
Larvicides
- Ivermectin is a broad-spectrum antiparasitic agent that may kill larvae, or at least cause them to migrate out of the...
- Mineral turpentine can be effective against Chrysomya larvae and may aid their removal in cases of wound myiasis.
- Ethanol spray and oil of betel leaf can be used topically to treat C. hominivorax myiasis.
What is the best treatment for myiasis?
Proper hygiene of wounds is very important when treating myiasis. Sometimes medication is given, depending on the type of larva that causes the problem. In which countries does myiasis occur? Myiasis occurs in tropical and subtropical areas. These can include countries in Central America, South America, Africa, and the Caribbean Islands.
How is Cochliomyia hominivorax myiasis treated?
Ethanol spray and oil of betel leaf can be used topically to treat Cochliomyia hominivorax myiasis. A surgical incision is made.
Which specialist consultations are needed for the treatment of myiasis?
Depending on the location of the larval infestation, dermatologists (wound and furuncular myiasis), ophthalmologists (ophthalmomyiasis), or otorhinolaryngologists (oral, facial, nasal myiasis) may need to be consulted. Care must be taken to extract the larva whole, otherwise a considerable foreign body reaction may ensue.
What is cutaneous myiasis?
Cutaneous myiasis is myiasis affecting the skin. Cutaneous myiasis presentations include furuncular, migratory, and wound myiasis, depending on the type of infesting larvae. Myiasis is rarely acquired in the United States; people typically get the fly larva (maggot) infection when they travel to tropical areas in Africa and South America.
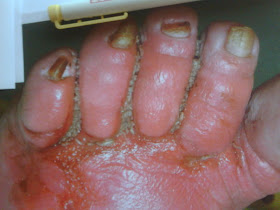
How do I get rid of myiasis?
How is myiasis treated? The larvae need to be surgically removed by a medical professional. Typically, the wound is cleaned daily after the larvae are removed. Proper hygiene of wounds is very important when treating myiasis.
How can I treat myiasis at home?
Mineral turpentine can be effective against Chrysomya larvae and may aid their removal in cases of wound myiasis. Ethanol spray and oil of betel leaf can be used topically to treat C. hominivorax myiasis.
What medicine treats myiasis?
Systemic/topical ivermectin An alternative treatment for all types of myiasis is oral ivermectin or topical ivermectin (1% solution), proven especially helpful with oral and orbital myiasis.
What does myiasis look like?
Typical symptoms of furuncular myiasis include itching, a sensation of movement, and sometimes sharp, stabbing pain. At first, people have a small red bump that may resemble a common insect bite or the beginning of a pimple (furuncle). Later, the bump enlarges, and a small opening may be visible at the center.
What kills maggots fast?
Boiling waterBoiling water. It's free, it's quick, it's effective, and it kills maggots in an instant. No bug sprays or other insecticides required.
What is myiasis vagina?
Myiasis is a parasitic infestation caused by larvae of several fly species. Diagnosis and treatment are straightforward. However, this infestation is extremely rare in the vagina. Infestation of vagina with larvae and maggots is called vaginal myiasis.
How is myiasis diagnosed?
Diagnostic Findings. The diagnosis of myiasis is made by the finding of fly larvae in tissue. Identification to the genus or species level involves comparing certain morphological structures on the larvae, including the anterior and posterior spiracles, mouthparts and cephalopharyngeal skeleton, and cuticular spines.
Can ivermectin treat myiasis?
Ivermectin is a common endectoparasiticide which is mostly used orally and subcutaneously for the treatment of various parasitic diseases. Topical use of the diluted injectable drug has been shown to be effective at killing fly larvae (maggots) in the treatment of myiasis.
Can you get myiasis in your vagina?
However, I did quickly learn that it is possible for maggots to infest a vagina — a condition that's called myiasis of the vagina, which itself is not an STD.
How do you know if you have parasites under your skin?
Signs & Symptoms Tissue under the skin is infiltrated by developing larvae of the parasitic worm known as Dracunculus medinensis, or Guinea worm. A female worm ready to release larvae produces stinging elevated spots (papules), causing redness and itching of the skin.
What is myiasis caused by?
Myiasis is an infestation of the skin by developing larvae (maggots) of a variety of fly species (myia is Greek for fly) within the arthropod order Diptera. Worldwide, the most common flies that cause the human infestation are Dermatobia hominis (human botfly) and Cordylobia anthropophaga (tumbu fly).
Can maggots grow inside you?
Intestinal myiasis Myiasis occurs when a person becomes infested with fly larvae. The larvae live on or inside the person and survive by feeding off their tissues. Intestinal myiasis is a type of myiasis that can occur when a person ingests larvae that survive inside the gastrointestinal tract.
What is the best treatment for myiasis?
An alternative treatment for all types of myiasis is oral ivermectin or topical ivermectin (1% solution), proven especially helpful with oral and orbital myiasis.
How to prevent wound myiasis?
To prevent wound myiasis, simple antisepsis is usually adequate. Wounds should be cleaned and irrigated intermittently, and proper dressings should be applied. Patients with any type of wound should not be permitted to sleep outside and, if in an indoor or hospital environment, the windows should never be opened, unless properly screened. [ 20]
How to remove a larva from a punctum?
The skin lesion is locally anesthetized with lidocaine and excised surgically followed by primary wound closure. Alternatively, lidocaine can be injected forcibly into the base of the lesion in an attempt to create enough fluid pressure to extrude the larvae out of the punctum. [ 20] The larvae are anchored deeply to the subcutaneous by anterior hooklets and it is important to remove all parts from the site to prevent a foreign body reaction. [ 2] Another surgical approach would be to perform a 4- to 5-mm punch excision of the overlying punctum and surrounding skin to gain better access to and visibility of the larva. The larva can then be removed carefully using toothed forceps (experience of B.B. Wilson, MD).
What is used to capture botflies?
This noninvasive approach includes placing petroleum jelly, liquid paraffin, beeswax or heavy oil, or bacon strips over the central punctum and has been used to coax the larvae to emerge spontaneously head-first over the course of several hours, at which time, tweezers (or forceps) aid in the capture. Enlarging the punctum beforehand may make it easier to remove the larvae later as it emerges and is usually needed for botflies. [ 17] Anecdotal evidence has shown the larvae to emerge within 3-24 hours after application of suffocating material. [ 18, 19]
Why can't larvae be removed through the punctum?
The larva should not be forcibly removed through the central punctum because its tapered shape with rows of spines and hooks prevents simple extrusion.
What to do if you have a pyogenic infection?
Also, in the case of secondary pyogenic infection, appropriate antibiotics should be administered.
Who treats myiasis larvae?
Depending on the location of the larval infestation, dermatologists (wound and furuncular myiasis), ophthalmologists (ophthalmomyiasis), or otorhinolaryngologists (oral, facial, nasal myiasis) may need to be consulted.
