Some of the treatments for cyanosis are the following:
- Oxygen therapy
- Warming of affected areas
- Surgery
- Intravenous (IV) fluids
- Drug treatment
What are the signs and symptoms of cyanosis?
Cyanotic congenital heart disease involves defects in your heart that reduce the amount of oxygen throughout your body. Most babies with CCHD will need treatment to survive. Treatments include oxygen therapy and surgery to repair the defects or redirect blood flow. Reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional. References
What is circumoral cyanosis, and what are its causes?
· Treatments for cyanotic congenital heart disease Treatment for CCHD may or may not be necessary depending on the severity of symptoms. In many cases, surgery to correct the physical defects in the...
Is cyanosis an early symptom of hypoperfusion?
Sometimes, symptoms that are associated with cyanotic heart disease can be managed with medication. Your child's pediatric cardiologist may prescribe a drug or combination of drugs to help manage these symptoms. Surgery. If your child's cyanotic heart disease treatment includes surgery, doctors at Children's Colorado will schedule open-heart surgery. The doctor will …
What is the basic cause of symptoms of cyanosis?
· Since cyanosis is a symptom of a disease or condition, treating it depends on the underlying cause. Often, the first step is to give supplemental oxygen to reverse hypoxia, which is low oxygen levels. Then, doctors can address the root cause. The goal is to restore oxygenated blood supply if possible.

What is the best treatment for for cyanosis?
Treatment for peripheral cyanosis depends on the underlying cause of the problem. Doctors may prescribe medications to treat heart and lung conditions. These help improve blood flow and oxygen supply to the organs and tissues. Some people may need oxygen therapy to restore healthy levels.
What is the treatment of cyanotic heart disease?
The treatment of choice for most congenital heart diseases is surgery to repair the defect. There are many types of surgery, depending on the kind of birth defect. Surgery may be needed soon after birth, or it may be delayed for months or even years. Some surgeries may be staged as the child grows.
What happens when someone is cyanotic?
Blood that has lost its oxygen is dark bluish-red. People whose blood is low in oxygen tend to have a bluish color to their skin. This condition is called cyanosis. Depending on the cause, cyanosis may develop suddenly, along with shortness of breath and other symptoms.
What is the best treatment for congenital heart disease?
A child may need open-heart surgery or minimally invasive heart surgery to repair a congenital heart defect. The type of heart surgery depends on the specific defect. Heart transplant. If a serious heart defect can't be repaired, a heart transplant may be needed.
Is cyanotic heart disease curable?
False. There is no cure for CHD. Many people have surgeries to repair their heart, however, they are not cured. There may be long-term effects of heart surgery, such as abnormal heartbeats.
Is cyanosis an emergency?
Blue skin and lips is usually caused by low blood oxygen levels or poor circulation. It can be a sign of a serious problem. Call 999 or go to your nearest emergency department immediately if you notice an adult or child suddenly turning blue.
Can cyanosis cause death?
Most causes of cyanosis are serious and a symptom of your body not getting enough oxygen. Over time, this condition will become life-threatening. It can lead to respiratory failure, heart failure, and even death, if left untreated.
How long does cyanosis last?
Q. How long does Cyanosis last? It is a common finding and may persist for 24 to 48 hours. Central cyanosis caused by reduced arterial oxygen saturation lasts for nearly 5 to 10 minutes in a newborn infant as the oxygen saturation rises to 85 to 95 percent by 10 minutes of age.
What is cyanosis a sign of?
Cyanosis is a sign of a serious medical condition and requires immediate medical treatment. If you or a loved one are exhibiting any symptoms of cyanosis, such as difficulty breathing and/or a bluish tinge to your skin, nails, mucous membranes, call 911 immediately.
How to tell if you have cyanosis?
Symptoms. The typical primary symptom of cyanosis is a bluish, grayish, or purplish cast to the skin and/or mucous membranes. A mild case may be difficult to detect even in light-skinned people, so you might not notice the signs until the oxygen content of your blood drops significantly. Normal blood oxygen saturation is in the range ...
Can cyanosis be found on the skin?
If you have dark skin, you might not notice cyanosis on your skin but may instead see it on the membranes around the lips, gum s, and nail beds . These might turn purple instead of blue. The skin around the eyes might also take on that bluish or purplish tinge.
Can you get oxygen therapy for cyanosis?
If you have cyanosis, it's likely that you'll receive oxygen therapy to help boost your blood oxygen levels quickly, but any additional treatment you may receive for cyanosis will depend on the root cause of your condition. For example, treatment for COPD may include inhaled corticosteroids and pulmonary rehabilitation.
What are the best ways to treat cyanosis in infants?
These include chest X-rays and echocardiograms. Medication can help relieve symptoms of cyanosis. Ultimately, most infants need to have surgery to correct the defects causing the disease. The success of the surgery depends on the severity of the defects.
What is cyanosis in the body?
Cyanotic congenital heart disease. Cyanotic congenital heart disease (CCHD) is a condition present at birth. CCHD causes low levels of oxygen in the blood. A common symptom is a bluish tint to the skin, called cyanosis. Several birth defects can cause this type of heart disease, including:
Can cyanosis cause heart problems?
Symptoms such as cyanosis, rapid heartbeat, and abnormal heart sounds can lead your child’s doctor to suspect heart defects are present. The observation of symptoms isn’t enough to make a diagnosis, though. To understand which defects are present, your child’s doctor will use tests to confirm a diagnosis.
What are the symptoms of cyanotic congenital heart disease?
Symptoms of cyanotic congenital heart disease. The classic symptom of CCHD is cyanosis, or the blue coloring of the skin. This often occurs in the lips, toes, or fingers. Another common symptom is difficulty breathing, especially after physical activity. Some children also experience spells during which their oxygen levels are very low.
Is cyanotic heart disease genetic?
Risk factors for cyanotic congenital heart disease. In many cases, an infant will be born with this disease in association with a genetic factor. An infant is more at risk for CCHD when there’s a family history of congenital heart diseases. Certain genetic syndromes can be accompanied by defects that cause CCHD.
Can a cyanosis be present in a CCHD?
abnormalities in the large blood vessels leading to or from the heart. In many cases, if only one defect is present, there’s no cyanosis. Often more than one defect is present in CCHD. Doctors use imaging tests to confirm the presence of defects that lead to CCHD. These include chest X-rays and echocardiograms.
Can birth defects cause cyanosis?
Several birth defects can cause this type of heart disease, including: issues with the heart valves, which are the flaps in the heart that make sure the blood flows through in the right direction. In many cases, if only one defect is present, there’s no cyanosis. Often more than one defect is present in CCHD.
What are the causes of cyanosis?
Heart valve defects that can cause cyanosis include: Tricuspid valve (the valve between the 2 chambers on the right side of the heart) may be absent or unable to open wide enough. Pulmonary valve (the valve between the heart and the lungs) may be absent or unable to open wide enough.
What is the difference between cyanotic and cyanosis?
Definition. Cyanotic heart disease refers to a group of many different heart defects that are present at birth (congenital). They result in a low blood oxygen level. Cyanosis refers to a bluish color of the skin and mucous membranes.
How to treat congenital heart disease?
Treat abnormal heartbeats or rhythms. The treatment of choice for most congenital heart diseases is surgery to repair the defect. There are many types of surgery, depending on the kind of birth defect. Surgery may be needed soon after birth, or it may be delayed for months or even years.
What are some examples of cyanotic heart disease?
Some examples include: Genetic and chromosomal syndromes, such as Down syndrome, trisomy 13, Turner syndrome, Marfan syndrome, and Noonan syndrome.
Can cyanotic heart disease cause chest pain?
Infants may get tired or sweat while feeding and may not gain as much weight as they should. Fainting (syncope) and chest pain may occur. Other symptoms depend on the type of cyanotic heart disease, and may include: Feeding problems or reduced appetite, leading to poor growth. Grayish skin.
How to treat cyanotic heart disease in children?
Medication. Sometimes, symptoms that are associated with cyanotic heart disease can be managed with medication. Your child's pediatric cardiologist may prescribe a drug or combination of drugs to help manage these symptoms. Surgery. If your child's cyanotic heart disease treatment includes surgery, doctors at Children's Colorado will schedule ...
What happens if a child has cyanotic heart disease?
If your child has pediatric cyanotic heart disease, he or she may not have enough oxygen in the blood circulating from the lungs to other tissues of the body. With cyanotic heart disease, there is mixing of blue blood (blood already used by the body) with red blood (oxygen-rich blood from the lungs).
Can a newborn have cyanosis?
Note: Just because your child has cyanosis does not necessarily mean they have cyanotic heart disease; cyanosis can also occur from a pulmonary issue. Sometimes acrocyanosis (blue hands and feet) is seen in normal newborn babies, and is due to poor peripheral circulation, but this is a normal condition.
Can cyanosis cause breathlessness?
Infants and babies with cyanotic heart disease may have trouble feeding and decreased appetite. Older children with cyanosis may not have as much energy as other children their age, and exercise often makes the blue color worse and can cause breathlessness.
Is cyanotic heart disease a congenital heart disease?
Typically, cyanotic heart disease is present at birth. It can be seen more in families with a history of congenital heart disease, may be present in association with some genetic syndromes (such as Turner syndrome or Marfan syndrome ), may occur with certain environmental exposures in utero, or may occur sporadically.
Can cyanotic heart disease be treated with surgery?
If your child's cyanotic heart disease treatment includes surgery, doctors at Children's Colorado will schedule open-heart surgery. The doctor will determine the timing of surgery based on the type of defect and the overall well-being of your child.
What happens when blood is cyanotic?
Oxygenated blood flows to cells and tissues in the rest of your body, and releases the oxygen as it captures waste carbon dioxide, at which point the blood turns blue— it becomes cyanotic.
Why does cyanosis occur?
Cyanosis occurs either when there is insufficient fresh oxygen getting to the bloodstream or when sluggish blood can’t reoxygenate quick enough. Abnormal hemoglobin or an overall lack of oxygen can cause cyanosis.
What causes cyanosis in the respiratory system?
Respiratory causes of cyanosis. Cyanosis can also be caused by respiratory disorders including: Asthma. Bronchiolitis (inflammation of the small airways in the lungs) and bronchitis (inflammation of the large airways) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease ( COPD, includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis)
What are the symptoms of cyanosis?
Cyanosis may accompany other symptoms affecting the heart or respiratory system including: Chest pain. Difficulty breathing. Leaning forward when sitting to breathe more easily. Rapid breathing (tachypnea) or shortness of breath. Squatting (young children) Use of rib cage muscles in an attempt to breathe more easily.
Does cyanosis affect the circulatory system?
Cyanosis may accompany other symptoms that vary depending on the underlying disease, disorder or condition. Symptoms that frequently affect the circulatory system may also involve other body systems.
What to do if your child has bluish skin?
Also seek immediate medical care (call 911) if you are with a child who has bluish skin and is having: Chest muscles pulling in with every breath or flaring nostrils with breathing. Difficulty breathing or rapid breathing. Fussiness or irritability. Grunting.
What is the color of the skin due to lack of oxygen?
What is cyanosis? The cyanosis definition is a bluish hue to the skin, gums, fingernails, or mucous membranes due to a lack of oxygen in the blood. When blood is fully oxygenated it appears bright red; when it lacks oxygen supply, the blood is a dark purple or bluish red. This lack of oxygen in the blood supply to a body part, such as the nail bed, ...
What is the cause of cyanosis in the hands?
It may also be the result of low oxygen levels in the red blood cells.
How much hemoglobin is needed for cytonosis?
Cyanosis is typically noticeable when the concentration of deoxygenated hemoglobin is at least 3 to 5 g/dL.
What is Raynaud's phenomenon?
Raynaud’s phenomenon, which is decreased blood flow to areas such as the fingers
What is the term for a bluish cast on the skin?
What is peripheral cyanosis? Cyanosis refers to a bluish cast to the skin and mucous membranes. Peripheral cyanosis is when there is a bluish discoloration to your hands or feet. It’s usually caused by low oxygen levels in the red blood cells or problems getting oxygenated blood to your body.
Is cyanosis off label?
Using these medications to treat peripheral cyanosis is considered off-label drug use.
What is the pathophysiology of cyanosis?
The pathophysiology of cyanosis is as follows:[11][12] Hypoxic Hypoxia: Due to decreased oxygen tension and content in arterial and venous blood, the oxygen diffusion to the tissues is decreased. [13] Inspired air is low in oxygen content: Sea level, high altitude.
What causes peripheral cyanosis?
Reduced cardiac output in heart failure and shock can lead to peripheral cyanosis, if severe. Lack of pressure prevents an adequate supply of oxygen-rich blood to the extremities. Also, hypotension produces reflex cutaneous vasoconstriction to shunt blood from extremities to the internal organs. This redistribution of blood flow from extremities causes cyanosis of extremities.
Why does cold cause cyanosis?
Exposure to cold increases the transit time through capillary beds. This results in cyanosis due to increased unloading of oxygen from the blood to the tissues.
Why does cyanosis occur in the peripheral blood?
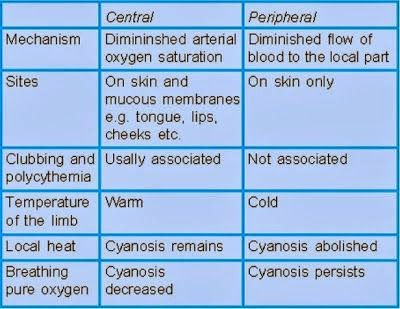
Peripheral cyanosis occurs due to the inability of the body to deliver oxygen-rich blood to the peripheral tissues. Congestive peripheral cyanosis can be caused due to the slowing of blood flow. Ischemic peripheral cyanosis occurs when vasoconstriction leads to diminished peripheral blood flow. In peripheral cyanosis, there is normal arterial oxygen saturation but increased oxygen extraction by the peripheral tissue in the capillary bed in the setting of peripheral vasoconstriction and decreased peripheral blood flow. This results in a significant difference in the saturation between the arterial and venous blood, with increased deoxygenated blood on the venous side of the capillary beds. [14]
Can central cyanosis cause peripheral cyanosis?
All causes of central cyanosis can also cause peripheral cyanosis. Cardiopulmonary causes and hemoglobin abnormalities are the common causes of central cyanosis.
What causes a bluish discoloration of the mucous membranes?
Central cyanosis is a generalized bluish discoloration of the body and the visible mucous membranes, which occurs due to inadequate oxygenation secondary to conditions that lead to an increase in deoxygenated hemoglobin or presence of abnormal hemoglobin.
Is cyanosis a life threatening condition?
Mucous membranes are generally not involved. Peripheral cyanosis is rarely a life-threatening medical emergency. However, it is essential to determine the underlying cause.

Definition
Causes
Symptoms
Exams and Tests
- Timely and swift treatment can help prevent any further complications of low blood oxygen. If you have cyanosis, it's likely that you'll receive oxygen therapy to help boost your blood oxygen levels quickly, but any additional treatment you may receive for cyanosis will depend on the root cause of your condition. For example, treatment for COPD may...
Treatment
Possible Complications
When to Contact A Medical Professional
- Normally, blood returns from the body and flows through the heart and lungs. 1. Blood that is low in oxygen (blue blood) returns from the body to the right side of the heart. 2. The right side of the heart then pumps the blood to the lungs, where it picks up more oxygen and becomes red. 3. The oxygen-rich blood returns from the lungs to the left side of the heart. From there, it is pumped to …
Prevention
- Some heart defects cause major problems right after birth. The main symptom is cyanosis is a bluish color of the lips, fingers, and toes that is caused by the low oxygen content in the blood. It may occur while the child is resting or only when the child is active. Some children have breathing problems (dyspnea). They may get into a squatting position after physical activity to relieve brea…