, DCIS accounts for 20% of breast cancer diagnoses and would be the fifth most common cancer in women if classified independently. Apar Gupta. Often called “stage zero breast cancer,” DCIS growths are confined to the inside ...
What is stage zero breast cancer?
Apar Gupta. Often called “stage zero breast cancer,” DCIS growths are confined to the inside of the breast’s milk ducts, and many never develop into invasive cancers. Several treatment options are available, and opinions about the optimal treatment for DCIS vary widely among doctors.
Does radiation help with survival?
It’s important to understand that radiation and hormone treatments do not change survival—the 10-year survival rate for women diagnosed with DCIS is 98% regardless of whether they receive either treatment. These treatments instead reduce the risk of breast cancer down the road. Since treatment of DCIS after surgery doesn’t improve survival, ...
Is DCIS a pre-invasive cancer?
“DCIS is considered a pre-invasive cancer, but the current standard of care is to treat it like an early-stage invasive breast cancer,” says Apar Gupta, MD, ...
What is the treatment for breast cancer?
Partial mastectomy. Breast-conserving surgery. Segmental mastectomy. After breast-sparing surgery, most women also receive radiation therapy. The main goal of this treatment is to keep cancer from coming back in the same breast. Some women will also need chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and/or targeted therapy.
How to do breast reconstruction?
The first step is called tissue expansion. This is when the plastic surgeon places a balloon expander under the chest muscle. Over many weeks, saline (salt water) will be added to the expander to stretch the chest muscle and the skin on top of it.
What is a mastectomy?
In a mastectomy, the surgeon removes the whole breast that contains the DCIS or cancer. There are two main types of mastectomy. They are: Total mastectomy. The surgeon removes your whole breast. Sometimes, the surgeon also takes out one or more of the lymph nodes under your arm. Also called simple mastectomy.
What to do after talking to a surgeon?
After talking with a surgeon, think about getting a second opinion. A second opinion means getting the advice of another surgeon. This surgeon might tell you about other treatment options. Or, he or she may agree with the advice you got from the first doctor.
What is breast surgery?
Breast-sparing surgery means the surgeon removes only the DCIS or cancer and some normal tissue around it. If you have cancer, the surgeon will also remove one or more lymph nodes from under your arm. Breast-sparing surgery usually keeps your breast looking much like it did before surgery. Other words for breast-sparing surgery include:
Can you have a mastectomy with DCIS?
Most women with DCIS or breast cancer can choose to have breast-sparing surgery, usually followed by radiation therapy. Most women with DCIS or breast cancer can choose to have a mastectomy. You have small breasts and a large area of DCIS or cancer . You have DCIS or cancer in more than one part of your breast.
What is a radical mastectomy?
Modified radical mastectomy. The surgeon removes your whole breast, many of the lymph nodes under your arm, and the lining over your chest muscles. Some women will also need radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and/or targeted therapy.
What is DCIS in breast cancer?
Doctors often call this type of breast cancer ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). It gets this name because the cancer is only in the breast ducts that carry milk.
How to treat DCIS?
Surgery is the most common way that doctors treat DCIS. Most often, it’s done with a procedure called a lumpectomy. A surgeon removes only the affected area of the breast while leaving healthy tissue. Doctors also call this breast-conserving surgery. Sometimes, a doctor might suggest removing the whole breast.
What happens after breast surgery?
What Happens After Surgery? 1 Radiation of the whole breast is the most common treatment. A machine delivers the radiation, often 5 days a week for several weeks. 2 It might be an option to get radiation for only part of the breast. It’s not clear if this works as well as whole breast radiation. 3 Instead of using a machine, a doctor might insert a radioactive seed or pellet into your breast. It’s not yet clear if this works as well to prevent cancer from coming back.
What to do after a lumpectomy?
After a lumpectomy or mastectomy, some women may choose to have surgery to reconstruct their breast. The decision to have breast reconstruction is a personal one.
Can chemo kill cancer cells?
No, most likely not. Chemotherapy uses drugs given throughout the body to kill fast-growing cells, including cancer. Because DCIS is only in the breast ducts, doctors don’t usually recommend chemotherapy to treat it.
Do you need a second lumpectomy?
Sometimes after a first lumpectomy, a doctor may need to do a second one. This usually happens when the tissue removed in the first surgery doesn’t have enough healthy tissue around it for doctors to be sure they got it all. At this point, you might also consider a mastectomy to make sure all the cancer is gone.
Do you need radiation after a mastectomy?
After a lumpectomy, you usually have radiation treatment to lower the chance the cancer will come back. If you had a mastectomy , you usually won’t need radiation. There are different ways you may get radiation for DCIS. Radiation of the whole breast is the most common treatment. A machine delivers the radiation, ...
What is the treatment for DCIS?
Depending on the size and location of the affected cells, treatment of DCIS may involve a lumpectomy or mastectomy. Treatment could also include radiation and hormone therapy to prevent the cancer cells from returning. Overall, DCIS has a very good outlook. Last medically reviewed on March 10, 2021.
What is DCIS in breast cancer?
DCIS happens when a group of abnormal cells starts growing inside the lining of a milk duct. Because these cancerous cells haven’t spread beyond the duct to other breast tissue, it’s known as a preinvasive or noninvasive cancer.
How to diagnose DCIS?
If your doctor thinks you might have DCIS, you’ll probably need further tests to confirm the diagnosis. These tests may include: 1 a diagnostic mammogram 2 an ultrasound 3 an MRI 4 a biopsy
How does radiation therapy work?
Radiation therapy uses high energy beams to damage the DNA of cancer cells. This helps to destroy the abnormal cells. Radiation therapy is a localized type of treatment, which means it only targets the specific area that’s being radiated. This helps limit the damage to healthy cells.
What are the factors that contribute to the risk of breast cancer?
The following factors may contribute to a higher risk of breast cancer: Some risk factors — your age, for example — are things beyond your control. But some aspects of your lifestyle can affect your overall health and your risk of developing breast cancer.
Can breast cancer be metastasized?
Sometimes, especially if these abnormal cells aren’t treated early on, they can become an invasive form of breast cancer. Invasive breast cancer has the capacity to spread to other parts of your body. When this happens, the breast cancer is said to have metastasized. According to the American Cancer Society, DCIS accounts for about 16 percent ...
What is a DCIS?
The bottom line. Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a preinvasive breast cancer that has a very high cure rate . DCIS generally doesn’t have any symptoms and is most often detected during a mammogram. Depending on the size and location of the affected cells, treatment of DCIS may involve a lumpectomy or mastectomy.
What is ductal carcinoma in situ?
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS) About 1 in 5 new breast cancers will be ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). Nearly all women with this early stage of breast cancer can be cured. DCIS is also called intraductal carcinoma or stage 0 breast cancer. DCIS is a non-invasive or pre-invasive breast cancer.
Is DCIS invasive or noninvasive?
DCIS is a non-invasive or pre-invasive breast cancer. This means the cells that line the ducts have changed to cancer cells but they have not spread through the walls of the ducts into the nearby breast tissue.

Diagnosis
- Breast imaging
DCIS is most often discovered during a mammogram used to screen for breast cancer. If your mammogram shows suspicious areas such as bright white specks (microcalcifications) that are in a cluster and have irregular shapes or sizes, your radiologist likely will recommend additional … - Removing breast tissue samples for testing
During a core needle biopsy, a radiologist or surgeon uses a hollow needle to remove tissue samples from the suspicious area, sometimes guided by ultrasound (ultrasound-guided breast biopsy) or by X-ray (stereotactic breast biopsy). The tissue samples are sent to a lab for analysis…
Treatment
- Treatment of DCIS has a high likelihood of success, in most instances removing the tumor and preventing any recurrence. In most people, treatment options for DCIS include: 1. Breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy) and radiation therapy 2. Breast-removing surgery (mastectomy) In some cases, treatment options may include: 1. Lumpectomy only 2. Lumpectomy and hormon…
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Alternative Medicine
- No alternative medicine treatments have been found to cure DCIS or to reduce the risk of being diagnosed with an invasive breast cancer. Instead, complementary and alternative medicine treatments may help you cope with your diagnosis and the side effects of your treatment, such as distress. If you're distressed, you may have difficulty sleeping and find yourself constantly thinki…
Coping and Support
- A diagnosis of DCIS can be overwhelming and frightening. To better cope with your diagnosis, it may be helpful to: 1. Learn enough about DCIS to make decisions about your care. Ask your doctor questions about your diagnosis and your pathology results. Use this information to research your treatment options. Look to reputable sources of information, such as the Nationa…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Make an appointment with your doctor if you notice a lump or any other unusual changes in your breasts. If you have already had a breast abnormality evaluated by one doctor and are making an appointment for a second opinion, bring your original diagnostic mammogram images and biopsy results to your new appointment. These should include your mammography images, ultrasound …