What is chorea and how can it be treated?
Expert commentary: Inhibitors of presynaptic vesicular monoamine transporter type 2 (VMAT2) that cause striatal dopamine depletion, such as tetrabenazine, deutetrabenazine, and valbenazine, are considered the treatment of choice in patients with chorea.
Can chorea be cured?
Treatment for Huntington's disease is supportive, while treatment for Sydenham's chorea usually involves antibiotic drugs to treat the infection, followed by drug therapy to prevent recurrence. Adjusting medication dosages can treat drug-induced chorea. Metabolic and endocrine-related choreas are treated according to the cause (s) of symptoms.
What are the common causes of chorea?
The treatment of chorea can be considered in three main categories: (1) terminating or modifying exposure to the causative agent, (2) symptomatic treatment of chorea, and (3) treatment targeting the underlying etiology. Symptomatic treatment decision of chorea should be based on the functional impact on the child caused by chorea itself.
How to prevent chorea?
Even though doctors may use brain surgery to treat chorea, it can cause serious complications. Deep brain stimulation is another technique being tested as a …
See more
Jul 01, 2019 · The most widely used agents in the treatment of chorea are the neuroleptics. The basis of their mechanism of action is thought to be related to blocking of dopamine receptors. Neuroleptics can be...

Can chorea be cured?
Sydenham's chorea is treatable and curable. The prognosis for individuals with chorea varies depending on the type of chorea and the associated disease. Huntington's disease is a progressive, and ultimately, fatal disease.Mar 27, 2019
Does chorea go away in sleep?
Overall, chorea can affect various body parts, and interfere with speech, swallowing, posture and gait, and disappears in sleep.
Is chorea an emergency?
Although chorea gravidarum is rarely an emergency, it is likely that neurologists will encounter this entity in the context of an emergent inpatient consultation on a maternity ward. The antiphospholipid syndrome may result in acute generalized chorea.
What triggers chorea?
Chorea can be caused by a variety of abnormal processes in the body, including metabolic derangements, exposure to certain drugs or toxins, genetic and degenerative diseases of the brain, infections, tumors, and disorders of the immune and inflammatory systems of the body.
How long does chorea last?
Sydenham chorea symptoms usually resolve within three weeks to six months. However, symptoms may last longer than one year.
Can anxiety cause chorea?
Chorea is usually worsened by anxiety and stress and subsides during sleep. Most patients attempt to disguise chorea by incorporating it into a purposeful activity.
What does chorea feel like?
The most common symptom is jerky movements of the arms and legs, known as 'chorea'. Chorea usually starts as mild twitching and gradually increases over the years. A person with Huntington's disease may also have difficulties with speech, swallowing and concentration.
What is chorea gravidarum?
Chorea gravidarum (CG) is the term given to chorea occurring during pregnancy. This is not an etiologically or pathologically distinct entity but rather a generic term for chorea of any cause starting during pregnancy. Therefore, CG is regarded as a syndrome rather than a specific disease entity.Jun 29, 2021
What does Sydenham's chorea look like?
SC is characterized by rapid, irregular, and aimless involuntary movements of the arms and legs, trunk, and facial muscles. It affects girls more often than boys and typically occurs between 5 and 15 years of age.Mar 27, 2019
Which part of the brain is affected in chorea?
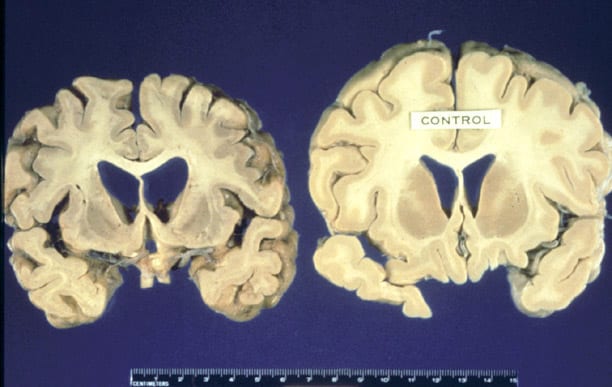
Chorea and athetosis result from overactivity in the basal ganglia, the part of the brain that helps initiate and smooth out and coordinate intended (voluntary) movements initiated by nerve impulses from the brain.
What is a chorea?
What is chorea? Chorea is a movement disorder that causes involuntary, irregular, unpredictable muscle movements. The disorder can make you look like you’re dancing (the word chorea comes from the Greek word for “dance”) or look restless or fidgety.
What is chorea in medical terms?
Chorea is a movement disorder that occurs in many different diseases and conditions. Dozens of genetic conditions, autoimmune and infectious diseases, endocrine disorders, medications and even pregnancy can have chorea as a symptom. Treatment is based on cause of the chorea.
How many people have chorea?
No one knows for sure how many people experience chorea. Chorea is usually a symptom of another disorder. About 30,000 people in the United States have Huntington’s disease (a genetic condition that causes chorea). Doctors estimate another 200,000 people have a risk of developing Huntington’s disease because their parents have the genetic condition.
When do you develop Huntington's disease?
Usually, people develop symptoms of Huntington’s disease between ages 40 and 50. Huntington’s disease is the most common inherited type of chorea. Children who have had rheumatic fever: Kids and adolescents can develop Sydenham chorea after rheumatic fever, which is a complication of untreated strep throat.
How long does it take for Huntington's disease to get worse?
Symptoms of Huntington’s disease get worse over time (usually over 10 to 20 years). Rheumatic fever: Around one to eight months after having rheumatic fever, children can develop Sydenham chorea (also called St. Vitus dance).
What is the most common symptom of Huntington's disease?
Chorea is the most common symptom of Huntington’s disease. In the United States, about 4,000 kids a year develop Sydenham chorea after having rheumatic fever. Rheumatic fever is a serious complication of untreated strep throat. Girls are more likely than boys to get rheumatic fever.
What are the causes of chorea?
Endocrine and metabolic disorders: Hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia, hyperthyroidism, hypoparathyroidism, hyperparathyroidism, hyponatremia, hypernatremia, hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia, polycythemia vera and hepatic failure are some of the conditions that can cause chorea.
How to treat chorea?
Treatment depends on the type of chorea and the associated disease. Treatment for Huntington's disease is supportive, while treatment for Sydenham's chorea usually involves antibiotic drugs to treat the infection, followed by drug therapy to prevent recurrence.
What is a chorea?
View Full Treatment Information. Definition. Chorea is an abnormal involuntary movement disorder, one of a group of neurological disorders called dyskinesias, which are caused by overactivity of the neurotransmitter dopamine in the areas of the brain that control movement. Chorea is characterized by brief, irregular contractions ...
What is the NINDS research?
The NINDS supports research on movement disorders such as chorea. The goals of this research are to increase understanding of these disorders and to find ways to prevent and treat them. Information from the National Library of Medicine’s M...
What is chorea in the brain?
Definition. Chorea is an abnormal involuntary movement disorder, one of a group of neurological disorders called dyskinesias, which are caused by overactivity of the neurotransmitter dopamine in the areas of the brain that control movement.
Is Huntington's disease a progressive disease?
Huntington's disease is a progressive, and ultimately, fatal disease. Sydenham's chorea is treatable and curable. The prognosis for individuals with chorea varies depending on the type of chorea and the associated disease. Huntington's disease is a progressive, and ultimately, fatal disease.
What is chorea in neuroscience?
NINDS Clinical Trials. Definition. Chorea is an abnormal involuntary movement disorder, one of a group of neurological disorders called dyskinesias, which are caused by overactivity of the neurotransmitter dopamine in the areas of the brain that control movement.
Is chorea a disease?
Chorea is a primary feature of Huntington's disease, a progressive, hereditary movement disorder that appears in adults, but it may also occur in a variety of other conditions. Sydenham's chorea occurs in a small percentage (20 percent) of children and adolescents as a complication of rheumatic fever.
What is a chorea?
What to Know About Chorea. Chorea is a movement disorder that stems from something wrong with the basal ganglia nerve structure deep in your brain. It causes involuntary movements of the hands, feet, and face. These movements may be small and fidgety or big and vigorous.
What are the symptoms of chorea?
Symptoms of Chorea. The uncontrolled movements in chorea can take many forms. Some people with mild chorea can mask the movements as restlessness. In its more severe forms, chorea can be a series of violent movements that flow from one part of the body to another. Certain types of movements are typical of chorea.
Where does chorea originate?
Chorea originates in the basal ganglia — an area of the brain that controls movement. Scientists believe that chorea is triggered when the basal ganglia receive too much dopamine — a chemical that helps nerves function. Too much of dopamine can cause problems.#N#
When do Huntington's disease symptoms start?
. The first sign of this disease is movement problems, which usually begin between the ages of 35 and 40 years.
What causes chorea in children?
The most widely recognized cause of chorea is Huntington's disease — a hereditary disorder. But, there can be many other causes, some of which are very rare. A child who got rheumatic fever after a strep throat or scarlet fever infection may show a temporary form of chorea.
What is it called when you stick your tongue out?
Jack-in-the-box tongue. When someone with chorea tries to stick out their tongue, it pops in and out of the mouth. This symptom is also called harlequin' s tongue. Distinctive gait.
What are the two types of neuroleptics?
Neuroleptics can be classified as typical and atypical. Typical neuroleptics include haloperidol and fluphenazine. Atypical neuroleptics include risperidone, olanzapine, clozapine, and quetiapine.
Is Q10 a coenzyme?
Coenzyme Q10 alone and in combination with minocycline have been proposed as potential therapies and have shown promise in HD rodent models. Coenzyme Q10 is thought to target mitochondrial dysfunction, which has been implicated as one of the pathologic mechanisms of mutant huntingtin.
Does minocycline cause apoptosis?
Minocycline, one of the tetracyclines, is known to have anti-apoptosis effects. [ 10, 11] Intravenous immunoglobulin and plasmapheresis may shorten the course of the illness and decrease symptom severity in patients with Sydenham chorea. Chorea following cardiac transplantation has been reported to be responsive to steroid treatment.
Is chorea a symptom?
Only symptomatic treatment is available for patients with chorea. Chorea may be a disabling symptom, leading to bruises, fractures, and falls, and may impair the ability of patients to feed themselves. In addition, patients sometimes express a desire for antichorea treatment for cosmetic reasons. The most widely used agents in the treatment ...
What is chorea in biology?
What is chorea? Chorea refers to involuntary movements characterized by their random, brief, and non-rhythmic character. They are often described as seeming to “flow” from one body part to another unpredictably, though they can also be confined to a single area of the body (such as the mouth area or hands).
What is included in a clinical evaluation?
The clinical evaluation includes a detailed history of other medical problems, prior surgeries, previous infections you may have had, exposures to medications and toxins (including alcohol and illegal drugs), and a family history of diseases that occurred in your relatives.
Is cholera a disease?
Chorea is a symptom and not a specific disease, similar to the way a fever can happen for many different reasons. Chorea can be caused by a variety of abnormal processes in the body, including metabolic derangements, exposure to certain drugs or toxins, genetic and degenerative diseases of the brain, infections, tumors, ...
Can Parkinson's cause dystonia?
These movements occur secondary to the anti-parkinsonian medications and are not caused by Parkinson’s disease directly. Medications that are used to treat Parkinson’s disease can sometimes cause other abnormal movements as well, such as dystonia. My doctor mentioned athetosis.
Can chorea be treated?
In some cases in which chorea is due to prior damage to the brain or an ongoing degenerative process, there may not be a treatment available to influence the underlying disease process. The choreic movements themselves can be treated with medications that can help to suppress them.
Is athetosis a form of dystonia?
When both chorea and athetosis occur at the same time, it is sometimes referred to as choreoathetosis. Athetosis and choreoathetosis can sometimes be mistaken for another involuntary movement called dystonia.
How to treat chorea?
Surgical procedures, which can help in treating chorea, include deep brain stimulation where electrodes are implanted in the brain to help regulate the nerve impulses. This procedure is recommended if the chorea is not responding to medications. It does not cure chorea, but helps in alleviating the symptoms.
What are some medications that help with chorea?
These medications include: Fluphenazine, haloperidol, olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone.
How to diagnose chorea?
There are some laboratory tests which can indicate chorea, such as: 1 A low level of copper indicates Wilson disease, which is a genetic disorder that causes chorea. 2 If the blood test shows spiky red blood cells or erythrocytes, then it indicates neuroacanthocytosis. 3 Blood test to check for thyroid or parathyroid hormones can indicate endocrine or metabolic-related chorea. 4 Imaging studies can be done to check the brain activity and these include MRI or CT scan of the brain. This can help in diagnosing Huntington’s disease which causes chorea.
What are the symptoms of chorea?
Symptoms of chorea range from minor movements, such as fidgeting to more severe and profound uncontrolled movements of the arms and legs. Treatment for Chorea comprises of treating the underlying condition which is causing chorea.
What causes chorea?
A thorough medical history is required to determine the exact cause. Some of the causes of Chorea include: Advertisement. AIDS. Immune disorders, such as SLE or systemic lupus erythematosus can cause Chorea.
Is chorea a symptom of Huntington's disease?
Chorea is a common symptom in patients with adult-onset Huntington’s disease and is less common in patients who have Huntington’s as children or have juvenile Huntington’s disease. Gradually there is worsening of the symptoms affecting arms and legs. Advertisement.
What is the difference between a chorea and a ballismus?
According to research, chorea is one of the three types of hyperkinetic disorder. Chorea is a type which causes involuntary rapid movements. Ballismus or choreoballismus is another type which causes a more severe type of jerking movements, which are potentially dangerous as they can cause injury. Athetosis, also known as choreoathetosis, is ...