- Diet and discontinuation of medication. Treatment usually begins with changes to your diet and medications that may help relieve persistent diarrhea.
- Medications
- Surgery. When the symptoms of microscopic colitis are severe, and medications aren't effective, your doctor may recommend surgery to remove all or part of your colon.
What is the best antibiotic for colitis?
ulcerative colitis, inflammation can develop in the pouch (pouchitis). Pouchitis is often effectively managed with antibiotics. Medication Details Although there are several antibiotics that may be effective, the most commonly prescribed in IBD are: • Metronidazole (Flagyl®) • Ciprofloxacin (Cipro®) • Vancomycin (Vancocin®)
What drugs are used for colitis?
Medications for People with Ulcerative Colitis
- Aminosalicylates (5-ASA drugs)
- Corticosteroids
- Immunomodulator drugs
- Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors
- Biologics
- Other medications
- Medications to avoid
- Talk with your doctor
How to treat ulcerative colitis naturally at home?
Supplements and herbal remedies for ulcerative colitis
- Probiotics. Probiotics introduce healthy gut bacteria to restore and maintain a natural microbial flora in the gut.
- Ginseng. Although there is a lack of human research studying how ginseng affects UC, some animal studies have shown that ginseng may be effective in the treatment of UC by ...
- Psyllium seed/husk. ...
- Boswellia. ...
- Bromelain. ...
- Turmeric. ...
- Gingko biloba. ...
How to reduce colitis pain?
Understanding Ulcerative Colitis Pain: How to Find Relief During a Flare-Up
- Over-the-counter medications. If you have mild pain, medications such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) may be enough to do the trick. ...
- Dietary changes. ...
- Stress-reduction strategies. ...
- Anti-inflammatory medication. ...
- Immunosuppressant medication. ...
- Surgery. ...
- Complementary and alternative remedies. ...

How do I stop diarrhea from colitis?
In addition to following a low-residue diet, you may find diarrhea relief by avoiding carbonated drinks, prune juice, milk, and gum. You also may find that eating smaller meals helps.
What is the best treatment for colitis?
What is the best medication for colitis?Best medications for colitisImodium A-D (loperamide)Antidiarrheal agentOralAzulfidine (sulfasalazine)Anti-inflammatory agentOral, rectal, or enemaApriso (mesalamine)Anti-inflammatory agentOral, rectal, or enemaPrednisoneCorticosteroidOral7 more rows•Apr 6, 2021
Can chronic colitis be cured?
Ulcerative colitis can be debilitating and can sometimes lead to life-threatening complications. While it has no known cure, treatment can greatly reduce signs and symptoms of the disease and bring about long-term remission.
Can colitis cause chronic diarrhea?
Signs and symptoms of microscopic colitis include: Chronic watery diarrhea. Abdominal pain, cramps or bloating.
What is the latest treatment for colitis?
Federal regulators have approved the new drug Zeposia for treating moderate to severe ulcerative colitis in adults. The medication is the latest in a line of drugs used to treat symptoms of this particular type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
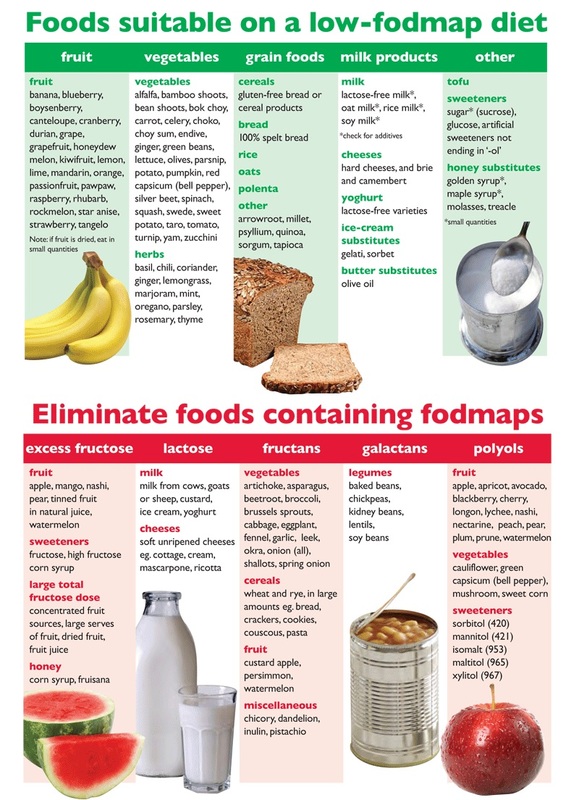
What foods trigger colitis?
What foods trigger colitis? There are several foods that may trigger your symptoms, including fatty and greasy foods, spicy foods, high-sugar foods, caffeine, alcohol, and carbonated beverages.
What is the most common cause of colitis?
Causes of colitis include: Infections caused by a virus or a parasite. Food poisoning due to bacteria. Crohn disease.
What does colitis poop look like?
Stool-related symptoms of ulcerative colitis include: diarrhea. bloody stools that may be bright red, pink, or tarry. urgent bowel movements.
What foods help heal colitis?
The following foods may be suitable for a person who has just had a flare-up of Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis:diluted juices.applesauce.canned fruit.oatmeal.plain chicken, turkey, or fish.cooked eggs or egg substitutes.mashed potatoes, white rice, or noodles.sourdough or white bread.
What are the 3 types of colitis?
Types and causesproctosigmoiditis, which affects the rectum and lower portion of the colon.left-sided ulcerative colitis, which affects the left side of the colon beginning at the rectum.pancolitis, which affects the entire large intestine.
What is the difference between colitis and ulcerative colitis?
What's the difference between colitis and ulcerative colitis? Colitis means your colon is inflamed, or irritated. This can be caused by many things, such as infections from viruses or bacteria. Ulcerative colitis is more severe because it is not caused by an infection and is lifelong.
How fast does prednisone work for ulcerative colitis?
According to The Arthritis Society, prednisone usually works within 1–4 days if a person takes the appropriate dosage. But some people may experience symptom relief within just a few hours.
How long does diarrhea last?
Many people experience diarrhea at some point. These bouts are often acute and resolve in a couple of days with no complications. Other people, however, live with diarrhea that persists for more than two to four weeks.
What to do if you have diarrhea and a blood test can't identify it?
alcohol abuse. If a blood test or a stool sample can’t identify the cause of diarrhea, your doctor may suggest an ultrasound or CT scan of your abdomen, but only if you have other symptoms like pain or bloody stools. These imaging tests will check your organs for problems.
What are the symptoms of diarrhea?
Symptoms of chronic diarrhea. The main symptom of chronic diarrhea is loose or watery stools that persist for weeks. These stools may or may not be accompanied by a sense of urgency. You may have other symptoms as well, such as: abdominal cramps. bloating. nausea.
Why does food pass through my colon?
Certain ingredients speed up the rate of digestion, causing food to pass rapidly through the colon. Common culprits include milk and artificial sweeteners (sorbitol and fructose). Other causes of chronic diarrhea may include: medications — NSAIDs, antibiotics, antacids. diabetes.
What does it mean when you have fat in your stool?
This sample may also reveal fat in your stool, which can indicate chronic pancreatitis (damage to the pancreas from prolonged inflammation) or celiac disease. Your diet can also play a role in chronic diarrhea. Certain ingredients speed up the rate of digestion, causing food to pass rapidly through the colon.
What to do if you don't have a medical condition?
If you don’t have a medical condition, keeping a food journal, watching your diet, and making lifestyle changes may also provide relief. The important thing is that you don’t ignore the problem. The sooner you speak with your doctor, the sooner you can get relief. Last medically reviewed on September 25, 2017.
Can chronic diarrhea be prevented?
Chronic diarrhea caused by an underlying medical condition isn’t always preventable. But you can prevent chronic diarrhea due to infection by taking steps to keep your food and water supply clean. For example:
What is the best treatment for ulcerative colitis?
Anti-inflammatory drugs. Anti-inflammatory drugs are often the first step in the treatment of ulcerative colitis and are appropriate for the majority of people with this condition. These drugs include: 5-aminosalicylates.
What is the only way to diagnose ulcerative colitis?
Endoscopic procedures with tissue biopsy are the only way to definitively diagnose ulcerative colitis. Other types of tests can help rule out complications or other forms of inflammatory bowel disease, such as Crohn's disease.
What is the name of the drug that neutralizes the immune system?
Infliximab (Remicade), adalimumab (Humira) and golimumab (Simponi). These drugs, called tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, or biologics, work by neutralizing a protein produced by your immune system. They are for people with severe ulcerative colitis who don't respond to or can't tolerate other treatments.
What does it mean when you have a white blood cell in your stool?
Stool studies. White blood cells or certain proteins in your stool can indicate ulcerative colitis.
What is the procedure to remove a colon and rectum?
In most cases, this involves a procedure called ileoanal anastomosis (J-pouch) surgery. This procedure eliminates the need to wear a bag to collect stool.
How often do you need a colonoscopy?
If your disease involves more than your rectum, you will require a surveillance colonoscopy every one to two years, beginning as soon as eight years after diagnosis if the majority of your colon is involved, or 15 years if only the left side of your colon is involved.
What is the test for sigmoid colon?
A tissue sample is necessary to make the diagnosis. Flexible sigmoidoscopy . Your doctor uses a slender, flexible, lighted tube to examine the rectum and sigmoid colon — the lower end of your colon. If your colon is severely inflamed, your doctor may perform this test instead of a full colonoscopy.
How to treat colitis?
Treatment of colitis depends upon the cause and often is focused on symptom relief, supportive care, and maintaining adequate hydration and pain control. Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat infectious causes of colitis. Some bacterial infections that cause colitis resolve without any antibiotic treatment.
What is the definition of colitis?
Colitis definition and facts. Colitis refers to inflammation of the inner lining of the colon. There are numerous causes of colitis including infection, inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are two types of IBD ), ischemic colitis, allergic reactions, and microscopic colitis. Symptoms of colitis depend upon the cause ...
What is the name of the inflammation of the colon?
Colitis describes inflammation of the colon (col=colon + itis=inflammation). Examples of causes (types) of colitis include. infection, for example, caused by bacteria like C. difficile, viruses, and parasites; inflammatory bowel disease like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis,
Why does my stool have blood in it?
Common causes of blood in the stool include hemorrhoids; however, other serious causes of bleeding need to be investigated. Colitis is not the only cause of rectal bleeding. Other causes include diverticular disease of the colon ( diverticulitis ), colon polyps, anal fissures, and cancer.
What is the inflammation of the inner lining of the colon?
Colitis describes inflammation of the inner lining of the colon and can be associated with diarrhea, abdominal pain, bloating, and blood in the stool. This inflammation may be due to a variety of reasons, including the following: An illustration of the colon anatomy.
What causes a person to have diarrhea and pain?
Ischemia or lack of blood supply causes inflammation of the colon leading to pain, fever, and diarrhea (bowel movements may contain blood). As a person ages, the arteries that supply blood to the colon gradually narrow and can cause ischemic colitis.
What are the symptoms of colitis?
Symptoms of colitis depend upon the cause and may include. abdominal pain, cramping, diarrhea, with or without blood in the stool (one of the hallmark symptoms of colitis). Associated symptoms depend upon the cause of colitis and may include. fever, chills, fatigue,
Causes
An overgrowth of C. difficile bacteria usually happens due to a disruption of typical intestinal bacteria following a course of antibiotics. Certain strains of C. difficile are resistant to some antibiotics, may be able to overgrow, and can cause inflammation and bleeding.
Treatment
A person with this condition will need to stop taking any drugs that are causing the issue. A doctor may prescribe medications such as vancomycin or fidaxomicin (Dificid).
Causes
It is not certain what causes microscopic colitis, but doctors believe a combination of genetics and atypical immune system responses may be the reason.
Treatment
Doctors may prescribe the following medications for microscopic colitis:
Causes
Ischemic colitis is caused by reduced blood flow to the colon. This can happen for various reasons, such as hardened arteries in people with peripheral vascular disease or coronary artery disease.
Treatment
Treatment for ischemic colitis depends on the severity of the condition. A doctor may treat mild cases with:
Symptoms
For some people, CMV colitis does not usually present any symptoms or it may be a self-limited disease, meaning it goes away on its own.
How to treat persistent diarrhea?
Your doctor may recommend that you: Eat a low-fat, low-fiber diet. Foods that contain less fat and are low in fiber may help relieve diarrhea. Discontinue dairy products, gluten or both .
What test is used to rule out diarrhea?
In addition to a colonoscopy or flexible sigmoidoscopy, you may have one or more of these tests to rule out other causes for your symptoms. Stool sample analysis to help rule out infection as the cause of persistent diarrhea. Blood test to look for signs of anemia or infection.
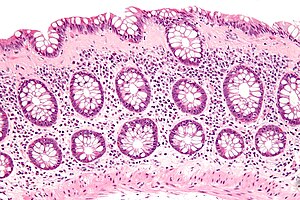
How to confirm microscopic colitis?
To help confirm a diagnosis of microscopic colitis, you may have one or more of the following tests and procedures: Colonoscopy. This exam allows your doctor to view your entire colon using a thin, flexible, lighted tube (colonoscope) with an attached camera. The camera sends images of your rectum and entire colon to an external monitor, ...
What medications can cause microscopic colitis?
Your doctor will also ask about any medications you are taking — particularly aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others), naproxen sodium (Aleve), proton pump inhibitors, and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) — which may increase your risk of microscopic colitis.
What steroid is used for diarrhea?
Steroids such as budesonide (Entocort EC) Medications that block bile acids (which can contribute to diarrhea) such as cholestyramine/aspartame or cholestyramine (Prevalite), or colestipol (Colestid) Anti-inflammatory medications such as mesalamine (Delzicol, Apriso, others) to help control colon inflammation.
What test is used to test for celiac disease?
Blood test to look for signs of anemia or infection. Upper endoscopy with biopsy to rule out celiac disease. Doctors use a long, thin tube with a camera on the end to examine the upper part of your digestive tract. They may remove a tissue sample (biopsy) for analysis in the laboratory.
Can you take a tissue sample during a colonoscopy?
A tissue sample can be taken through the scope during the exam. Because intestinal issues often appear normal in microscopic colitis, a definite diagnosis of microscopic colitis requires a colon tissue sample (biopsy) obtained during a colonoscopy or flexible sigmoidoscopy. In both subtypes of microscopic colitis, ...
How long does diarrhea last after taking corticosteroids?
If grade 2 diarrhea persists more than two to three days after holding the treatment, prescribe prednisone or methylprednisolone 1 mg/kg per day. With steroids, early intervention is key.
Can peptic ulcers cause blood in stool?
Immune-related toxicity and infection may coexist, and blood in the stools may also indicate a gastro intestinal bleed from peptic ulcer disease or malignancy. Immune-mediated colitis and inflammatory bowel disease appear similar on endoscopy; however, immune-mediated colitis has more neutrophilic inflammation without chronic inflammation.
Does T cell activation cause diarrhea?
The mechanisms by which immune-related diarrhea and colitis occur are not clear. However, T-cell activation leads to high levels of CD4 T-helper cell cytokines and cytolytic CD8 T-cell tissue infiltration. Some research suggests that depleting regulatory T cells also induces autoimmunity. Additionally, blocking CTLA-4 disables its protection ...
Is diarrhea a toxicity in immunotherapy?
Manage Immunotherapy-Related Diarrhea and Colitis. Although immunotherapy has a unique set of toxicities compared to traditional chemotherapy, in general, grade 3 or 4 toxicities are rare—with the exception of grade 3 diarr hea and colitis. The mechanisms by which immune-related diarrhea and colitis occur are not clear.
How long does diarrhea last with lymphocytic colitis?
This diarrhea does not have blood. You may have several of these watery bowel movements each day. This may last for weeks or months. For most people, this diarrhea goes away for a while, but then it comes back later. Other symptoms of lymphocytic colitis may include: Weight loss. Belly pain. Bloating.
What causes diarrhea in the abdomen?
Your healthcare provider will rule out other causes of your diarrhea. These can include an infection or another inflammatory bowel disease. Your healthcare provider will also do other tests.
What causes watery diarrhea and pain in the belly?
Lymphocytic colitis is a condition that affects your large intestine. It leads to episodes of watery diarrhea and belly pain. Bacterial and viral infections, certain medicines, or certain foods may trigger lymphocytic colitis in some people. Symptoms of lymphocytic colitis include watery diarrhea, belly pain, and fatigue.
How to tell if you have lymphocytic colitis?
Symptoms of lymphocytic colitis include watery diarrhea, belly pain, and fatigue. You may have a colonoscopy to diagnose this condition. During this test, your healthcare provider may take out a sample of your large intestine and look at it through a microscope. You may need to take medicines to treat your condition.
What is the cause of watery diarrhea?
Lymphocytic colitis is a health problem that causes inflammation of your large intestine. It causes episodes of watery diarrhea and belly pain. Your large intestine is part of your digestive (gastrointestinal or GI) tract. It includes both the colon and rectum.
What is the function of the large intestine?
The large intestine receives the broken-down products of food from the small intestine. One of its main jobs is to reabsorb water and electrolytes, such as salt . The colon leads to the rectum, which stores your feces before your body expels them. In lymphocytic colitis, inflammatory cells from your immune system travel to your large intestine.
What foods can make diarrhea worse?
You may need to stay away from foods that make your diarrhea worse. These can include dairy products, caffeine, artificial sweeteners, and foods high in fat. Some people with this condition also do well on a gluten-free diet.
Diagnosis
Treatment
- Ulcerative colitis treatment usually involves either drug therapy or surgery. Several categories of drugs may be effective in treating ulcerative colitis. The type you take will depend on the severity of your condition. The drugs that work well for some people may not work for others, so it may take time to find a medication that helps you. In addi...
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Sometimes you may feel helpless when facing ulcerative colitis. But changes in your diet and lifestyle may help control your symptoms and lengthen the time between flare-ups. There's no firm evidence that what you eat actually causes inflammatory bowel disease. But certain foods and beverages can aggravate your signs and symptoms, especially during a flare-up. It can be helpfu…
Alternative Medicine
- Many people with digestive disorders have used some form of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM). However, there are few well-designed studies showing the safety and effectiveness of complementary and alternative medicine. Although research is limited, there is some evidence that adding probiotics along with other medications may be helpful, but this has …
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Symptoms of ulcerative colitis may first prompt you to visit your primary care doctor. Your doctor may recommend you see a specialist who treats digestive diseases (gastroenterologist). Because appointments can be brief, and there's often a lot of information to discuss, it's a good idea to be well prepared. Here's some information to help you get ready, and what to expect from your doct…