Medication
Treating Carotid Artery Stenosis with Stents Sometimes a patient is not a candidate for carotid endarterectomy. This can help because of his or her general health. It can also happen is the narrow portion of the artery is too high up the neck to reach with surgery. In these cases, a stent can be placed in the carotid artery.
Procedures
Carotid endarterectomy: Severe cases of stenosis often require carotid endarterectomy. A surgeon makes an incision to remove plaque and any diseased portion of the artery while the patient is under general anesthesia. Carotid artery angioplasty and stenting: A less invasive option used for severe stenosis. During this procedure, the doctor threads a catheter from an incision …
Self-care
For most patients, a carotid endarterectomy is the safest procedure to treat carotid artery stenosis. This is a surgical procedure during which the artery is opened in the neck and the plaque is cleaned out. The surgery is very effective at lowering your risk of stroke.
Nutrition
During the angioplasty procedure, a carotid stent (a small, metal mesh tube) is placed inside the carotid artery at the site of the blockage and provides support to keep the artery open. The stent stays in place permanently and acts as a scaffold to support the artery and keep it open. After several weeks, the artery heals around the stent.
See more
· A less-invasive option, called carotid stenting, involves inserting a catheter into an artery in the groin, advancing it to the carotid artery, opening the blockage with a balloon, and leaving behind a wire cage (or stent) to hold the artery open. …
How do you treat carotid stenosis?
What percentage of carotid stenosis requires surgery?
What is the prognosis for carotid stenosis?
What percentage of carotid stenosis requires surgery?
Surgery is best for most patients with symptoms: Carotid endarterectomy should be strongly considered for symptomatic patients with 70 to 99 percent blockage in the carotid artery. It also should be considered for those with 50 to 69 percent stenosis.
How do you clear a blocked carotid artery without surgery?
Balloon angioplasty appears to be just as good as surgery to unblock carotid arteries. Date of last review, March 25, 2020Opening a blocked heart artery with a balloon and then propping it open with a wire-mesh stent is more commonly used than bypass surgery for restoring blood flow to the heart.
How long can you live with blocked carotid artery?
In this long-term follow-up, the median survival after carotid endarterectomy for patients with an asymptomatic stenosis was 10.2 years.
What is the most common cause of carotid artery stenosis?
Carotid artery disease is caused by a buildup of plaques in arteries that deliver blood to your brain. Plaques are clumps of cholesterol, calcium, fibrous tissue and other cellular debris that gather at microscopic injury sites within the artery. This process is called atherosclerosis.
Is carotid artery surgery considered major surgery?
Carotid artery surgery is major surgery with risks and potential complications. You may have less invasive treatment options.
When should you have carotid artery surgery?
This procedure is done if your doctor has found narrowing or a blockage in your carotid artery. Your health care provider will have done one or more tests to see how much the carotid artery is blocked. Surgery to remove the buildup in your carotid artery may be done if the artery is narrowed by more than 70%.
Do cardiologists treat carotid artery blockage?
Diagnosing and treating carotid artery disease When a primary care physician or cardiologist suspects that a patient may have carotid stenosis, they will refer them to a vascular surgeon, who will typically perform an ultrasound.
What is the death rate of carotid artery surgery?
Results— There were 4149 patients who underwent carotid endarterectomy; 1376 (33.1%) were symptomatic. Overall mortality rate was 0.5%.
What kind of doctor treats carotid blockage?
Vascular surgeons perform carotid endarterectomy to remove plaque from the carotid arteries and lower your stroke risk.
Does aspirin reduce plaque in arteries?
"Our findings show that aspirin not only decreases inflammation in the arteries and the growth of the atherosclerotic plaque, but it also beneficially alters the consistency of the plaque that remains."
How fast does carotid stenosis progress?
Of those who progressed, 116 (2.3%) progressed to level 4 (80%-99% stenosis) from any starting level during a median time of 11.5 months, with an average starting level of 2.1 (40%-59% stenosis).
How serious is carotid stenosis?
Carotid artery stenosis can lead to a stroke. People who have carotid artery stenosis are at increased risk for a stroke, which can lead to disability or death. Sometimes, strokes can be mild and recoverable. In other cases, strokes are very large and devastating.
Can carotid artery blockage be reversed naturally?
Medical treatment, regular exercise, and dietary changes can be used to keep atherosclerosis from getting worse and stabilize the plaque, but they aren't able to reverse the disease.
How do you dissolve plaque in the carotid artery?
The most common way to do that is with a surgery called “carotid endarterectomy.” It's performed by making an incision along the front of the neck, opening the carotid artery and removing the plaque.
Can you unblock an artery without surgery?
Through angioplasty, our cardiologists are able to treat patients with blocked or clogged coronary arteries quickly without surgery. During the procedure, a cardiologist threads a balloon-tipped catheter to the site of the narrowed or blocked artery and then inflates the balloon to open the vessel.
Can carotid artery blockage be treated with medication?
Mild to moderate blockages in the carotid artery are treated with medications called antiplatelet agents, such as aspirin, that block the formation of blood clots. In addition, treatment involves identifying and reducing risk factors, such as cigarette smoking and high blood pressure.
What is the best treatment for carotid stenosis?
Carotid endarterectomy is the traditional surgical treatment for carotid artery disease. Carotid endarterectomy has been proven to be beneficial for symptomatic patients with a 50 percent or greater carotid stenosis (blockage) and for asymptomatic patients with a 60 percent or greater carotid stenosis.
What is the cause of carotid artery stenosis?
Carotid artery disease, also called carotid artery stenosis, is the narrowing of the carotid arteries, usually caused by atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is the buildup of cholestero l, fat and other substances traveling through the bloodstream, such as inflammatory cells, cellular waste products, proteins and calcium.
Where are the carotid arteries located?
There are two carotid arteries (one on each side of the neck) that supply blood to the brain. The carotid arteries can be felt on each side of the lower neck, immediately below the angle of the jaw. The carotid arteries supply blood to the large, front part of the brain, where thinking, speech, personality and sensory and motor functions reside.
Which arteries supply blood to the brain?
The carotid arteries supply blood to the large, front part of the brain, where thinking, speech, personality and sensory and motor functions reside. The vertebral arteries run through the spine and supply blood to the back part of the brain (the brainstem and cerebellum).
What happens when plaque builds up in the carotid artery?
Plaque buildup can lead to narrowing or blockage in the carotid artery which, when significant, can put an individual at increased risk for stroke.
What are the signs of a stroke?
However, there are warning signs of a stroke. A transient ischemic attack (also called TIA or "mini-stroke") is one of the most important warning signs of a stroke. A TIA occurs when a blood clot briefly blocks an artery that supplies blood to the brain.
How long does a TIA last?
The following symptoms of a TIA, which are temporary and may last a few minutes or a few hours, can occur alone or in combination: Weakness and/or numbness on one side of the face, or in one arm or leg, or one side of the body.
How to treat carotid artery disease?
The options include: Carotid endarterectomy, the most common treatment for severe carotid artery disease. After making an incision along the front of your neck, the surgeon opens the affected carotid artery and removes the plaques. The artery is repaired with either stitches or a graft.
How is carotid endarterectomy done?
Treatment. In carotid endarterectomy, your surgeon opens the carotid artery to remove atherosclerotic plaques. In carotid angioplasty, a long, hollow tube (catheter) is threaded through the arteries to the narrowed carotid artery in the neck. A filter is inserted to catch any debris that may break off during the procedure.
What is the purpose of a carotid endarterectomy?
In carotid endarterectomy, your surgeon opens the carotid artery to remove atherosclerotic plaques. In carotid angioplasty, a long, hollow tube (catheter) is threaded through the arteries to the narrowed carotid artery in the neck. A filter is inserted to catch any debris that may break off during the procedure.
What is a carotid stent?
Carotid stenting. In carotid stenting, a long, hollow tube (catheter) is threaded through the arteries to the narrowed carotid artery in the neck. A metal mesh tube (stent) is inserted into the vessel to serve as a scaffold that helps prevent the artery from narrowing again. The catheter and the filter — which catches any debris ...
What to do if you have a blood clot?
Medication to control blood pressure or lower cholesterol. Your doctor may also recommend taking a daily aspirin or other blood-thinning medication to prevent blood clots.
What is the purpose of CT scans?
CT or MRI, to look for evidence of stroke or other abnormalities. CT angiography or MR angiography, which provides additional images of blood flow in the carotid arteries. A contrast dye is injected into a blood vessel, and a CT scan or an MRI gathers images of your neck and brain.
What are the risk factors for carotid artery stenosis?
Risk factors for carotid artery stenosis include age, smoking, high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity and an in active lifestyle.
What is the narrowing of the carotid artery?
What is carotid artery stenosis? Carotid artery stenosis is a narrowing in the large arteries located on each side of the neck that carry blood to the head, face and brain. The narrowing usually results from atherosclerosis, or a build-up of plaque on the inside of the arteries.
Can stenosis cause a stroke?
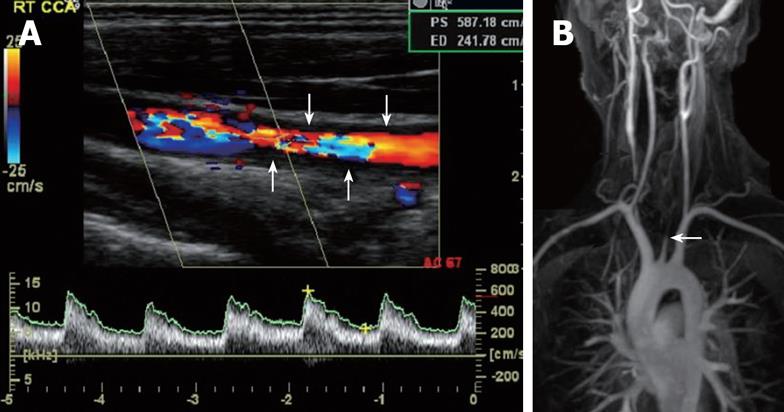
Stenosis can worsen over time to completely block the artery which may lead to stroke. Your doctor may use carotid ultrasound, CT angiography (CTA), magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), or cerebral angiography to determine the presence and location of stenosis.
What is the best test for stenosis?
Imaging tests to diagnose, localize and measure stenosis include: Carotid ultrasound ( including Doppler ultrasound): This test uses sound waves to create real-time pictures of the arteries and locate blockages. Doppler is a special ultrasound technique that can detect areas of restricted blood flow in the artery.
What causes a narrowing of the arteries in the neck?
This narrowing is usually the result of a build-up of plaque within the arteries, a condition called atherosclerosis. Stenosis can worsen over time to completely block the artery which may lead to stroke.
What is the narrowing of the arteries on either side of the neck?
Carotid artery stenosis is a narrowing of the large arteries on either side of the neck that carry blood to the head, face and brain. This narrowing is usually the result of a build-up of plaque within the arteries, a condition called atherosclerosis.
Is a TIA a stroke?
A TIA is usually brief and leaves no lasting damage; it is due to a very small, temporary occlusion of a small artery but often a warning sign. A stroke is often associated with permanent injury of a part of the brain due to loss of its blood supply and can result in severe disability or death. top of page.
How do you treat carotid artery disease?
Carotid artery disease can be treated medically, interventionally or surgically. Once the doctor confirms that you have carotid artery disease, the treatment will depend on the degree of narrowing and if you are having symptoms.
What is the most common procedure for carotid artery disease?
Carotid endarterectomy is the most commonly performed surgical treatment for carotid artery disease. During carotid endarterectomy, the surgeon reduces the risk of stroke from the operation by shunting (using a plastic tube to re-route blood flow to the brain) and monitoring the patient carefully.
What is carotid stenting?
For patients who meet certain eligibility criteria, carotid stenting offers an alternative approach to repairing the blockage in the artery. Carotid stenting is approved as a carotid artery disease surgical treatment for patients who are experiencing symptoms, have a carotid artery that is blocked 70 percent or more, and for whom surgery would be high risk. Some examples of patients who might benefit from this approach as opposed to carotid endarterectomy include patients who have had prior surgery or radiation surgery in the neck.
Why do doctors vary in quality?
Doctors vary in quality due to differences in training and experience; hospitals differ in the number of services available. The more complex your medical problem, the greater these differences in quality become and the more they matter.
Is carotid endarterectomy effective?
Class I evidence shows that carotid endarterectomy ( CEA) is effective in preventing ipsilateral ischemic events in patients with symptomatic moderate- and high-grade stenosis. The procedure is also effective in selected patients with asymptomatic stenosis, but the benefit is marginal.
What is CEA in medical?
Antiplatelet therapy and aggressive treatment of vascular risk factors are the mainstays of medical therapy. Class I evidence shows that carotid endarterectomy (CEA) is effective in preventing ipsilateral ischemic events in patients with symptomatic moderate- and high-grade stenosis.
How to treat carotid artery disease?
These healthy changes can also help you maintain a healthy weight and manage high blood pressure and cholesterol. Eat a healthy, low-fat diet. Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables.
Can a stroke be caused by a narrowed carotid artery?
Carotid artery stenosis occurs when the carotid arteries become narrowed or blocked. This can lead to stroke. Whether or not your doctor recommended surgery to unblock narrowed arteries, medicines and lifestyle changes can: Prevent further narrowing of these important arteries. Prevent a stroke from occurring.
Where is the carotid artery located?
The carotid arteries provide the main blood supply to the brain. They are located on each side of your neck. You can feel their pulse under your jawline. Carotid artery stenosis occurs when the carotid arteries become narrowed or blocked. This can lead to stroke.
How to get rid of a swollen artery?
Choose high-fiber foods, such as whole-grain breads, pastas, cereals, and crackers. Eat lean meats and skinless chicken and turkey. Eat fish twice a week. Fish is good for your arteries. Cut back on saturated fat, cholesterol, and added salt and sugar. Be more active.
Does aspirin help with high blood pressure?
This helps lower high blood pressure. Blood-thinning medicines, such as aspirin or clopidogrel, decrease the chance of blood clots forming and help lower your risk of stroke. These medicines can have side effects. If you notice side effects, be sure to tell your doctor.
Does aspirin help with stroke?
Blood-thinning medicines, such as aspirin or clopidogrel, decrease the chance of blood clots forming and help lower your risk of stroke. These medicines can have side effects. If you notice side effects, be sure to tell your doctor. Your doctor may change the dose or type of medicine you take to help reduce side effects.
What to do if you think you have a stroke?
If you think you have symptoms of stroke, go to the emergency room or call 911 or the local emergency number immediately. Symptoms of a stroke include: Get help as soon as symptoms occur. The sooner you receive treatment, the better your chance for recovery.