
Medication
Only one among every three patients survive for more than five years. Nonetheless, controlling the complications and symptoms derived due to different forms of cardiomyopathy is controllable with the help of medication, lifestyle changes, and surgery. A few categories of the cardiomyopathy have no preventive measures.
Procedures
You can minimize your risk of heart disease or help treat existing heart disease through exercise. Exercise lowers your blood pressure and your heart rate. It also helps your brain release some endorphins, which makes you feel better in general.
Nutrition
When treating cardiomyopathy, objectives include:
- Stopping the disease from getting worse
- Managing any conditions that cause or contribute to the disease
- Reducing complications and the risk of sudden cardiac arrest (SCA)
- Controlling symptoms so that you can live as normally as possible
See more
Over time, cardiomyopathy can weaken the heart, negatively affecting its ability to maintain a normal electric rhythm and/or pump enough blood to the body. This can lead to a variety of issues and complications, including arrhythmias, heart valve problems and even heart failure. Does cardiomyopathy make you tired? Still, it’s serious.
What is the normal life expectancy with mild cardiomyopathy?
Can you be cured of cardiomyopathy?
How to treat cardiomyopathy using natural remedies?
What is cardiomyopathy and how serious is it?
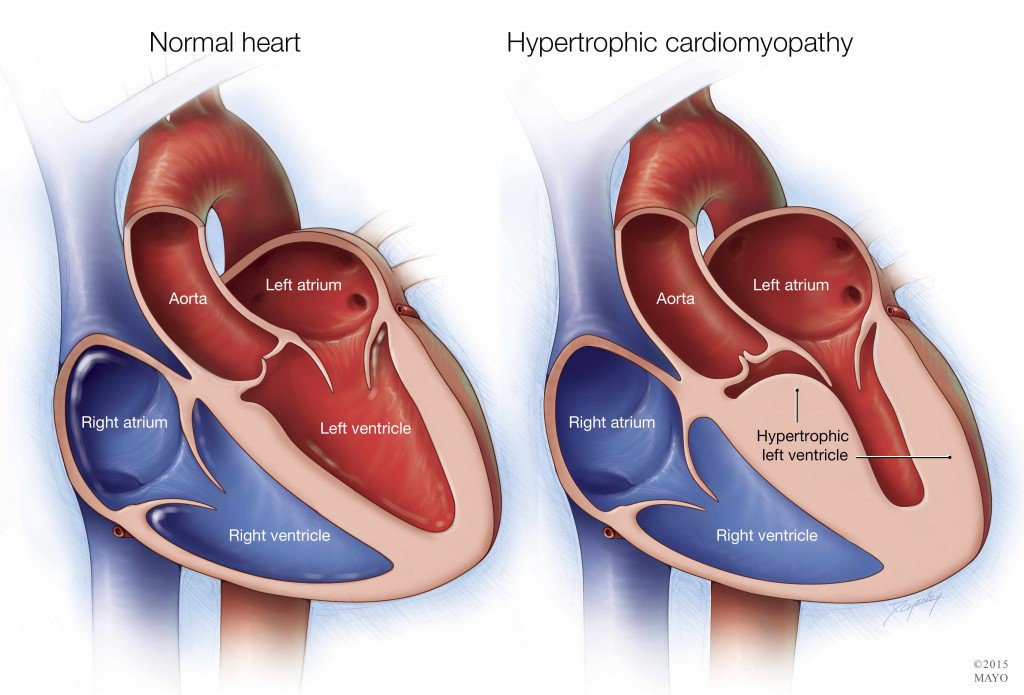
What is the most common treatment for cardiomyopathy?
Treatment options for cardiomyopathyLifestyle changes. Stopping alcohol use. Monitoring salt intake.Medicines. Lower blood pressure. ... Surgically implanted device that helps maintain proper heart rhythm.Ablation procedure. Removes extra heart tissue to reduce thickening. ... Heart transplant (for a severely damaged heart)
Can you recover from cardiomyopathy?
For example, patients with a very low ejection fraction can eventually completely recover from peripartum cardiomyopathy. Some patients recover only part of their heart function over a period of six months or longer. With others, the heart returns to full strength in as little as two weeks.
What is the main cause of cardiomyopathy?
The most common cause is coronary artery disease or heart attack. However, it can also be caused by genetic changes. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. This type involves abnormal thickening of the heart muscle, which makes it harder for the heart to work.
Can cardiomyopathy be treated with medication?
A combination of medications may be used to treat dilated cardiomyopathy and prevent any complications. Medications are used to: Control the heart's rhythm. Help the heart pump better.
Can I live a long life with cardiomyopathy?
With proper care, many people can live long and full lives with a cardiomyopathy diagnosis. When recommending treatment, we always consider the least invasive approach first. Options range from lifestyle support and medications to implantable devices, procedures, and surgeries.
How many years can you live with cardiomyopathy?
Although there have been recent improvements in congestive heart failure treatment, researchers say the prognosis for people with the disease is still bleak, with about 50% having an average life expectancy of less than five years. For those with advanced forms of heart failure, nearly 90% die within one year.
What are the warning signs of cardiomyopathy?
Signs and symptoms of cardiomyopathy include:Shortness of breath or trouble breathing, especially with physical exertion.Fatigue.Swelling in the ankles, feet, legs, abdomen and veins in the neck.Dizziness.Lightheadedness.Fainting during physical activity.Arrhythmias (abnormal heartbeats)More items...•
What is the difference between cardiomyopathy and heart failure?
Heart failure can occur when the heart muscle is weak (systolic failure) or when it is stiff and unable to relax normally (diastolic failure). Cardiomyopathy, which means “disease of the heart muscle,” is one of many causes of heart failure.
What happens if cardiomyopathy goes untreated?
If untreated, cardiomyopathy can weaken the heart, leading to more serious conditions, including lessened blood flow, arrhythmia (irregular heartbeats), problems with the heart's valves and heart failure.
What are the stages of cardiomyopathy?
There are four stages of heart failure, named A, B, C and D.Heart Failure Stage A. Pre-heart failure, which means that you are at high risk of developing heart failure.Heart Failure Stage B. ... Heart Failure Stage C. ... Heart Failure Stage D.
Does exercise help cardiomyopathy?
Daily light exercise is safe for most people with cardiomyopathy and heart failure and can help them to manage symptoms. Over time, it can reduce heart rate and blood pressure. Your NYU Langone heart specialist can recommend an exercise program that's right for you. It may include walking, cycling, or jogging.
Is cardiomyopathy considered a terminal illness?
Over the last 10 years, there has been a realisation that heart failure (itself the final common pathway of several aetiologies such as hypertension, ischaemic and valvular heart disease, and cardiomyopathy) is a terminal illness.
What are the goals of cardiomyopathy?
When treating cardiomyopathy, objectives include: Stopping the disease from getting worse. Managing any conditions that cause or contribute to the disease. Reducing complications and the risk of sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) Controlling symptoms so that you can live as normally as possible.
What is the best medicine to slow down your heart rate?
Beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, and digoxin are examples of medicines that slow the heart rate. Beta blockers and calcium channel blockers also are used to lower blood pressure. Keep your heart beating with a normal rhythm. These medicines, called antiarrhythmics, help prevent arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats).
What are the medicines that help prevent arrhythmias?
These medicines, called antiarrhythmics, help prevent arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats). Balance electrolytes in your body. Electrolytes are minerals that help maintain fluid levels and the acid-base balance in your body. Electrolytes also help muscle and nerve tissues work properly.
What is a heart transplant?
Heart Transplant – In a heart transplant surgery, a person’s diseased heart is replaced with a healthy donor heart. A heart transplant is a last resort for people who have end-stage heart failure. (“End-stage” means that all other treatment options have been explored, without success.)
How to lower blood pressure?
Choose and prepare foods with little salt (sodium). Too much salt can raise your risk of high blood pressure. Studies show that following a Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) eating plan can lower blood pressure. Choose foods and beverages that are low in added sugar. Avoid drinking alcohol.
Can you prevent cardiomyopathy?
You cannot prevent inherited types of cardiomyopathy. But you can take steps to lower your risk for conditions that may lead to (or complicate) cardiomyopathy, such coronary heart disease, high blood pressure and heart attack . Cardiomyopathy can be precipitated by an underlying disease or condition.
Does dilated cardiomyopathy go away?
Sometimes, dilated cardiomyopathy that comes on suddenly may even go away on its own. In other instances, treatment is needed. Treatment hinges on a few factors: the type of cardiomyopathy, the severity of your symptoms and complications as well as your age and overall health.
How many patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy will have obstruction?
And the obstruction to the left ventricular outflow tract is an indication for operation in patients that have symptoms. So we know now that 2/3 of the patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and obstruction are candidates for surgery.
How many people have hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
In the United States alone, there are over a half a million people that have hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, many of whom are completely asymptomatic and unaware of their diagnosis. Some people can die suddenly. Sudden cardiac death occurs randomly without warning.
What test is used to diagnose hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Echocardiogram. An echocardiogram is commonly used to diagnose hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. This test uses sound waves (ultrasound) to see if your heart's muscle is abnormally thick.
What is the term for the thickened area of the heart?
In a type called apical myectomy, the thickened area is removed from the area near the tip of the heart. Several different surgeries or procedures are available to treat cardiomyopathy or its symptoms. They range from open-heart surgery to implantation of a device to control your heart rhythm. Septal myectomy.
What is an echocardiogram?
Sometimes, an echocardiogram is done while you exercise, usually on a treadmill. This is called an exercise stress test.
How to cope with a syphilis?
Follow lifestyle changes your doctor recommends. Making healthy lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet and maintaining a healthy weight, can help you cope with living with your condition.
Is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy inherited?
Steve R. Ommen: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the most common inherited cardiomyopathy or heart muscle disease. People are born with the genetics for it, but the hypertrophy doesn't appear to start developing until adolescence, growth spurts, or beyond. It is possible for infants to born with thick heart muscles, but that's really quite rare and usually more severe expressions of the disease. And it's also been described as not coming on until people were in their fifth or sixth decade of life. So really, the onset can be at any time of life. And certainly the symptoms can occur throughout life.
How to treat hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Usually this requires taking a beta blocker or calcium channel blocker. A medication to prevent abnormal heart rhythms may also be needed.
How to diagnose cardiomyopathy?
The diagnosis of cardiomyopathy is often clear from an individual's descriptions of his or her symptoms, the results of a physical examination, and the results of a chest x-ray, echocardiogram, and electrocardiogram.
What is the term for the invasion of the heart muscle by abnormal cells?
invasion of heart muscle by abnormal cells or other material (restrictive cardiomyopathy). an inherited condition called hypertrophic cardiomyopathy which causes a thickening of the heart muscle, especially the wall between the two ventricles.
What is the term for a heart disease that causes a heart muscle to weaken?
Any heart disease in which the heart muscle (myocardium) weakens can be known as cardiomyopathy . This broad term covers many conditions, all of which result in injury to the heart muscle and impaired heart function. Cardiomyopathy often leads to heart failure.
Why is myocarditis dangerous?
Cardiomyopathy can be caused by: myocarditis, an inflammation of the heart muscle, often due to a viral infection or a chronic inflammatory condition such as lupus.
What is the test called for a heart biopsy?
Occasionally, a test called an endomyocardial biopsy is necessary. In this test, a catheter is inserted into a vein in the neck and passed down into the heart. A small piece of the inner heart wall is removed using a tiny metal device at the tip of the catheter.
What is the term for the accumulation of cholesterol-filled plaque in the arteries that nourish the heart?
coronary artery disease, the accumulation of cholesterol-filled plaque in the arteries that nourish the heart. It can weaken the heart muscle by reducing blood flow to much of the heart.
When does cardiomyopathy occur?
Most of the following types of cardiomyopathy belong to one of the previous four classifications, but each has unique causes or complications. Peripartum cardiomyopathy occurs during or after pregnancy. This rare type occurs when the heart weakens within five months of delivery or within the final month of pregnancy.
What are the risks of cardiomyopathy?
Cardiomyopathy can affect people of all ages. Major risk factors include the following: 1 a family history of cardiomyopathy, sudden cardiac arrest, or heart failure 2 coronary heart disease 3 diabetes 4 severe obesity 5 sarcoidosis 6 hemochromatosis 7 amyloidosis 8 heart attack 9 long-term high blood pressure 10 alcoholism
What is the term for a heart muscle that is too weak to pump blood?
Dilated cardiomyopathy. The most common form, dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), occurs when your heart muscle is too weak to pump blood efficiently. The muscles stretch and become thinner. This allows the chambers of your heart to expand. This is also known as enlarged heart.
What is the term for a progressive disease of the heart muscle?
Cardiomyopathy is a progressive disease of the myocardium, or heart muscle. In most cases, the heart muscle weakens and is unable to pump blood to the rest of the body as well as it should. There are many different types of cardiomyopathy caused by a range of factors, from coronary heart disease to certain drugs.
What is the term for a condition where blood is not flowing through the heart?
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is believed to be genetic. It occurs when your heart walls thicken and prevent blood from flowing through your heart. It’s a fairly common type of cardiomyopathy. It can also be caused by long-term high blood pressure or aging.
Why does alcohol cause cardiomyopathy?
Alcoholic cardiomyopathy is due to drinking too much alcohol over a long period of time, which can weaken your heart so it can no longer pump blood efficiently. Your heart then becomes enlarged. This is a form of dilated cardiomyopathy.
How does cardiomyopathy affect your life?
Cardiomyopathy can be life-threatening and can shorten your life expectancy if severe damage occurs early on. The disease is also progressive, which means it tends to get worse over time. Treatments can prolong your life. They can do this by slowing the decline of your heart’s condition or by providing technologies to help your heart do its job.
How can cardiomyopathy improve your life?
If you have cardiomyopathy, seek treatment from a cardiologist (heart specialist). Medication, surgery or other treatments can increase your quality of life and help you live longer.
What are the two categories of cardiomyopathy?
Healthcare professionals may categorize cardiomyopathy based on the general cause. These two categories are: Ischemic cardiomyopathy, caused by heart attacks or coronary artery disease (CAD). Non-ischemic cardiomyopathy, types unrelated to CAD. Sometimes, experts don't know the cause of cardiomyopathy (idiopathic).
How many people have cardiomyopathy?
About 1 in 500 adults have cardiomyopathy. Some types of cardiomyopathy are more likely in some people than in others. For example, dilated cardiomyopathy is more common in Black people. Dilated and arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy are more likely in males.
What are the diseases that affect the heart?
Autoimmune diseases, such as connective tissue diseases. Conditions that damage the heart, such as high cholesterol diseases, hemochromatosis or sarcoidosis. Endocrine conditions, such as diabetes or thyroid disease. Family history of heart failure, cardiomyopathy or sudden cardiac arrest. Previous heart attacks.
What is the term for the condition where the heart is weak?
Cardiomyopathy refers to conditions that affect the myocardium (heart muscle). Cardiomyopathy can make your heart stiffen, enlarged or thickened and can cause scar tissue. As a result, your heart can’t pump blood effectively to the rest of your body. In time, your heart can weaken and cardiomyopathy can lead to heart failure.
Can cardiomyopathy cause shortness of breath?
If you have cardiomyopathy, your heart can’t efficiently pump blood to the rest of your body. As a result, you may experience fatigue, shortness of breath or heart palpitations. Cardiomyopathy gets worse over time. Treatment can slow the progression and improve your quality of life. Appointments 800.659.7822.
Is cardiomyopathy a disease?
Cardiomyopathy refers to diseases of your heart muscle. There are many types of cardiomyopathy. Some are inherited. Others develop from underlying conditions such as coronary artery disease. Treatment for cardiomyopathy may include medications, lifestyle changes or surgery. Although there is no cure for cardiomyopathy, you can manage the condition. People who receive treatment can live a high quality of life with cardiomyopathy.
How to test for dilated cardiomyopathy?
Exercise stress test. During this test, you walk on a treadmill or ride a stationary bike while attached to an ECG. Exercise testing can help reveal the cause and severity of dilated cardiomyopathy. If you're unable to exercise, you may be given medication to mimic the effect of exercise on your heart.
How to make your heart work harder?
Maintain a healthy weight. Extra weight makes your heart work harder. Lose weight if you're overweight or obese. Eat a heart-healthy diet. This includes eating whole grains and a variety of fruits and vegetables, and limiting salt, added sugar, and cholesterol, saturated fats and trans fats.
What is the name of the device that doctors use to test your heart?
Your doctor will perform a physical exam and ask questions about your personal and family medical history. He or she will use a device called a stethoscope to listen to your heart and lungs. You may be referred to a heart specialist (cardiologist) for testing.
Can you get a heart transplant if you have dilated cardiomyopathy?
Your doctor may recommend a heart transplant if medications and other treatments for dilated cardiomyopathy no longer work for you.
What is cardiomyopathy?
Overview. Cardiomyopathy (kahr-dee-o-my-OP-uh-thee) is a disease of the heart muscle that makes it harder for your heart to pump blood to the rest of your body. Cardiomyopathy can lead to heart failure. The main types of cardiomyopathy include dilated, hypertrophic and restrictive cardiomyopathy. Treatment — which might include medications, ...
What are the different types of cardiomyopathy?
The main types of cardiomyopathy include dilated, hypertrophic and restrictive cardio myopathy. Treatment — which might include medications, surgically implanted devices, heart surgery or, in severe cases, a heart transplant — depends on which type of cardiomyopathy you have and how serious it is.
What is the name of the heart valve that can't pump blood out of the heart?
Types of cardiomyopathy include: Dilated cardiomyopathy. In this type of cardiomyopathy, the pumping ability of your heart's main pumping chamber — the left ventricle — becomes enlarged (dilated) and can't effectively pump blood out of the heart.
What happens when your heart is weak?
As your heart weakens, such as in heart failure, it begins to enlarge, which forces your heart to work harder to pump blood to the rest of your body. Cardiomyopathy can lead to serious complications, including: Heart failure. Your heart can't pump enough blood to meet your body's needs.
What is the name of the condition where the muscle in the right ventricle is replaced by scar tissue?
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia. In this rare type of cardiomyopathy, the muscle in the lower right heart chamber (right ventricle) is replaced by scar tissue, which can lead to heart rhythm problems. It's often caused by genetic mutations. Unclassified cardiomyopathy.
What are the conditions that affect the heart?
Conditions that affect the heart, including a past heart attack, coronary artery disease or an infection in the heart (ischemic cardiomyopathy) Obesity, which makes the heart work harder. Long-term alcohol misuse. Illicit drug use, such as cocaine, amphetamines and anabolic steroids.
Can dilated cardiomyopathy cause heart failure?
Compared with a normal heart, a heart with dilated cardiomyopathy has enlarged chambers of the heart, which can lead to heart failure if left untreated.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support
- Your health care provider is likely to perform a physical examination and ask questions about your personal and family medical history. You'll also be asked when your symptoms occur — for example, whether exercise triggers your symptoms. If your provider thinks you have cardiomyop…
Preparing For Your Appointment