
Medication
Mar 24, 2022 · Some medicines treat the underlying cause of cardiogenic shock, which is usually a heart attack. Medicines to restore a regular heartbeat are called anti-arrhythmia medicines. Blood thinners or antiplatelet medicines can dissolve blood clots and reduce platelets that may be blocking the coronary arteries.
Procedures
Feb 09, 2021 · They include: Angioplasty and stenting. If a blockage is found during a cardiac catheterization, your doctor can insert a long, thin... Balloon pump. Your doctor inserts a balloon pump in the main artery off of your heart (aorta). The pump inflates and... Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). ...
Self-care
These include: Clot-busting drugs, such as tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) to dissolve coronary artery clots Anticlotting medicines – such as aspirin, clopidogrel or heparin – to prevent new clots Drugs to increase the heart's pumping ability, such as dobutamine, dopamine and norepinephrine ...
Nutrition
Mar 24, 2022 · Treatment focuses on getting blood flowing properly and protecting organs from damage. Some people may need a heart transplant or a permanently implanted device to help keep blood flowing to the heart. If not treated quickly, cardiogenic shock can be fatal or lead to organ failure or brain injury. Next Symptoms Last updated on March 24, 2022
How does one prevent cardiogenic shock?
Feb 06, 2020 · To treat cardiogenic shock, your doctor must find and treat the cause of the shock. If heart attack is the cause, your doctor may give you …
What do you need to know about cardiogenic shock?
Jun 25, 2021 · Early restoration of coronary blood is the most important intervention and is the standard therapy for patients with cardiogenic shock due to myocardial infarction. The management of cardiogenic shock involves the following: Medical Management
What are the mortality rates for cardiogenic shock?
Treatment may include: Life support to restore blood flow to major organs Medication to prevent blood clots, make the heart stronger and get more blood to major organs Devices to help the heart pump enough blood to the organs and rest of the body
How to recognize cardiogenic shock?
This review will address the pathophysiology, incidence, current outcome and treatment options of patients with cardiogenic shock complicating acute myocardial infarction. The major focus will be on the current evidence based on randomized clinical trials and the current guideline recommendations for the treatment of cardiogenic shock.
See more
Feb 09, 2021 · Exercise can lower your blood pressure and improve the overall health of your blood vessels and heart. Get at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous aerobic activity a week, or a combination of moderate and vigorous activity. It's recommended to spread out this exercise during the course of a week.
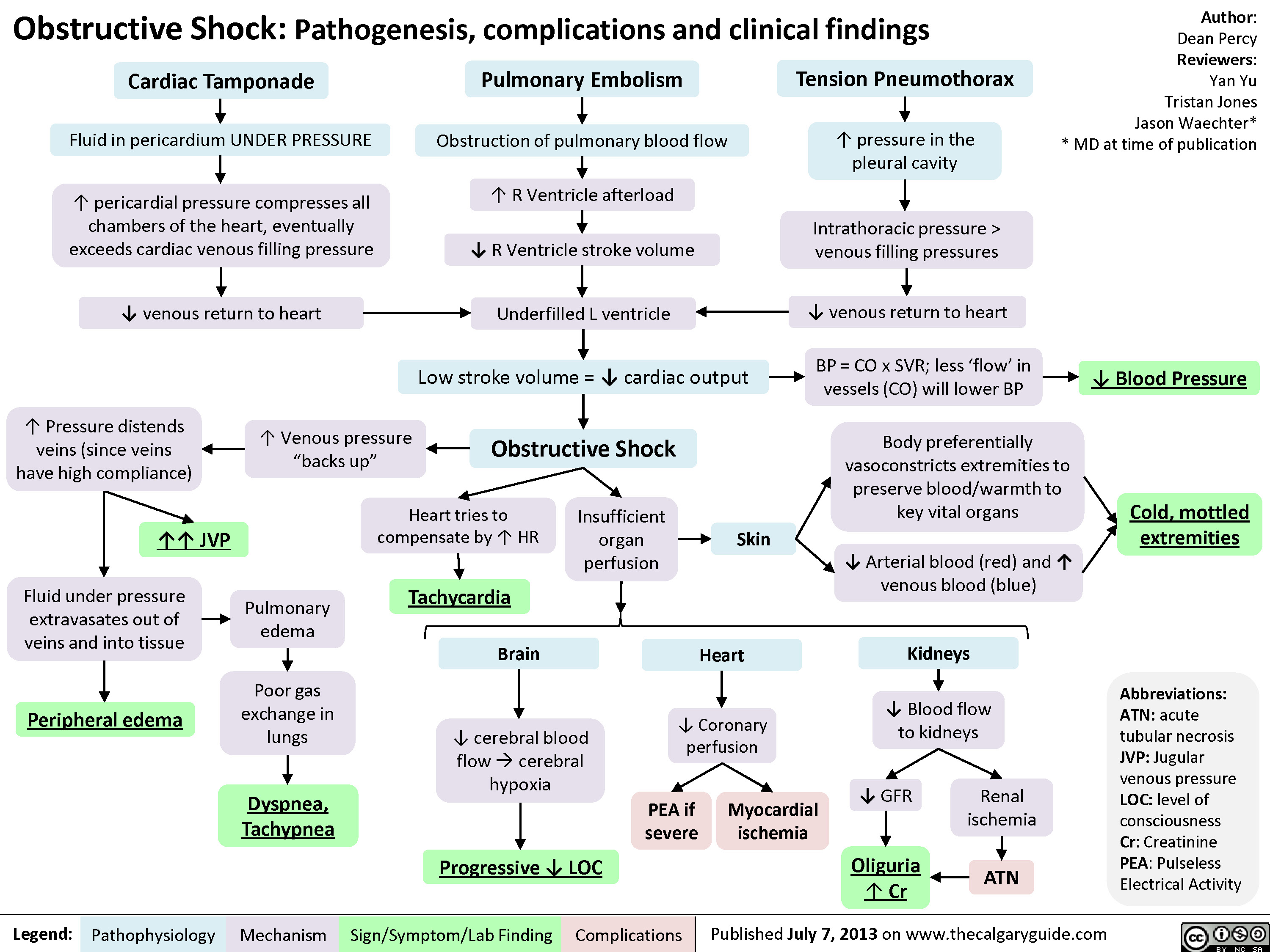
Which drug is most commonly used to treat cardiogenic shock?
Sympathomimetic amines with both alpha- and beta-adrenergic effects are indicated for persons with cardiogenic shock. Dopamine and dobutamine are the drugs of choice to improve cardiac contractility, with dopamine the preferred agent in patients with hypotension.Aug 6, 2019
What is the treatment priority for cardiogenic shock?
Is cardiogenic shock treatable?
What treatment should be used cautiously in patients with cardiogenic shock?
What is the first step in the collaborative management of cardiogenic shock?
How does dobutamine treat cardiogenic shock?
What happens cardiogenic shock?
What is the most common cause of cardiogenic shock?
What are signs of cardiogenic shock?
- Rapid breathing.
- Severe shortness of breath.
- Sudden, rapid heartbeat (tachycardia)
- Loss of consciousness.
- Weak pulse.
- Low blood pressure (hypotension)
- Sweating.
- Pale skin.
Which vasopressor is the drug of choice for cardiogenic shock?
Why is aspirin given for STEMI?
What is the major clinical use of dobutamine?
How to treat cardiogenic shock?
Medical procedures to treat cardiogenic shock usually focus on restoring blood flow through your heart. They include: 1 Angioplasty and stenting. If a blockage is found during a cardiac catheterization, your doctor can insert a long, thin tube (catheter) equipped with a special balloon through an artery, usually in your leg, to a blocked artery in your heart. Once in position, the balloon is briefly inflated to open the blockage.#N#A metal mesh stent might be inserted into the artery to keep it open over time. In most cases, you doctor will place a stent coated with a slow-releasing medication to help keep your artery open. 2 Balloon pump. Your doctor inserts a balloon pump in the main artery off of your heart (aorta). The pump inflates and deflates within the aorta, helping blood flow and taking some of the workload off your heart. 3 Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). ECMO helps improve blood flow and supplies oxygen to the body. Blood is pumped outside of your body to a heart-lung machine that removes carbon dioxide and sends oxygen-filled blood back to tissues in the body.
How is plasma given in cardiogenic shock?
Fluids and plasma are given through an IV. Medications to treat cardiogenic shock are given to increase your heart's pumping ability and reduce the risk of blood clots.
What is the procedure to remove carbon dioxide from the body?
If medications and other procedures don't work to treat cardiogenic shock, your doctor might recommend surgery. Coronary artery bypass surgery.
What is the best medicine for clots?
Antiplatelet medication. Emergency room doctors might give you drugs similar to aspirin to help prevent new clots from forming. These medications include clopidogrel (Plavix), tirofiban (Aggrastat) and eptifibatide (Integrilin). Other blood-thinning medications.
How to keep artery open?
A metal mesh stent might be inserted into the artery to keep it open over time. In most cases, you doctor will place a stent coated with a slow-releasing medication to help keep your artery open.
What is the best way to repair a heart injury?
Surgery to repair an injury to your heart. Sometimes an injury, such as a tear in one of your heart's chambers or a damaged heart valve, can cause cardiogenic shock. Surgery might correct the problem.
What are the drugs that help the heart pump?
They include dopamine, epinephrine (Adrenaline, Auvi-Q), norepinephrine (Levophed) and others. Inotropic agents. These medications, which help improve the pumping function of the heart, may be given until other treatments start to work. They include dobutamine, dopamine and milrinone.
What is the treatment for cardiogenic shock?
Possibilities include surgery to repair or replace a faulty valve, mechanical circulatory support (devices that assist the heart's pumping action) or heart transplantation.
What is cardioversion in medicine?
Cardioversion – Medication or a brief electric shock resets the heart and restores a normal heartbeat.
What is the best medicine for clots?
Anticlotting medicines – such as aspirin, clopidogrel or heparin – to prevent new clots
What is the procedure to create a new route that allows blood to flow around a narrowed or blocked
Coronary bypass surgery – a procedure to create a new route that allows blood to flow around a narrowed or blocked artery
What is ECMO in medical terms?
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) – An external device is used to pump and oxygenate your blood, allowing your heart and lungs to rest.
What is cardiogenic shock?
Cardiogenic shock is most commonly the result of a heart attack. During a heart attack, the flow of blood through the arteries is restricted or blocked completely. This restriction can lead to cardiogenic shock. Other conditions that may cause cardiogenic shock include:
How to diagnose cardiogenic shock?
To diagnose cardiogenic shock, your doctor will complete a physical exam. The exam will gauge pulse and blood pressure.
What happens when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to the vital organs of the body?
Cardiogenic shock occurs when the heart is unable to supply enough blood to the vital organs of the body. As a result of the failure of the heart to pump enough nutrients to the body, blood pressure falls and organs may begin to fail. Cardiogenic shock is uncommon, but when it does occur, it’s a serious medical emergency.
What are the risk factors for cardiogenic shock?
Risk factors for cardiogenic shock include: previous history of heart attack. plaque build up in the coronary arteries (arteries supplying blood to the heart) long-term valvular disease (disease affecting the valves of the heart)
What is ECG in cardiology?
Electrocardiogram (ECG) This procedure shows the electrical activity of the heart. The test may show irregular heart rates (arrhythmias), such as ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. These arrhythmias may be the cause of the cardiogenic shock. An ECG may also show a quickened pulse.
How to reduce cholesterol?
Exercise regularly to manage your weight. Eat a healthy diet to help manage your cholesterol levels. If you smoke, quit. Here’s how to quit cold turkey. Most importantly, call 911 or visit an emergency room immediately if you experience a heart attack or any of the symptoms associated with cardiogenic shock.
What to do if you have a heart attack?
If you see someone having a heart attack or believe you may be having a heart attack, get medical help immediately. Early medical attention may be able to prevent cardiogenic shock and decrease damage to the heart. The condition is fatal if it’s left untreated. To diagnose cardiogenic shock, your doctor will complete a physical exam.
What is the most important intervention for cardiogenic shock?
Early restoration of coronary blood is the most important intervention and is the standard therapy for patients with cardiogenic shock due to myocardial infarction.
What is cardiogenic shock?
Cardiogenic shock is a primary cardiac disorder characterized by a low cardiac output state of circulatory failure that results in end-organ hypoperfusion and tissue hypoxia. This activity reviews the evaluation and management of cardiogenic shock and explains the role of the interprofessional team in improving care for patients with this condition.
What is the pathophysiology of cardiogenic shock?
This, in turn, leads to a potentially catastrophic and vicious spiral of reduced cardiac output and low blood pressure, perpetuating further coronary ischemia and impairment of contractility. Several physiologic compensatory processes ensue. These include:
What is the best medication for myocardial infarction?
Patients with myocardial infarction or acute coronary syndrome are given aspirin and heparin. They have been shown to be effective in reducing mortality.
What is therapeutic hypothermia?
Therapeutic hypothermia is established for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest patients with shockable rhythm to prevent brain injury and improve survival.
Is vasoactive agent optimal for cardiogenic shock?
The optimal choice of a vasoactive agent in cardiogenic shock is unclear.
What is cardiogenic shock?
Cardiogenic shock is a life-threatening condition where your heart suddenly stops pumping enough oxygen-rich blood to your body. This condition is an emergency situation that is usually brought on by a heart attack. It is discovered as it happens and requires immediate treatment in the hospital. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical ...
How does cardiogenic shock affect your life?
The impact cardiogenic shock has on your life depends on how quickly you get treatment. The less time you are in shock, the better because there is less damage to major organs. Without treatment, the condition can lead to death.
What does it feel like to be in shock?
Pain or discomfort in your upper body and/or down your left arm. Trouble breathing. Sweating or “cold sweats”. Fast or irregular heartbeat . Feeling very weak, light-headed and/or anxious. Other symptoms related to cardiogenic shock can include: Confusion or not being alert. Fainting.
How to prevent cardiogenic shock?
The best way to prevent cardiogenic shock is to make lifestyle changes to keep your heart healthy and your blood pressure in check. Don't smoke, and avoid secondhand smoke. If you smoke, the best way to reduce your heart attack risk is to quit. Maintain a healthy weight.
How to reduce the risk of heart disease?
Eat less cholesterol and saturated fat. Limiting these, especially saturated fat, can reduce your risk of heart disease. Avoid trans fats. Use less salt. Too much salt (sodium) leads to fluid buildup in the body, which can strain the heart. Aim for less than 2,300 milligrams (mg) a day of sodium.
What causes a weak heart?
Inflammation of the heart muscle (myocarditis) Infection of the heart valves (endocarditis) Weakened heart from any cause. Drug overdoses or poisoning with substances that can affect your heart's pumping ability.
Did Greg Williams need a heart transplant?
Told he needed a heart transplant to stay alive, Greg Williams could have simply sat back and waited. Instead, he chose to take ownership of his health by exercising in his hospital room at Mayo Clinic right up until the day of his transplant in hopes of preparing his body and mind as best he [...]
Can you survive a heart attack with cardiogenic shock?
The condition is most often caused by a severe heart attack, but not everyone who has a heart attack has cardiogenic shock. Cardiogenic shock is rare. It's often deadly if not treated immediately. When treated immediately, about half the people who develop the condition survive.
What Are the Causes of Cardiogenic Shock?
In 81% of cases, the underlying cause is a blockage of blood from the heart, which causes a heart attack.
What Are the Symptoms of Cardiogenic Shock?
The most dangerous symptom of cardiogenic shock is organ failure that begins when a fresh supply of oxygen is cut off. If this goes on for too long, you will die. It's important to call 911 or have someone drive you to the emergency room as soon as you begin to feel a combination of the following symptoms:
What Are the Treatments for Cardiogenic Shock?
There's a 50% survival rate for people who get treatment immediately. The sooner you get medical help, the less likely your organs will fail.
What Happens After Cardiogenic Shock?
You may still have several symptoms after surviving cardiogenic shock. Any damage to the liver, kidneys, heart, and other organs can cause lasting problems. The extent of the damage and severity of symptoms depends on how long the oxygen supply was cut off. If this time was too great, you may not survive.
