Medication
In the presence of discordance between the test result and strong clinical features of deficiency, treatment should not be delayed to avoid neurological impairment. Treatment of cobalamin deficiency is recommended in line with the British National Formulary.
Self-care
Treatment of cobalamin deficiency is very simple, and can be attempted as a sole therapy, or in conjunction with treatment for the underlying disease process. I have had certain canine patients respond to cobalamin supplementation alone, and resolve their underlying symptoms associated with enteropathy.
Nutrition
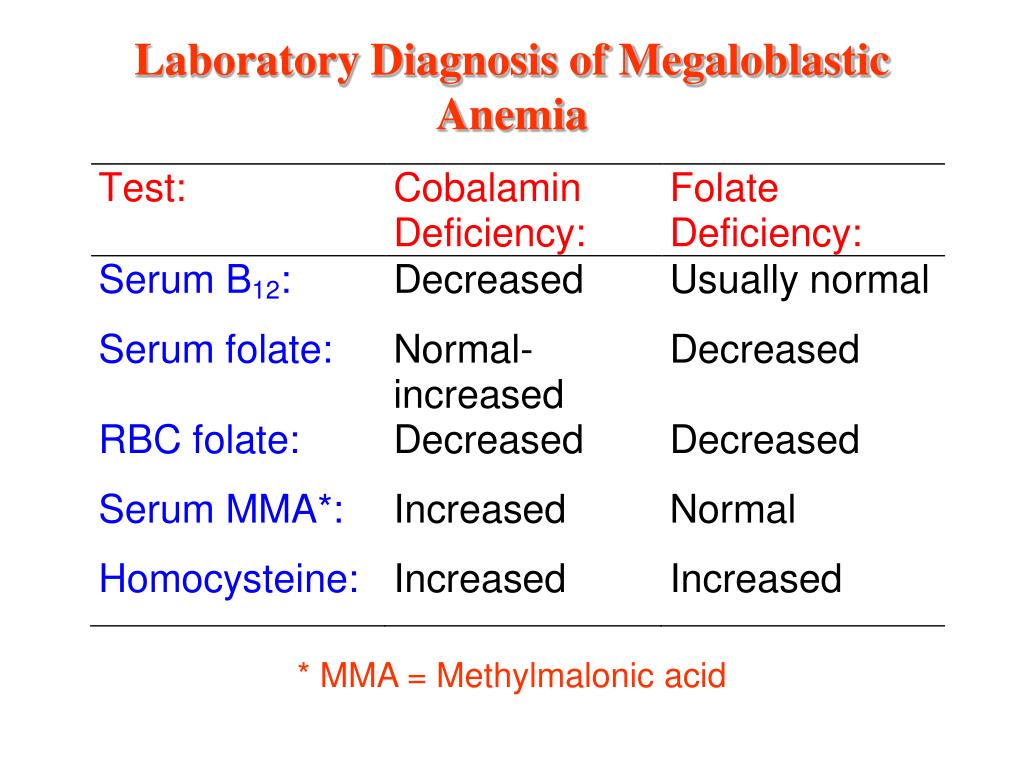
There are multiple methods to diagnose cobalamin deficiency, from simply measuring a serum cobalamin level, to running serum homocysteine and methylmalonic acid (MMA) levels, as well as running MMA urine levels.
See more
Pathophysiologically based management requires systematic attention to each of its individual components: correctly diagnosing cobalamin deficiency, reversing it, defining its underlying cause, preventing relapse, managing the underlying disorder and its complications, and educating the patient. Introduction
When should treatment of cobalamin deficiency be delayed?
How do you treat cobalamin deficiency in dogs?
How is cobalamin deficiency diagnosed?
What is pathophysiologically based management of cobalamin deficiency?
See more

What is the best treatment for vitamin B12 deficiency?
You can change your diet to include vitamin B12-fortified grains, a supplement or B12 injections, or a high-dose oral vitamin B12 if you are deficient. Older adults who have a vitamin B12 deficiency will likely have to take a daily B12 supplement or a multivitamin that contains B12.
How do you increase cobalamin?
To increase the amount of vitamin B12 in your diet, eat more of foods that contain it, such as:Beef, liver, and chicken.Fish and shellfish such as trout, salmon, tuna fish, and clams.Fortified breakfast cereal.Low-fat milk, yogurt, and cheese.Eggs.
Can vitamin B12 deficiency be corrected?
A serious vitamin B12 deficiency can be corrected two ways: weekly shots of vitamin B12 or daily high-dose B12 pills. A mild B12 deficiency can be corrected with a standard multivitamin. In many people, a vitamin B12 deficiency can be prevented.
What is the most common cause of cobalamin deficiency?
The most frequent cause of cobalamin malabsorption is pernicious anemia [14] in which the atrophy of the gastric parietal cells results in a lack of secretion of both IF and chlorhydric acid.
How long does it take to recover from B12 deficiency?
Once you begin treating your vitamin B12 deficiency, it can take up to six to 12 months to fully recover. It is also common to not experience any improvement during the first few months of treatment. If you can, it's a good idea to address what's causing the deficiency.
Can I get a vitamin B12 injection?
Vitamin B12 Shots Are Very Effective Vitamin B12 shots are the most common way to prevent or treat a deficiency. The injections are prescribed by a doctor and given intramuscularly, or into muscle. Injections are usually given as hydroxocobalamin or cyanocobalamin.
Do you need a prescription for B12 injections?
Do you need a prescription for b12 injections? Yes, you need a prescription. Perfect Health providers are able to evaluate patients for B12 deficiency.
What foods are high in cobalamin?
High vitamin B12 foods include clams, fish, crab, low-fat beef, fortified cereal, fortified soymilk, fortified tofu, low-fat dairy, cheese, and eggs.
Is B12 deficiency serious?
If left untreated, the symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency tend to worsen and irreversible problems involving the nerves and brain may develop. The risk of experiencing a number of serious complications, including heart failure, may also increase.
Is it good to take vitamin B12 tablets?
When taken at appropriate doses, vitamin B-12 supplements are generally considered safe. While the recommended daily amount of vitamin B-12 for adults is 2.4 micrograms, higher doses have been found to be safe. Your body absorbs only as much as it needs, and any excess passes through your urine.
What are the challenges of cobalamin deficiency?
The challenges in medical management of cobalamin deficiency lie in attention to the unique pathophysiology that underlies cobala min deficiency , more than in the mechanics of therapy. The central physiologic principles are that clinically important deficiency is more likely to occur (and progress) when intrinsic factor–driven absorption fails than when diet is poor and that most causes take years to produce clinically obvious deficiency. Transient defects have little clinical impact. The key management principle is the importance of follow-up, which also requires knowing how the deficiency arose. The virtues of these principles are not always fully appreciated. Recent developments have made diagnosis and management more difficult by diminishing the ability to determine cobalamin absorption status. Clinicians must also grapple with premature medicalization of isolated, mild biochemical changes that added many asymptomatic cases of still undetermined medical relevance to their caseload, often expanded by inflated cobalamin level criteria. The potential for misattribution of cobalamin-unrelated presentations to nongermane cobalamin and metabolite abnormalities has grown. Pathophysiologically based management requires systematic attention to each of its individual components: correctly diagnosing cobalamin deficiency, reversing it, defining its underlying cause, preventing relapse, managing the underlying disorder and its complications, and educating the patient.
What is the first section of Cobalamin?
The first section reviews the essentials of pathophysiologically coherent management of cobalamin deficiency in adults. Where relevant, diagnostic issues are included because diagnosis is crucial to management, which has several coequal components.
How does cobalamin differ from other vitamins?
The pathophysiology of cobalamin differs in important ways from most other vitamins, such as folate. 25 The daily requirement is so small relative to stores ( Table 1) that deficiency typically takes years to develop in adults and only infrequently reaches the depletion point necessary for clinical consequences. Cobalamin is also tightly chaperoned everywhere by specific binding proteins and receptors that regulate how much traverses gut and other cell membranes, how much is reabsorbed after biliary secretion, and how much is retained by the body. 26 As long as specific absorption via IF remains intact, cobalamin economy is usually maintained. Transport defects at other sites are usually genetic and thus rare.
What is IF based malabsorption?
Based on the foregoing, clinical signs of deficiency suggest IF-based malabsorption until proven otherwise. However, management decisions must be provisional until the disorder (which is often not PA) and its prognosis are identified ( Table 3 ). For nearly 50 years, the diagnostic search began with the Schilling test, which not only identified abnormal IF-related absorption but also distinguished between gastric and intestinal defects. The underlying diseases themselves (eg, PA) are often asymptomatic and could not be detected otherwise. 1 An abnormal Schilling test result also helps select the optimal final test (eg, intestinal biopsy).
Is cobalamin used for fatigue?
One legacy of the misuse of cobalamin as a tonic for fatigue and other nonspecific symptoms 51 has been misperception of the serious medical nature of clinical deficiency. Education helps prevent patients from abandoning treatment after achieving symptomatic improvement. The implications for prognosis and monitoring must be explained clearly, discussing lifelong therapy with those patients needing it, duration of therapy with those having reversible causes, and the need for follow-up with those whose underlying cause was not identified. It is useful to include family members in the discussion and to provide a written description of relevant facts. It also does not hurt to tell patients the grim history of PA before Minot and Murphy. Extra effort is needed for patients choosing oral therapy, who may confuse their therapy with optional self-supplementation.
Can cobalamin deficiency be treated?
Cobalamin deficiency rarely requires instant therapy. Several days' delay to assure diagnostic certainty is acceptable even with neurologic symptoms, but treatment should be started expeditiously for severe neurologic symptoms with their risk of irreversibility (eg, extensive sensory defects, gait disturbances, mental changes).
Is FBCM high after gastrectomy?
The risk of FBCM and subclinical deficiency is high after subtotal gastrectomy 33 or bariatric surgery. 39 Preventive supplementation with daily 1000-μg doses, preferably on an empty stomach, is warranted.
What is the role of cobalamin in the ileum?
Cobalamin is an essential cofactor for certain enzyme systems, nucleic acid synthesis, amino acid metabolism and hematopoiesis. Intrinsic factor is required for absorption of cobalamin in the ileum.
Where is cobalamin released?
As cobalamin is only acquired from dietary intake, once ingested, it is bound to the transport protein haptocorrin, and is subsequently delivered to the small intestine for absorption. Free cobalamin is released in the small intestine and bound to intrinsic factor (IF), a glycoprotein produced by the parietal cells of the stomach (humans/ dogs) ...
Why are Shar Peis deficient in cobalamin?
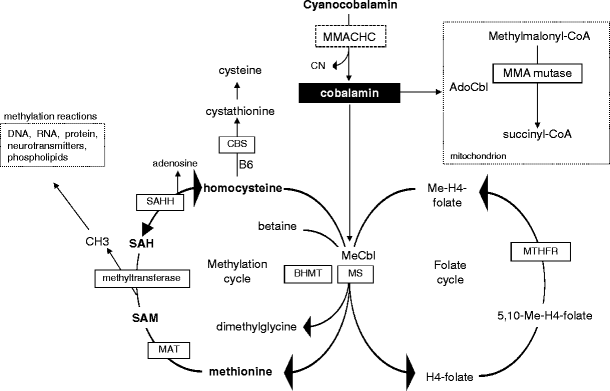
In Shar Peis, due to the nature of the genetic defect, not only are these dogs deficient in cobalamin they may have 10x higher levels of serum methylmalonic acid than other cobalamin deficient dogs/breeds (once again refer to diagram/mitochondrial pathway).
What is the B12 vitamin?
[email protected]. 617-541-5186. Cobala min, or vitamin B12, is a water soluble vitamin that is an essential cofactor for many enzyme systems in humans and animals. Animals are unable to synthesize cobalamin and are dependent on nutritional sources. Deficiency in this very important vitamin is common, and only occurs where ...
Can cats have cobalamin deficiency?
Breed- related congenital defects in cobalamin metabolism have not been identified in cats. Cobalamin deficiency is observed with several diseases, including: Inflammatory bowel disease, GI lymphoma, intestinal dysbiosis, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, short bowel syndrome, pancreatitis, as well as in cases of gastrinoma, ...
Can cobalamin deficiency cause anemia?
Cobalamin deficiency in humans can result in failure to thrive, pernicious anemia (normocytic/ nonregenerative), proteinuria and neurological damage (human infants ). In dogs, congenital cobalamin deficiency can result in clinical abnormalities including failure to thrive, poor body condition, weight loss, inability to gain weight, cachexia, lethargy, weakness, anorexia, diarrhea, vomiting, dysphagia, oral ulcerations, hematopoietic abnormalities (nonregenerative anemia, neutropenia), and proteinura. Symptoms can occur as early as 6-12 weeks of age, with cases being identified clinically in patients up to 3-4 years of age.
What is the cobalamin that is bound to TC?
Cobalamin that is bound to TC is called holotranscobalamin (holoTC) which is the metabolically active vitamin B12 fraction.
Can humans synthesize cobalamin?
Neither humans nor animals are able to synthesize this vitamin. Foods of animal source are the only natural source of cobalamin in human diet. There are only two enzymatic reactions in mammalian cells that require cobalamin as cofactor. Methylcobolamin is a cofactor for methionine synthase. The enzyme methylmalonyl-CoA-mutase requires ...
Is cobalamin deficiency common?
Cobalamin deficiency is common worldwide. Cobalamin malabsorption is common in elderly subjects which might explain low vitamin status. Subjects who ingest low amount of cobalamin like vegetarians develop vitamin deficiency. No single parameter can be used to diagnose cobalamin deficiency.
How to treat anemia related to vitamin C deficiency?
Treatment for anemia related to vitamin C deficiency is with vitamin C tablets. Additionally, you increase your intake of foods and beverages that contain vitamin C.
How to treat folate deficiency anemia?
Folate deficiency anemia treatment. Treatment involves eating a healthy diet and taking folic acid supplements as prescribed by your doctor. In most cases, folic acid supplements are taken orally. Once your body's level of folate increases to normal, you may be able to stop taking the supplements. But if the cause of your folate deficiency can't be ...
What test can be performed to determine if you have vitamin deficiency?
If blood tests reveal a vitamin deficiency, your doctor may perform other tests to determine the type and cause, such as: Antibodies test. Your doctor may draw a sample of your blood to check for antibodies to intrinsic factor. Their presence indicates pernicious anemia. Methylmalonic acid test.
What does methylmalonic acid mean in blood test?
Their presence indicates pernicious anemia. Methylmalonic acid test. You may undergo a blood test to measure the presence of a substance called methylmalonic acid. The level of this substance is higher in people with vitamin B-12 deficiency.