Management
- Chemotherapy. Peritoneal carcinomatosis can in some cases be treated with intraperitoneal and/or intravenous chemotherapy.
- Embolisation. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolisation (TACE) has resulted in a successful outcome, particularly in patients with neuroendocrine tumours and colorectal metastases.
- Radiotherapy. ...
- Surgery. ...
What is the life expectancy of someone with peritoneal cancer?
The average life expectancy for mesothelioma patients is approximately 18 – 31 months. Life expectancy for pleural mesothelioma is about 18 months on average. Peritoneal mesothelioma patients generally have a life expectancy of two years or more.
What is the best treatment for primary peritoneal cancer?
Treatment for peritoneum cancer will depend on a number of factors, including:
- The stage of your cancer, or how advanced it is
- How extensively your cancer has metastasized, or spread to other parts of the body
- Your general health
How severe is Stage 4 peritoneal cancer?
With stage 4 peritoneal cancer, the tumor has usually metastasized to organs in the abdomen, such as the liver, or to other regions of the body, such as the lungs. The treatment for peritoneal cancer will depend on a number of factors, including the location of cancer, the stage of cancer, and a person's general health.
What is the prognosis for cancer in the omentum?
Omentum cancer diagnosis
- Is Omentum and Peritoneal cancer the same thing?
- Is it terminal? My DR. stated treatment would be chemo therapy and stated removing the tumor would be problematic, so wonder if the chemo shrinks the tumor? ...
- My Dr. spoke of a specific tumor and I am reading at these message boards that perhps some of you have many small nodules.

Can you survive carcinomatosis?
Median survival of CRC PC without any treatment is approximately 4-7 months, while palliative systemic therapy may extend this to 12-23 months based on several series [13–15].
What kind of cancer is carcinomatosis?
A serious condition in which cancer cells from an original (primary) tumor spread to form many tumors throughout the body or to a large area of the body. In most cases, carcinomatosis is a sign that the cancer is getting worse and cannot be cured.
Is carcinomatosis a cause of death?
'Carcinomatosis' simply means that there was no definite single cause of death; carcinomatosis is carcinoma that has spread widely throughout the body via the lymphatic system, bloodstream or across the peritoneal cavity.
How is carcinomatosis diagnosed?
How Doctors Diagnose Peritoneal Carcinomatosis. If a doctor thinks you have peritoneal carcinomatosis, you may get a blood test, CT scan, MRI, or biopsy to confirm it. Sometimes, peritoneal carcinomatosis is diagnosed during a surgery for another cancer, when a surgeon notices tumors in the peritoneum.
What is the survival rate of carcinomatosis?
Results: The median survival was 21.8 months. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival rates were 75%, 28%, and 19%, respectively. The Kaplan-Meier curve reached a plateau of 18% at 54 months. In 59 patients a complete cytoreduction was achieved, and in 41 patients there was minimal residual disease.
How fast does carcinomatosis grow?
Scientists have found that for most breast and bowel cancers, the tumours begin to grow around ten years before they're detected. And for prostate cancer, tumours can be many decades old. “They've estimated that one tumour was 40 years old. Sometimes the growth can be really slow,” says Graham.
Can chemo cause sudden death?
Chemotherapy. Antineoplastic chemotherapeutic agents can cause complications potentially leading to cardiopulmonary arrest. Angina, myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, hypotension, arrhythmia and sudden death have been reported as complications of treatment with several cytotoxic chemotherapy drugs.
What happens in the last few weeks of life?
Everyone's experiences are different, but there are changes that sometimes happen shortly before a person dies. These include loss of consciousness, changes to skin colour, and changes to breathing.
How do you know if chemo is killing you?
Here are some signs that chemotherapy may not be working as well as expected: tumors aren't shrinking. new tumors keep forming. cancer is spreading to new areas....Along the way, the timeline may have to be adjusted due to:low blood counts.adverse effects to major organs.severe side effects.
What is Stage 3 peritoneal carcinomatosis?
Stage III: The cancer involves 1 or both of the ovaries or fallopian tubes, or it is peritoneal cancer. It has spread to the peritoneum outside the pelvis and/or to lymph nodes in the retroperitoneum (lymph nodes along the major blood vessels, such as the aorta) behind the abdomen.
Can the peritoneum be removed?
If surgery is possible, the operation is called a peritonectomy. This means removing part or all of the lining of the abdomen (peritoneum). The aim is to reduce symptoms.
Is peritoneal carcinomatosis painful?
Abstract. Background: Patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis often report abdominal pain, which is relatively refractory to morphine.
How to treat peritoneal carcinomatosis?
Relapsing is further prevented by second-look surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy reserved for patients at high risk for recurrence. Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy can also be used to treat or prevent carcinomatosis during primary colorectal cancer resection in some patients.
What is the treatment for leptomeningeal carcinoma?
As far as leptomeningeal carcinomatosis is concerned, treatment may include intrathecal chemotherapy, intravenous chemotherapy, whole brain radiotherapy and radiotherapy to the spinal leptomeninges and it has also contributed to the improvement of survival rates in patients with metastases secondary to breast cancer [13]. A drug that has been evaluated as safe and effective in cases of HER-2 positive breast cancer patients is trastuzumab (intrathecal) [15].
How long does leptomeningeal carcinomatosis last?
Median survival is 4 to 6 weeks without treatment and 2-3 months with appropriate treatment [9]; it is therefore deemed a terminal condition.
What is peritoneal carcinoma?
Peritoneal carcinomatosis is a manifestation of dissemination occurring from multiple malignancies, especially gastrointestinal tract carcinomas and ovarian cancer. Various cancer types and non-malignant conditions may present with findings that could indicate PC in radioimaging (CT) and it has been suggested that, due to the severity of the condition, the existence of peritoneal carcinomatosis should be evaluated first.
What is the best way to diagnose peritoneal carcinoma?
The radiologic technique most widely used to assess patients suspected of peritoneal carcinomatosis is the CT scan; secondarily, MRI scans, ultrasound and, possibly, barium studies can also provide some information on the abdominal condition. The CT scan provides a reliable tool in order to detect PC and any other condition presenting with a similar symptomatology. The definitive diagnosis and characterization of the lesions observed is made possible through tissue biopsy, also conducted with the help of a CT scan, a procedure which facilitates the evaluation of the patient prior to surgery or any other treatment plan.
What is the treatment for disseminated metastatic disease?
Another method that is expected to play an important role in the treatment of disseminated, metastatic disease is the transcatheter arterial chemoembolization ( TACE) [16]. It has proven effective, especially against neuroendocrine tumors and colorectal metastases.
Is carcinoma a primary condition?
Carcinomatosis may present as a primary condition, without any precedent, or as a complication of a known malignancy. It may also exhibit a recurrence pattern. Its clinical presentation varies, depending on the location of carcinomatosis:
How to treat carcinomatosis?
This often requires removing involved organs such as portions of the small intestine or colon, the spleen, or the ovaries. An additional measure that may be recommended is the delivery of heated chemotherapy directly in to the abdomen during surgery; this is commonly referred to as HIPEC. The exact treatment plan is developed by the surgeon, the medical oncologist and the patient, and the plan is tailored based on other factors such as the cause of the carcinomatosis and other medical conditions.
What is carcinomatosis in the abdomen?
What is carcinomatosis? Carcinomatosis is the spread of a tumor on the surfaces of the organs within the abdomen. The tumors may also spread to the lining of the abdomen which is termed the peritoneum. Because of this, sometimes carcinomatosis may be referred to as ‘peritoneal surface disease’.
Is carcinomatosis stage 4?
In general, carcinomatosis is considered stage 4 disease for most cancers or tumors. However, there is a wide range of outcomes with carcinomatosis. Some cancers behave more aggressively and quickly spread throughout the abdomen, while others may grow slowly over months to years. The aggressiveness of the tumor can be partially predicted based on biopsies and knowledge of the source of carcinomatosis.
Does Washington University treat carcinomatosis?
Washington University Colorectal can provide treatment options for carcinomatosis. Meet our specialists below.
Can a tumor be predicted based on biopsies?
The aggressiveness of the tumor can be partially predicted based on biopsies and knowledge of the source of carcinomatosis. What are the symptoms of carcinomatosis? Patients with carcinomatosis may note increasing abdominal bloating or distension. They may develop cramping abdominal pains, particularly after eating.
What is the best treatment for peritoneal cancer?
Depending on your particular case, other treatment options may also be available. Cytoreductive surgery. A surgeon removes any tumors on the peritoneum and, in some cases, nearby abdominal organs. Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy.
What is cytoreductive surgery?
Cytoreductive surgery. A surgeon removes any tumors on the peritoneum and, in some cases, nearby abdominal organs.
What is peritoneal carcinoma?
Peritoneal carcinomatosis is a rare form of cancer affecting the peritoneum, the thin membrane surrounding your abdominal organs. Finding out that you or a loved one has it can be tough, and understanding this cancer can help give you a sense of control. Peritoneal carcinomatosis most often develops when other abdominal tumors spread to ...
What is the procedure to remove the peritoneum?
A peritonectomy is surgery to remove your peritoneum.
Is peritoneal carcinoma hard to treat?
Since peritoneal carcinomatosis is usually an advanced form of invasive cancer that has spread from another tumor, it can be hard to treat. Most peritoneal carcinomatosis tumors don’t shrink very much, or at all, in response to chemotherapy. Because of that, many doctors focus on palliative care to manage symptoms, ease pain, and improve your quality of life. There are doctors who specialize in palliative care, which is for anyone with a serious illness. Hospice care is an option if end-of-life concerns start to become a need.
Can cancer cause symptoms in early stages?
There may be no symptoms in the early stages, or you may have vague symptoms that resemble other conditions. In later stages, the cancer causes symptoms such as:
Is peritoneal carcinomatosis a risk factor?
Since peritoneal carcinomatosis most often develops when existing cancers spread , the main risk factor is having other advanced cancers, including:
What kind of doctor is used for peritoneal carcinoma?
Our team of doctors works closely to care for patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis. Surgical oncologists consult with radiologists (medical imaging experts) and other doctors to review your test results and decide the next steps in your care. All patients are discussed at our multi-disciplinary tumor board.
What is a team of highly trained cancer doctors with different areas of expertise?
A team of highly trained cancer doctors with different areas of expertise collaborates to determine the most appropriate treatment for you.
What is peritoneal carcinoma?
Peritoneal carcinomatosis is also called peritoneal surface malignancy. It refers to any cancer that spreads to the abdominal cavity (the space between internal organs in the abdomen) after developing elsewhere in the body (like the colon). Peritoneal carcinomatosis is different from p rimary peritoneal cancer, ...
How does cytoreductive surgery work?
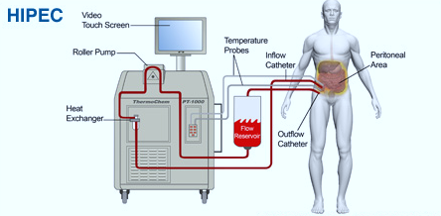
During cytoreductive surgery with HIPEC, surgeons first remove all signs of cancerous tissue. They then apply a concentrated dose of heated chemotherapy medicine to the abdominal cavity to treat remaining cancer cells directly.
What tests are done to detect peritoneal carcinoma?
If our specialists suspect peritoneal carcinomatosis, they may order one or more tests: Imaging tests like CT or MRI scans capture fine details of the abdominal cavity and help doctors pinpoint the location of cancer cells and potential cancer spread.
Where is Mays Cancer Center?
Mays Cancer Center is the only National Cancer Institute (NCI)-designated cancer center in South Texas, which may give you early access to clinical trials, if you are eligible. Clinical trial opportunities for peritoneal carcinomatosis. Meet our team.
Can you get chemotherapy before surgery?
Some patients may benefit from additional chemotherapy before or after surgery. Your care team will make treatment recommendations based on your situation and input.
How long do you live after peritoneal carcinomatosis?
Results: Forty patients affected with extensive peritoneal carcinomatosis underwent peritonectomy, with no residual macroscopic disease except in four cases. Seventy-five percent of the patients underwent locoregional chemotherapy. Major complications were observed in 40% of the patients and led to death in five; there was a direct correlation to the duration of surgery (P = 0.03). At a mean follow-up of 20 months, the overall 2-year survival was 61.4%, with a median survival of 30 months.
Can a low grade malignant tumor be redistributed?
Background and objectives: Low-grade malignant tumors arise in the abdomen, do not infiltrate, and "redistribute" on the peritoneum with no extraregional spreading. In these cases, aggressive surgery combined with localized chemotherapy may provide cure.
What are the Treatment for Peritoneal Carcinomatosis?
Treatment for this is quite aggressive, since it is an advance and complex type of cancer.
What is chemo called?
Chemotherapy called Heated Intraoperative Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy Administration . Dissect using electro-evaporative surgery with Intraperitoneal chemotherapy to altogether uproot the cancer cells. Surgery and medical treatment like chemotherapy etc is a matter of choice and can turn out to be an expensive affair.
What does it mean when peritoneal cancer spreads?
When abdominal cancer spreads to the peritoneum, it indicates that abdominal cancer has reached an advanced stage.
What happens if you have cancer at an advanced stage?
If the first cancer was at an advanced stage and could not get wiped out from the root for any reason, then the remaining cancer residues spread to other parts of body or implant themselves in the lining resulting in Peritoneal Carcinomatosis.
What is the name of a very thin coating of tissue?
Peritoneum is name of a very thin coating of tissue.
Which organ is more prone to getting attacked by remaining cancer cells after treatment?
Any part or organ of the body that is close to abdomen is more prone to getting attacked by remaining cancer cells after treatment. Moreover, internal spreading germs and infection by way of ulcers rupturing when it comes to cancer of stomach or intestine etc.
Is chemotherapy expensive?
Surgery and medical treatment like chemotherapy etc is a matter of choice and can turn out to be an expensive affair.
What is peritoneal carcinomatosis?
Peritoneal Carcinomatosis (PC) is a late stage manifestation of several gastrointestinal malignancies characterized by tumor deposition across the peritoneal surface [1]. This can be entirely asymptomatic in its early stages, or as the disease progresses, symptoms such as nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain, bloating, and weight loss may develop [1]. The disease is often discovered when ascites or intestinal obstruction develop, occurring generally with greater tumor burden which is more difficult to treat [2]. Early PC detection when there is limited tumor burden may increase the effectiveness of current treatment options [3].
What are exosomes used for?
When exosomes were exposed to RNase the contained RNAs were protected from degradation while cellular RNA was degraded by the same RNase [45]. Exosomes hold great potential for both diagnosis and prognosis of diseases and are exceptionally useful as cancer biomarkers [47]. When a panel of lung cancer associated miRs was examined in solid tumors and tumor exosomes from patient plasma, most of the miRs were found to have highly comparable expression levels (see Table Table33for the miRs) [48, 49]. Cervical cancer cell line tumor derived exosomes (TEXs) contain survivin, which contributes to cancer aggressiveness and metastatic potential [50, 51]. In a study of ovarian cancer, greater numbers of cancer exosomes were found in the serum as more advanced cancer stages were examined [52]. Furthermore, approximately four times more serum exosomes were discovered in lung cancer patients as compared to cancer free controls and the exosomes contained more than twice the miRs [48]. In our research, we found increased serum exosome levels in patients with prostate and breast cancers as compared to disease free controls [53–55]. TEXs are prevalent in patient serum from multiple cancer types and protect labile biomarkers from degradation [42, 45, 48, 53–55].
What is CC in cytoreduction?
CC is the completeness of cytoreduction score
