Oesophageal cancer treatment
- Oesophageal cancer surgery. It may be possible to remove the tumour. ...
- Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is a treatment of cancer by using anti-cancer medicines which kill cancer cells, or stop them from multiplying.
- Radiotherapy. Radiotherapy is a treatment which uses high-energy beams of radiation which are focused on cancerous tissue.
What is the life expectancy of someone with esophageal cancer?
If the cancer is in the upper part of the esophagus (in the neck), chemoradiation may be recommended as the main treatment instead of surgery. For some patients, this may cure the cancer. Close follow-up with endoscopy is very important in …
How deadly is esophageal cancer?
Jul 15, 2021 · Table 12. Standard Treatment Options for Esophageal Cancer; Stage (TNM Staging Criteria) Treatment Options ; Stage 0 Esophageal Cancer: Surgery: Endoscopic resection: Stage I Esophageal Cancer: Chemoradiation therapy followed by surgery: Surgery alone: Stage II Esophageal Cancer: Chemoradiation followed by surgery: Surgery alone: Chemotherapy …
What is the best treatment for esophageal cancer?
Nov 18, 2021 · Treatment of recurrent esophageal cancer may include the following: Use of any standard treatments as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life. Immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors ( nivolumab and ipilimumab ). Immunotherapy with an immune checkpoint ...
How to beat esophageal cancer?
Immunotherapy, a related treatment, works by strengthening the body’s natural defense systems against cancer. Often, treatment for esophageal cancer includes a combination of chemotherapy and radiation therapy before surgery. Chemotherapy can cause many side effects like nausea, hair loss and increased risk of infection.
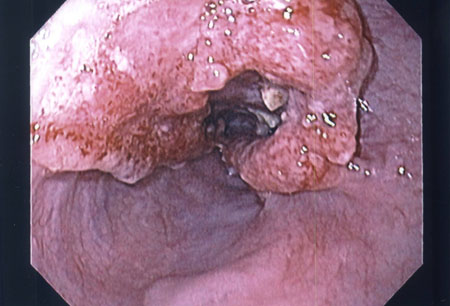
Does esophageal cancer spread quickly?
What is the survival rate for cancer of the esophagus?
Is it possible to survive esophageal cancer?
How easy is it to cure esophageal cancer?
Is esophagus cancer a death sentence?
Is esophageal cancer a terminal?
Where does esophagus cancer spread first?
Is cancer of the Oesophagus curable?
What were your first signs of esophageal cancer?
- Trouble swallowing.
- Chest pain.
- Weight loss.
- Hoarseness.
- Chronic cough.
- Vomiting.
- Bone pain (if cancer has spread to the bone)
- Bleeding into the esophagus. This blood then passes through the digestive tract, which may turn the stool black.
How many rounds of chemo are needed for esophageal cancer?
Can chemo cure esophageal cancer?
Do you feel ill with esophageal cancer?
Treating Stage 0 Esophagus Cancer
A stage 0 tumor is not true cancer. It contains abnormal cells called high-grade dysplasia and is a type of pre-cancer. The abnormal cells look lik...
Treating Stage I Esophagus Cancer
In this stage the cancer has grown into some of the deeper layers of the esophagus wall (past the innermost layer of cells) but has not reached the...
Treating Stages II and III Cancer of The Esophagus
Stage II includes cancers that have grown into the main muscle layer of the esophagus or into the connective tissue on the outside of the esophagus...
Treating Stage IV Cancer of The Esophagus
Stage IV esophageal cancer has spread to distant lymph nodes or to other distant organs.In general, these cancers are very hard to get rid of compl...
Is treatment information given here official policy of the American Cancer Society?
The treatment information given here is not official policy of the American Cancer Society and is not intended as medical advice to replace the expertise and judgment of your cancer care team. It is intended to help you and your family make informed decisions, together with your doctor.
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
What are the best doctors for cancer?
Doctors on your cancer treatment team might include: 1 A thoracic surgeon: a doctor who treats diseases of the chest with surgery 2 A surgical oncologist: a doctor who uses surgery to treat cancer 3 A radiation oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with radiation therapy 4 A medical oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with medicines such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapy 5 A gastroenterologist: a doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal (digestive) system
What is the name of the doctor who treats cancer?
A thoracic surgeon: a doctor who treats diseases of the chest with surgery. A surgical oncologist: a doctor who uses surgery to treat cancer. A radiation oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with radiation therapy. A medical oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with medicines such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapy.
What is the number to call for cancer treatment?
Call our National Cancer Information Center at 1-800-227-2345 and speak with one of our trained specialists. Palliative Care. Find Support Programs and Services in Your Area.
What is local treatment?
Local treatments treat the tumor in a specific location, without having major effects on the rest of the body. These treatments are more likely to be useful for earlier stage (less advanced) cancers, although they might also be used in some other situations.
What is systemic therapy?
These are called systemic therapies because they travel through your whole system, allowing them to reach cancer cells almost anywhere in the body. Depending on the type of esophageal cancer, several different types of drugs might be used. Chemotherapy for Esophageal Cancer. Targeted Drug Therapy for Esophageal Cancer.
What is the procedure to remove esophagus cancer?
One operation used to treat esophageal cancer is esophagectomy. During esophagectomy, your surgeon removes the portion of your esophagus that contains the tumor, along with a portion of the upper part of your stomach, and nearby lymph nodes. The remaining esophagus is reconnected to your stomach.
How does esophageal cancer surgery work?
During esophagectomy, your surgeon removes the portion of your esophagus that contains the tumor, along with a portion of the upper part of your stomach, and nearby lymph nodes. The remaining esophagus is reconnected to your stomach. Usually this is done by pulling the stomach up to meet the remaining esophagus.
What tests are done to determine if esophageal cancer is spread?
Tests may include: Bronchoscopy. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)
What is the stage of esophageal cancer?
The stages of esophageal cancer are indicated by Roman numerals that range from 0 to IV, with the lowest stages indicating that the cancer is small and affects only the superficial layers of your esophagus. By stage IV, the cancer is considered advanced and has spread to other areas of the body.
What is stage IV cancer?
By stage IV, the cancer is considered advanced and has spread to other areas of the body. The cancer staging system continues to evolve and is becoming more complex as doctors improve cancer diagnosis and treatment. Your doctor uses your cancer stage to select the treatments that are right for you.
How to treat esophageal obstruction?
If your esophageal cancer has narrowed your esophagus, a surgeon may use an endoscope and special tools to place a metal tube (stent) to hold the esophagus open.
Can esophageal cancer cause pain?
For instance, people with esophageal cancer may experience pain caused by cancer treatment or by a growing tumor. Your doctor can work to control your pain by treating the cause or with medications. Still, pain may persist, and complementary and alternative therapies may help you cope. Options include:
Is esophageal cancer curable?
In most cases, esophageal cancer is a treatable disease, but it is rarely curable. The 5-year relative survival rate is 19.9%. Patients with early-stage disease have a better chance of survival; 17.5% of patients are diagnosed at the local stage and have a 5-year relative survival rate of 46.4%. [ 6] References.
How long does esophageal cancer last?
The survival rate of patients with esophageal cancer is poor. Surgical treatment of resectable esophageal cancers results in 5-year survival rates of 5% to 30%, with higher survival rates in patients with early-stage cancers. [ 7] .
What is the median age for esophageal cancer?
In the United States, the median age of patients who present with esophageal cancer is 68 years. [ 6] . Most adenocarcinomas are located in the distal esophagus. The cause for the rising incidence and demographic alterations is unknown.
What is the objective response rate for esophageal cancer?
Esophageal cancer responds to many anticancer agents. Objective response rates of 30% to 60% and median survivals of less than 1 year are commonly reported with platinum-based combination regimens with fluorouracil, taxanes, topoisomerase inhibitors, hydroxyurea, or vinorelbine. [ 1, 4, 9] Trastuzumab may be effective in combination with chemotherapy among patients with tumors that overexpress HER2-neu. [ 10 ] [ Level of evidence: 1iiA]
Is palliation a problem for esophageal cancer patients?
Palliation presents difficult problems for all patients with recurrent esophageal cancer. All patients should be considered candidates for clinical trials as outlined in the Treatment Option Overview for Esophageal Cancer section of this summary.
What is PDQ cancer?
This PDQ cancer information summary for health professionals provides comprehensive, peer-reviewed, evidence-based information about treatment of adult esophageal cancer. It is intended as a resource to inform and assist clinicians who care for cancer patients. It does not provide formal guidelines or recommendations for making health care decisions.
Which neoplasms are most common in the esophagus?
Related Summaries. Two histologic types account for the majority of malignant esophageal neoplasms: adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Adenocarcinomas typically start in the lower esophagus and squamous cell carcinoma can develop throughout the esophagus. The epidemiology of these types varies markedly.
Can esophageal cancer be cured?
Esophageal cancer is often in an advanced stage when it is diagnosed. At later stages, esophageal cancer can be treated but rarely can be cured.
What is the name of the cancer that forms in the esophagus?
The two most common forms of esophageal cancer are named for the type of cells that become malignant ( cancerous ): Squamous cell carcinoma: Cancer that forms in the thin, flat cells lining the inside of the esophagus.
What are the symptoms of esophageal cancer?
Signs and symptoms of esophageal cancer are weight loss and painful or difficult swallowing. Tests that examine the esophagus are used to diagnose esophageal cancer. Certain factors affect prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options.
Does smoking increase the risk of esophageal cancer?
Smoking, heavy alcohol use, and Barrett esophagus can increase the risk of esophageal cancer. Anything that increases your risk of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer; not having risk factors doesn't mean that you will not get cancer.
What is the purpose of esophageal cancer tests?
After esophageal cancer has been diagnosed, tests are done to find out if cancer cells have spread within the esophagus or to other parts of the body.
What is the process used to find out if cancer cells have spread within the esophagus?
The process used to find out if cancer cells have spread within the esophagus or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment. The following tests and procedures may be used in the staging process:
What is it called when cancer spreads to another part of the body?
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis . Cancer cells break away from where they began (the primary tumor) and travel through the lymph system or blood.
What is the treatment for esophageal cancer?
Often, treatment for esophageal cancer includes a combination of chemotherapy and radiation therapy before surgery. Chemotherapy can cause many side effects like nausea, hair loss and increased risk of infection. Your medical team will work with you to manage pain and any other side effects during your treatment.
What is the procedure to remove esophageal cancer?
Types of Esophageal Cancer Surgery. Surgical treatments for esophageal cancer include: Transhiatal surgery: In this procedure, the surgeon makes incisions in the neck and abdomen in order to remove the tumor.
Where does esophageal cancer develop?
Esophageal Cancer. Esophageal cancer develops in the esophagus, which is the tube that connects your throat to your stomach. Most esophageal cancer cases aren’t discovered until they are in advanced stages when immediate treatment is necessary. Treatment options may include:
What is the treatment for cancer?
Radiation therapy: The use of X-rays, gamma rays and charged particles to shrink tumors. Chemotherapy: The use of drugs and other medicines that help the body fight cancerous cells. Surgery: The removal of cancerous tissue in the esophagus and surrounding areas.
How does chemo help with esophageal cancer?
Chemotherapy for esophageal cancer. Chemotherapy, or medical oncology, uses powerful drugs to kill cancerous cells and prevent them from coming back. It is one of the most common cancer treatments. In most cases, chemotherapy works by interfering with the cancer cells’ ability to grow and reproduce. Immunotherapy, a related treatment, works by ...
What is HER2 in cancer?
HER2 protein research for esophageal cancer: In breast cancer, chemotherapy drugs target HER2, a protein that responds to treatment with a certain class of drugs. Researchers have found that same protein in esophageal cancer and hope to understand whether esophageal cancer responds to similar treatment. Small molecule drug research: Small molecule ...
How does esophageal cancer affect the body?
Esophageal cancer uniquely affects the body’s ability to receive nutrition normally (through eating and drinking). Many people experience malnutrition and dehydration before receiving an esophageal cancer diagnosis. Your treatment plan might include a phase of healing and building up your body’s strength before tackling the cancer itself.
Can esophageal cancer be treated with surgery?
However, currently, surgery is used as the main treatment only for early-stage esophageal cancer. For most people with locally advanced esophageal cancer, ASCO recommends chemoradiotherapy or chemotherapy before surgery to shrink the tumor (see above).
What is the most common treatment for esophageal cancer?
Surgery is the removal of the tumor and some surrounding healthy tissue during an operation. A surgical oncologist is a doctor who specializes in treating cancer using surgery. Surgery has traditionally been the most common treatment for esophageal cancer. However, currently, surgery is used as the main treatment only for early-stage esophageal cancer.
What is standard of care for esophageal cancer?
This section explains the types of treatments that are the standard of care for esophageal cancer. “Standard of care” means the best treatments known. When making treatment plan decisions, you are encouraged to consider clinical trials as an option.
What is the treatment for cancer called?
Cancer and its treatment cause physical symptoms and side effects, as well as emotional, social, and financial effects. Managing all of these effects is called palliative care or supportive care. It is an important part of your care that is included along with treatments intended to slow, stop, or eliminate the cancer.
What is the name of the doctor who treats cancer?
This is called palliative surgery. To do this, surgeons and doctors called gastroenterologists, who specialize in the gastrointestinal tract, can:
How is medication used to treat cancer?
Medication may be given through the bloodstream to reach cancer cells throughout the body. When a drug is given this way, it is called systemic therapy . Medication may also be given locally, which is when the medication is applied directly to the cancer or kept in a single part of the body.
What is it called when cancer spreads to another part of the body?
If cancer spreads to another part in the body from where it started, doctors call it metastatic cancer. If this happens, it is a good idea to talk with doctors who have experience in treating it. Doctors can have different opinions about the best standard treatment plan. Clinical trials might also be an option. Learn more about getting a second opinion before starting treatment, so you are comfortable with your chosen treatment plan.
What is the best treatment for esophageal cancer?
Surgery: Surgery is used to remove as much of the esophageal cancer as possible. Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy uses high energy x-rays or other types of radiation to kill the cancer cells. Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses anti-cancer drugs to kill the cancer cells. Chemotherapy is used when the cancer cells have spread to other parts ...
What are the symptoms of esophageal cancer?
Weight loss for no known reason. Hiccups. Throwing up with streaks of blood. Streaks of blood in mucus coughed up from the lungs. Imaging: If you have symptoms of esophageal cancer, your doctor will use imaging scans such as a Barium Swallow, CT, PET, and ultrasound to see where the tumor is and how big it is.
How do you know if you have esophageal cancer?
Many people with esophageal cancer do not have symptoms when the cancer first starts. Later, when the tumor gets larger, symptoms can include: 1 Trouble swallowing 2 Weight loss for no known reason 3 Hiccups 4 Throwing up with streaks of blood 5 Streaks of blood in mucus coughed up from the lungs
What are the two most common types of esophageal cancer?
It is part of the digestive system. The two most common types of esophageal cancer are adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Esophageal adenocarcinoma forms in the glandular cells. These cells are in the lining of the esophagus and make fluids, such as mucus. Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma forms in the squamous cells in the esophagus.
Is esophageal cancer rare?
Esophageal cancer is a rare type of cancer, making up about 1% of cancer cases in the United States. The rate of new cases per year is about 4 for every 100,000 people. In other parts of the world, esophageal cancer is more common. In the United States, esophageal adenocarcinoma is more common than esophageal squamous cell carcinoma ...
Is esophageal cancer more common in men than women?
In the United States, esophageal adenocarcinoma is more common than esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and makes up about 80% of esophageal cancer cases. Esophageal cancer is more common in men than women.
When is chemotherapy used?
Chemotherapy is used when the cancer cells have spread to other parts of the body. Targeted therapy: Targeted therapy is aimed at the changes in cancer cells that help them grow, divide, and spread.
How to treat esophagus cancer?
There are many ways to treat esophagus cancer: Surgery and radiation therapy are mainly used to treat only the cancer. They do not affect the rest of the body. Chemotherapy and targeted therapy and immunotherapy go through the whole body. They can reach cancer cells almost anywhere in the body.
What is the treatment for esophageal cancer?
Immunotherapy is treatment that either boosts your own immune system or uses man-made versions of parts of the immune system that attack the esophagus cancer cells. Immunotherapy drugs may be given into a vein.
What is the name of the cancer that starts in the esophagus?
Cancer that starts growing in the esophagus is called esophagus cancer or esophageal cancer . It starts when cells in the inner lining of the esophagus grow out of control and crowd out normal cells. Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body. Cancer cells in the esophagus can sometimes travel to the liver and grow there.
What are the symptoms of esophagus cancer?
Some symptoms of esophagus cancer may be trouble swallowing, chest pain, weight loss, hoarse voice, and constant cough. Your doctor will ask you questions about your health and will use exams and tests to find out what’s causing your symptoms.
What test is done to see if you have esophagus cancer?
If signs are pointing to esophagus cancer, here are some of the tests you may need: Barium swallow: This is sometimes the first test done in people who have trouble swallowing. It’s a series of x-rays taken after you swallow barium, a thick, chalky liquid that shows up on x-rays.
Where does cancer grow?
Cancer cells in the esophagus can sometimes travel to the liver and grow there. When cancer cells do this, it’s called metastasis. To doctors, the cancer cells in the new place look just like the ones from the esophagus. Cancer is always named for the place where it starts. So when esophagus cancer spreads to the liver (or any other place), ...
Where do squamous cells grow?
Squamous cell carcinoma: Squamous cells line the inside of the esophagus. Cancer that starts in these cells can grow anywhere along the esophagus. Adenocarcinoma: These cancers start in gland cells. These cancers are mainly in the lower part of the esophagus, near the stomach.
Can esophageal cancer be treated with surgery?
Unfortunately, most esophageal cancers are not found early enough for doctors to cure them with surgery. Often a small part of the stomach is removed as well. The upper part of the esophagus is then connected to the remaining part of the stomach. Part of the stomach is pulled up into the chest or neck to become the new esophagus.
Can esophageal cancer be removed?
Minimally invasive esophagectomy: For some early (small) cancers, the esophagus can be removed through several small incisions instead of large incisions.
What are the risks of esophageal surgery?
Possible risks of esophagectomy 1 Short-term risks include reactions to anesthesia, more bleeding than expected, blood clots in the lungs or elsewhere, and infections. Most people will have at least some pain after the operation, which can usually be helped with pain medicines. 2 Lung complications are common. Pneumonia may develop, leading to a longer hospital stay, and sometimes even death. 3 Some people might have voice changes after the surgery. 4 There may be a leak at the place where the stomach (or intestine) is connected to the esophagus, which might require another operation to fix. This is not as common as it used to be because of improvements in surgical techniques. 5 Strictures (narrowing) can form where the esophagus is surgically connected to the stomach, which can cause problems swallowing for some patients. To relieve this symptom, these strictures can be expanded during an upper endoscopy procedure. 6 After surgery, the stomach may empty too slowly because the nerves that cause it to contract can be damaged by surgery. This can sometimes lead to frequent nausea and vomiting. 7 After surgery, bile and stomach contents can back up into the esophagus because the ring-shaped muscle that normally keeps them inside the stomach (the lower esophageal sphincter) is often removed or changed by the surgery. This can cause symptoms such as heartburn. Sometimes antacids or motility drugs can help these symptoms.
What is the procedure to remove the esophagus?
Esophagectomy. Surgery to remove some or most of the esophagus is called an esophagectomy. If the cancer has not yet spread far beyond the esophagus, removing the esophagus (and nearby lymph nodes) may cure the cancer. Unfortunately, most esophageal cancers are not found early enough for doctors to cure them with surgery.
Is esophageal surgery a simple procedure?
Esophagectomy can be done in different ways. No matter which technique is used, esophagectomy is not a simple operation, and it may require a long hospital stay. It is very important to have it done at a center that has a lot of experience treating these cancers and performing these procedures.
How many lymph nodes are removed during surgery?
Typically, at least 15 lymph nodes are removed during surgery. If the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes, the outlook is not as good, and the doctor may recommend other treatments (like chemotherapy and/or radiation) after surgery.
Is esophageal surgery dangerous?
Like most serious operations, surgery of the esophagus has some risks. Short-term risks include reactions to anesthesia, more bleeding than expected, blood clots in the lungs or elsewhere, and infections. Most people will have at least some pain after the operation, which can usually be helped with pain medicines.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Alternative Medicine
- Complementary and alternative therapies may help you cope with the side effects of cancer and cancer treatment. For instance, people with esophageal cancer may experience pain caused by cancer treatment or by a growing tumor. Your doctor can work to control your pain by treating the cause or with medications. Still, pain may persist, and complementary and alternative therapies …
Coping and Support
- Coping with the shock, fear and sadness that come with a cancer diagnosis can take time. You may feel overwhelmed just when you need to make crucial decisions. With time, each person finds a way of coping and coming to terms with the diagnosis. Until you find what brings you the most comfort, consider trying to: 1. Find out enough about esophageal cancer to make decision…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- If your family doctor suspects you have esophageal cancer, you may be referred to a number of doctors who will help evaluate your condition. Your health care team may include doctors who: 1. Evaluate the esophagus (gastroenterologists) 2. Treat cancer with chemotherapy and other medications (oncologists) 3. Perform surgery (surgeons) 4. Use radiati...