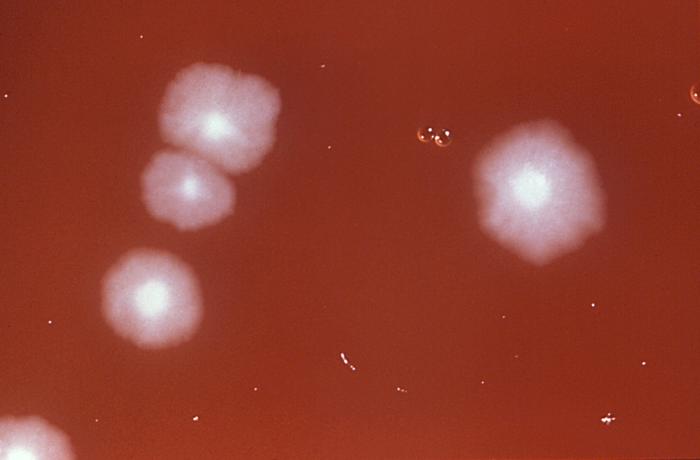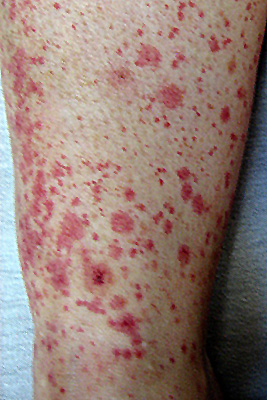
Medication
diff again is to:
- Work with your healthcare professional to avoid taking unnecessary antibiotics.
- Tell your healthcare professional if you’ve had a C. diff infection. ...
- Wash your hands with soap and water every time you use the bathroom and before you eat anything.
Procedures
difficile infection, review the need to continue any treatment with:
- proton pump inhibitors
- other medicines with gastrointestinal activity or adverse effects, such as laxatives
- medicines that may cause problems if people are dehydrated, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin‑2 receptor antagonists and diuretics.
Self-care
diff
- Clostridioides difficile fact sheet
- Burden of Clostridium difficile infection in the United States
- Asymptomatic carriage of Clostridium difficile and serum levels of IgG antibody against toxin A
- Probiotics in Clostridium difficile infection
- Management of clostridiodes difficile infection
Nutrition
Yes, it is absolutely possible for c-diff to go away on its own. In fact, the first course of action is to stop the offending antibiotic (if you are on one) and see if it will improve on its own. What type of test did they do? Some tests can give false positives. The PCR and LAMP are more accurate.
How can you clean to get rid of C diff?
What antibiotics are used to treat C diff?
What drugs treat C diff?
Will cdiff go away on its own?

What is the best antibiotic to treat C. diff?
What is the best medication for C. diff? Vancomycin and fidaxomicin are the most effective antibiotics against Clostridium difficile infections. They are both equally effective at wiping out an initial infection.
How long does it take to fully recover from C. diff?
Your symptoms should improve a few days after starting the new course of antibiotics. But it may be 1 to 2 weeks before the infection clears up completely.
What is the first line treatment for C. diff?
Fidaxomicin as First Line Very simply and clearly, fidaxomicin is now recommended as the preferred agent for Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) over vancomycin.
How long is a person contagious with C. diff?
C. difficile diarrhea may be treated with a course of antibiotics prescribed by your doctor and taken by mouth. Once you have completed treatment and diarrhea is resolved, your infection is no longer contagious and you no longer need to take any special precautions.
Should someone with C. diff be quarantined?
Isolate patients with possible C. diff immediately, even if you only suspect CDI. Wear gloves and a gown when treating patients with C. diff, even during short visits.
Is C. diff serious?
C. diff (also known as Clostridioides difficile or C. difficile) is a germ (bacterium) that causes severe diarrhea and colitis (an inflammation of the colon). It's estimated to cause almost half a million infections in the United States each year.
Can C. diff go away by itself?
For asymptomatic carriers or patients with antibiotic-associated diarrhea, antibiotics to target C. diff aren't needed. “This will usually resolve on its own,” Dr.
What happens if C. diff goes untreated?
Left untreated or treated unsuccessfully, Clostridium difficile infection can lead to sepsis, an intestinal perforation, or death. Patients with severe Clostridium difficile infections are typically treated with the antibiotics vancomycin or metronidazole.
Should I take Imodium if I have C. diff?
The use of antimotility agents such as narcotics and loperamide in active C difficile infection is discouraged because use of these agents may result in more severe colitis.
What are the warning signs of C. diff?
Signs and symptoms of severe infection include:Watery diarrhea as often as 10 to 15 times a day.Abdominal cramping and pain, which may be severe.Rapid heart rate.Dehydration.Fever.Nausea.Increased white blood cell count.Kidney failure.More items...•
Should I be hospitalized for C. diff?
Your GP will decide whether you need hospital treatment (if you're not already in hospital). If the infection is relatively mild, you may be treated at home. If you're in hospital, you might be moved to a room of your own during treatment to reduce the risk of the infection spreading to others.
What color is stool with C. diff?
Greenish stools were more common among the control cases. Another study correlated nurses' response as to whether a stool was positive or not for C. difficile based on stool odor.
How do I restore my gut after C. diff?
Probiotics – Live microorganisms or 'good bacteria' are found in yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, tempeh (fermented soybean), kimchi (fermented cabbage), pickles, and kombucha (fermented tea). These help to restore the natural bacteria in the gut, reducing C. difficile symptoms.
Can C. diff cause long term problems?
Since the mechanism of action of these agents is similar to C. difficile, we hypothesized that patients with CDAD have greater likelihood of developing IBS and other functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs) in the long-term as compared to a general sample of recently hospitalized patients.
Does C. diff stay in your system forever?
No, because once you recover from your C. diff infection, you could still be carrying the germs. A test would only show the germs are still there, but not whether you're likely to become sick again.
Can C. diff last for months?
Once your body is colonized with C. diff, you can remain colonized for several months. Colonization is more common than C. diff infection and does not require treatment.
What is the treatment for C diff?
C Diff Treatment – Vancocin. This is the oral form of the common vancomycin drug used for many other conditions. It takes the medication directly to the infected area and is effective for many patients.
How long does it take for C diff to go away?
This is effective against mild to moderate strains. For many people this c diff treatment works and it goes away after 7-14 days. About 20% of the patients are not cured and more powerful drugs must be used.
What is a CDI guideline?
This clinical practice guideline is a focused update on management of Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) in adults specifically addressing the use of fidaxomicin and bezlotoxumab for the treatment of CDI. This guideline was developed by a multidisciplinary panel representing the Infectious Dis …
What antibiotic is used for Clostridioides difficile?
Fidaxomicin should be the antibiotic of choice when treating adults with Clostridioides difficile infection, according to new guidance from the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America.
How many people die from Clostridioides difficile?
In the United States, Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) is the leading cause of healthcare-associated infection, affecting nearly half a million people and resulting in more than 20,000 in-hospital deaths every year. It is therefore imperative to better characterize the intricate inter …
Is C. difficile a NAP1 or 027?
There are many different strains of c.difficile. The NAP1 or 027 strain is often caught in hospital and is much more destructive than other strains. A test will help ensure the right antibiotic treatment for your strain.
Does CDI cause lower Cdiff32?
Recurrent CDI, severe CDI, and the number of stools were linked to lower Cdiff32 scores.
How to prevent C diff?
Keeping Clean. The main focus of C. diff prevention is cleanliness , including frequent, thorough hand-washing, not only after using the bathroom but before eating as well. Hand sanitizer doesn’t kill C. diff spores, so washing with soap and water is best at preventing infection.
What antibiotics are used for C diff?
Although antibiotics can cause the infection to develop, different antibiotics are often used to treat it. These antibiotics may include vancomycin, fidaxomicin, and metronidazole. Supportive care such as intravenous fluids ...
What Is C. Diff?
C. diff is a contagious bacteria that can cause an infection in the colon. Anyone can become infected, although many infections typically develop in the days or weeks after taking broad-spectrum antibiotics such as:
How long after diagnosis can you take antibiotics for C diff?
Supportive care such as intravenous fluids and electrolytes are also often given. Antibiotics may need to be taken for weeks after diagnosis to fully treat the infection. C. diff infection can be difficult to treat and can recur frequently, so adherence to prescribed therapy is critical.
What is the best antibiotic for C diff?
Clindamycin. Amoxicillin. In addition to killing the disease-causing bacteria responsible for infection, antibiotics can kill the helpful bacteria that the colon needs to keep a healthy biome. When good bacteria are killed, C. diff can start to grow and cause an infection.
What to avoid during C diff?
What To Avoid During C. Diff Infection. Using antimotility agents such as Imodium (loperamide) is generally not recommended during a C. diff infection, as it can lead to further inflammation and worsening of symptoms.
How long does C diff live on a surface?
These bacteria then form spores outside the body and can live for months or even years on solid surfaces.
What antibiotics are used for C diff?
Common antibiotics used to treat C. diff infections include: Oral fidaxomicin and oral vancomycin are both first-line treatment options for C. diff, according to recent clinical practice guidelines.
How to get rid of C diff bacteria?
Keep surfaces in high-use areas clean. This includes bathrooms and kitchens. Try to periodically clean these areas with products containing bleach. Bleach is effective against the C. diff bacterium.
What is C diff?
C. diff is short for Clostridium difficile, an infectious bacterium that causes a condition known as clostridium difficile colitis. Colitis refers to inflammation of the wall of your colon. It can produce a range of symptoms.
How to prevent a bacterial infection?
Follow these tips to reduce your risk: 1 Wash your hands regularly with soap and warm water. This is especially important after using the bathroom and before eating. 2 Don’t take antibiotics unnecessarily. Keep in mind that antibiotics are only effective for bacterial infections and won’t treat a viral infection, such as the flu or common cold. 3 Keep surfaces in high-use areas clean. This includes bathrooms and kitchens. Try to periodically clean these areas with products containing bleach. Bleach is effective against the C. diff bacterium.
How do you know if you have C diff?
Other symptoms include: abdominal pain or cramps. nausea. fever. loss of appetite. dehydration. blood in stool (in severe cases) Symptoms of a C. diff infection can range from mild to severe. Call your doctor if you notice you’re having diarrhea three or more times a day or your symptoms aren’t going away after two or three days.
How long does it take to cure C diff?
Most C. diff infections respond well to a 10-day course of oral antibiotic treatment.
What is the procedure to test for C diff?
They can analyze it for toxins or toxin genes of the C. diff bacterium. If your symptoms are severe, they may also perform a procedure called a sigmoidoscopy. A long, thin device called a sigmoidoscope is inserted into your colon.
How to get rid of C diff?
Drink plenty of fluids that have water, salt, and sugar, such as broth and fruit juices. If there's been damage to your intestines, you may need surgery to remove the affected areas. Sometimes, a C. diff infection can come back. Doctors sometimes recommend a treatment to help repopulate the colon with healthy bacteria.
What happens if you have C diff?
This can happen because C. diff can cause the colon -- also called the large intestine -- to get inflamed. When this happens, tissue in the colon can bleed or make pus. Other symptoms of a serious infection include: Diarrhea more than 10 times a day. Severe cramping.
What Is Clostridium Difficile (C. diff)?
Clostridium difficile (C. diff) is a type of bacteria that can cause colitis, a serious inflammation of the colon. Infections from C. diff often start after you've been taking antibiotics. It can sometimes be life-threatening.
How long does C diff live on surfaces?
C. diff bacteria that are outside the body turn into spores that can live on surfaces for weeks or months. These spores are not "active," but they can turn active after you swallow them and they get into your intestines. Some people have the bacteria in their intestines and never have any symptoms.
What antibiotics cause C diff?
diff could grow unchecked and make you sick. The antibiotics that are most linked to a risk of C. diff infection are: Fluoroquinolones. Cephalosporins.
Why are older people at risk for C diff?
That's because the human body contains thousands of different types of bacteria -- some good, some bad. If the antibiotics kill enough healthy bacteria, the ones that cause C. diff could grow unchecked and make you sick.
What happens if you have a C diff infection?
If a C. diff infection isn't treated quickly, you could become dehydrated due to severe diarrhea. This loss of fluids might also affect your:
What is the best treatment for C. difficile?
The two most common drugs used to treat C. difficileare metronidazole (500 mg PO TID) and vancomycin (125 mg PO QID) for 10–14 days. The standard first-line therapy in both the inpatient and outpatient settings remains oral metronidazole, unless there are contraindications to the medicine such as first trimester of pregnancy or inability to tolerate it. For severe disease, initial therapy with vancomycin is now recommended (Table 1). In all patients with CDAD, inciting antibiotics should be discontinued, if possible, or changed to a regimen with a narrower spectrum. Antimotility agents should not be used, even in mild cases.
What are the symptoms of C. difficile?
Of patients with C. difficileinfection, 3–8% develop fulminant colitis.14Markers of disease severity include ileus, renal insufficiency, colon wall thickening on computed tomography imaging, and endoscopic visualization of pseudomembranes , as well as the usual signs of septic physiology: fever, significant leukocytosis, hypotension requiring fluid resuscitation, and tachypnea. These markers may portend toxic megacolon, imminent intestinal perforation, or fulminant colitis, and they may predict a significantly higher risk of colectomy or death. Empiric therapy should be started for ill patients as soon as C. difficileis suspected, to avoid any delay related to obtaining the results of stool or equivocal examinations. As stool examinations are imperfect, clinical judgment is still vital.
What is the best antibiotic for CDAD?
Several other antibiotics are being studied in the treatment of CDAD. One is nitazoxanide, a nitrothiazolide antibiotic. Musher and associates published a prospective double-blinded study in 2006 comparing metronidazole and nitazoxanide as initial therapy and concluded that nitazoxanide was as effective as metronidazole.25Of note, this initial study excluded ICU patients and those with hemodynamic instability, IBD, advanced liver disease, or renal disease. The same group of researchers recently published an open-label study of nitazoxanide in patients who had failed metronidazole therapy. Twenty-eight patients who had experienced no improvement in symptoms after 14 days of metronidazole (mean duration of treatment, 22.4 days) were prescribed 10 days of 500 mg of nitazoxanide twice daily. Twenty patients (71%) experienced rapid resolution of symptoms, but 6 of these patients later experienced disease recurrence.26Nitazoxanide may have an emerging role in stable patients who do not improve with metronidazole. Although nitazoxanide is relatively expensive, it still costs less than vancomycin; in 2006, the average wholesale price of a 10-day course of nitazoxanide was approximately $240.27
How to diagnose CDAD?
Diagnosis of CDAD is usually confirmed by detection of toxins A and/or B in stools or culture, though the latter does not confirm toxin production . Enzyme immunoassay (EIA) examinations have largely replaced cytotoxin tissue culture assay for toxin B, though their sensitivity and specificity are not as good. False-negative examinations are an important concern for clinicians. Some EIA examinations can detect both toxin A and B; others test only for toxin A and a common clostridial antigen that acts as surrogate marker for the presence of clostridia. As these examinations test for toxin A alone, they do not detect the 2–3% of strains that produce only toxin B. Thus, confirmation for toxin B via examinations such as toxin B assay or polymerase chain reaction is necessary when the EIA for toxin A is negative but the common clostridial antigen is positive. In short, clinical judgment is still very important in diagnosis.
What are modifiable practices that may decrease initial treatment failures?
Modifiable practices that may decrease initial treatment failures include avoiding the use of antimotility agents and discontinuing the causative antibiotic, if possible.
Is clindamycin a risk factor for C. difficilecolitis?
Cephalosporin and clindamycin usage have long been recognized as risk factors for C. difficilecoli tis, but until recently, fluoroquinolones had not been considered a significant risk. In 2000, Muto and associates noted a spike in fluoroquinolone use in a Pittsburgh hospital that predated the increase of severe CDAD cases by 9 months. A comparison of the 12-month period beginning in March of 1998 with the one beginning in March of 1999 demonstrated that use of fluoroquinolones rose from 217 daily doses to 275 daily doses per 1,000 patient-days.2This coincided with the emergence of a hypervirulent strain, BI/NAP1/027, which had been identified as early as 1984. This strain produces a binary toxin of unknown significance and has an 18 bp deletion in a gene that regulates toxin production. This mutation allows for increased production of toxins A and B in vitro, which may explain why it appears to cause more severe disease. Prior to 2001, BI/NAP1/027 isolates were resistant to clindamycin and levofloxacin (levaquin, Ortho-McNeil). The strain has since acquired resistance to gatifloxacin and moxifloxacin.8In some hospitals, formulary changes to these drugs have predated epidemics.
Does C difficile respond to antibiotics?
Lack of response to therapy does not appear to result from C. difficileresistance to the treating antibiotic. Although one study from Spain suggested that drug resistance was a contributing factor,22this pattern of antibiotic resistance has not been verified in the United States. With severe disease that does not respond to therapy, urgent surgical intervention is of critical importance.
What is C diff?
diff. C. diff (also known as Clostridioides difficile or C. difficile) is a germ (bacterium) that causes severe diarrhea and colitis (an inflammation of the colon). It’s estimated to cause almost half a million infections in the United States each year.
How to keep C diff from spreading?
To keep from spreading C. diff to others: Wash hands with soap and water every time you use the bathroom and always before you eat. Try to use a separate bathroom if you have diarrhea. Take showers and wash with soap.
What are the risk factors for C diff?
A weakened immune system, such as people with HIV/AIDS, cancer, or organ transplant patients taking immunosuppressive drugs. Previous infection with C. diff or known exposure to the germs.
How long does it take for a C diff to die?
One in 11 people over age 65 diagnosed with a healthcare-associated C. diff infection die within one month.
What to do if you have symptoms again?
If you start having symptoms again, seek medical care.
Where is C. difficile found?
C. difficile bacteria are found throughout the environment — in soil, air, water, human and animal feces, and food products, such as processed meats. A small number of healthy people naturally carry the bacteria in their large intestines and don't have ill effects from the infection.
How do you know if you have C. difficile?
difficile infection are: Watery diarrhea three or more times a day for two or more days. Mild abdominal cramping and tenderness.
How many people get C. difficile each year?
Each year in the United States, about a half million people get sick from C. difficile, and in recent years, C. difficile infections have become more frequent, severe and difficult to treat. Recurrent C. difficile infections also are on the rise. C. difficile infection care at Mayo Clinic.
How many people are infected with C. difficile?
It most commonly affects older adults in hospitals or in long-term care facilities. In the United States, about 200,000 people are infected annually with C. difficile in a hospital or care setting. These numbers are lower than in previous years because of improved prevention measures.
Where do C. difficile infections occur?
difficile infections occur in people who are or who have recently been in a health care setting — including hospitals, nursing homes and long-term care facilities — where germs spread easily, antibiotic use is common and people are especially vulnerable to infection.
Which is more likely to have C. difficile infection, women or men?
Women are more likely than men to have C. difficile infection, for reasons that are not clearly understood.
Can you get C difficile in your intestines?
Some people carry C. difficile bacteria in their intestines but never become sick. These individuals are carriers of the bacteria and may spread infections.
How to protect yourself from C diff?
While you may not have a severe diarrhea infection, protect yourself and others by staying home. Take a sick day at work or keep your child home from school so that the infection does not spread.
How to tell if C diff is worse?
diff is worsening. Check your stool for blood or pus. If you notice either of these in your stool, call your doctor!
How many times a day can you get diarrhea from C diff?
Mild cases of a C. diff infection involve watery diarrhea at least 3 times per day for multiple days and some minor abdominal cramping or pain. More severe cases may involve frequent diarrhea (as much as 10 to 15 times per day), fever, intense abdominal cramping and pain, weight loss, dehydration and blood or pus in the stool.
What to do when you have diarrhea?
However, when you’re sick with diarrhea, protect yourself and others from spreading the infection. In fact, when someone is admitted to the hospital with a severe C. diff infection, hospital staff must wear special gowns, gloves and masks for a contact precaution!
How to clean up diarrhea in a house?
The CDC recommends making your own cleaner by mixing 1 part bleach to 9 parts water.
Can you have diarrhea with C diff?
You may be experiencing diarrhea and not know if it is caused by C. diff. Keeping track of your symptoms and self-monitoring how your illness progresses is essential. Severe forms of a C. diff infection will need immediate medical attention.
Can Clostridium difficile cause diarrhea?
Clostridium difficile is a bacterium that can aggravate the colon and cause a wide array of issues. Sometimes C. diff only causes diarrhea and goes away on its own, whereas other people can develop life-threatening colitis, dehydration, organ failure, bowel perforation, bowel rupture and/or death. C. diff is no little stomach bug!