Medication
MANHASSET, N.Y., February 14, 2022 -- ( BUSINESS WIRE )--Patients who undergo cardiac surgery are at higher risk for developing postoperative atrial fibrillation (POAF) and current POAF drug therapies used to prevent it are not fully effective.
Procedures
It may help to try the following relaxation techniques:
- meditation
- deep breathing
- journaling
- yoga
- spending time outdoors
- exercising
- taking short breaks from work or school
- using a method of guided imagery, these are available to purchase online
Therapy
There is no universal cure for arrhythmia. Depending on the type and severity of your arrhythmia, medication and other forms of treatment can help reduce symptoms and regulate your heartbeat. Some arrhythmias are due to heart damage. You can prevent this damage by leading a healthy lifestyle: eat right, lower your blood pressure, do not smoke and exercise regularly.
Self-care
Are You Living With a life threatening Arrhythmia? Heart Arrhythmia. As mentioned, there are many different types of arrhythmias, each with their own symptoms and complications. Risk Factors. Many things increase your risk for arrhythmia, including your age and gender. ... Signs and Symptoms. ... Arrhythmia Prevention. ...
Nutrition
How to cure heart arrhythmia?
How to stop arrhythmia at home?
Is there a cure for arrhythmia?
Which are life-threatening arrhythmias?
What is the best medicine for cardiac arrhythmia?
Beta blockers may stop the arrhythmia occurring but, more often, are useful for slowing down the heart rate during the arrhythmia without actually terminating it. Calcium channel blockers such as verapamil and diltiazem work in a similar way. Digoxin is also commonly prescribed for AF to help control the rate.
What is the most common treatment for arrhythmia?
The most common medications in this class are:amiodarone (Cordarone, Pacerone)flecainide (Tambocor)ibutilide (Corvert), which can only be given through IV.lidocaine (Xylocaine), which can only be given through IV.procainamide (Procan, Procanbid)propafenone (Rythmol)quinidine (many brand names)tocainide (Tonocarid)
Can cardiac arrhythmia be cured?
When you have atrial fibrillation, or AFib, your heart has an irregular, sometimes quick rhythm. The condition can boost your chances for a stroke, heart failure, or other heart problems. Right now, there's no cure for it.
What is the first line treatment for arrhythmia?
Beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers are first-line agents for rate control in AF. These drugs can be administered either intravenously or orally. They are effective at rest and with exertion.
Is arrhythmia a serious heart condition?
Most people have experienced an arrhythmia, or irregular heartbeat. Although usually harmless, sometimes an arrhythmia increases your risk of a more serious heart condition. "While most arrhythmias are harmless, some may be a sign of a more serious heart condition or require treatment," says Dr.
How do you feel when you have arrhythmia?
An arrhythmia is an irregular heartbeat. It means your heart is out of its usual rhythm. It may feel like your heart skipped a beat, added a beat, or is "fluttering." It might feel like it's beating too fast (which doctors call tachycardia) or too slow (called bradycardia). Or you might not notice anything.
What happens if arrhythmia is left untreated?
Untreated arrhythmia in some individuals may increase the risk of stroke, heart attack, dementia, and heart failure. Untreated arrhythmia in some individuals may increase the risk of stroke, heart attack, dementia, and heart failure.
What is a natural remedy for arrhythmia?
Vitamin C. Arrhythmias and other heart conditions are associated with oxidant stress and inflammation. Antioxidants like vitamin C and vitamin E appear to be effective in reducing these. You can use vitamin C to treat colds, the flu, and even cancer, and it can also help with arrhythmia.
Can anxiety cause arrhythmias?
Can anxiety contribute to arrhythmias? Yes. As described above, when we are stressed or anxious our heart perceives this as an impending threat, triggering our fight or flight response in which adrenaline is released, which can trigger arrhythmia, in turn triggering an additional release of adrenaline.
How do I get my irregular heartbeat back to normal?
If you think you're having an attack, try these to get your heartbeat back to normal:Breathe deeply. It will help you relax until your palpitations pass.Splash your face with cold water. It stimulates a nerve that controls your heart rate.Don't panic. Stress and anxiety will make your palpitations worse.
Which beta blocker is best for arrhythmia?
Arrhythmias: bisoprolol and metoprolol succinate are often preferred. Beta-blockers are the first-line treatment for long-term symptomatic rate control in patients with a range of cardiac arrhythmias, including atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia.
Is a pacemaker better than ablation?
Conclusions: In patients with paroxysmal AF-related tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome, AF ablation seems to be superior to a strategy of pacing plus AAD. Pacemaker implantation can be waived in the majority of patients after a successful ablation.
What is the ablation of arrhythmia?
In atrial fibrillation ablation, small scars are intentionally created to break up the electrical signals that cause the irregular heartbeats in a condition known as atrial fibrillation.
What is the term for an irregular heartbeat?
Arrhythmia is an irregularity in either the rate or rhythm of the heartbeat. The heart may beat too fast, too slow or inconsistently. Treatment for arrhythmia can take on many different forms, depending on the type and severity of the irregular heartbeat and what’s causing it.
What is CRT therapy?
Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) uses a pacemaker to restore normal heartbeat timing. Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) treatment helps regulate the heartbeat and will send a “shock,” or defibrillation, to reset the rhythm and prevent cardiac arrest.
Is electric shock as strong as defibrillation?
The electric shock used in electrical cardioversion is not as strong as the one used in defibrillation. Implantable arrhythmia treatments involve surgical implantation of devices that monitor, synchronize, and/or reset the heart rhythm.
How to treat arrhythmias in the heart?
In cases of severe coronary artery disease causing arrhythmia, your doctor may recommend a coronary bypass to improve the blood supply to your heart. 3 During this procedure, a blood vessel grafted from your chest, leg, or arm is used to connect your aorta to your coronary artery, creating a new channel for blood to flow through. Once the surgery is complete, you will have to spend a few days in the intensive care unit (ICU) where doctors will continuously monitor your heart rate and blood pressure. 18
Why do you need to take medication for cardiac arrhythmia?
In general, there are two reasons your doctor might want to place you on medication for a cardiac arrhythmia. First, the arrhythmia might be causing you to have symptoms, such as palpitations or lightheadedness, and treatment may be important to relieve those symptoms . Second, the arrhythmia may be causing you harm or may be threatening to do so , as certain arrhythmias can increase your risk of cardiac arrest , heart attack, and stroke. 2
What is the purpose of antiarrhythmic drugs?
Antiarrhythmic Drugs. Antiarrhythmic drugs are medications that change the electrical properties of cardiac tissue, and by doing so, change the way your heart's electrical signal spreads across your heart. Since the tachycardias (arrhythmias that cause a rapid heart rate) are usually related to abnormalities in the electrical signal, ...
How do drugs reduce cardiac arrest?
A few drugs are thought to reduce the risk of sudden cardiac arrest, presumably by reducing the risk of ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation, the arrhythmias that produce cardiac arrest. Research shows that beta blockers seem to reduce the risk of sudden cardiac arrest by blocking the effect ...
What is the best medicine for sudden cardiac arrest?
Other drugs that your doctor may prescribe if you are at risk for sudden cardiac arrest include angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, and the antiarrhythmic drug amiodarone. 3.
What is the most common form of ablation?
While ablation procedures can be performed in the operating room during open-heart surgery, by far the most common form of ablation is accomplished during a specialized form of cardiac catheterization called an electrophysiology study (EPS).
How to slow down supraventricular tachycardia?
If you have a supraventricular tachycardia, easy exercises known as vagal maneuvers may help to slow it down or even stop it. These maneuvers work by affecting the vagus nerve, which controls your heartbeat, and include: 1 Dunking your face in ice water or applying an ice-cold, wet towel to the face for 15 seconds to trigger the diving reflex 2 Holding your breath while trying to forcefully exhale for 10-30 seconds (valsalva maneuver)
What drugs can you take to treat arrhythmia?
Street drugs such as cocaine, marijuana and “speed” or methamphetamines. If you're being treated for arrhythmia and use any of these substances, be sure to discuss this with your doctor.
How to prevent AFIB?
Especially for people with AFib, prevent blood clots from forming to reduce stroke risk. Control your heart rate within a relatively normal range. Restore a normal heart rhythm, if possible. Treat heart disease/condition that may be causing arrhythmia. Reduce other risk factors for heart disease and stroke.
What are the causes of irregular heartbeats?
Certain substances can contribute to an abnormal/irregular heartbeat, including: Caffeine. Tobacco. Alcohol. Cold and cough medications. Appetite suppressants. Psychotropic drugs (used to treat certain mental illnesses) Antiarrhythmics (paradoxically, the same drugs used to treat arrhythmia can also cause arrhythmia.
What is clinical trial?
Clinical trials are scientific studies that determine if a possible new medical advance can help people and whether it has harmful side effects. Find answers to common questions about clinical trials in our Guide to Understanding Clinical Trials.
What is cardiac arrhythmia?
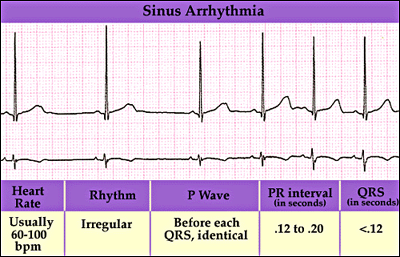
What are Cardiac Arrhythmias? A cardiac arrhythmia is any abnormal heart rate or rhythm. In normal adults, the heart beats regularly at a rate of 60 to 100 times per minute. And the pulse (felt at the wrist, neck or elsewhere) matches the contractions of the heart's two powerful lower chambers, called the ventricles.
Why do you have to have a heart test for cardiac arrhythmias?
This is because certain cardiac arrhythmias cause a mismatch of the pulse and the heart sounds.
What are the symptoms of a ventricular arrhythmia?
Supraventricular tachyarrhythmias - These can cause palpitations (awareness of a rapid heartbeat), low blood pressure and fainting.
What is the prognosis for ventricular fibrillation?
The prognosis for ventricular fibrillation is grave, and death follows quickly without emergency treatment.
Where do cardiac arrhythmias originate?
Cardiac arrhythmias sometimes are classified according to their origin as either ventricular arrhythmias (originating in the ventricles) or supraventricular arrhythmias (originating in heart areas above the ventricles, typically the atria ).
What is the treatment for sinus node dysfunction?
Sinus node dysfunction - In people with frequent, severe symptoms, the usual treatment is a permanent pacemaker. Supraventricular tachyarrhythmias - The specific treatment depends on the cause of the arrhythmia. In some people, massaging the carotid sinus in the neck will stop the problem.
What is the heart's upper chamber called?
The heart's two upper chambers, called the atria, also contract to help fill the ventricles. But this milder contraction occurs just before the ventricles contract, and it is not felt in the pulse. Under normal circumstances, the signal for a heartbeat comes from the heart's sinus node.
What are the arrhythmias that start in the atria?
Arrhythmias that start in the atria are called atrial or supraventricular (above the ventricles) arrhythmias. Rapid heart rhythms originating in the atria include atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and supraventricular tachycardia.
What are the two types of arrhythmias?
Types of Arrhythmia? There are two major types of arrhythmia: Tachycardia, where the heart beat is too fast - more than 100 beats per minute. Bradycardia , where the heartbeat is to slow – less than 60 beats per minute.
What is the most common cause of sudden cardiac arrest?
Ventricular fibrillation is the most common cause of sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) and is fatal if not treated within a few minutes. Slow heart rhythms occur when the hearts normal pacemaker fails or when there is a conduction block within the conduction pathways.
How do you know if you have an arrhythmia?
In fact, your doctor might find you have an arrhythmia during a routine examination. Symptoms of a heart arrhythmia include: A “fluttering” sensation in your chest. A racing heartbeat (tachycardia) A slow heartbeat (bradycardia) Chest pain. Shortness of breath. Lightheadedness.
Why does my heart beat so fast?
Arrhythmias can occur when the electrical impulses that coordinate your heart rhythm do not travel normally. This causes the heart to beat too fast, too slow, or with an irregular rhythm. Almost everyone has felt their heart "skip" or “flutter” a beat or two, and speed up in times of fear or excitement or during exercise.
What is the procedure called to assess the conduction system of the heart?
An invasive procedure called an electrophysiology study is sometimes performed to assess the conduction system of the heart.
Can caffeine cause heart palpitations?
Too much caffeine and certain medications also can cause heart palpitations ( heart racing or fluttering) in some people. These types of arrhythmias are generally harmless. While most arrhythmias are harmless, some can be serious or even life threatening.
How to treat bradycardia?
Actions such as taking a warm bath, brewing strong coffee or tea, performing special physical exercises (walking down the stairs, running or walking in the open air) can help to reduce the manifestations of the disease. In bradycardia, a person may lose consciousness and then it is necessary to carry out artificial respiration and indirect heart massage until the arrival of ambulance. Frequently arising arrhythmia requires medication that is prescribed by the cardiologist. If it does not produce results, then the pacemaker is implanted.
How to treat sinus tachycardia?
Treatment of pathological sinus tachycardia often lies at the border of cardiology with other narrow specializations - psychotherapy, neurology or endocrinology. General guidelines can help reduce the frequency of attacks in the first phase. To do this, you must overeat, worry, be stressed and over-tired. It is better to go for a walk in the open air, eat well and carry out permissible physical work. Pathological arrhythmia should be treated together with the main disease - thyrotoxicosis, anemia, chronic heart failure. Otherwise, taking only arrhythmic drugs will not have a positive effect.
What is pathology in cardiac disease?
Pathology can be expressed in various forms of rhythm disturbance, starting with relatively non-dangerous sinus arrhythmias and ending with a serious symptom of cardiac arrhythmias - atrial fibrillation. For each form, a specific treatment is performed. Asymptomatic arrhythmias do not require medication therapy. It is enough to reduce physical activity or reduce weight. Clinically expressed arrhythmias, but without significant hemodynamic disturbances, can be treated with arrhythmic drugs. If the patient has a cardiac pathology and in addition, he is in a risk group, for example, after age 55, then additional thrombolytics are prescribed.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
- To diagnose a heart arrhythmia, the doctor will usually do a physical exam and ask questions about your medical history and symptoms. Tests may be done to confirm an irregular heartbeat and look for conditions that can cause arrhythmias, such as heart disease or thyroid disease. Te…
Mayo Clinic Heart Rhythm Program
- Treatment for heart arrhythmias depends on whether you have a fast heartbeat (tachycardia) or slow heartbeat (bradycardia). Some heart arrhythmias do not need treatment. Your doctor may recommend regular checkups to monitor your condition. Heart arrhythmia treatment is usually only needed if the irregular heartbeat is causing significant symptoms, or if the condition is putti…
Prescriptions
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Implantable Devices
- If you have heart disease or a heart condition, your doctor will likely recommend making lifestyle changes to keep your heart as healthy as possible. Examples of heart-healthy lifestyle changes are: 1. Eat heart-healthy foods.Eat a healthy diet that's low in salt and solid fats and rich in fruits, vegetables and whole grains. 2. Exercise regularly.Aim to exercise for at least 30 minutes on mo…
Specialist-Driven Procedures
- If you think you may have a heart arrhythmia, make an appointment with your doctor. If a heart arrhythmia is found early, treatment may be easier and more effective. You may be referred to a doctor trained in heart conditions (cardiologist). If a heart arrhythmia persists for more than a few minutes or is accompanied by fainting, shortness of breath or chest pain, call 911 or your local e…
Lifestyle Changes
- Arizona
1. Mayo Clinic Heart Rhythm Program 2. 13400 E. Shea Blvd. Scottsdale, AZ 85259 3. Phone: 800-446-2279 - Florida
1. Mayo Clinic Heart Rhythm Program 2. 4500 San Pablo Road Jacksonville, FL 32224 3. Phone: 904-953-0859
Complementary Medicine
A Word from Verywell
- Some types of arrhythmias may require an implantable device to help regulate your heart's rhythm or provide an electric shock if needed.